Reaction characteristics of low temperature oxidation of light crude oil with disoxidation air
-
摘要:
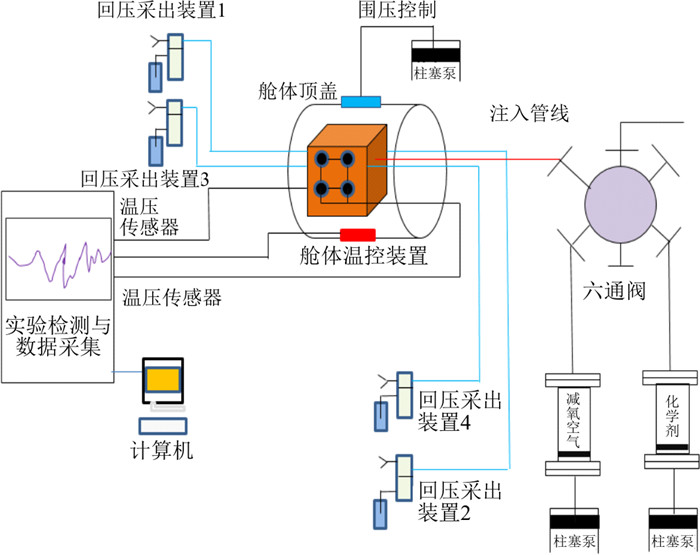
塔河北区块轻质原油与减氧空气在温度和压力作用下,探究其组分变化情况和耗氧量规律。在室内使用高温高压反应釜开展原油静态氧化实验,较为系统地研究不同含氧量及不同注气量的减氧空气对原油的氧化作用;并利用色谱分析对烃类分析,收集反应气体进行气体分析,气体组分和原油组分都有不同程度的变化。研究结果表明:①原油样本与减氧空气发生低温氧化反应,重质组分C21以上的组分均下降,低于C13的轻质组分含量均上升;②原油氧化效果随着含氧量上升而增强,反应过程组分对应"拐点"靠前;③含氧量一定时,改变油气比,反应对应的"拐点"不变;含氧量为下降趋势后趋于平缓;④低温氧化过程生成的CO2含量为上升趋势后趋于平缓;⑤在油藏温度(160℃)下,原油主要涉及2个反应热裂解和加氧反应。热裂解反应与含氧量无关,和温度有关,主要反应温度是160~200℃。高碳组分沥青质等重质组分会分解成饱和烃。加氧反应主要是芳香烃,胶质加氧反应也会生成沥青质。当2种反应同时存在时,沥青质参与热裂解的含量大于加氧反应芳香烃等生成的沥青质量,会导致沥青质含量减少。
Abstract:With the temperature and pressure effect, the composition change and oxygen consumption law of light crude oil and discoxidation air in Tahei North Block were studied. The static oxidation experiment of crude oil was carried out in a high temperature and high pressure reactor indoors to systematically study the oxidation effect of crude oil by disoxidation air with different oxygen content and different gas injection volume; the hydrocarbon was analyzed by chromatographic analysis, and the reaction gas was collected for gas analysis. The results showed that: ① The low-temperature oxidation reaction between crude oil sample and disoxidation air decreased the components above C21 and increased the content of light components below C13; ② The oxidation effect of crude oil increased with the increase of oxygen content, and the components in the reaction process corresponded to the "inflection point" in the front; ③ When the oxygen content was constant, the "inflection point" corresponding to the reaction remained unchanged by changing the oil-gas ratio; In the overall reaction process, the oxygen content decreased and then tended to be flat; ④ CO2 was generated in the process of low-temperature oxidation, and the CO2 content tended to be flat after increasing; ⑤At reservoir temperature (160℃), crude oil mainly involves two reaction thermal cracking and oxygenation reactions. The thermal cracking reaction is not related to the oxygen content, but to the temperature. The main reaction temperature is 160-200℃. Heavy components such as high-carbon asphaltene will be decomposed into saturated hydrocarbons. The oxygenation reaction is mainly aromatic hydrocarbon, and the resin oxygenation reaction will also produce asphaltene. When the two reactions exist at the same time, the content of asphaltene participating in thermal cracking is greater than the quality of asphaltene generated by oxygenation reaction aromatic hydrocarbon, which will lead to the decrease of asphaltene content.
-
Key words:
- disoxidation air /
- oxygen content /
- low temperature oxidation /
- light crude oil /
- composition change
-
表 1 塔河北区块轻质原油组分分布
Table 1. Composition distribution of light crude oil in Tahe North Block
碳数烃的分布 体积分数φB/% C10 6.15 C11~C15 35.89 C16~C20 27.31 C21~C25 15.80 C26~C30 9.73 C31~C35 4.37 >C35 0.75 总计 100.00 表 2 塔河北区块轻质原油在21%、12%、6%含氧量下族组分变化
Table 2. Change in 21%, 12% and 6% group components of light crude oil in Tahe North Block
含氧量
φB/%芳香烃 饱和烃 胶质 沥青质 wB/% 原油 28.69 43.03 16.60 11.68 6 11.56 65.09 19.16 5.19 12 7.49 68.69 21.59 4.23 21 1.49 72.66 24.91 2.94 -
[1] 赵永攀, 洪玲, 江绍静, 等. 水驱后特低渗透油藏氮气驱驱油特性分析[J]. 油田化学, 2013, 30(3): 376-379. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJHX201303014.htmZhao Y P, Hong L, Jiang S J, et al. Analysis on oil displacement characteristics of nitrogen flooding in ultra-low permeability reservoir after water flooding[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2013, 30(3): 376-379(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJHX201303014.htm [2] 魏浩光, 马坤, 岳湘安. 特低渗透油藏水驱后氮气驱油实验[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2013, 32(2): 118-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201302023.htmWei H G, Ma K, Yue X A. Nitrogen flooding experiment after water flooding in ultra-low permeability reservoir[J]. Daqing Petroleum Geology and Development, 2013, 32(2): 118-121(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201302023.htm [3] 蒋有伟, 张义堂, 刘尚奇, 等. 低渗透油藏注空气开发驱油机理[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(4): 471-476. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201004013.htmJiang Y W, Zhang Y T, Liu S Q, et al. Oil displacement mechanism of air injection development in low permeability reservoir[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(4): 471-476(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201004013.htm [4] 赵明国, 孙忠新. 气体性质对特低渗透油藏气驱效果的影响: 以大庆油田芳48断块为例[J]. 特种油气藏, 2007, 14(4): 75-77, 108-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ200704023.htmZhao M G, Sun Z X. Influence of gas properties on gas drive effect of ultra-low permeability reservoir: Taking fault block Fang 48 in Daqing Oilfield as an example[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoir, 2007, 14(4): 75-77, 108-109(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ200704023.htm [5] 谷潇雨, 蒲春生, 黄海, 等. 渗透率对致密砂岩储集层渗吸采油的微观影响机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(6): 948-954. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201706013.htmGu X Y, Pu C S, Huang H, et al. Micro influence mechanism of permeability on imbibition oil production in tight sandstone reservoir[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(6): 948-954(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201706013.htm [6] 肖佃师, 卢双舫, 陆正元, 等. 联合核磁共振和恒速压汞方法测定致密砂岩孔喉结构[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(6): 961-970. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201606014.htmXiao D S, Lu S F, Lu Z Y, et al. Determination of pore throat structure of tight sandstone by nuclear magnetic resonance and constant velocity mercury injection[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(6): 961-970(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201606014.htm [7] Kumar V K, Fassihi M R. Case history and appraisal of the medicine pole hills unit air injection project[J]. SPE Reservoir Engineering, 1997, 10(3): 198-202. [8] 郭平, 苑志旺, 廖广志. 注气驱油技术发展现状与启示[J]. 天然气工业, 2009, 29(8): 92-96, 143-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200908040.htmGuo P, Yuan Z W, Liao G Z. Development status and enlightenment of gas injection flooding technology[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2009, 29(8): 92-96, 143-144(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200908040.htm [9] 王敬, 姬泽敏, 刘慧卿, 等. 裂缝-孔洞型储集层注氮气辅助重力泄油实验[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(2): 342-353. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201902018.htmWang J, Ji Z M, Liu H Q, et al. Experiment of nitrogen injection assisted gravity oil drainage in fractured vuggy reservoir[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(2): 342-353(in Chinese with English abstract https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201902018.htm [10] 胡永乐, 郝明强, 陈国利, 等. 中国CO2驱油与埋存技术及实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(4): 716-727. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201904011.htmHu Y L, Hao M Q, Chen G L, et al. China CO2 oil displacement and buried technology and practice[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(4): 716-727(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201904011.htm [11] 廖广志, 王红庄, 王正茂, 等. 注空气全温度域原油氧化反应特征及开发方式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(2): 334-340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202002013.htmLiao G Z, Wang H Z, Wang Z M, et al. Oxidation reaction characteristics and development mode of crude oil in full temperature range of air injection[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(2): 334-340(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202002013.htm [12] Ren S R, Greaves M, Rathbone R R. Air injection LTO process: An IOR technique for light-oil reservoirs[J]. SPE Journal, 2002, 7(1): 90-99. [13] 王正茂, 廖广志, 蒲万芬, 等. 注空气开发中地层原油氧化反应特征[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(3): 314-319. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201803006.htmWang Z M, Liao G Z, Pu W F, et al. Characteristics of formation crude oil oxidation reaction in air injection development[J]. Journal of Petroleum, 2018, 39(3): 314-319(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201803006.htm [14] 张世明. 低渗透油藏CO2驱气窜通道识别方法[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(1): 101-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202001016.htmZhang S M. Identification method of gas channeling channel in CO2 flooding in low permeability reservoir[J]. Oil and Gas Geology and Recovery, 2020, 27(1): 101-106(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202001016.htm [15] 韦琦, 侯吉瑞, 郝宏达, 等. 特低渗油藏CO2驱气窜规律研究[J]. 石油科学通报, 2019, 4(2): 145-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE201902004.htmWei Q, Hou J R, Hao H D, et al. Study on gas channeling law of CO2 flooding in ultra-low permeability reservoir[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2019, 4(2): 145-153(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE201902004.htm [16] 张迎春, 杨莉, 顾文欢, 等. 深海挥发性油藏注气开发气油比变化规律研究及应用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2019, 31(5): 107-112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201905011.htmZhang Y C, Yang L, Gu W H, et al. Study and application of gas oil ratio change law in gas injection development of deep-sea volatile reservoir[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2019, 31(5): 107-112(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201905011.htm [17] Lu X B, Wang Y, Tian F, et al. New insights into the carbonate karstic fault system and reservoir formation in the southern Tahe area of the Tarim Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 86: 587-605. [18] Denney D. 30 Years of successful high-pressure air injection: Performance evaluation of Buffalo Field, South Dakota[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 2011, 63(1): 50-53. [19] Kumar V K, Gutierrez D, Moore R G, et al. Air injection and waterflood performance comparison of two adjacent units in the Buffalo Field[J]. SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering, 2008, 11(5): 848-858. [20] Fassihi M R, Yannimaras D V, Kumar V K. Estimation of recovery factor in light-oil air-injection projects[J]. SPE Reservoir Engineering, 1997, 12(4): 173-178. [21] Guo W H, Mower J P. Evolution of plant mitochondrial intron-encoded maturases: Frequent lineage-specific loss and recurrent intracellular transfer to the nucleus[J]. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 2013, 77(1/2): 43-54. [22] 李继庆. "双高"阶段砂岩储层水驱剩余油富集模式模拟[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(3): 137-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201703019.htmLi J Q. Simulation of water drive residual oil enrichment model of sandstone reservoir in "double high" stage[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(3): 137-143(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201703019.htm [23] 李冰环. 气相色谱方法测定原油全烃碳数分布[J]. 复杂油气藏, 2020, 13(1): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ202001002.htmLi B H. Determination of total hydrocarbon carbon number distribution of crude oil by gas chromatography[J]. Complex Oil and Gas Reservoir, 2020, 13(1): 1-4(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ202001002.htm [24] 王腾飞. 注空气采油低温氧化催化机理研究[D]. 山东青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2016.Wang T F. Study on catalytic mechanism of low temperature oxidation in air injection oil recovery[D]. Qingdao Shandong: China University of Petroleum(East China), 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] 于彪, 刘建良, 杨贵丽, 等. 渤海海域东部不同富油凹陷烃源岩生烃特征差异及意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 104-114, 130. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0407Yu B, Liu J L, Yang G L, et al. Differences and significance of hydrocarbon generation characteristics of source rocks in different oil-rich depressions in the eastern Bohai Sea[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 104-114, 130(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0407 [26] 宋志峰, 张建光. 缝洞型碳酸盐岩靶向酸压目标体分类与建模[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 78-84. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0303Song Z F, Zhang J G. Classification and modeling of targeted acid fracturing targets in fractured vuggy carbonate rocks[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 78-84(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0303 [27] 刘凯, 石万忠, 王任, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区盒1段致密砂岩孔隙结构分形特征及其与储层物性的关系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 57-68. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0102Liu K, Shi W Z, Wang R, et al. Fractal characteristics of pore structure of tight sandstone in he 1 member in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin and its relationship with reservoir physical properties[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 57-68(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0102 -





 下载:
下载: