Application of a tracing experiment in the prediction of water and mud inrush in the Wantan Tunnel
-
摘要:
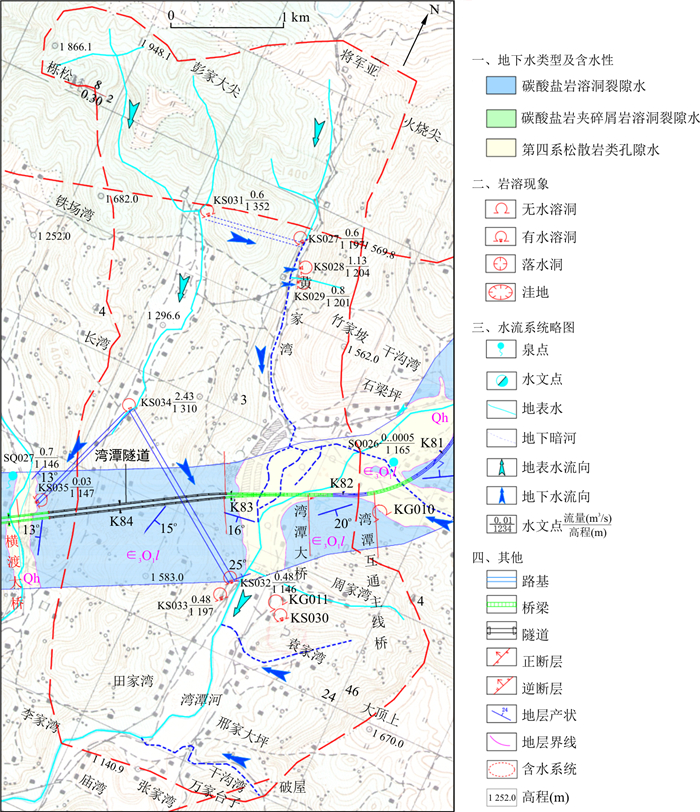
以宜来高速湾潭隧道为研究对象, 通过现场调查、地下水示踪实验、地下水流量监测, 以及采用大气降雨入渗法计算隧道的平均涌水量和丰水期涌水量, 同时采用RFPA渗流软件对隧道涌突水的可能性进行判别。现场调查及示踪试验结果显示湾潭隧道岩溶管道为多支, 混合型岩溶管道, 水文地质条件复杂, 丰水期涌水量约为平均隧道涌水量的4.6倍。数值模拟结果表明, 隧道涌水突泥破坏要历经裂隙萌生、裂隙扩展、裂隙进一步扩展、贯通破坏阶段。同时当岩溶管道处的过水流量达到初始值(37 248 m3/d)约2.7~3.5倍之间时便可出现涌水突泥破坏, 也即出水口2流量达到10 000~13 000 m3/d时, 湾潭隧道具有极高的涌水突泥风险。
Abstract:Taking the Wantan Tunnel of Yilai Highway as the study case, the average water inflow and the water inflow in the wet season of the tunnel are calculated through field investigation, groundwater tracer experiment, groundwater flow monitoring, and atmospheric rainfall infiltration method. Meanwhile, the realistic failure process analysis(RFPA) is used to analyze the possibility of tunnel water inrush is judged. The results of field survey and tracer test show that the karst pipeline of Wantan Tunnel is a multi-branched, mixed-type karst pipeline with complicated hydrogeological conditions. The water inflow in wet season is about 4.6 times of the average tunnel water inflow. Mud failure will go through the stages of crack initiation, crack expansion, further crack expansion, and through-through failure. At the same time, when the water flow at the karst pipeline reaches about 2.7 to 3.5 times the initial value (37 248 m3/d), water gushing and mud inrush damage will occur, that is, when the flow of water outlet 2 reaches 10 000 to 13 000 m3/d, There is a very high risk of water and mud gushing in the Wantan Tunnel.
-
表 1 测试区地下水示踪剂背景值
Table 1. Background values of groundwater tracers in test area
岩溶泉点 荧光素钠/10-9 湾潭隧道监测点1 28.97 湾潭隧道监测点2 26.32 表 2 数值模拟参数
Table 2. Parameters of numerical simulation
岩体抗压强度/MPa 泊松比 密度/(kg·m-3) 孔隙压力系数 弹性模量/GPa 内摩擦角/(°) 渗透系数/(m·d-1) 38 0.25 2 670 0.5 10 39 0.1 -
[1] Wan F, Zhang X, Wang Z Q. Analysis on the influence of water pressure on the safety of karst tunnel lining structure[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 769(3): 1755-1758. [2] Wang S, Li S C, Li L P, et al. Study on early warning method for water inrush in tunnel based on fine risk evaluation and hierarchical advance forecast[J]. Geosciences, 2019, 9(9): 343-377. [3] Yuan Y C, Li S C, Zhang Q Q, et al. Risk assessment of water inrush in karst tunnels based on a modified grey evaluation model: Sample as Shangjiawan Tunnel[J]. Geomechanics and Engineering, 2016, 11(4): 493-513. doi: 10.12989/gae.2016.11.4.493 [4] Dong X, Lu H, Huang H X, et al. Failure mode of the water-filled fractures under hydraulic pressure in karst tunnels[J]. Open Geosciences, 2017, 9(1): 186-196. [5] 杨兵. 宜万铁路马鹿箐隧道岩溶灾害的工程处治技术[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2011, 7(3): 581-586. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0836.2011.03.029Yang B. Treatment techniques for karst disaster of Maluqing Tunnel on Yichang-Wanzhou Railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2011, 7(3): 581-586(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0836.2011.03.029 [6] 罗明明, 周宏, 郭绪磊, 等. 峡口隧道间歇性岩溶涌突水过程及来源解析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 9(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202106027.htmLuo M M, Zhou H, Guo X L, et al. Processes and sources identification of intermittent karst water inrush in Xiakou Tunnel[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 9(1): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202106027.htm [7] 李喜, 殷坤龙, 陈标典, 等. 武汉白沙洲长江两岸岩溶塌陷易发性评价与地铁建设过程中的防治对策[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 121-130. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0612Li X, Yin K L, Chen B D, et al. Evaluation of susceptibility to karst collapse on both sides of the Yangtze River in Baishazhou, Wuhan and preventive measures in the process of metro construction[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 121-130(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0612 [8] 金新锋, 夏日元, 梁彬. 宜万铁路马鹿箐隧道岩溶突水来源分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2007, 34(2): 71-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200702016.htmJin X F, Xia R Y, Liang B. Analysis of bursting water source of Maluqing Tunnel, Yichang-Wanzhou Railway[J]. Hydrogeology Engineering Geology, 2007, 34(2): 71-74(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200702016.htm [9] 邬立, 万军伟, 陈刚, 等. 宜万铁路野三关隧道"8.5"突水事故成因分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2009, 28(2): 212-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200902024.htmWu L, Wan J W, Chen G, et al. Cause of the " 8.5" water burst incident at Yesanguan Tunnel along the Yi-Wan Railway[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2009, 28(2): 212-218(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200902024.htm [10] 徐红星, 邓谊明. 野三关隧道DK 124+602突水相关水文地质分析[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2010, 27(4): 29-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC201004008.htmXu H X, Deng Y M. Analysis of hydrogeology problems related to water bursting in area of DK 124+602 at Yesanguan Tunnel of Yichang-Wanzhou Railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2010, 27(4): 29-34(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC201004008.htm [11] 付成华, 陈胜宏. 基于突变理论的地下工程洞室围岩失稳判据研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2008(1): 167-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX200801033.htmFu C H, Chen S H. Study on instability criteria of surrounding rock of underground engineering cavern based on catastrophe theory[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008(1): 167-172(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX200801033.htm [12] Wang S S, Song B L. Application of fuzzy analytic hierarchy process in sandstone aquifer water yield property evaluation[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021(22): 1014-1020. [13] 张钧帅, 汪丙国, 刘天奇. 江汉平原浅层地下水防污性能模糊综合评价与验证[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 154-164. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0617Zhang J S, Wang B G, Liu T Q. Fuzzy comprehensive evaluationand its validation for shallow groundwater vulnerability in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 154-164(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0617 [14] 谭松林, 黄玲, 李亚伟. 模糊层次综合评价在深埋隧道围岩质量分级中的应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2009, 28(1): 105-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200901019.htmTan S L, Huang L, Li Y W. Application of fuzzy-AHP comprehensive evaluation to the quality classification of wall-rock in deep buried tunnels[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2009, 28(1): 105-108(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200901019.htm [15] Xu Y, Li B, Liu X. The rock slopes classification research of ordinary roads in Liaoning Province[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014(838/841): 1245-1249. [16] Aguiar G Z D, Lins L, Paulo M F D, et al. Dielectric permittivity effects in the detection of tree roots using ground-penetrating radar[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2021, 193: 1141-1150. [17] Shi L Q, Wang Y, Qiu M, et al. Application of three-dimensional high-density resistivity method in roof water advanced detection during working stope mining[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2019, 12(15): 411-420. [18] Fu H G. Application of sodium chloride in groundwater tracer test in karst area[J]. Advances in Environmental Protection, 2020, 10(2): 223-228. [19] Zhang X W, Wang T, Cheng S G. Application of tracer test in survey of hydraulic connection between water gushing and fracture water in karst tunnel: Taking Zhongjiashan as an example[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014(1006/1007): 115-120. [20] 曹弘, 补建伟, 潘钊, 等. 黑河上游红泥沟小流域基于溶解硅的降雨径流路径示踪[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(4): 219-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201804030.htmCao H, Bu J W, Pan Z, et al. Flow concentration route of precipitation based on dissolved silicon in small watershed of Hongnigou in the upper reaches of Heihe River[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(4): 219-224(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201804030.htm [21] 田清朝, 万军伟, 黄琨, 等. 高家坪隧道岩溶水系统识别及涌水量预测[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2016, 23(5): 13-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201605003.htmTian Q C, Wan J W, Huang K, et al. Karst water system identification and water inflow prediction in Gaojiaping Tunnel[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2016, 23(5): 13-19(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201605003.htm [22] 罗素蓉, 承少坤, 肖建庄, 等. 纳米改性再生骨料混凝土单轴受压疲劳性能[J]. 工程力学, 2021(10): 134-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX202110014.htmLuo S R, Cheng S K, Xiao J Z, et al. Fatigue behavior of nano-modified recycled aggregate concrete under uniaxial compression[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021(10): 134-144(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCLX202110014.htm -





 下载:
下载: