Hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of karst groundwater in middle and upper reaches of Dawen River basin
-
摘要:
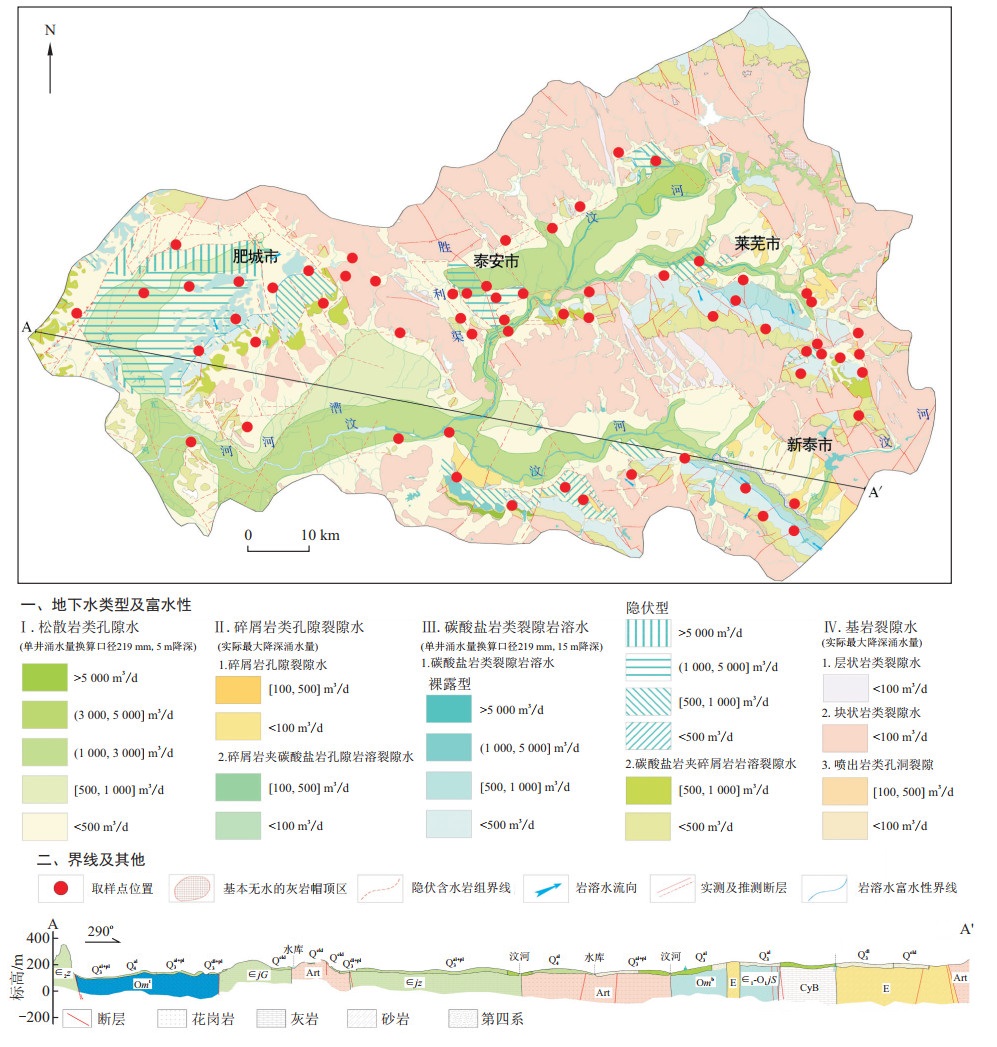
为查明大汶河流域中上游地区岩溶地下水水化学特征和离子来源, 基于2018年枯、丰两期采集的岩溶地下水样品水化学数据, 综合运用数理统计、相关性分析、Piper图、Gibbs图以及离子比值等方法, 对大汶河流域中上游地区岩溶地下水水化学特征及其控制因素进行了分析。结果表明,大汶河流域中上游地区枯、丰水期岩溶地下水的pH均值分别为7.6和7.5, 整体表现为弱碱性。岩溶地下水中Ca2+为占优势的阳离子, HCO3-和SO42-为主要阴离子。枯、丰期岩溶地下水中
ρ (TDS)均值分别为645.4, 648.4 mg/L。按照TDS划分, 大汶河流域中上游地区岩溶地下水均属于淡水或微咸水;枯、丰水期岩溶地下水水化学类型均以HCO3·SO4-Ca为主。岩石风化作用是控制区内岩溶地下水水化学特征的主要控制因素, 碳酸盐岩和硅酸盐岩矿物的溶解是地下水主要离子的重要来源。同时, 大汶河流域中上游地区岩溶地下水还受到了比较明显的人为输入影响, 地下水中NO3-主要来自于农业生产活动。该研究成果为水资源利用提供了指导作用。Abstract:To determine the hydrochemical characteristics and ion sources of karst groundwater in the middle and upper reaches of the Dawen River basin, based on karst groundwater samples collected in dry and wet periods in 2018, hydrochemical data were analyzed by means of mathematical statistics, correlation analysis, Piper diagram, Gibbs diagram and ion ratios. The results showed that the average pH values of karst groundwater in dry and wet periods in the middle and upper reaches of the Dawen River basin were 7.6 and 7.5, respectively, showing weak alkaline conditions as a whole. Ca2+ was the dominant cation in karst groundwater, and HCO3- and SO42- were the main anions. The average contents of TDS in karst groundwater during the dry and wet periods were 645.4 mg/L and 648.4 mg/L, respectively. According to TDS, the karst groundwater in the upper and middle reaches of the Dawen River basin belonged to freshwater or brackish water; hydrochemical types of karst groundwater in dry and wet periods were mainly HCO3·SO4-Ca. Rock weathering was the main controlling factor affecting the hydrochemical characteristics of karst groundwater in the area. The dissolution of carbonate and silicate minerals was an important source of groundwater ions. At the same time, the karst groundwater in the upper and middle reaches of the Dawen River basin was also affected obviously by human activities, and NO3- in groundwater mainly came from agricultural production activities.
-
表 1 地下水水化学统计结果
Table 1. Statistical results of groundwater hydrochemistry
时间 项目 K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- NO3- TH TDS pH ρB/(mg·L-1) 丰水期 平均值 1.3 23.4 151.2 25.7 60.6 142.5 287 87.1 483.4 648.4 7.5 最小值 0.26 3.7 49.7 1.5 8.5 18.3 74 8.6 153.6 228 6.9 最大值 8.3 90.9 348.3 52.5 274.8 468.8 587 272.9 1051 1 495 8 标准差 1.35 19.6 55.9 9.74 46.1 97.5 85.6 54.5 164.6 255.5 0.18 变异系数 1.04 0.84 0.37 0.38 0.76 0.68 0.30 0.63 0.34 0.39 0.02 枯水期 平均值 1.5 34.6 143 26.8 71 138.1 268 84.8 467.4 645.4 7.6 最小值 0.34 6.6 47.1 5.4 12.76 31.7 73 25 139.6 275 7.1 最大值 7.09 134.1 397.8 59.4 317 649.4 502 359.1 1196 1610 8.1 标准差 1.28 27.1 65.9 10 63.6 103.2 68.4 58 194.9 291.2 0.22 变异系数 0.85 0.78 0.46 0.37 0.90 0.75 0.26 0.68 0.42 0.45 0.03 表 2 地下水主要化学组分相关关系矩阵
Table 2. Correlation coefficients between major ions in groundwater
项目 丰水期 K+ Na+ Ca+ Mg2+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- NO3- TH TDS K+ 1 Na+ 0.356** 1 Ca+ 0.383** 0.696** 1 Mg2+ 0.261* 0.373** 0.538** 1 Cl- 0.544** 0.737** 0.772** 0.454** 1 SO42- 0.445** 0.658** 0.801** 0.686** 0.642** 1 HCO3- -0.064 0.431** 0.603** 0.375** 0.234 0.287* 1 NO3- 0.307* 0.430** 0.593** 0.239 0.492** 0.285* 0.183 1 TH 0.388** 0.681** 0.979** 0.700** 0.765** 0.846** 0.602** 0.561** 1 TDS 0.456** 0.798** 0.966** 0.643** 0.818** 0.861** 0.530** 0.623** 0.976** 1 项目 枯水期 K+ Na+ Ca+ Mg2+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- NO3- TH TDS K+ 1 Na+ 0.573** 1 Ca+ 0.25 0.630** 1 Mg2+ 0.313* 0.538** 0.678** 1 Cl- 0.494** 0.857** 0.795** 0.621** 1 SO42- 0.292* 0.623** 0.862** 0.759** 0.694** 1 HCO3- -0.03 0.400** 0.545** 0.438** 0.267* 0.388** 1 NO3- 0.287* 0.322* 0.623** 0.381** 0.495** 0.300* 0.15 1 TH 0.278* 0.646** 0.988** 0.784** 0.803** 0.889** 0.553** 0.607** 1 TDS 0.395** 0.776** 0.968** 0.765** 0.874** 0.882** 0.511** 0.620** 0.979** 1 *表示在0.05水平上显著相关;**表示在0.01水平上显著相关 -
[1] Li P Y, Qian H. Water resources research to support a sustainable China[J]. International Journal of Water Resources Development, 2018, 34(3): 327-336. doi: 10.1080/07900627.2018.1452723 [2] 刘文悦, 高宗军, 徐源, 等. 济南市岩溶地下水化学特征及基于模糊评价法的水质评价[J/OL]. 中国岩溶: 1-17[2022-07-29]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/45.1157.P.20220411.1928.005.html.Liu W Y, Gao Z J, Xu Yuan, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of karst groundwater in Jinan City[J/OL]. Carsologica Sinica: 1-17[2022-07-29]http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/45.1157.P.20220411.1928.005.html. (in Chinese with English abstract). [3] 刘伟江, 袁祥美, 张雅, 等. 贵阳市岩溶地下水水化学特征及演化过程分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(6): 245-251 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201806031.htmLiu W J, Yuan X M, Zhang Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of karst groundwater in Guiyang City[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(6): 245-251(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201806031.htm [4] Chemseddine F, Dalila B, Fethi B. Characterization of the main karst aquifers of the Tezbent Plateau, Tebessa Region, Northeast of Algeria, based on hydrogeochemical and isotopic data[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 74(1): 241-250. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4480-x [5] 高旭波, 王万洲, 侯保俊, 等. 中国北方岩溶地下水污染分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(3): 287-298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202003001.htmGao X B, Wang W Z, Hou B J, et al. Analysis of karst groundwater pollution in northern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3): 287-298(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202003001.htm [6] 冯建国, 赫明浩, 李贵恒, 等. 泰莱盆地孔隙水水化学特征及其控制因素分析[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(11): 2594-2600. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201911021.htmFeng J G, He M H, Li G H, et al. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of porewater in the Tailai Basin[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(11): 2594-2600(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201911021.htm [7] 李贵恒, 冯建国, 鲁统民, 等. 泰莱盆地地下水水化学特征及水质评价[J]. 水电能源科学, 2019, 37(4): 52-55, 121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY201904014.htmLi G H, Feng J G, Lu T M, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of groundwater in Tailai Basin[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2019, 37(4): 52-55, 121(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY201904014.htm [8] 杨海博, 朱文峰, 周良, 等. 肥城盆地区域地下水化学特征及水质评价[J]. 山东国土资源, 2020, 36(2): 50-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI202002008.htmYang H B, Zhu W F, Zhou L, et al. Evaluation on chemical characteristics and water quality of groundwater in Feicheng Basin[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2020, 36(2): 50-55(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI202002008.htm [9] 刘元晴, 周乐, 马雪梅, 等. 莱芜盆地地下水开发利用中的环境地质问题及成因[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020, 34(11): 118-124.Liu Y Q, Zhou L, Ma X M, et al. Evaluation on chemical characteristics and water quality of groundwater in Feicheng Basin[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2020, 34(11): 118-124(in Chinese with English abstract). [10] Piper A M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses[J]. Transactions American Geophysical Union, 1944, 25(6): 914-923. doi: 10.1029/TR025i006p00914 [11] Ren C B, Zhang Q Q. Groundwater chemical characteristics and controlling factors in a region of northern China with intensive human activity[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(23): 9126. https://ideas.repec.org/a/gam/jijerp/v17y2020i23p9126-d458255.html [12] Zhou P P, Wang Z M, Zhang J Y, et al. Study on the hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater along the Taklimakan Desert Highway[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(20): 1378. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6204-2 [13] 梁杏, 张婧玮, 蓝坤, 等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 21-33. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103Liang X, Zhang J W, Lan K, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 21-33(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103 [14] Gibbsr R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 1970, 170: 1088-1090. [15] Liu J T, Gao Z J, Wang Z Y. et al. Hydrogeochemical processes and suitability assessment of groundwater in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2020, 192(6): 384. [16] Gaillardet J, Dupré B, Louvat P, et al. Global silicate weathering and CO2, consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 159(1): 3-30. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254199000315 [17] Arunprakash M, Giridharan L, Krishnamurthy R R. et al. Impact of urbanization in groundwater of South Chennai City, Tamil Nadu, India[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 71(2): 947-957. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2496-7 [18] 江欣悦, 李静, 郭林, 等. 豫北平原浅层地下水化学特征与成因机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 290-300. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0511Jiang X Y, Li J, Guo L, et al. Chemical characteristics and formation mechanism of shallow groundwater in the northern Henan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 290-300(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0511 [19] Jalali M. Chemical characteristics of groundwater in parts of mountainous region, Alvand, Hamadan, Iran[J]. Environmental Geology, 2008, 51(3): 433-446. doi: 10.1007/s00254-006-0338-6 [20] Gao Z, Liu J, Xu X, et al. Temporal variations of spring water in karst areas: A case study of Jinan spring area, northern China[J]. Water, 2020, 12(4): 1009. [21] Zhu G F, Su Y H, Huang C L, et al. Hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Heihe River Basin, Northwest China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2010, 60(1): 139-153. doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0175-5 [22] 李舒, 杨佳雪, 李小倩, 等. 地下水化学组成的时空聚类分析与多级嵌套水流系统识别[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 309-318. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0028Li S, Yang J X, Li X Q, et al. Lumped cluster analysis for understanding spatial and temporal patterns of groundwater geochemistry and hierarchically nested flow systems[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 309-318(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0028 [23] 黄艳雯, 杜尧, 徐宇, 等. 洞庭湖平原西部地区浅层承压水中铵氮的来源与富集机理[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 165-174. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0618Huang Y W, Du Y, Xu Y, et al. Source and enrichment mechanism of ammonium in shallow confined aquifer inthe west of Dongting Plain. [J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 165-174(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0618 [24] Fan B L, Zhao Z Q, Tao F X, et al. Characteristics of carbonate, evaporite and silicate weathering in Huanghe River basin: A comparison among the upstream, midstream and downstream[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 96: 17- 26. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912014003964 [25] 赵江涛, 周金龙, 曾妍妍, 等. 新疆焉耆盆地平原区地下水质量评价与污染成因探讨[J]. 地球与环境, 2015, 43(6): 628-636. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201506005.htmZhao J T, Zhou J L, Zeng Y Y, et al. Assessment of groundwater quality and pollution causes discussion for the plain area of Yanqi Basin, Xinjiang Autonomous Region, China[J]. Earth and Environment, 2015, 43(6): 628-636(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201506005.htm -





 下载:
下载: