Characteristic analysis of deep water gravity flow sediments in Ch6-Ch7 Section of Yanchang Formation in the Binchang Block, southern Ordos Basin, China
-
摘要:
鄂尔多斯盆地南部彬长区块的延长组长6-长7段发育厚层无沉积构造的块状砂岩,具有良好的油气显示和开发效益,然而关于该套砂岩的形成机制尚不清晰。确定长6-长7段砂岩的沉积相及沉积模式,对于该套低渗砂岩储层"甜点"形成机制的理解,"甜点"分布模式的预测,以及后续勘探开发都具有重要的指导意义。对彬长区块36口取心井的长6-长7段1 024 m长的岩心进行了沉积学特征描述,结合粒度分析资料及地质制图分析,确定了该套厚层砂岩的沉积相及沉积模式。结果表明:鄂尔多斯盆地南部彬长区块的延长组长6-长7段砂岩共发育15种岩相和3种主要沉积微相类型,即:砂质碎屑流、浊积岩和震积滑塌岩微相,以及它们在空间上的3类组合关系。其深水重力流沉积模式可以概括为扇根(坡折带斜坡上半部分)的震积滑塌相-砂质碎屑流亚相(沉积组合)、扇中(斜坡中下部位-坡脚)的砂质碎屑流-浊积岩沉积亚相(沉积组合)和扇端(坡脚-盆底)浊积砂等亚相(沉积组合)。通过对彬长区块延长组长6-长7段发育的致密砂岩沉积特征的分析与讨论,确定了该厚层块状砂岩的主要沉积相及沉积微相的特征及分布,为致密砂岩储层的高效开发及"甜点"预测提供了科学依据与良好借鉴。
Abstract:Massive sandstone without sedimentary structure is developed in the Ch6-Ch7 Section of Yanchang Formation in the Binchang Block, Southern Ordos Basin, which has a good oil and gas show, good productivities and good exploration and development prospect. However, the formation mechanism of the sandstone is still in dispute. It is of great significance to determine the sedimentary facies and sedimentary model of the sandstone in Ch6-Ch7 Section in order to analyze the formation mechanism of sweet spot in the low permeability sandstone reservoirs, to predict the sweet spot distribution model and guide the subsequent exploration and development. In this paper, 15 lithofacies and 3 main types of sedimentary microfacies, namely, sandy debris flow, turbidite and seismite slump microfacies, have been identified by using a large amount of core sedimentary description data, grain size analysis data and geological mapping analysis, and these three kinds of sedimentary assemblies in space. The deep water gravity flow deposition model in the Ch6-Ch7 Section can be summarized as the sublacustrine fan model and can be divided into three subfacies or assemblies: the upper fan subfacies dominated by the assembly of seismite-slump and sandy debris flow, the mid-fan subfacies dominated by the assembly of the sand debris flow-turbidite microfacies and the lower-fan subfacies dominated by turbidite flow-basin plain microfacies assembly.
-
Key words:
- Ordos Basin /
- Binchang Block /
- Ch6-Ch7 section /
- sandy debris flow /
- gravity flow sediment
-
深水沉积是油气勘探的新领域,被全世界石油工业界所关注[1-2]。近年来,国际上在美国墨西哥湾,南美巴西、西非和东非的大西洋及印度洋沿岸地区[3],以及我国南海地区和我国大多数陆相深水湖盆,均发现了大量的常规及非常规油气资源[4-5],促进了深水勘探的不断加强。同时,随着多种重力流理论的提出,国内外学术界关于深水重力流沉积物的研究也有了很大的进步[6]。沉积物重力流理论经历了早期以鲍马序列[7-8]为核心的浊流沉积及湖底扇沉积模式阶段[9-11],到以砂质碎屑流理论为主导的深水斜坡扇沉积模式阶段[12-13],以及近年来的以异重流为核心的水道-湖底扇沉积模式的演化[14]。这些理论与模式在解释过去在盆地中心深水部位遇到的许多无法解释的沉积现象中发挥了重要作用。
Middleton等[15]根据支撑机制将深水重力流沉积物划分为4种类型:颗粒流、沉积物液化流、碎屑流与浊流,并统称为浊积岩,因而导致深水浊积砂岩的广泛分布。Lowe[16-17]在1979和1982年提出了基于流变学和支撑机制的重力流沉积物分类,提出了高密度和低密度浊流的概念,认为两者均属于液体流。Mulder等[18-19]根据流体的物理性质和颗粒搬运机制,提出了一种新的沉积物重力流分类方案,该方案根据沉积物重力流是否具有黏结性,将其划分为黏结流和摩擦流两大类;再根据颗粒含量和支撑机制将摩擦流进一步细分为超高密度流、高密度流和浊流3类。这些分类虽然划分出了不同密度流,但不同密度浊流的密度(或沉积物浓度)界限完全不统一,且流体类型也不完全相同,因而产生了争议[20]。事实上,大多数学者已经意识到影响流体流变学性质的主要因素是沉积物的浓度,其次还包括一些次要因素。当沉积物的浓度增加到一定程度,其流变性将趋向于从牛顿型向塑性、从紊流到层流的变化,而其搬运及沉积机制(支撑机制)不仅有浊流(紊流),也还有其他的形式(如内聚强度、摩擦强度及浮力)。浊流是一种流动状态为紊流的牛顿型流体,紊流是浊流的根本特征。而非紊流的高浓度沉积物不能定义为浊流沉积。因此,厚层深水重力流沉积物中真正意义上的浊流沉积并非浊流沉积。Shanmugam等[12-14]是最早意识到早期浊积沉积中所谓的高密度浊流存在沉积机制解释的矛盾,因此,他们在对野外露头观察及岩心分析的基础上结合室内实验,提出了砂质碎屑流的概念,并将沉积物重力流划分为牛顿流体(浊流)和塑性流体(砂质碎屑流),强调了流变学在深水重力流沉积物分类中的重要性,否认Lower[16-17]将浊流分为高密度浊流与低密度浊流的观点,并提出了砂质和泥质碎屑流,认为浊流只有低密度而无高密度。所谓高密度浊流实际上是砂质碎屑流成因,其塑性流型和层流流态的流变学特征与低密度浊流的牛顿型流体及紊流流态的流变学特征的搬运及沉积机制是完全不同的。因此,深水大量发育的厚层块状砂岩存在多种成因机制[21]。其中低密度浊流才是真正意义上的浊流,高密度浊流从流变学特征上应该属于砂质碎屑流沉积。多种流动机制(滑动、滑塌、碎屑流和浊流,甚至包括牵引流)共同组成了深水沉积物重力流的沉积机制,这种机制能够较好地解释现有的沉积相分布规律。由此可见,在深水重力流沉积物中,真正的浊流沉积所占比例应该较小,而绝大部分为砂质碎屑流与底流改造沉积物[12]。
鄂尔多斯盆地南部上三叠统延长组长6-长7段的深湖相中广泛发育厚层块状砂岩[22-24]。近年来,在深湖相厚层块状砂岩中,发现了包括彬长区块在内的多个千万吨级储量油田,表明深湖相厚层块状砂岩在鄂尔多斯盆地南部具有重要勘探价值。同时,这类过去普遍被解释为浊积砂砂体的成因机制和沉积模式也被许多沉积学者所关注。在21世纪初,有学者认为这套块状砂体是辫状河三角洲前缘水下分流水道沉积[25-26],同时,也有许多学者认为是深湖浊积扇(湖底扇)及震积岩沉积[22-24]。还有个别学者认为鄂尔多斯盆地南部长7段主要发育以等深流、内波、内潮汐为主要类型的深水牵引流沉积[27]。2009年之后,随着砂质碎屑流理论的引入,有不少学者[28-34]认为是砂质碎屑流沉积。近年来,随着异重流理论的引入,研究者认为鄂南长6-长7厚层块状砂岩的主要形成机制是异重流沉积[32, 35-37]。也有学者对比分析了异重流和滑塌型重力流的沉积特征,并总结了识别标准[38],但总体来讲,关于鄂尔多斯盆地南部长6-长7段深水重力流沉积成因的认识仍未统一,从而制约了彬长区块延长组的油气勘探与开发。
因此,笔者将针对彬长区块长6-长7段的厚层块状砂岩的成因及分布模式开展分析;对工区36口取心井长6-长7段1 024 m长的岩心进行沉积学特征的观察,并结合测井相分析以及砂体形态分析等资料,对彬长区块长6-长7段砂体的深水重力流沉积特征、沉积微相及沉积组合和沉积模式进行分析,为彬长区块长6-长7段致密砂岩“甜点”储层评价,以及进一步指导勘探和开发提供地质认识基础。
1. 地质背景
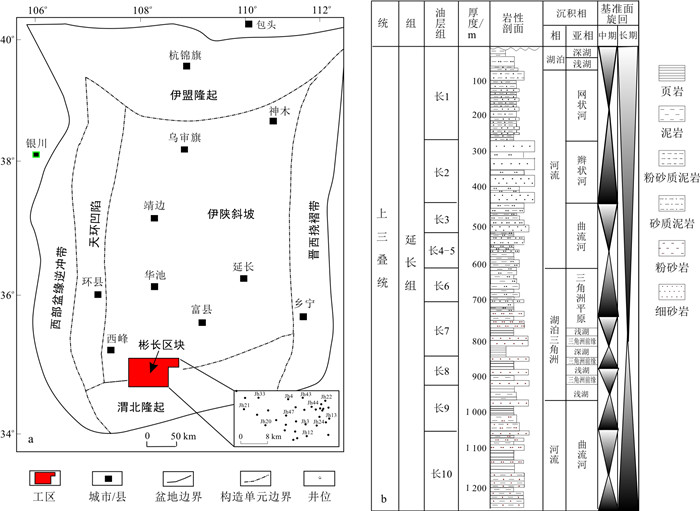
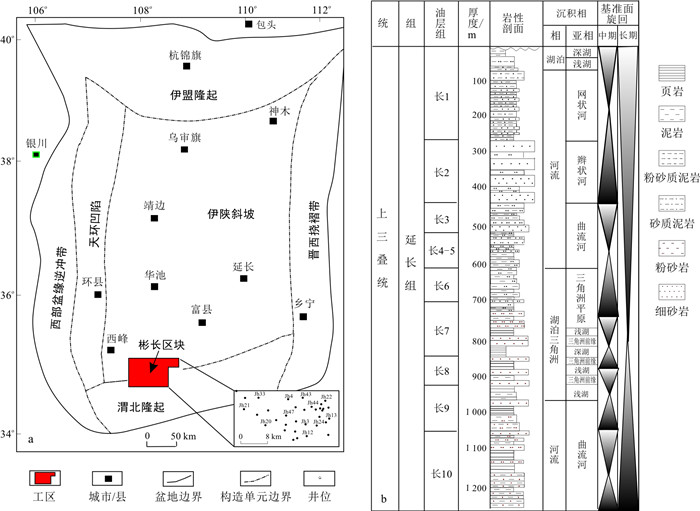
鄂尔多斯盆地北与河套盆地为邻,南接渭北隆起,东邻晋西挠褶带与吕梁隆起呼应,西缘以冲断构造带与六盘山对峙,主体位于伊陕斜坡带。内部构造简单,为平均地层坡度不足1°的不对称西倾单斜构造[39-41]。可划分为伊陕斜坡、天环凹陷、伊盟隆起、晋西挠褶带、渭北隆起,以及西部盆缘逆冲带六大构造单元。研究区彬长区块位于鄂尔多斯盆地渭北隆起和伊陕斜坡结合部位(图 1-a)。
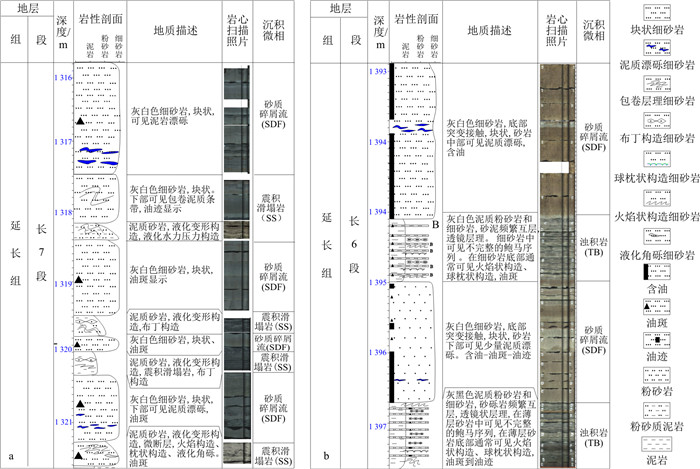
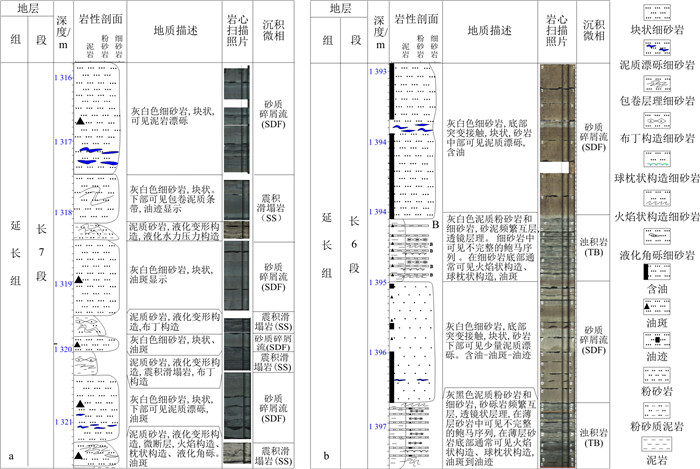
盆地在晚三叠世主要发育延长组地层,自下而上划分为5个岩性段、10个油层组(图 1-b)。其中长6-长7段为湖盆扩展发育阶段,在盆地南部普遍发育半深湖、深湖相沉积[42]。在盆地中心半深湖、深湖沉积环境中广泛发育厚层块状砂岩(厚度20~60 m),具有良好油气显示,钻井揭示具有较好的产能。
鄂尔多斯盆地古地貌在长7-长6段具有“南陡北缓、西陡东缓”的特点[29, 43]。在长7沉积期,印支运动导致西秦岭快速隆升造山,受其影响在盆地西南缘的古生代碳酸盐岩及砂泥岩地层被挤压隆起,隆起过程中同时伴随着地震以及火山活动,导致砂岩中碳酸盐岩和凝灰岩岩屑含量较高。湖盆“南陡北缓”样式的加剧,以及半深湖、深湖环境,为鄂尔多斯盆地南部发育多种深水重力流沉积提供了有利的大地构造背景[39-45]。
2. 彬长区块长7-长6段深水重力流岩石相及沉积微相
2.1 岩性及岩石相
对长6-长7段16口井共177个样品的砂岩薄片分析数据的统计分析表明,岩性主要为细粒长石岩屑砂岩和岩屑长石砂岩。石英颗粒体积分数平均为48.02%;长石颗粒体积分数平均为28.05%;岩屑颗粒体积分数平均为23.43%。砂岩成分成熟度低。砂岩中碳酸盐岩屑体积分数平均为0.5%。砂岩颗粒呈线接触凹凸接触,颗粒磨圆为次棱-次圆,分选中等,砂岩结构成熟度中-差。砂岩中泥质杂基体积分数变化在0.5%~18%之间,平均为5.15%。胶结物体积分数平均为7.8%,主要为碳酸盐胶结物。
对彬长区块34口井,长度约1 024 m的岩心进行了详细观察,在长6-长7段识别出了细砂岩、粉砂岩和泥质岩类三大类岩石相。
根据沉积构造类型,细砂岩岩相进一步划分为:①块状层理细砂岩相(Sfm);②含泥砾块状细砂岩相(Sfmfc);③反递变层理细砂岩(Sfigb);④似平行层理细砂岩相(Sfpl);⑤平行层理细砂岩相(Sfp);⑥含泥质底砾的细砂岩岩相(Sftmc);⑦递变层理细砂岩相(Sfng);⑧负载构造细砂岩相(Sfls);⑨液化构造细砂岩相(Sfliq);⑩滑塌变形构造细砂岩相(Sfd)。
本研究将粉砂岩岩相划分为波状交错纹理粉砂岩相(Ssw)、水平纹理粉砂岩相(Sspl)和滑塌变形构造粉砂岩相(Ssd);将泥质岩岩相划分为油页岩相(Mosh)和深灰色泥岩相(M)等15小类岩石相(表 1)。
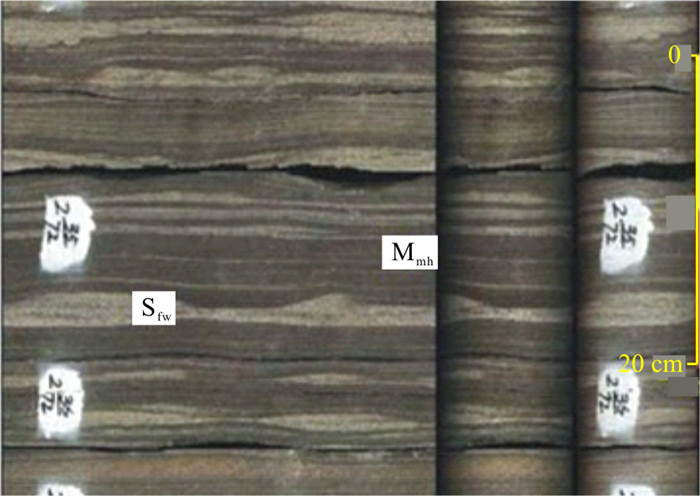
表 1 彬长区块长6-长7段岩石相特征Table 1. Lithofacies characteristics of Ch6-Ch7 Section of the Binchang Block岩性 岩石相 代码 沉积特征 沉积解释 细砂岩 块状层理细砂岩相 Sfm 灰色、褐色,细粒,均质,块状,泥质含量低,砂质较纯。底部突变接触,或见滑动剪切构造,顶面突变接触或浊积成因的砂泥薄互层。含油性较好 砂质碎屑流(塑性流型、层流流体) 含泥砾细砂岩相 Sfmfc 灰色、灰褐色,块状,砂岩中上部含伸长状或浑圆状泥砾,漂浮顺层分布,含油性较好 反递变细砂岩 Sfigb 灰白色,下部为泥质含量较高的泥质细砂岩,致密,含油性较差,上部为块状细砂岩,泥质含量低,物性好,粒级明显呈反递变特征 似平行层理细砂岩 Sfpl 灰白,灰褐色,层理面隐约断续平行状,似平行层理 含撕裂泥砾细砂岩相 Sftmc 灰色,块状,位于块状砂岩底部,底部侵蚀接触,砂岩中含伸长状两端卷曲的撕裂泥砾,平行/紊乱分布,为浊流沉积产物 浊流 牛顿型流体 平行层理细砂岩相 Sfp 灰白,灰褐色,平行层理,薄砂泥互层中出现,鲍马序列中的B段 牵引流 递变层理细砂岩相 Sfgb 灰白色,层薄,小于20 cm,正递变,鲍马序列A段。底部可见槽模构造 浊流 负载构造细砂岩 Sfls 灰白色,砂岩底部发育负载、火焰状、球状、挤入、枕状、底劈构造、布丁构造、环形层构造。差异负载沉降、垂直应力剪切等作用形成 震积-液化-滑动-滑塌作用 液化构造细砂岩 Sfliq 灰白色,碟状构造,沙火山、液化泄水构造、液化卷曲构造、液化角砾、液化水压构造等。由地震滑塌过程中的液化作用形成 滑塌变形构造细砂岩相 Sfd 浅灰色、灰白色变形层理细砂岩,可见包卷变形层理构造和地震活动标志,如:微褶皱、微断层、液化卷曲构造等,为地震滑塌过程中变形作用的产物 粉砂岩 波状及透镜状层理粉砂岩相 Ssw 浅灰色、灰色,砂泥薄互层,厚度5~10 cm,波状及透镜状层理,鲍马序列C段 牵引流(底流) 水平纹理粉砂岩相 Sspl 灰色,浅灰色,水平纹理发育,鲍马序列D段 滑塌变形构造粉砂岩相 Ssd 灰黑色泥质粉砂岩,砂泥岩薄互层,可见包卷层理和微地震标志,为地震滑塌形成 滑塌作用 泥质岩 油页岩 Mosh 灰黑色,水平纹理发育。高GR、高电阻率、高声波和高中子、低密度 悬浮沉积 深灰色泥岩相 M 深灰色,块状,水平层理,含植物碎屑。鲍马序列E段 通过对上述岩石相沉积特征及组合特征进行分析,可以确定其主要的沉积机制及沉积微相,为建立该地区长7-长6段的深水重力流沉积模式提供依据。
2.2 深水重力流沉积物的沉积微相
2.2.1 砂质碎屑流微相沉积特征
砂质碎屑流沉积物主要岩石相类型主要有Sfm,Sfmfc,Sfigb和Sfpl等。砂岩类型为细粒岩屑长石砂岩和长石岩屑砂岩(图 2)。
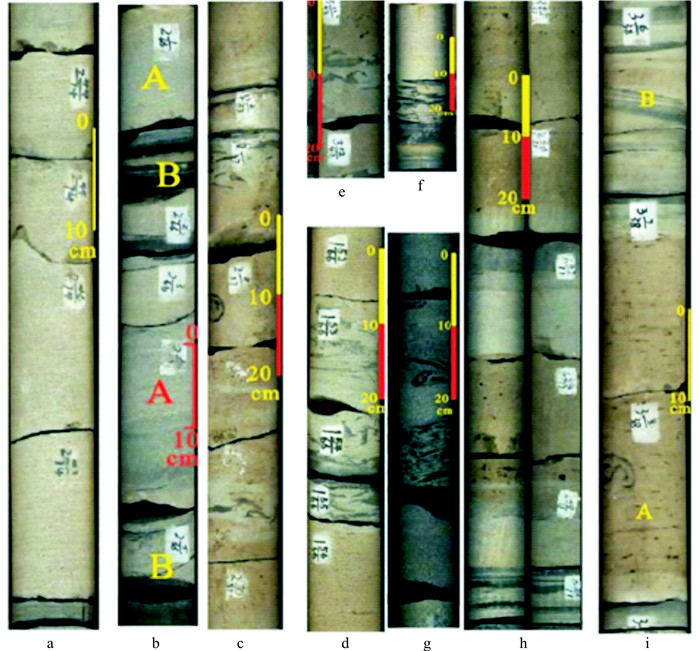
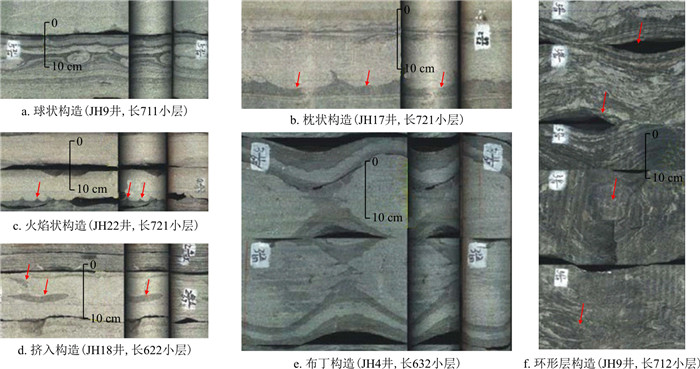
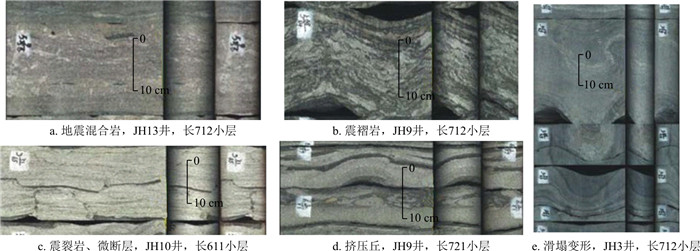
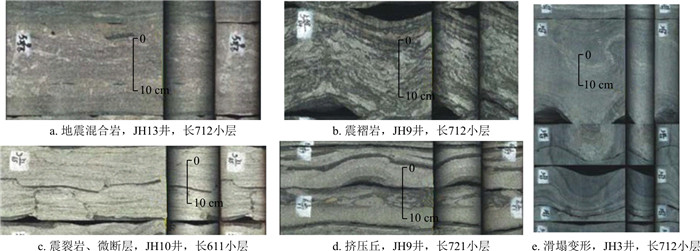
 图 2 砂质碎屑流主要岩石相a. 块状层理细砂岩(Sfm),JH8井,长7段,底部突变接触,滑动作用形成;b. 块状层理细砂岩(Sfm),JH9井,长6段,A为块状砂岩,B为砂岩底部的滑动剪切带;c~g.含(泥)砾细砂岩(Sfmfc),撕裂状的泥砾顺层分布在块状砂岩中;c.JH7井,长712小层;d. JH8井,长632小层;e, f.JH9井,长632小层;g.JH2井,长711小层;h.反递变细砂岩(Sfigb),JH9,长721小层,基质强度阻碍沉降而形成;i.似平行层理细砂岩(Sfpl),JH7,长722小层,A为砂质碎屑塑性层流沉积产物,B为流动分层产生的浊流沉积Figure 2. Main lithofacies of sandy debris flow
图 2 砂质碎屑流主要岩石相a. 块状层理细砂岩(Sfm),JH8井,长7段,底部突变接触,滑动作用形成;b. 块状层理细砂岩(Sfm),JH9井,长6段,A为块状砂岩,B为砂岩底部的滑动剪切带;c~g.含(泥)砾细砂岩(Sfmfc),撕裂状的泥砾顺层分布在块状砂岩中;c.JH7井,长712小层;d. JH8井,长632小层;e, f.JH9井,长632小层;g.JH2井,长711小层;h.反递变细砂岩(Sfigb),JH9,长721小层,基质强度阻碍沉降而形成;i.似平行层理细砂岩(Sfpl),JH7,长722小层,A为砂质碎屑塑性层流沉积产物,B为流动分层产生的浊流沉积Figure 2. Main lithofacies of sandy debris flow块状层理细砂岩相(Sfm),灰色、褐色,细粒,均质,块状构造,泥质含量低,砂质较纯。含油性较好。底部突变接触,无侵蚀现象,为砂体滑动作用的产物(图 2-a)。顶面突变接触或浊积成因的砂泥薄互层(图 2-b)。Shanmugam[12]认为由于“滑行效应”的存在,即使地形坡度很缓的情况下,砂体也可以搬运到很远的深湖相。砂岩底部的剪切破裂,反映砂体滑动过程中产生了剪切,形成了低角度剪切破裂。Sfm被认为是砂质碎屑流中的具有多种支撑机理(例如,黏性强度、摩擦强度及浮力)的典型岩石相。
含砾细砂岩相(Sfmfc),灰色、灰褐色,块状。含油性较好。块状砂岩中上部可见零散分布的含伸长状泥岩碎片/泥砾,直径为2~6 cm,呈漂浮状,且有伸长撕裂现象,两端呈尖灭状,有顺层分布的趋势,也可见漂浮的石英砾石和碎屑出现(图 2-c~f)。块状砂岩中出现的砾岩漂砾,反映了砂质碎屑流的塑性流体性质,也就是说砂质碎屑流砂体在搬运过程中,砂体前缘浊流对下部泥岩进行了侵蚀,产生了大量撕裂的泥屑,并被裹进砂体中,受到塑性流体内部结构强度的阻碍,撕裂的泥屑在层流牵引下,顺层分布在砂质碎屑流中上部。
反递变细砂岩(Sfigb),灰白色,下部为泥质含量较高的泥质细砂岩,致密,含油性较差(图 2-h)。上部为块状细砂岩,泥质含量低,中部为泥质细砂岩,下部为泥质粉砂岩,粒级明显呈反递变特征。这种反粒序的成因机制一般解释为是由于砂质碎屑流的基质强度阻碍了颗粒沉降而形成的。
似平行层理细砂岩(Sfpl),灰白色,灰褐色,层理面隐约为断续平行状,为似平行层理(图 2-i)。砂岩的含油显示顺纹理断续出现,显示出似平行层理的特征。这种层理被解释为砂质碎屑层流流态下的沉积产物。
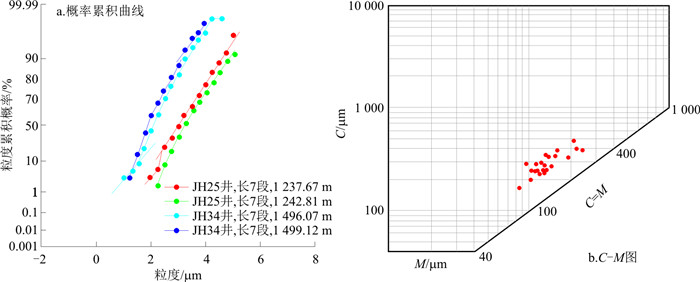
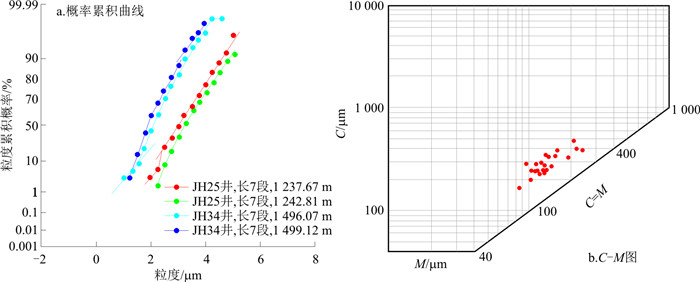
从流变学角度来看,砂质碎屑流为塑性流体,既表现为重力流,又表现为层状流特征。所以,砂质碎屑流的C-M粒度分布图显示出重力流特征,在粒度累积概率曲线可见不明显的牵引流特征,但主要是重力流整体搬运沉积特征(图 3)。
砂质碎屑流砂体的单砂体厚度一般大于0.5 m,最大可达数十米,平均8 m左右。横向变化快;砂岩填隙物主要为杂基(水云母)和胶结物,其中杂基体积分数为5.15%左右,为砂质碎屑流提供了基质强度。
2.2.2 浊积岩微相
长6-长7段普遍发育流态为紊流的浊流沉积,主要岩石相类型主要有Sftmc、Sfgb、Sfp、Ssw,Sspl和M等。
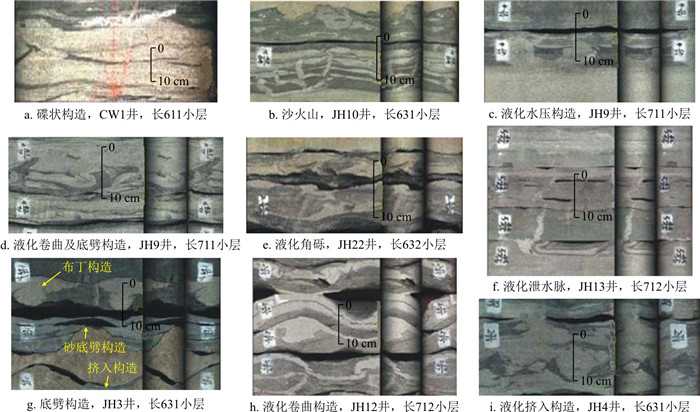
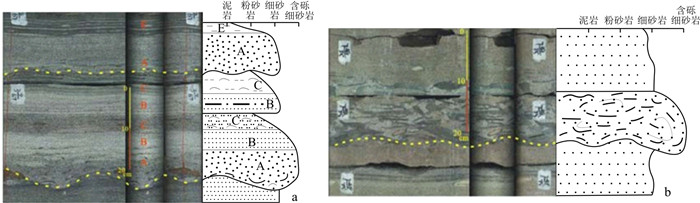
严格意义上讲,真正的浊积岩相只有递变层理细砂岩相(Sfgb)和含底砾细砂岩相(Sftmc)。平行层理细砂岩相(Sfp)、波状-透镜状层理粉砂岩相(Ssw)、水平纹理粉砂岩相(Ssh)和深灰色泥岩相(M)等岩石相属于牵引流沉积产物。牵引流既可以是由于砂质碎屑流沉积物浓度变稀而转化过来,也可以是盆地深湖环境中发育的底流或等深流而形成[12]。这些岩相与Sfgb或Sftmc一起构成了浊积岩沉积序列,即鲍马序列。鲍马序列是在一次浊流沉积事件过程中形成的,可以是完整的,也可以是不完整的[8]。因此,将这些岩石相归为浊积岩序列。含底砾细砂岩相(Sftmc)是该地区比较特殊的反映浊积沉积的岩石相(图 4)。该岩石相为灰白色细砂岩,砂岩中普遍发育撕裂状的泥砾,呈伸长状,2~5 cm,两端呈卷曲状,呈紊流状分布,为砂质碎屑流底部由于流动分层作用,在砂体底部形成高能浊流,对下部底形的刻蚀,流体呈紊流态,撕裂的泥砾被紊流翻滚而形成紊流状分布(图 4-a, b)。
总体来看,浊流形成的浊积岩主要有以下特征:
(1) 薄层细砂岩中可见向上变细的正递变层理。正递变的形成是由于浊流内部的颗粒是由紊流支撑,当浊流速度减缓或内部水流扰动强度降低时,内部的颗粒将发生沉积。在重力作用下,大和重的颗粒首先沉降,然后是细或轻的颗粒,从而在其沉积物中产生正粒序。
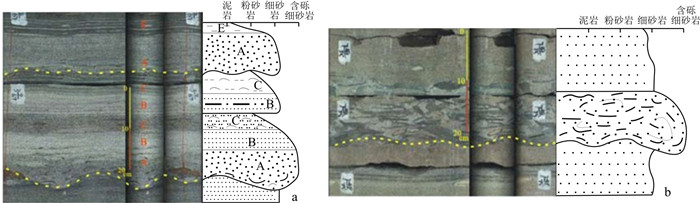
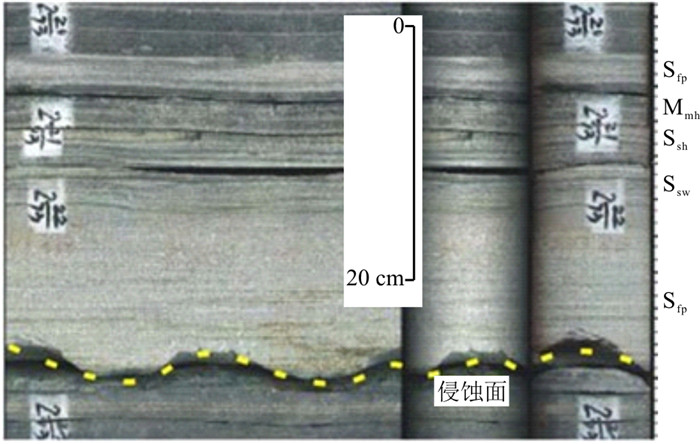
(2) 递变层理砂岩常以砂泥岩薄互层形式出现,构成多个韵律层,侧向延伸稳定,厚度变化小,单砂层厚度从数厘米至数十厘米不等,为浊积席状砂沉积,最大不超过0.5 m(图 5)。
(3) 发育正递变层理的砂岩可与上覆具平行、波状纹理和水平纹层的细砂岩、粉砂岩和泥岩一起构成完整或不完整的鲍马序列,常见各种组合类型,如图 4-a中的ABC-BC-AE组合和图 6中的BCDE-BE组合。
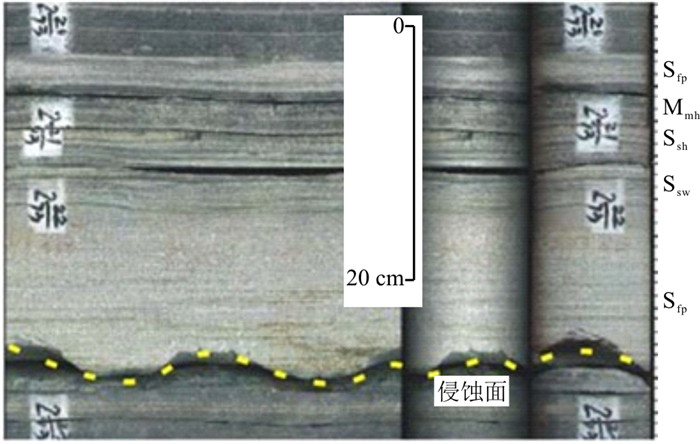
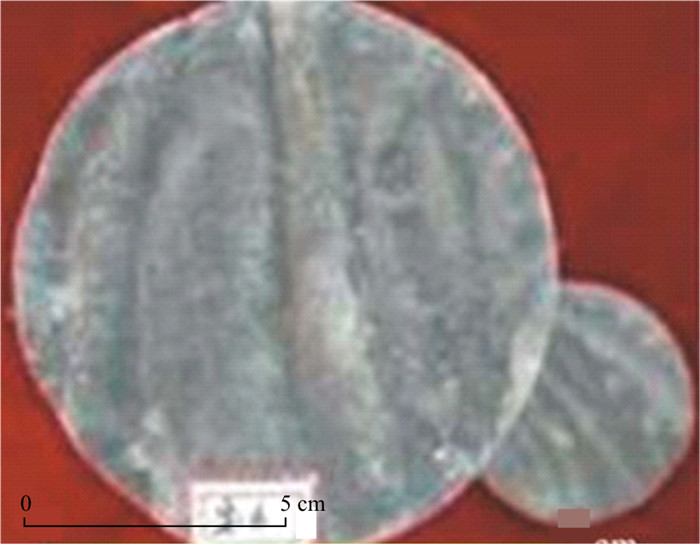
(4) 砂岩底部不平整,岩性突变,常发育槽模构造(图 7),与部分砂枕、砂球、火焰等准同生构造共生。
(5) 泥质漂砾呈现出紊乱的分布现象(图 4)。
(6) 从粒度曲线看,经典浊积岩在C-M图上表现为平行于C-M基线的直线段,反映了重力流的特征。
2.2.3 震积滑塌岩微相
滑塌岩是在深水环境中受滑动和滑塌作用形成的滑塌变形体。深水环境存在滑动、滑塌、碎屑流和浊流等多种重力驱动作用,将沉积物从陆架边缘沿斜坡向下搬运至深水斜坡和盆地环境[12]。长6-长7段滑塌岩的特征为砂泥混杂并存在多种液化变形构造,此外,砂泥混杂的滑塌岩中还经常可见震积岩的特点,例如存在微褶皱、微断层、布丁构造、环形层、沙火山、泄水脉、液化水压构造以及各种负载构造等。这些特征表明,滑塌岩的形成是由地震触发,在滑塌-沉积过程中受到地震作用的改造[46]。因此,我们将具有滑塌和震积特征的变形体称之为震积滑塌岩,它是砂质碎屑流-浊流发育的开始。
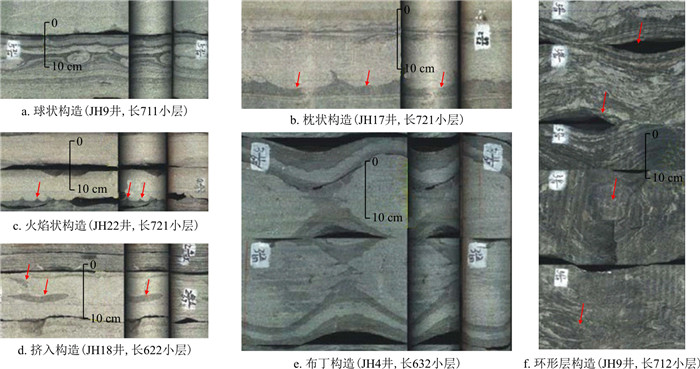
震积滑塌岩微相的主要岩石相类型有:负载构造粉细砂岩(Sfls)、液化构造粉-细砂岩(Sfliq)和滑塌变形构造粉细砂岩相(Sfd)。负载构造细砂岩(Sfls)为灰白色,砂岩底部发育球枕状构造(图 8-a, b)、火焰状构造(图 8-c)、挤入构造(图 8-d)、布丁(又称为“石香肠”)构造(图 8-e)和环形层构造(图 8-f), 为砂岩快速滑动沉积过程中,差异沉降且在差异沉降过程中产生垂向剪切作用而形成。负载构造细砂岩(Sfls)岩石相存在许多震积岩特征,例如,微褶皱、微断层、地震混合岩等(图 8)。
布丁构造(石香肠)以及环形层构造均发育在砂泥互层的背景下,受到垂向挤压应力的作用,塑性岩石(泥岩)垂向挤压相对刚性的砂岩层段,产生水平方向的拉伸,垂向剪切破裂而形成布丁(石香肠)构造。如果是薄砂泥纹层的条件下,则形成环形层构造。这种形成布丁构造(石香肠)或环形层构造的垂向应力主要来自于地震的垂向震动,因此,这类构造反映的是滑塌岩受到地震作用的影响。
液化构造细砂岩(Sfliq)为灰白色,发育各种与地震滑塌-液化有关的沉积构造类型,如:碟状构造(图 9-a),沙火山(图 9-b)、液化水压构造(图 9-c)、液化卷曲及底劈构造(图 9-d, g, h)、液化泄水脉(图 9-f)、液化挤入构造(图 9-i)、液化角砾(图 9-e)等。这些沉积构造均为坡折带沉积物受地震触发产生滑动,在滑塌过程中砂岩不断液化,在液化作用下形成。这类沉积构造发反映了地震作用下的滑塌及液化作用,是滑塌岩的主要标志。
滑塌变形构造粉砂岩(Ssd)和滑塌变形构造细砂岩相(Sfd),灰黑色,泥质粉砂岩,细砂岩、砂泥岩薄互层,砂泥岩可见包卷弯曲变形,为沉积物滑塌形成。另外,受地震触发及地震改造的影响,这类砂岩常见震积岩标志,例如:地震混合岩(图 10-a)、微褶皱(图 10-b, d, e)、微断层(图 10-c)、震裂岩(图 10-c);此外,还可见砂岩液化及变形和差异负载构造,也反映了地震活动的影响是砂质碎屑流的触发机制。
3. 彬长区块长7-长6段深水重力流沉积组合及沉积模式
3.1 彬长区块长7-长6段深水重力流沉积沉积组合及时空变化
根据大量岩心及粒度分析资料,识别了3类沉积微相,研究不同微相的组合形式以及空间分布规律,对于理解沉积物形成的过程具有重要意义。
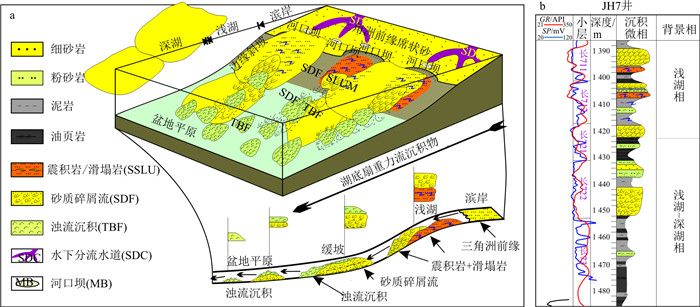
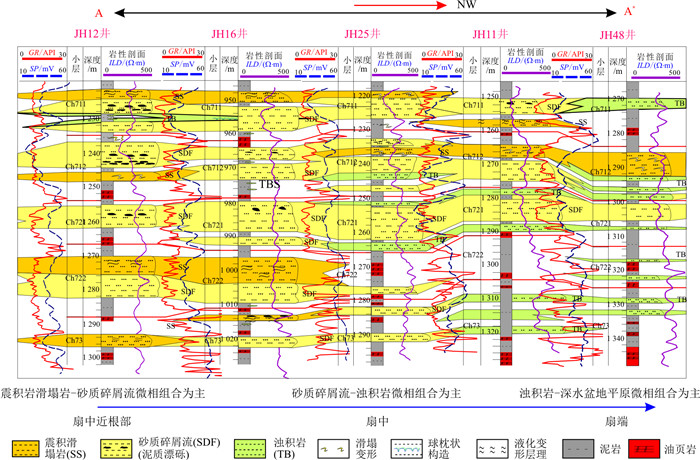
根据岩心分析结果,识别了3种主要垂向沉积微相组合类型:①震积滑塌相-砂质碎屑流沉积组合(图 11-a);②砂质碎屑流浊积岩相(浊积席状砂和浊积水道)沉积组合(图 11-b);③浊流和深湖相组合。
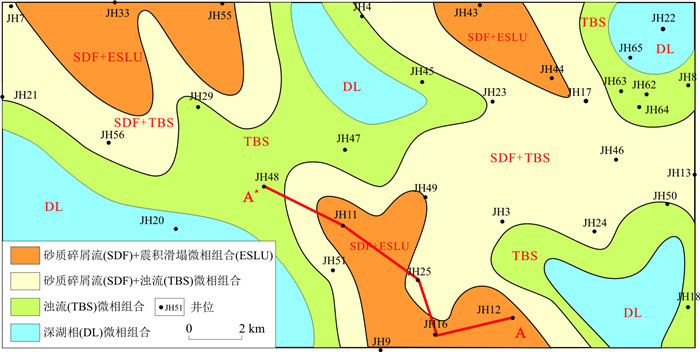
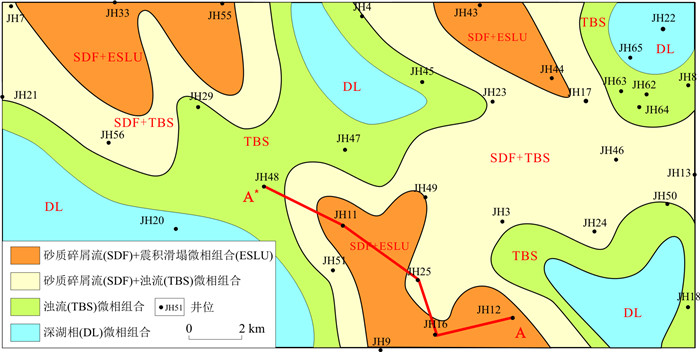
由于地震以及古地貌坡折是震积岩发育的基本条件,因此从3种相组合的平面分布应表现为:第一种微相组合分布在坡折带附近,第二类微相组合发育在斜坡坡底部位,第三类微相组合分布在深水湖盆盆底部位。
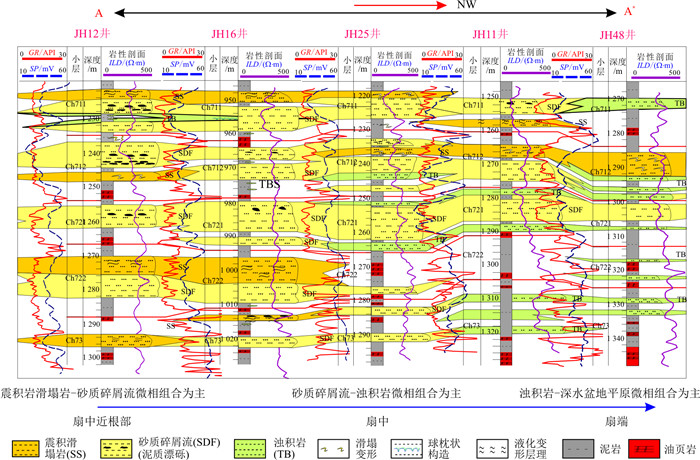
图 12为彬长区块长711小层沉积微相平面分布图。其中,物源来自研究区的南部。从图中可以看出南部为震积滑塌相和砂质碎屑流沉积组合,向北为砂质碎屑流和浊积岩微相(浊积席状砂和浊积水道)沉积组合,远端部为浊流和深湖相沉积组合。从南北向剖面图(图 13)也可以看出,震积滑塌相主要发育在南部,北部主要为浊流沉积,中部为砂质碎屑流沉积。
 图 13 彬长区块长711-长73小层湖底扇沉积微相剖面分布图(剖面位置见图 12)Figure 13. Profile distribution map of sedimentary microfacies of sublacustrine fan in Ch711-Ch73 Member of the Binchang Block
图 13 彬长区块长711-长73小层湖底扇沉积微相剖面分布图(剖面位置见图 12)Figure 13. Profile distribution map of sedimentary microfacies of sublacustrine fan in Ch711-Ch73 Member of the Binchang Block从沉积微相平面形态来看,一般为朵状和伸长朵状。地震相一般呈团块状分布,很少见带状特征,很明显,这种特征是不支持过去传统的辫状分流河道砂体解释的认识。
3.2 深水沉积物重力流沉积模式
Shanmugam[12]在对前人以浊积沉积为主的深水海底扇模式批判的基础上,也提出了自己的以砂质碎屑流主导的深水斜坡模式,并进一步划分为非水道体系(non channelized)和水道体系(channelized)2种类型。邹才能等[28]根据控制沉积物重力流发育的坡折带到盆地平原位置,将白豹地区长6段深水沉积物重力流沉积模式划分为3个相带,即坡折带附近的滑塌相带、斜坡上的砂质碎屑流相带和盆地平原部位的浊流及底流改造相带。这些模型有利于研究区沉积模式的构建。
参考上述研究成果,本研究根据彬长区块整体位于鄂尔多斯盆地南部坡折带,整体并未完全进入盆地的古地貌特征,结合沉积特征分析,将彬长地区长6-长7段的深水重力流沉积物归纳为非水道型的斜坡-湖盆底的斜坡-湖底扇沉积模式。
图 14概括了彬长区块长6-长7段沉积过程和沉积模式。总体上,彬长区块在长8段沉积之后,受印支运动及与盆地西南边缘毗邻的西秦岭强烈造山活动的影响,鄂尔多斯盆地的基底不对称挠曲变形,从而形成有利于砂质碎屑流发育的“南陡北缓”的盆地古地貌格局。李相博等[29-30]和刘化清等[42]根据地震剖面结构分析,结合长7段油页岩厚度分析,指出在长6-长7段沉积时期,盆内南部普遍发育坡折带,古坡度在3.5°~5°之间。根据国外对砂质碎屑流沉积发育的古坡度研究(包括实验、野外观察和现代滑坡沉积观察)表明,大规模粉细砂岩的砂质碎屑流沉积可以在坡度最小小于1°的斜坡上滑行很长距离[12]。这表明在彬长区块南缘,这种古地貌非常有利于斜坡扇滑塌沉积。
坡折带大量堆积的三角洲前缘沉积物在地震外力触发下,在重力作用下,沿斜坡向下滑动和滑塌。在这个过程中,受地震震动的影响,湖水不断进入沉积物中,导致沉积物不断液化,形成大量准同生液化构造、卷曲变形构造、包卷层理和各种震积岩构造[47-48]。随着震积滑塌岩继续不断地液化,砂岩由于孔隙中的超压流体、砂岩颗粒相互碰撞以及水黏土的黏结等多种机制支撑,进行了整体搬运(砂质碎屑流)。在这个过程中,受流动分层作用的影响,在砂质碎屑流边缘,由于流动分层而形成浊流,同时,随着流体浓度的降低,在进入到斜坡底-盆地中心部位时,流体变成低密度浊流(图 14)。
从微相类型来看,主要发育震积滑塌微相、砂质碎屑流微相、浊积岩等微相。平面上,可以根据坡折带-湖盆平原的位置,将湖底扇相划分为:扇根(坡折带-斜坡上半部分)的震积滑塌相-砂质碎屑流亚相(沉积组合)、扇中(斜坡中下部位-坡脚)的砂质碎屑流-浊积岩沉积亚相(沉积组合)和扇端(坡脚-盆底)浊积砂等亚相(沉积组合)(表 2)。
表 2 彬长区块长6-长7段沉积相、沉积组合(亚相)和沉积微相划分Table 2. Division of sedimentary facies, sedimentary assemblages (subfacies) and sedimentary micro-facies in Ch6-Ch7 Section of the Binchang Block沉积相 亚相/沉积组合 古地理位置 主要微相(代码) 斜坡-湖底扇 扇根的(震积滑塌相-砂质碎屑流沉积组合) 坡折带-斜坡上半部分 震积滑塌岩(SSLM)和砂质碎屑流(SDF)微相 扇中(砂质碎屑流-浊积岩沉积组合) 斜坡中下部位-坡脚 砂质碎屑流(SDF)、浊积砂(TBF) 扇端(浊积岩沉积组合) 坡脚-盆底 浊积砂(TBF) 4. 结论
(1) 彬长区块位于鄂尔多斯盆地南缘,受南部扬子板块与北部华北板块挤压碰撞的影响,盆地南缘具有前陆盆地特征,剖面形态具有南陡北缓的不对称形态,发育良好的坡折带,为砂质碎屑流发育提供了良好的古地貌条件。
(2) 岩心沉积特征观察表明,泥岩主要为深灰色泥岩,油页岩发育,反映了深湖相沉积背景。将砂岩划分出以细砂岩和粉砂岩为主的15种岩石相类型;3种沉积微相:砂质碎屑流、浊积岩和震积滑塌岩;2类沉积组合:震积滑塌微相和砂质碎屑流微相的沉积组合、砂质碎屑流和浊积岩微相的沉积组合。
(3) 彬长区块长6-长7段的深水重力流沉积模式可以概括为扇根(坡折带-斜坡上半部分)的震积滑塌相-砂质碎屑流亚相(沉积组合)、扇中(斜坡中下部位-坡脚)的砂质碎屑流-浊积岩沉积亚相(沉积组合)和扇端(坡脚-盆底)浊积砂等亚相(沉积组合)。湖底扇重力流沉积过程可以理解为,在坡折带上受地震触发机制诱发,产生震积滑(塌)变形作用,在震动、滑动和滑塌过程中不断液化而形成塑性层流流体(砂质碎屑流),经过流体分层作用而形成浊流,并在间歇期局部受弱的底流改造。
-
图 2 砂质碎屑流主要岩石相
a. 块状层理细砂岩(Sfm),JH8井,长7段,底部突变接触,滑动作用形成;b. 块状层理细砂岩(Sfm),JH9井,长6段,A为块状砂岩,B为砂岩底部的滑动剪切带;c~g.含(泥)砾细砂岩(Sfmfc),撕裂状的泥砾顺层分布在块状砂岩中;c.JH7井,长712小层;d. JH8井,长632小层;e, f.JH9井,长632小层;g.JH2井,长711小层;h.反递变细砂岩(Sfigb),JH9,长721小层,基质强度阻碍沉降而形成;i.似平行层理细砂岩(Sfpl),JH7,长722小层,A为砂质碎屑塑性层流沉积产物,B为流动分层产生的浊流沉积
Figure 2. Main lithofacies of sandy debris flow
图 13 彬长区块长711-长73小层湖底扇沉积微相剖面分布图(剖面位置见图 12)
Figure 13. Profile distribution map of sedimentary microfacies of sublacustrine fan in Ch711-Ch73 Member of the Binchang Block
表 1 彬长区块长6-长7段岩石相特征
Table 1. Lithofacies characteristics of Ch6-Ch7 Section of the Binchang Block
岩性 岩石相 代码 沉积特征 沉积解释 细砂岩 块状层理细砂岩相 Sfm 灰色、褐色,细粒,均质,块状,泥质含量低,砂质较纯。底部突变接触,或见滑动剪切构造,顶面突变接触或浊积成因的砂泥薄互层。含油性较好 砂质碎屑流(塑性流型、层流流体) 含泥砾细砂岩相 Sfmfc 灰色、灰褐色,块状,砂岩中上部含伸长状或浑圆状泥砾,漂浮顺层分布,含油性较好 反递变细砂岩 Sfigb 灰白色,下部为泥质含量较高的泥质细砂岩,致密,含油性较差,上部为块状细砂岩,泥质含量低,物性好,粒级明显呈反递变特征 似平行层理细砂岩 Sfpl 灰白,灰褐色,层理面隐约断续平行状,似平行层理 含撕裂泥砾细砂岩相 Sftmc 灰色,块状,位于块状砂岩底部,底部侵蚀接触,砂岩中含伸长状两端卷曲的撕裂泥砾,平行/紊乱分布,为浊流沉积产物 浊流 牛顿型流体 平行层理细砂岩相 Sfp 灰白,灰褐色,平行层理,薄砂泥互层中出现,鲍马序列中的B段 牵引流 递变层理细砂岩相 Sfgb 灰白色,层薄,小于20 cm,正递变,鲍马序列A段。底部可见槽模构造 浊流 负载构造细砂岩 Sfls 灰白色,砂岩底部发育负载、火焰状、球状、挤入、枕状、底劈构造、布丁构造、环形层构造。差异负载沉降、垂直应力剪切等作用形成 震积-液化-滑动-滑塌作用 液化构造细砂岩 Sfliq 灰白色,碟状构造,沙火山、液化泄水构造、液化卷曲构造、液化角砾、液化水压构造等。由地震滑塌过程中的液化作用形成 滑塌变形构造细砂岩相 Sfd 浅灰色、灰白色变形层理细砂岩,可见包卷变形层理构造和地震活动标志,如:微褶皱、微断层、液化卷曲构造等,为地震滑塌过程中变形作用的产物 粉砂岩 波状及透镜状层理粉砂岩相 Ssw 浅灰色、灰色,砂泥薄互层,厚度5~10 cm,波状及透镜状层理,鲍马序列C段 牵引流(底流) 水平纹理粉砂岩相 Sspl 灰色,浅灰色,水平纹理发育,鲍马序列D段 滑塌变形构造粉砂岩相 Ssd 灰黑色泥质粉砂岩,砂泥岩薄互层,可见包卷层理和微地震标志,为地震滑塌形成 滑塌作用 泥质岩 油页岩 Mosh 灰黑色,水平纹理发育。高GR、高电阻率、高声波和高中子、低密度 悬浮沉积 深灰色泥岩相 M 深灰色,块状,水平层理,含植物碎屑。鲍马序列E段 表 2 彬长区块长6-长7段沉积相、沉积组合(亚相)和沉积微相划分
Table 2. Division of sedimentary facies, sedimentary assemblages (subfacies) and sedimentary micro-facies in Ch6-Ch7 Section of the Binchang Block
沉积相 亚相/沉积组合 古地理位置 主要微相(代码) 斜坡-湖底扇 扇根的(震积滑塌相-砂质碎屑流沉积组合) 坡折带-斜坡上半部分 震积滑塌岩(SSLM)和砂质碎屑流(SDF)微相 扇中(砂质碎屑流-浊积岩沉积组合) 斜坡中下部位-坡脚 砂质碎屑流(SDF)、浊积砂(TBF) 扇端(浊积岩沉积组合) 坡脚-盆底 浊积砂(TBF) -
[1] Pettingill H S, Weimer P. Worldwide deepwater exploration and production: Past, present, and future[J]. The Leading Edge, 2002, 21(4): 371-376. doi: 10.1190/1.1471600 [2] 张功成, 屈红军, 赵冲, 等. 全球深水油气勘探40年大发现及未来勘探前景[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(10): 1447-1477. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201710001.htmZhang G C, Qu H J, Zhao C, et al. Giant discoveries of oil and gas exploration in global deepwaters in 40 years and the prospect of exploration[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(10): 1447-1477(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201710001.htm [3] 张功成, 米立军, 屈红军, 等. 全球深水盆地群分布格局与油气特征[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(3): 369-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201103000.htmZhang G C, Mi L J, Qu H J, et al. A basic distributional framework of global deepwater basins and hydrocarbon characteristics[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(3): 369-378(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201103000.htm [4] 操应长, 金杰华, 刘海宁, 等. 中国东部断陷湖盆深水重力流沉积及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(2): 247-257. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202102003.htmCao Y C, Jin J H, Liu H N, et al. Deep-water gravity flow deposits in a lacustrine rift basin and their oil and gas geological significance in eastern China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(2): 247-257(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202102003.htm [5] 张家强, 李士祥, 李宏伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组7油层组湖盆远端重力流沉积与深水油气勘探: 以城页水平井区长73小层为例[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(5): 570-587. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202105002.htmZhang J Q, Li S X, Li H W, et al. Gravity flow deposits in the distal lacustrine basin of the 7th reservoir group of Yanchang Formation and deepwater oil and gas exploration in Ordos Basin: A case study of Chang 73 sublayer of Chengye horizontal well region[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(5): 570-587(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202105002.htm [6] 秦雁群, 万仑坤, 计智锋, 等. 深水块体搬运沉积体系研究进展[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(1): 140-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201801015.htmQin Y Q, Wan L K, Ji Z F, et al. Progress of research on deep-water mass-transport deposits[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(1): 140-152(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201801015.htm [7] Kuenen P H, Migliorini C I. Turbidity currents as a cause of graded bedding[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1950, 58(2): 91-127. doi: 10.1086/625710 [8] Bouma A H. Sedimentology of some flysch deposits: A graphic approach to facies interpretation[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1962. [9] Normark W R. Growth patterns of deep-sea fans[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1970, 54(11): 2170-2195. [10] Normark W R. Fan valleys, channels, and depositional lobes on modern submarine fans: Characters for recognition of sandy turbidite environments[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1978, 62(6): 912-931. [11] Walker R G. Deep-water sandstone facies and ancient submarine fans: Models for exploration for stratigraphic traps[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1978, 62(6): 932-966. [12] Shanmugam G. 50 years of the turbidite paradigm (1950s-1990s): Deep-water processes and facies models: A critical perspective[J]. Marine and petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(2): 285-342. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00011-2 [13] Shanmugam G, Zimbrick G. Sandy slump and sandy debris flow facies in the Pliocene and Pleistocene of the Gulf of Mexico: Implications for submarine fan models[C]//Anon. Proceedings of American Association of Petroleum Geologists International Congress and Exhibition, Caracas. Venezuela-Official Program A, 1996: 45. [14] Shanmugam G. Ten turbidite myths[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2002, 58(3/4): 311-341. [15] Middleton G V, Hampton M A. Sediment gravity flows: Mechanics of flow and deposition[C]//Middleton G V, Bouma A H. Turbidites and deep sea sedimentation. [S. l. ]: Society Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists Special Publication, 1973: 1-38. [16] Lowe D R. Sediment gravity flows: Their classification and some problems of application to natural flows and deposits[C]//Doyle L J, Pilkey O H. Geology of continental slopes. [S. l. ]: Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists Special Publication, 1979, 27: 75-82. [17] Lowe D R. Sediment gravity flows: II. Depositional models with special reference to the deposits of high-density turbidity currents[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1982, 52(1): 279-297 [18] Mulder T, Alexander J. The physical character of subaqueous sedimentary density flows and their deposits[J]. Sedimentology, 2001, 48(2): 269-299. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3091.2001.00360.x [19] Mulder T, Syvitski J P M, Migeon S, et al. Marine hyperpycnalflows: Initiation, behavior and related deposits: A review[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2003, 20(6/8): 861-882. [20] 孙国桐. 深水重力流沉积研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(3): 30-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201503005.htmSun G T. A review of deep-water gravity-flow deposition research[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(3): 30-36(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201503005.htm [21] Mutti E. Distinctive thin-bedded turbidite facies and related depositional environments in the Eocene Hecho Group (South-central Pyrenees, Spain)[J]. Sedimentology, 1977, 24(1): 107-131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1977.tb00122.x [22] 夏青松, 田景春. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部上三叠统延长组震积岩的发现及地质意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(2): 246-252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2007.02.012Xia Q S, Tian J C. Characteristics and geological significance of seismites of the Yanchang Formation, Upper Triassic, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(2): 246-252(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2007.02.012 [23] 赵俊兴, 吕强, 李凤杰, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部延长组长6时期物源状况分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2008, 26(4): 610-616. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200804011.htmZhao J X, Lü Q, Li F J, et al. Sediment provenance analysis of the Chang 6 oil-bearing of Yanchang Formation in the south of Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2008, 26(4): 610-616(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200804011.htm [24] 李士春, 冯朝荣, 殷世江. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部中生界延长组沉积体系与油气富集[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2010, 22(2): 79-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2010.02.014Li S C, Feng C R, Yin S J. Sedimentary system and hydrocarbon enrichment of Yanchang Formation in southern Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2010, 22(2): 79-83(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2010.02.014 [25] 陈飞, 樊太亮, 高志前, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部上三叠统延长组物源方向与沉积体系分析[J]. 西安石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 24(6): 24-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2009.06.007Chen F, Fan T L, Gao Z Q, et al. Analysis of the provenance direction and the depositional systems of Yanchang Formation of Upper Triassic in the southern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University: Natural Science Edition, 2009, 24(6): 24-28(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2009.06.007 [26] 丁晓琪, 张哨楠, 熊迪, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘延长组湖盆底形演化研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报, 2011, 33(6): 1-6.Ding X Q, Zhang S N, Xiong D, et al. Study on the evolution of lake basin bottom shape of the Extension Group in the southwest margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University: Science & Technology Edition, 2011, 33(6): 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract). [27] 王振, 张元福, 张娜, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部旬邑地区延长组长7段深水牵引流的发现及其意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(2): 9-16(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201802002.htmWang Z, Zhang Y F, Zhang N, et al. Discovery and significance of deep-water tractive current deposits in Member 7 of Yanchang Formation in Xunyi area of southern Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(2): 9-16(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201802002.htm [28] 邹才能, 赵政璋, 杨华, 等. 陆相湖盆深水砂质碎屑流成因机制与分布特征: 以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(6): 1068-1075. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200906007.htmZou C N, Zhao Z Z, Yang H, et al. Genetic mechanism and distribution of sandy debris flows in terrestrial lacustrine basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(6): 1068-1075(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200906007.htm [29] 李相博, 刘化清, 陈启林, 等. 大型坳陷湖盆沉积坡折带特征及其对砂体与油气的控制作用: 以鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(4): 718-731. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201004008.htmLi X B, Liu H Q, Chen Q L, et al. Characteristics of slope break belt in large depression lacustrine basin and its controlling effect on sandbody and petroleum: Taking the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(4): 718-731(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201004008.htm [30] 李相博, 陈启林, 刘化清, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组3种沉积物重力流及其含油气性[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2010, 22(3): 16-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201003005.htmLi X B, Chen Q L, Liu H Q, et al. Three types of sediment gravity flows and their petroliferous features of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2010, 22(3): 16-22(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201003005.htm [31] 袁珍, 李文厚, 范萌萌, 等. 深水块状砂岩沉积特征及其成因机制探讨: 以鄂尔多斯盆地东南缘上三叠统长6油层组为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2011, 30(4): 43-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201104007.htmYuan Z, Li W H, Fan M M, et al. Genetic mechanism and sedimentary features of deep water massive sandstone: A case study of the Upper Triassic sandstones of Chang 6 Formation in the southeast of Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2011, 30(4): 43-49(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201104007.htm [32] 杨仁超, 金之钧, 孙冬胜, 等. 鄂尔多斯晚三叠世湖盆异重流沉积新发现[J]. 海相油气地质, 2016, 21(2): 47-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201501002.htmYang R C, Jin Z J, Sun D S, et al. Discovery of hyperpycnal flow deposits in the Late Triassic lacustrine Ordos Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2016, 21(2): 47-56(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201501002.htm [33] 唐武, 王英民, 仲米虹, 等. 异重流研究进展综述[J]. 海相油气地质, 2016, 21(2): 47-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ201602010.htmTang W, Wang Y M, Zhong M H, et al. Review of hyperpycnal flow[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2016, 21(2): 47-56(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ201602010.htm [34] 孙福宁, 杨仁超, 李冬月. 异重流沉积研究进展[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(3): 452-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201603003.htmSun F N, Yang R C, Li D Y. Research progresses on hyperpycnal flow deposits[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(3): 452-462(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201603003.htm [35] 潘树新, 刘化清, Zavala C, 等. 大型坳陷湖盆异重流成因的水道湖底扇系统: 以松辽盆地白垩系嫩江组一段为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(6): 860-870. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201706004.htmPan S X, Liu H Q, Zavala C, et al. Sublacustrine hyperpycnal channel-fan system in a large depression basin: A case study of Nen 1 Member, Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation in the Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(6): 860-870(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201706004.htm [36] 周立宏, 陈长伟, 韩国猛, 等. 断陷湖盆异重流沉积特征与分布模式: 以歧口凹陷板桥斜坡沙一下亚段为例[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2018, 23(4): 11-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201804003.htmZhou L H, Chen C W, Han G M, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and distribution patterns of hyperpycnal flow in rifted lacustrine basins: A case study on Lower Es1 of Banqiao slope in Qikou Sag[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2018, 23(4): 11-20(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201804003.htm [37] 张国栋, 鲜本忠, 晁储志, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三水河剖面上三叠统块状砂岩的异重流成因: 来自岩石结构的证据[J]. 沉积学报, 2019, 37(5): 934-943. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201905005.htmZhang G D, Xian B Z, Chao C Z, et al. Flood-generated massive sandstones of the Sanshuihe outcrop in the Triassic Ordos Basin: Evidence from sedimentary textural characteristics[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(5): 934-943(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201905005.htm [38] 王家豪, 王华, 肖敦清, 等. 陆相断陷湖盆异重流与滑塌型重力流沉积辨别[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(4): 392-411. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202004004.htmWang J H, Wang H, Xiao D Q, et al. Differentiation between hyperpycnal flow deposition and slump-induced gravity flow deposition in terrestrial rifted lacustrine basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(4): 392-411(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202004004.htm [39] 陈五泉, 陈凤陵. 鄂尔多斯盆地渭北地区延长组沉积特征及石油勘探方向[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2008, 22(4): 10-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN200804006.htmChen W Q, Chen F L. Sedimentary characteristics and petroleum exploration target of Yanchang Formation of Triassic at Weibei area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2008, 22(4): 10-13(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN200804006.htm [40] 吕强, 赵俊兴, 陈洪德, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部中生界延长组物源与盆地底形分析[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 35(6): 610-616. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200806002.htmLü Q, Zhao J X, Chen H D, et al. Analysis of the provenance and basin bottom shape of Yanchang Epoch of Mesozoic in Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2008, 35(6): 610-616(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200806002.htm [41] 庞军刚, 卢涛, 国吉安, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长期原型湖盆恢复及中部砂体成因[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2012, 24(4): 56-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201204016.htmPang J G, Lu T, Guo J A, et al. Reconstitution of original lake basin during Triassic Yanchang stage and sand body genesis in the center of Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2012, 24(4): 56-63(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201204016.htm [42] 刘化清, 李相博, 完颜容, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长8油层组古地理环境与沉积特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2011, 29(6): 1086-1095. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201106009.htmLiu H Q, Li X B, Wanyan R, et al. Palaeogeographic and sedimentological characteristics of the Triassic Chang 8, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(6): 1086-1095(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201106009.htm [43] Zavala C, Ponce J, Drittanti D, et al. Ancient lacustrine hyperpycnites: A depositional model from a case study in the Rayoso Formation(Cretaceous) of west-central Argentina[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2006, 76(1): 41-59. [44] Yang R C, Jin Z J, A.J. Van Loon T, et al. Climatic and tectonic controls of lacustrine hyperpycnite origination in the Late Triassic Ordos Basin, central China: Implications for unconventional petroleum development[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2017, 101(1): 95-117. [45] Bates C C. Rational theory of delta formation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1953, 37(9): 2119-2162. [46] 付鑫, 杜晓峰, 官大勇, 等. 地震沉积学在河流-浅水三角洲沉积相研究中的应用: 以渤海海域蓬莱A构造区馆陶组为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 96-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202103011.htmFu X, Du X F, Guan D Y, et al. Application of seismic sedimentology in reservoir prediction in fluvial to shallow water delta facies: A case study in Guantao Formation from the Penglai A structure area in Bohai Bay[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 96-108(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202103011.htm [47] 李安琪, 叶绮, 王真真, 等. 琼东南盆地陵水凹陷北部梅山组砂质碎屑流沉积特征及油气地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 110-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202101011.htmLi A Q, Ye Q, Wang Z Z, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and significance in hydrocarbon exploration of sandy debris flow in Meishan Formation of the northern Lingshui Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 110-118(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202101011.htm [48] 岳佳恒, 黄传炎, 曹兰柱, 等. 巴音都兰凹陷巴66扇体沉积特征及控制因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(2): 88-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202102011.htmYue J H, Huang C Y, Cao L Z, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and controlling factors of the Ba 66 fan in Bayindulan Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(2): 88-98(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202102011.htm 期刊类型引用(5)
1. 武芳芳,瞿璇,周宁杰,朱薇,李彦兵,周小平,张东阁,张庆军,郭岭. 鄂尔多斯盆地五蛟西地区长6段单砂体叠置特征研究. 地质科学. 2024(04): 1034-1047 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 雷涛,唐明远,任广磊,兰浩翔,杨帅杰,朱俊阳,崔梦迪,蔡忠辉. 非渗透层下白云岩断控成藏模式:以大牛地气田马家沟组中下组合为例. 地质科技通报. 2024(05): 18-30 .  本站查看
本站查看3. 李辉,张涛,侯雨庭,喻健,何鑫,陈世加,李勇. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段陆相页岩层系致密储层充注物性下限及其控制因素. 现代地质. 2024(06): 1498-1510 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 杨哲翰,刘江艳,吕奇奇,罗顺社,周新平,李士祥,张严,张孝国. 古地貌恢复及其对重力流沉积砂体的控制作用:以鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7_3亚段为例. 地质科技通报. 2023(02): 146-158 .  本站查看
本站查看5. 舒婷,刘桂珍,郭健. 鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区长6_3重力流沉积特征. 地质科技通报. 2023(06): 140-150 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(1)
-






 下载:
下载:











 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术