Characteristics of bitumen in sandstone-type copper-rhenium deposits in the Mishi Basin, Xichang, Sichuan Province, and its relationship with copper and rhenium enrichment mineralization
-
摘要:
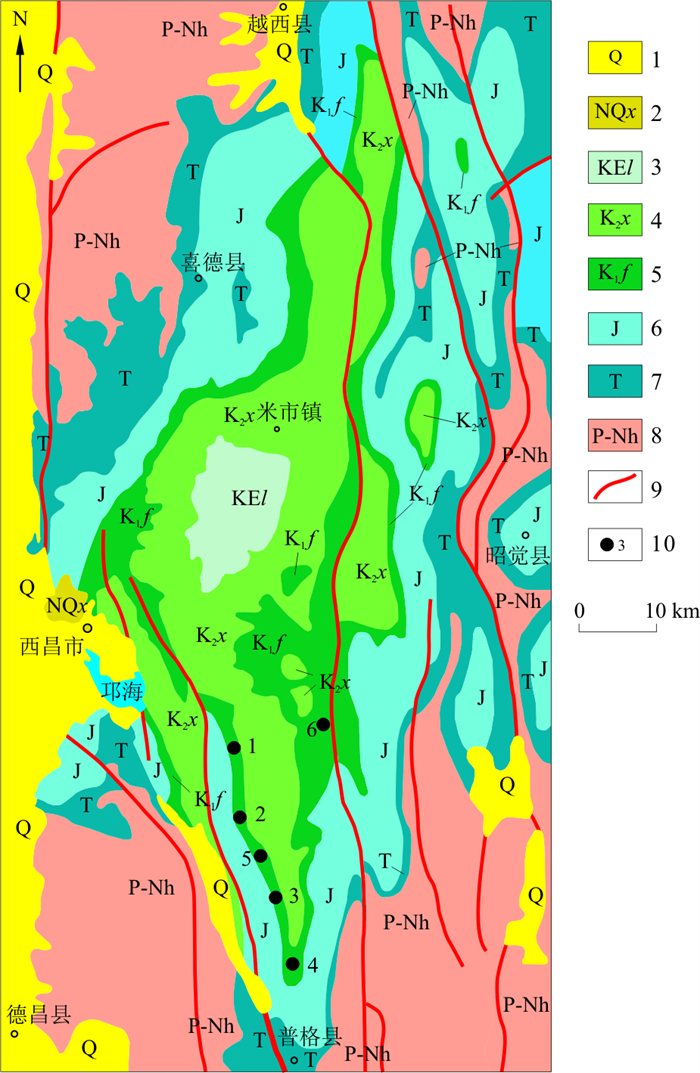
四川西昌地区的米市中生代陆相盆地位于扬子地台西缘。最近在盆地内下白垩统飞天山组(K1
f )中发现了与砂岩型铜矿伴生的铼。铜铼矿体赋存于飞天山组碎裂状、透镜状砂岩中,矿石中见有大量细脉状沥青分布。为探讨米市盆地砂岩型铜铼矿床(点)中有机质(沥青)对铜铼成矿的作用,对矿床(点)中矿石及沥青进行了矿相学、显微结构、红外光谱及有机碳同位素组成的研究。结果表明:铜矿物呈它形粒状分布于沥青之中,与之形成交代结构;沥青具有较高的Cu、Re含量;沥青是由下伏三叠系白果湾组中的古油藏发生热裂解形成的,证实了铜铼矿床的形成与古油藏有机质具有密切的空间和成因关系。该类型矿床的发现,为铼等分散元素超常富集成矿研究提供了新的对象。Abstract:The Mesozoic Mishi continental basin in the Xichang District, Sichuan Province, is located on the western margin of the Yangtze Craton. Rhenium associated with sandstone-type copper ore has recently been discovered in the Lower Cretaceous Feitianshan Formation (K1
f ) in the basin. Copper-rhenium ore bodies are found in fragmented, lenticular sandstones of the Feitianshan Formation. Numerous fine-veined bitumen could be found in the ore. To explore the effect of organic matter (bitumen) on copper-rhenium mineralization in sandstone copper-rhenium deposits (spots) in the Mishi Basin, the ore and bitumen in the deposits (spots) were studied on mineralography, microstructure, infrared spectroscopy and isotope composition of organic carbon. The results show that the copper minerals occur in the bitumen as anhedral grains and display athel metasomatic structure. The bitumen has high Cu and Re contents and is formed by thermal cracking in the ancient oil reservoir in the Lower Triassic Baiguowan Formation. The formation of the copper-rhenium deposit has a close spatial and genetic relationship with the organic matter of the ancient oil reservoir. This type of deposit provides a new object for the study of super-enrichment of rhenium and other dispersed elements. -
图 4 米市盆地铜铼矿床(点)与四川盆地有机碳同位素分布对比图(底图据文献[21])
Figure 4. Comparison of the organic carbon isotope distribution between copper-rhenium deposits (spots) in the Mishi Basin and Sichuan Basin
表 1 米市盆地铜铼矿床(点)地质特征
Table 1. Geological characteristics of copper-rhenium deposits (spots) in the Mishi Basin
序号 矿床(点) 矿体形态 矿化特征 样品数 品位wB 1 红莫依达 矿层厚0.5~1 m,地表可见延伸长200余米,深部延深超40 m 具孔雀石化、蓝铜矿化见铅灰-银灰色辉铜矿化团块矿石类型为具黑色沥青条带碎裂状砂岩 17 Cu: 0.06%~18.80%
Re: 0.03~29.72 g/t
Ag: 2.37~337 g/t2 白庙子 矿层厚0.4~0.8 m,地表可见断续延伸长240余米,深部延深超50 m 具孔雀石化、蓝铜矿化见银灰色辉铜矿化团块矿石类型为具黑色沥青条带碎裂状砂岩 14 Cu: 0.01%~12.66%
Re: 0.02~6.49 g/t
Ag: 2.79~384 g/t3 薄日泥堡 矿层厚0.3~0.7 m,地表可见断续延伸长120余米,深部延深超20 m 具孔雀石化、蓝铜矿化矿石类型为具黑色沥青条带碎裂状砂岩 8 Cu: 0.04%~6.83%
Re: 0.02~3.85 g/t
Ag: 9.40~103 g/t4 二虎村 矿层厚0.3~0.7 m,地表可见断续延伸长120余米,深部延深超30 m 孔雀石化、蓝铜矿化矿石类型为具黑色沥青条带碎裂状砂岩 11 Cu: 0.04%~3.13%
Re: 0.01~0.65 g/t
Ag: 9.07~149 g/t5 轿顶山 矿化好,地表断续延伸长超过1 000 m 孔雀石化、蓝铜矿化矿石类型为具黑色沥青条带碎裂状砂岩 7 Cu: 3.96%~14.79%
Re: 0.02~20.47 g/t
Ag:24.9~175 g/t6 拉基乡 矿层厚0.4~0.8 m,地表可见断续延伸长240余米,深部延深超30 m 具孔雀石化、蓝铜矿化见银灰-铅灰色辉铜矿团块矿石类型为具黑色沥青条带碎裂状砂岩 21 Cu: 0.05%~39.1%
Re: 0.02~131.49 g/t
Ag: 3.16~271 g/t表 2 沥青X射线能谱测试结果
Table 2. Result of the X-ray energy spectrum of bitumen
wB/% 样点 C S O Cu Re Os Mo Fe Se Pb 合计 S0120-b1 87.32 0.44 9.55 0.95 — — 1.04 0.57 — 0.13 100 S0120-b3 90.90 0.40 7.21 0.07 — 0.11 0.46 0.72 — 0.13 99.87 S0120 89.46 — 8.94 0.09 — — 0.55 0.76 0.07 0.25 100 注:“—"表示未检出;S0120-b1、S0120-b3、S0120采自红莫依达乡矿床 表 3 沥青的碳同位素组成
Table 3. Carbon isotopic composition of bitumen
样品号 δ13CorgPDB/‰ 样品号 δ13CorgPDB/‰ X2 -22.8 X5 -22.2 X3 -23.3 X6 -21.7 X4 -22.8 X7 -23.3 -
[1] John D A, Seal R R Ⅱ, Polyak D E. Rhenium[C]//Schulz K J, DeYoug J H Jr, Seal R R Ⅱ, et al. Critical mineral resources of the United States: Economic and environmental geology and prospects for future supply. [S. l. ]: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1802, 2017: 1-49. [2] 黎彤, 倪守斌. 地球和地壳的化学元素丰度[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990.Li T, Ni S B. Abundance of chemical elements in the earth and crust[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1990(in Chinese). [3] 涂光炽, 高振敏. 分散元素成矿机制研究获重大进展[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2003, 18(5): 358-361. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX200305009.htmTu G C, Gao Z M. Ore-forming mechanism of the dispersed elements[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2003, 18(5): 358-361(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX200305009.htm [4] 蒋少涌, 温汉捷, 许成, 等. 关键金属元素的多圈层循环与富集机制: 主要科学问题及未来研究方向[J]. 中国科学基金, 2019, 33(2): 112-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJJ201902003.htmJiang S Y, Wen H J, Xu C, et al. Earth sphere cycling and enrichment mechanism of critical metals: Major scientific issues for future research[J]. Science Foundation in China, 2019, 33(2): 112-118(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJJ201902003.htm [5] 温汉捷, 周正兵, 朱传威, 等. 稀散金属超常富集的主要科学问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(11): 3271-3291. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201911001.htmWen H J, Zhou Z B, Zhu C W, et al. Critical scientific issues of super-enrichment of dispersed metals[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(11): 3271-3291(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201911001.htm [6] 黄凡, 王登红, 王岩, 等. 中国铼矿成矿规律和找矿方向研究[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(6): 1252-1269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201906007.htmHuang F, Wang D H, Wang Y, et al. Study on metallogenic regularity rhenium deposits in China and their prospecting direction[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(6): 1252-1269(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201906007.htm [7] 王登红, 王瑞江, 李建康, 等. 中国三稀矿产资源战略调查研究进展综述[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(2): 361-370. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201302002.htmWang D H, Wang R J, Li J K, et al. The progress in the strategic research and survey of rare earth, rare metal and rare-scattered elements mineral resources[J]. Geology of China, 2013, 40(02): 361-370(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201302002.htm [8] 王瑞江, 王登红, 李建康, 等. 稀有稀土稀散矿产资源及其开发利用[M]. 北京, 地质出版社, 2015.Wang R J, Wang D H, Li J K, et al. Rare rare earth rare earth mineral resources and their development and utilization[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2015(in Chinese). [9] Dill H G. The "chessboard" classification scheme of mineral deposits: Mineralogy and geology from aluminum to zirconium[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2010, 100: 1-42. [10] 杨敏之. 分散元素矿床类型、成矿规律及成矿预测[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2000, 19(4): 381-383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2000.04.064Yang M Z. Types of dispersed element deposits, metallogenic laws and metallogenic predictions[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2000, 19(4): 381-383(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2000.04.064 [11] 周成胶, 张刚阳, 张丁川. 铼金属矿床类型、元素赋存形式和富集机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 115-130. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0431Zhou C J, Zhang G Y, Zhang D C. Types, element occurrence forms and enrichment mechanisms of rhenium metal deposits[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 115-130(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0431 [12] 郝雪峰, 彭宇, 唐屹, 等. 西昌普格地区飞天山组(K1f)中首次发现沉积砂岩型铼矿[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(16): 1975-1977. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202106023.htmHao X F, Peng Y, Tang Y, et al. First discovery of sedimentary sandstone-hosted rhenium deposit in the Feitianshan Formation(K1f) in the Puge area, Xichang[J]. Geology of China, 2021, 48(16): 1975-1977(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202106023.htm [13] 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 李葆华, 等. 沉积盆地中金属成矿与油气成藏的耦合关系[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(2): 83-105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201002013.htmGu X X, Zhang Y M, Li B H, et al. The coupling relationship between metallization and hydrocarbon accumulation in sedimentary basins[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(2): 83-105(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201002013.htm [14] 刘文均, 郑荣才. 花垣铅锌矿床包裹体气相组分研究: MVT铅锌矿床有机成矿作用研究(Ⅱ)[J]. 沉积学报, 1999, 17(4): 111-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199904016.htmLiu W J, Zheng R C. Research of fluid inclusion gas composititon in Huayuan lead-zinc deposits: Organic-mineralization study of MVT Lead-Zinc deposits(Ⅱ)[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(4): 111-117(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199904016.htm [15] 庄汉平, 卢家烂. 与有机质有成因联系的金属矿床[J]. 地质地球化学, 1996(4): 6-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ199604001.htmZhuang H P, Lu J L. Metal deposits with a genesis link to organic matter[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 1996(4): 6-11(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ199604001.htm [16] 李葆华, 李雯霞, 顾雪祥, 等. 贵州丹寨汞矿田甲烷包裹体研究及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(1): 55-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201301007.htmLi B H, Li W X, Gu X X, et al. A study of methane inclusions of the Danzhai mercury ore field in Guizhou Province and its geological significance[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(1): 55-63(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201301007.htm [17] Lee M K, Williams D D. Paleohydrology of the Delaware Basin, western Texas: Overpressure development, hydrocarbon migration, and ore genesis[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2000, 84(7): 961-974. [18] 方联华, 肖翔, 李科. 四川省攀西地区江舟、米市红盆砂岩型铜矿地质特征及远景预测[J]. 世界有色金属, 2019, 6: 108-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201911059.htmFang L H, Xiao X, Li K. Geological characteristics and prospect prediction of the red basin sandstone copper deposits in Jiangzhou and Mi City, Panxi region, Sichuan Province[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 6: 108-117(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201911059.htm [19] 边岩庆, 陶文. 石油的微生物降解过程中胶质沥青质的分子结构变化[J]. 长江大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 7(1): 177-179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJDL201001056.htmBian Y Q, Tao W. Changes in the molecular structure of colloidal asphaltene during microbial degradation of petroleum[J]. Journal of Yangtze University: Nature Science Edition, 2010, 7(1): 177-179(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJDL201001056.htm [20] 李炜光, 段炎红, 颜录科, 等. 利用石油沥青红外光谱图谱特征测定沥青的方法研究[J]. 石油沥青, 2012, 26(4): 9-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-OILE201204006.htmLi W G, Duan Y H, Yan L K, et al. Study on measuring method of asphalt using infrared spectrum characteristic of petroleum pitch[J]. Petroleum Asphalt, 2012, 26(4): 9-14(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-OILE201204006.htm [21] 田兴旺, 胡国艺, 李伟, 等. 四川盆地乐山-龙女寺古隆起地区震旦系储层沥青地球化学特征及意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(5): 982-990. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201305014.htmTian X W, Hu G Y, Li W, et al. Geochemical characteristics and significance of sinian reservoir bitumen in Leshan-Longnvsi paleo-uplift area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(5): 982-990(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201305014.htm [22] 蔡勋育, 朱扬明, 黄仁春. 普光气田沥青地球化学特征及成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(3): 340-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200603007.htmCai X Y, Zhu Y M, Huang R C. Geochemical behaviors and origin of reservoir bitumen in Puguang gas pool[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2006, 27(3): 340-347(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200603007.htm [23] 杨威, 魏国齐, 金惠, 等. 西昌盆地上三叠统白果湾组沉积相与油气勘探前景[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(3): 13-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202003003.htmYang W, Wei G Q, Jin H, et al. Sedimentary facies and oil and gas exploration prospect of the Upper Triassic Baiguowan Formation in the Xichang Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(3): 13-22(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202003003.htm [24] 魏洪刚, 陈燃, 牟必鑫, 等. 西昌盆地上三叠统白果湾组天然气地球化学特征及勘探潜力[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(11): 1637-1647. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202011012.htmWei H G, Chen R, Mu B X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and exploration potential of natural gas in Upper Triassic Baiguowan Formation, Xichang Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(11): 1637-1647(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202011012.htm [25] Spirakis C S, Heyl A V. Organic matter(bitumen and other forms) as the key to localization of Mississippi valley-type ores[C]//Parnell J, Kucha H, Landais P. Bitumen in ore deposits. Belin: Springer-Verlag, 1993: 381-398. [26] Sun Y Z, Wilhem Puttmann W. The role of organic matter during copper enrichment in Kupferschiefer from the Sangerhausen Basin, Germany[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31: 1143-1161. [27] 张复新. 砂岩型铀矿与浅层低温热液矿床[C]//刘池洋, 谭成仟, 孙卫. 盆地多种能源矿产共存富集成藏(矿)研究进展. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 164-171.Zhang F X. Sandstone-type uranium ore and shallow low-temperature hydrothermal deposits[C]//Liu C Y, Tan C Q, Sun W. Research progress on the coexistence of multiple energy minerals in the basin and the integration of rich reservoirs. Beijing: Science Press, 2005: 164-171(in Chinese). [28] Mossman D J. Carbonaceous substances in mineral deposits: Implications for geochemical exploration[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1999, 66(1/2): 241-247. [29] Broadbent G C, Myers R E, Wright J V. Geology and origin of shale-hosted Zn-Pb-Ag mineralization at the Century deposit, Northwest Queensland, Australia[J]. Economic Geology, 1998, 93: 1264-1294. [30] Zhuang H F, Lu J L, Fu J M, et al. Crude oil as carrier of gold: Petrological and geochemical evidence from Lannigou gold deposit in southwestern Guizhou, China[J]. Science in China, Series D, 1999, 28(6): 552-558. [31] 顾雪祥, 李葆华, 徐仕海, 等. 右江盆地含油气成矿流体性质及其成藏-成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2007, 14(5): 133-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200705015.htmGu X X, Li B H, Xu S H, et al. Characteristics of hydrocarbon-bearing ore-forming fluids in the Youjiang Basin, South China: Implications for hydrocarbon accumulation and ore mineralization[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(5): 133-146(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200705015.htm [32] 四川省地质调查院. 1: 50 000挖黑幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 成都: 四川省地质调查院, 2019.Geological Survey of Sichuan Province. 1: 50 000 regional geological survey report of Wahei[R]. Chengdu: Geological Survey of Sichuan Province, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [33] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The continental crust: Its composition and evolution[M]. London: Blackwell, 1985. [34] 廖仁强, 刘鹤, 李聪颖, 等. 从铼的地球化学性质看我国铼找矿前景[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(1): 55-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202001007.htmLiao R Q, Liu H, Li C Y, et al. Rhenium resource exploration prospects in China based on its geochemical properties[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(1): 55-67(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202001007.htm [35] 陶琰, 胡瑞忠, 唐永永, 等. 西南地区稀散元素伴生成矿的主要类型及伴生富集规律[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(6): 1210-1230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201906004.htmTao Y, Hu R Z, Tang Y Y, et al. Types of dispersed elements bearing ore-deposits and their enrichment regularity in Southwest China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(6): 1210-1230(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201906004.htm [36] 涂光炽. 中国层控矿床地球化学: 第三卷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1988.Tu G C. Geochemistry of stratified mineral deposits in China: Volume Ⅲ[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1988(in Chinese). [37] 傅家谟, 彭平安, 林清. 层控矿床有机地球化学研究的几个问题[C]//史继扬. 中国科学院地球化学研究所有机地球化学开发实验室研究年报(1988)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1990: 174-185.Fu J M, Peng P A, Lin Q. Some problems concerning study on organic geochemistry of stratified deposits[C]//Shi J Y. Annual report of the Organic Geochemistry Development Laboratory, Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences(1988)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1990: 174-185(in Chinese). [38] 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 吴程赟, 等. 黔西南卡林型金矿床与古油藏的成因联系: 有机岩相学证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(1): 92-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201301011.htmGu X X, Zhang Y M, Wu C Y, et al. The genetic relationship between Carlin-type gold deposits and paleo-petroleum reservoirs in SW Guizhou, China: Evidence from organic petrography[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(1): 92-106(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201301011.htm -





 下载:
下载: