Random noise reduction method of complex exploration based on a fractional optimal control network
-
摘要:
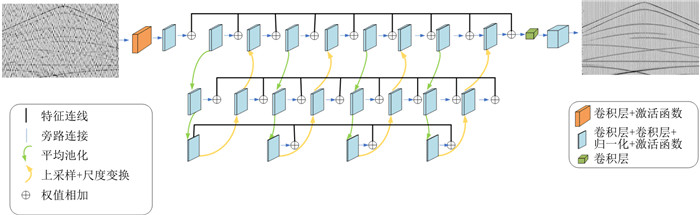
在实际勘探记录处理过程中,复杂随机噪声的出现严重影响了有效反射信息的提取,并对资料后续处理带来了不利影响。随着非常规油气资源开发,对勘探记录质量提出了更高的要求,常规方法在处理能力方面需要持续提升。为了解决复杂噪声消减问题,笔者将最优控制网络引入随机噪声消减领域。与传统的单一尺度消噪网络不同,FOC-NET具有分层结构,能够利用不同尺度信息并结合信息融合处理实现地震勘探数据潜在特征的高精度提取,克服了传统去噪网络单一尺度信息提取造成的有效特征损失问题。同时,在面对低信噪比勘探记录和弱反射同相轴时,多尺度特征交互方式同样可以有效提高噪声压制和信号恢复能力。合成记录和实际数据处理结果均表明,即使在低信噪比条件下,FOC-NET仍能有效地抑制随机噪声并准确重构出有效反射信息,极大提升勘探资料的质量。
Abstract:In field seismic prospecting, the existence of complex random noise strongly influences the detection of effective reflected signals and imposes adverse effects on the subsequent process of the data. With the exploration of unconventional petroleum resources, high-quality seismic records are needed, and the performance of conventional methods in processing needs to be further improved. To solve this problem, a fractional optimal control network (FOC-NET) is utilized to cope with complex noise reduction. Unlike conventional DnCNN, FOC-NET has a hierarchical architecture. It can cope with the feature loss caused by a single-scale feature extraction strategy. Then, the potential feature of the analyzed data can be accurately captured in combination with the different-scale information. Notably, the multi-scale fusion capability can also improve the recovery of weak reflection events and complex noise attenuation. Both synthetic and field experimental results demonstrate that FOC-NET can effectively suppress random noise and restore the desired signals, even under low-SNR conditions.
-
表 1 正演建模参数
Table 1. Parameters of forward modeling
参数 设置 子波模型 Ricker子波, 零相位小波和混合相位小波 主频/Hz 15~30 速度/(m·s-1) 500~7 000 道间距/m 20 采样间隔/ms 2 表 2 不同去噪方法SNR和RMSE比较结果
Table 2. Comparison of SNR and RMSE based on different denoising methods
处理前记录/dB 小波 带通 ED-NET DnCNN FOC-Net SNR/dB RMSE SNR/dB RMSE SNR/dB RMSE SNR/dB RMSE SNR/dB RMSE 0 4.82 0.167 5.34 0.161 12.61 0.031 12.77 0.029 14.51 0.024 -2 3.30 0.204 4.70 0.171 12.05 0.032 12.16 0.032 13.97 0.026 -4 1.51 0.252 4.17 0.182 10.88 0.038 11.33 0.035 13.36 0.027 -6 -0.93 0.335 4.65 0.172 10.43 0.039 10.88 0.038 12.88 0.028 -8 -2.33 0.411 3.51 0.211 9.29 0.044 10.02 0.041 12.16 0.032 -10 -4.22 0.481 0.73 0.283 7.91 0.053 9.67 0.043 11.43 0.034 -
[1] 李庆忠. 走向精确勘探的道路: 高分辨率地震勘探系统工程剖析[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1993.Li Q Z. The way to obtain a better resolution in seismic prospecting: A systematical analysis of high resolution seismic exploration[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1993(in Chinese). [2] Zhong T, Li Y, Wu N, et al. A study on the stationarity and Gaussianity of the background noise in land-seismic prospecting[J]. Geophysics, 2015, 80(4): 67-82. doi: 10.1190/geo2014-0153.1 [3] Zhong T, Cheng M, Dong X, et al. Seismic random noise suppression by using adaptive fractal conservation law method based on stationarity testing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 99: 1-13. [4] Wu N, Li Y, Ma H, et al. Intermediate-frequency seismic record discrimination by radial trace time-frequency filtering[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(7): 1280-1284. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2292114 [5] 曲志鹏, 王芳芳, 张云银, 等. 基于关联规则与随机森林的地震多属性砂体厚度预测[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 211-218. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0314Qu Z P, Wang F F, Zhang Y Y, et al. Thickness prediction of seismic multi-attributes sand based on association rules and random forests[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 211-218(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0314 [6] Mendel J M. White-noise estimators for seismic data processing in oil exploration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1977, 5: 694-706. [7] Canales L L. Random noise reduction[R]. [S. l. ]: SEG, 1984. [8] 刘喜武, 刘洪, 李幼铭. 独立分量分析及其在地震信号处理中的应用初探[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2003, 18(1): 90-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2003.01.015Liu X W, Liu H, Li Y M. Independent component analysis and its testing application on seismic signal processing[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2003, 18(1): 90-96(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2003.01.015 [9] 林红波, 马海涛, 许丽萍. 压制空间非平稳地震勘探随机噪声的ROAD径向时频峰值滤波算法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(7): 2546-2555. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201507029.htmLin H B, Ma H T, Xu L P. A radial time-frequency peak filtering based on ROAD for suppressing spatially nonstationary random noise in seismic data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(7): 2546-2555(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201507029.htm [10] Boashash B, Mesbah M. Signal enhancement by time-frequency peak filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(4): 929-937. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.823510 [11] Ma H, Yan J, Li Y, et al. Desert seismic random noise reduction based on LDA effective signal detection[J]. Acta Geophysica, 2019, 67(1): 109-121. doi: 10.1007/s11600-019-00250-0 [12] 刘彦锋, 张文彪, 段太忠, 等. 深度学习油气藏地质建模研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 235-241. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0417Liu Y F, Zhang W B, Duan T Z, et al. Progress of deep learning in oil and gas reservoir geological modeling[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 235-241(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0417 [13] Górszczyk A, Adamczy A, Malinous M, et al. Application of curvelet denoising to 2D and 3D seismic data: Practical considerations[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2014, 105: 78-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2014.03.009 [14] Moore R, Ezekiel S, Blasch E. Denoising one-dimensional signals with curvelets and contourlets[C]//Anon. IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference 2014. [S. l. ]: IEEE, 2014: 189-194. [15] 董新桐, 马海涛, 李月. 丘陵地带地震资料随机噪声压制新技术: 高阶加权阈值函数的Shearlet变换[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(10): 4039-4046. doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0582Dong X T, Ma H T, Li Y. The new technology for suppression of hilly land seismic random noise: Shearlet transform and the high order weighted threshold function[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(10): 4039-4046(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0582 [16] Chen Y, Fomel S. EMD-Seislet transform[J]. Geophysics, 2018, 85(1): 27-32. [17] Zhong T, Cheng M, Dong X, et al. Seismic random noise attenuation by appyling multi-scale denoising convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60(1): 1-13. [18] Azerad P, Bouharguane A, Crouzet J F. Simultaneous denoising and enhancement of signals by a fractal conservation law[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science & Numerical Simulation, 2012, 17(2): 867-811. [19] Zhou Q, Gao J, Wang Z, et al. Adaptive variable time fractional anisotropic diffusion filtering for seismic data noise attenuation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(4): 1905-1917. [20] Wang H, Cao S, Jiang K, et al. Seismic data denoising for complex structure using BM3D and local similarity[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2019, 170: 103759. [21] Zhu W, Mousavi S M, Beroza G C. Seismic signal denoising and decomposition using deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 9476-9488. [22] Zhang K, Zuo W, Chen Y, et al. Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3142-3155. [23] Dong X, Zhong T, Li Y. New suppression technology for low-frequency noise in desert region: The improved robust principal component analysis based on prediction of neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(7): 4680-4690. [24] Feng Q, Li Y. Denoising deep learning network based on singular spectrum analysis-das seismic data denoising with Multichannel SVDDCNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60(6): 5631-5641. [25] Li Y, Wang H, Dong X. The denoising of desert seismic data based on cycle-gan with unpaired data training[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 18(11): 1-5. [26] Wang S, Li Y, Zhao Y. Attribute-guided target data separation network for DAS VSP data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(6): 5304-5316. [27] Li Y, Luo X, Wu N, et al. The application of semisupervised attentional generative adversarial networks in desert seismic data denoising[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19(4): 5304-5316. [28] Jia X, Liu S, Feng X, et al. FOCNet: A fractional optimal control network for image denoising[C]//Anon. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2020. [S. l. ]: IEEE, 2020: 6047-6056. [29] Tai Y, Yang J, Liu X, et al. Memnet: A persistent memory network for image restoration[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2017. [S. l. ]: IEEE, 2017: 4539-4547. [30] Karpatne A, Ebert-Uphoff I, Ravela S, et al. Machine learning for the geosciences: Challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2019, 31(8): 1544-1554. -





 下载:
下载: