Pore structure and movable fluid characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs in the Lower Shihezi Formation in the Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
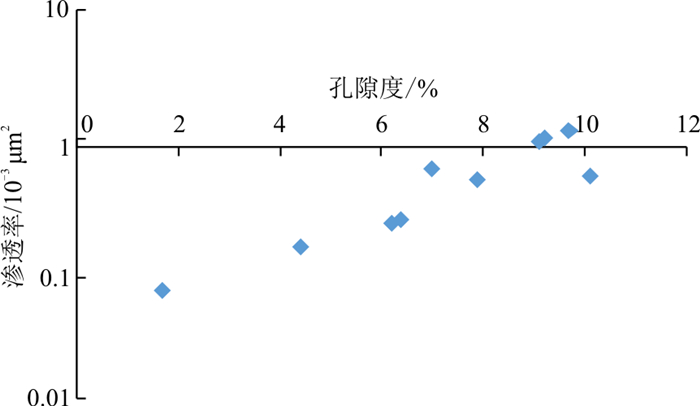
核磁共振(NMR)及CT扫描技术对致密砂岩储层评价正发挥越来越重要的作用。以杭锦旗地区下石盒子组盒1段致密砂岩储层为例, 基于NMR及CT扫描系统探讨了致密砂岩中不同类型孔隙的响应特征及流体识别能力。结果表明, 测试样品的孔隙度主要分布在1.7%~10%, 气测渗透率主要分布在0.1×10-3~1.4×10-3
μ m2,T 2弛豫时间截止值主要分布在1~14 ms, 平均值为6.11 ms, 属于典型的低孔、低渗型致密砂岩储层。根据离心前饱和分量T 2弛豫时间曲线, 盒1段储层孔隙类型为双峰型(左峰为主, 右峰不明显), 包括3个亚类: 微孔-小孔型、小孔-中孔型、微孔-小孔-中孔型, 所对应的T 2弛豫时间区间分别为0.1~10, 1~100, 0.1~100 ms。三维CT扫描结果显示, 小孔-中孔型储层的物性特征最好, 其次为微孔-小孔-中孔型储层, 而微孔-小孔型储层的物性相对较差。T 2截止值与样品可动流体含量负相关。盒1段可动流体孔隙度与渗透率具有良好的正相关性, 反映可动流体含量受储层渗透率与喉道显著影响。盒1段致密砂岩储层中可动水饱和度主要分布在4%~9%, 平均值为5.8%。开发实践显示, 盒1段原始可动水饱和度较低, 具有较大开发潜力, 从侧面证实了NMP和CT扫描技术结果的准确性。Abstract:Objective In recent years, new discoveries have been made in the He 1 Member of the Hangjinqi Gas Field. And the initial gas production of some wells by fracturing can reach 10×104 m3/d, which shows that the He 1 Member has great exploration potential. However, due to the strong heterogeneity of the He 1 Member, the gas production mechanism of the He 1 Member is not clear at present, which restricts its efficient development. To accurately and quantitatively characterize the microscopic pore structure and movable fluid characteristics of tight gas sandstone reservoirs.
Methods In this paper, taking the tight sandstone reservoir in the He 1 Member of the Shangshihezi Formation in the Hangjinqi Gas Field as an example, NMR and CT tests were used to study the response characteristics and fluid identification ability of different types of pores in tight sandstone.
Results The research shows that the porosity of the test samples is mainly distributed in 1.7%-10%, and the gas permeability is mainly distributed in 0.1×10-3-1.4×10-3
μ m2, which belongs to the typical low-porosity and low-permeability porous tight sandstone reservoir. According to theT 2 relaxation time curve of the saturation component before centrifugation, the pore type of the reservoir in the He 1 Member is bimodal (mainly the left peak, the right peak is not obvious), including 3 subtypes: micropore-small pore type, small pore-mesopore type, micropore-small pore-mesopore type. TheT 2 relaxation time intervals corresponding to the above three subtypes of pore types are 0.1-10 ms, 1-100 ms, and 0.1-100 ms, respectively. The results of 3D CT scans show that the micropore-mesopore reservoir has the best physical properties, followed by the micropore-small pore-mesopore type, and the micropore-small pore type reservoirs have relatively poor physical properties. TheT 2 cut-off values of the tested samples were mainly distributed between 1 and 14 ms, with an average value of 6.11 ms. There is a certain negative correlation between theT 2 cut-off value and the movable fluid percentage of the rock samples. The movable fluid porosity and permeability have a very good positive correlation, reflecting that the amount of movable fluid is significantly affected by the reservoir permeability and the number of throats. The movable water saturation in the tight sandstone reservoirs of He 1 Member in the study area is mainly distributed at 4%-9%, with an average value of 5.8%.Conclusion Overall, the original movable water saturation of the He 1 Member is low and has great development potential.
-
表 1 样品基本信息
Table 1. Basic information of the samples
样品编号 井号 深度/m 氦气孔隙度/% 气测渗透率/10-3 μm2 岩性 1 J119 3 372.44 7.0 0.69 中粗砂岩 2 J136 3 562.71 1.7 0.08 中砂岩 3 J120 2 572.29 4.2 0.26 中砂岩 4 J137 3 422.38 7.9 0.56 中砂岩 5 J137 3 422.93 6.2 0.26 粗砂岩 6 J119 3 368.12 7.3 0.71 粗砂岩 7 J137 3 424.08 9.1 1.13 中粗砂岩 8 J144 3 223.36 6.7 0.52 细砂岩 9 J137 3 474.10 9.2 1.19 中砂岩 10 J51 2 732.94 10.1 0.61 中砂岩 -
[1] Belikov B P, Aleksandrov K S, Ryzhova T V. Elastic constants of rock-forming minerals[M]. [S. l. ]: Nauka, 1970: 67-69. [2] Daigle H, Dugan B. Extending NMR data for permeability estimation in fine grained sediments[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(8): 1419-1427. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.02.008 [3] Nelson P H. Pore-throat sizes in sandstones, tight sandstones, and shales[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(3): 329-340. doi: 10.1306/10240808059 [4] Yang Q S, Carlos T V. Joint interpretation and uncertainty analysis of petrophysical properties in unconventional shale reservoirs[J]. Interpretation, 2015, 3(1): 33-49. [5] Menendez B, Zhu W L, Wong T F. Micromechanics of brittle faulting andcataclastic flow in Berea sandstone[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1996, 18(1): 1-16. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(95)00076-P [6] Wyllie M RJ, Spangler M B. Application of electrical resistivity measurements to problem of fluid flow in porous media[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1952, 36: 359-403. [7] Carman P C. Fluid flow through granular beds[J]. Transactions of the Institution of Chemical Engineers, 1937, 15: 150-166. [8] 刘凯, 石万忠, 王任, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区盒1段致密砂岩孔隙结构分形特征及其与储层物性的关系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 57-68. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0102Liu K, Shi W Z, Wang R, et al. Pore structure fractal characteristics and its relationship with reservoir properties of the First Member of Lower Shihezi Formation tight sandstone in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 57-68 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0102 [9] Keehm Y T, Mukerji, Nur A. Computational rock physics at the pore scale: Transport properties and diagenesis in realistic pore geometries[J]. The Leading Edge, 2001, 20: 180-183. doi: 10.1190/1.1438904 [10] 高树生, 胡志明, 刘华勋, 等. 不同岩性储层的微观孔隙特征[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(2): 248-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201602012.htmGao S S, Hu Z M, Liu H X, et al. Microscopic pore characteristics of diferent lithological reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(2): 248-256 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201602012.htm [11] Coates G R, Xiao L, Prammer M G. NMR logging principles and applications[M]. [S. l. ]: Halliburton Energy Services Publication, 1999: 104-106. [12] Reza R, Ali S, Ben C. Tight gas sands permeability estimation from mercury injection capillary pressure and nuclear magnetic resonance data[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2012, 88/89: 92-99. [13] Zhou S D, Liu D M, Cai Y D, et al. Fractal characterization of pore-fracture in low-rank coals using a low-field NMR relaxation method[J]. Fuel, 2016, 181: 218-226. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.04.119 [14] 尹相东, 蒋恕, 吴鹏, 等. 致密砂岩酸性和碱性成岩环境特征及对储层物性的控制: 以鄂尔多斯盆地临兴和神府地区为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(01): 142-151. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0109Yin X D, Jiang S, Wu P, et al. Features of the acid and alkaline diagenetic environment of tight sandstones and thecontrol of the reservoir physical properties: A case study of the Linxing and Shenfu district, eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Buletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 142-151 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0109 [15] 支鑫, 熊伟, 高树生, 等. 苏里格致密砂岩气藏可动水饱和度分布[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2015, 34(2): 86-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201502016.htmZhi X, Xiong W, Gao S S, et al. Distribution of the movable water saturation in Sulige tight gas reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology and Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2015, 34(2): 86-89 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201502016.htm [16] 刘永利, 尤东华, 李海英, 等. 超深层碳酸盐岩层系硅质岩储层表征与评价: 以塔里木盆地塔深6井为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(3): 547-556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202103003.htmLiu Y L, You D H, Li H Y, et al. Characterization and evaluation of chert reservoirs in ultra-deep carbonate rock formations: A case study on Well TS 6 in the Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(3): 547-556 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202103003.htm [17] 董怀民, 孙建孟, 林振洲, 等. 基于CT扫描的天然气水合物储层微观孔隙结构定量表征及特征分析[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 42(6): 40-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201806005.htmDong H M, Sun J M, Lin Z Z, et al. Quantitative characterization and characteristics analysis of microscopic pore structure in natural gas hydrate based on CT scanning[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2018, 42(6): 40-49 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201806005.htm [18] 苟启洋, 徐尚, 郝芳, 等. 纳米CT页岩孔隙结构表征方法: 以JY-1井为例[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(11): 1253-1261. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201811005.htmGou Q Y, Xu S, Hao F, et al. Characterization method of shale pore structure based on nano-CT: A case study of Well JY-1[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(11): 1253-1261 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201811005.htm [19] 尹帅, 孙晓光, 邬忠虎, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘上古生界构造演化及裂缝耦合控气作用[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 53(9): 3724-3737. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD202209033.htmYin S, Sun X G, Wu Z H, et al. Coupling control of tectonic evolution and fractures on the Upper Paleozoic gas reservoirs in the northeastern margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2022, 53(9): 3724-3737(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD202209033.htm [20] 尹帅, 邬忠虎, 吴晓明, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东洪德地区侏罗系延安组油藏富集规律研究[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(5): 1167-1179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202205013.htmYin S, Wu Z H, Wu X M, et al. Oil enrichment law of the Jurassic Yan'an Formation, Hongde block, Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(5): 1167-1179(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202205013.htm [21] 曾宏斌, 王芙蓉, 罗京, 等. 基于低温氮气吸附和高压压汞表征潜江凹陷盐间页岩油储层孔隙结构特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 1-12. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0022Zeng H B, Wang F R, Luo J, et al. Characterization of pore structure of inter salt shale oil reservoir by low temperature nitrogen adsorption and high pressure mercury pressure methods in Qianjiang Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 1-12(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0022 -





 下载:
下载: