Overview of groundwater modeling technology and its application in karst areas with multiple-void media
-
摘要:
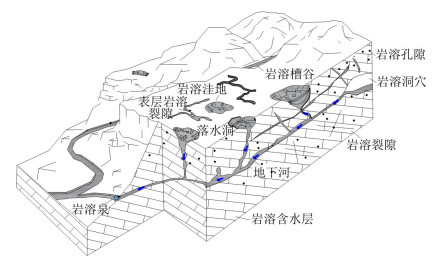
由于岩溶发育的极不均匀性和岩溶含水介质的多重介质性等特征, 使得岩溶水系统的地下水运动规律呈现出复杂多变的特点, 在孔隙或微小裂隙含水介质中岩溶水满足达西流, 而在岩溶管道中可能出现非达西运动, 这给岩溶区地下水模拟带来了极大挑战。系统地梳理了岩溶水流和溶质运移模拟的主要方法, 总结了复杂岩溶多重介质系统地下水模拟技术的现状, 并结合我国南方岩溶和北方岩溶各自的特点, 提出岩溶水模型在实际应用中需要关注的要点。主要包括: 需加强野外调查和观测, 提高模型中对岩溶含水介质结构非均质性表征的精度; 进一步深化对岩溶水运动机理的研究, 刻画岩溶多重介质的水流特征以及水交换机理; 针对北方岩溶水系统模拟, 可选择等效连续多孔介质模型, 重在耦合区域分布的岩溶溶孔-裂隙介质中慢速渗流与脉状分布的强径流带快速流; 对于南方岩溶区, 建议考虑建立分布式流域水文模型与能刻画集中管道流多流态变化的多重介质模型的岩溶地下水耦合模型。
Abstract:Due to the extremely heterogeneous distribution of karst and the multi-media nature of karst aquifer medium, the groundwater flow in karst water system presents complex and changeable characteristics. It follows Darcy flow law in the pores or fissures, and non-Darcy flow law in the karst pipelines, which brings great challenges to groundwater modeling in karst areas. This paper systematically worked through the main methods of karst water flow and solute transport simulation, summarized the current situation of groundwater simulation technology in complex karst multimedia systems, and pointed out the key issues that should be considered in the practical application of karst water modeling according to the characteristics of karst in south and north China. The main findings include: it is necessary to strengthen field investigations and observations to improve the accuracy of the characterization of the heterogeneity of karst aquifer media in the model. Furthermore, the research on the mechanism of karst water movement should be deepened to depict the flow characteristics and the water exchange mechanism in the karst multimedia. For the simulation of karst water systems in North China, the equivalent continuous porous media model can be selected, focusing on the coupling model of slow seepage in the karst pore fissure media with the rapid flow in the strong runoff zone. For the karst area in South China, it is suggested to consider the establishment of a coupling model between the distributed watershed hydrological model and the multimedia karst groundwater model that can describe the changes in various flow regimes in complex multiple-void media.
-
表 1 岩溶地下水各类模拟方法对比
Table 1. Comparison of various methods for karst groundwater simulation
一级分类 二级分类 特点 适用范围 物理模型 缩尺模型 成本低、容易控制影响因子,但不能详细描述对地下水运动空间分布特征 适用于地下水在岩溶含水介质中运动机理研究 集总参数式模型 流量衰减模型水箱模型 不考虑下垫面和气象条件在空间上的变化 适用于大尺度模拟 分布式岩溶水模型 分布式岩溶水文模型 可充分考虑流域下垫面和气象条件的时空变化 适用于岩溶水文流域模拟 等效多孔介质模型 假设含水层参数差异较小,对管道、裂隙进行高度概化,建模效率高但精度较低;无法刻画非达西流及管道(裂隙)之间水分交换 适用于岩溶发育程度较低的地区,可用于大尺度模拟 离散网络介质模型 对岩溶裂隙、管道进行刻画,地下水仅在随机裂隙中进行运动;对裂隙、管道数据要求高,难以获取 适用于裂隙为主的小尺度模拟 双重连续介质模型 考虑了含水介质的非均质性,地下水流为达西流,不能刻画管道流;交换系数难以准确确定 适用于岩溶发育程度较低地区模拟,且多为小尺度模型 三重介质模型 可以较全面地刻画了岩溶水动态的特征,但模型构建难度较高,限制了实际应用 适用于中小尺度模拟 -
[1] Olarinoye T, Tgleeson T, Marx V, et al. Global karst springs hydrograph dataset for research and management of the world's fastest-flowing groundwater[J]. Science Data, 2020, 59(7): 1-9. [2] Zheng X K, Yang Z B, Wang S, et al. Evaluation of hydrogeological impact of tunnel engineering in a karst aquifer by coupled discrete-continuum numerical simulations[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 597: 125765. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125765 [3] 刘久荣, 王新娟, 王荣, 等. 岩溶水数值模拟研究进展[J]. 城市地质, 2012, 7(4): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2012.04.001Liu J R, Wang X J, Wang R, et al. Advances in research of karst water numerical simulation[J]. Urban Geology, 2012, 7(4): 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1903.2012.04.001 [4] Wu J, J Chao, Li J R, et al. Solute transport characteristics of karst water tracing and its engineering application[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2021, 14(9): 1-14. [5] Zhang N, Zheng Q, Elbaz K, et al. Water inrush hazards in the Chaoyang Tunnel, Guizhou, China: A preliminary investigation[J]. Water (Basel), 2020, 1083: 1-10. [6] 徐中平, 周训, 崔相飞, 等. 岩溶区地下水数值模拟研究进展[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(4): 475-483. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201804001.htmXu Z P, Zhou X, Cui X F, et al. Research advances of numerical simulation of groundwater in karst areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(4): 475-483(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201804001.htm [7] 何满潮. 工程地质数值法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006.He M C. Engineering geology numerical method[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006(in Chinese). [8] Luo M M, Chen Z H, Criss R E, et al. Dynamics and anthropogenic impacts of multiple karst flow systems in a mountainous area of South China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2016, 24: 1993-2002. doi: 10.1007/s10040-016-1462-3 [9] 罗明明. 南方岩溶水循环的物理机制及数学模型研究: 以香溪河岩溶流域为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2017.Luo M M. The physical machanism and methematical model of karst water circulation: A case study of the Xiangxi River karst basin, South China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [10] Hartmann A, Goldscheider N, Wagener T. Karst water resources in a changing world: Review of hydrological modeling approaches[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2014, 52: 218-242. doi: 10.1002/2013RG000443 [11] 成建梅, 陈崇希. 广西北山岩溶管道-裂隙-孔隙地下水流数值模拟初探[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1998, 25(4): 50-54. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.1998.04.021Cheng J M, Chen C X. Preliminary study on numerical simulation of karst pipe line-fissure-pore groundwater flow in Beishan of Guangxi[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1998, 25(4): 50-54(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.1998.04.021 [12] 刘丽红, 李娴, 鲁程鹏. 岩溶含水系统水动力特征研究进展[J]. 水电能源科学, 2012, 30(7): 21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7709.2012.07.006Liu L H, Li X, Lu P C. Research progress on hydrodynamic characteristics of karstic water system[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2012, 30(7): 21-24(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7709.2012.07.006 [13] Mishra S, Raziperchikolaee S, Le-Gallo Y. Modeling aspects of CO2 injection in a network of fractures[C]//de Dios J C, Mishra S, Poletto F, et al. CO2 injection in the network of carbonate fractures. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2021. [14] 陈雨孙, 边际. 岩溶水的介质和运动[J]. 中国岩溶, 1988, 7(3): 229-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198803013.htmChen Y S, Bian J. Medium and movement of karst water[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1988, 7(3): 229-234(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198803013.htm [15] Guo X L, Chen Q L, Huang H, et al. Water source identification and circulation characteristics of intermittent karst spring based on hydrochemistry and stable isotope: An example from southern China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2022, 141: 105309. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105309 [16] 卢海平, 张发旺, 赵春红, 等. 我国南北方岩溶差异[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(增刊2): 317-319. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2018S2085.htmLu H P, Zhang F W, Zhao C H, et al. Differences between southern karst and northern karst besides scientific issues that need attention[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(S2): 317-319(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2018S2085.htm [17] 梁永平. 中国北方岩溶地下水环境问题与保护[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014.Liang Y P. Problems of karst groundwater environment and its protection in North China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2014(in Chinese). [18] 梁永平, 王维泰. 中国北方岩溶水系统划分与系统特征[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(6): 860-868. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201006017.htmLiang Y P, Wang W T. The division and characteristics of karst water systems in northern China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(6): 860-868(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201006017.htm [19] 张远海, 朱德浩. 中国大型岩溶洞穴空间分布及演变规律[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2012, 32(1): 20-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2012.01.003Zhang Y H, Zhu D H. Large karst caves distribution and development in China[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2012, 32(1): 20-28(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2012.01.003 [20] 周训, 胡伏生, 何江涛, 等. 地下水科学概论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009.Zhou X, Hu F S, He J T, et al. Introduction to groundwater science[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009(in Chinese). [21] 韩行瑞. 岩溶水文地质学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015.Han X R. Karst hydrogeology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015(in Chinese). [22] Goldscheider N, Drew D. Methods in karst hydrogeology[M]. London: Taylor & Francis Group, 2007. [23] 马志敬. 黑龙洞泉域岩溶水循环演变规律研究[D]. 河北邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2021.Ma Z J. Study onkarst water cycle evolution law in Heilongdong spring area[D]. Handan Hebei: Hebei University of Engineering, 2021(in Chinese with English abstract). [24] 熊兵. 基于数值模拟的北方典型岩溶区地下水污染控制方案研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.Xiong B. Study on groundwater pollution control programme of typical northern karst area based on numerical simulation[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] 何宇彬. 关于"喀斯特水系统"研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 1997, 16(1): 67-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR701.011.htmHe Y B. Research on karst water system[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1997, 16(1): 67-73(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR701.011.htm [26] 姜光辉, 于奭, 常勇. 利用水化学方法识别岩溶水文系统中的径流[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2011, 41(5): 1535-1541. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201105030.htmJiang G H, Yu S, Chang Y. Identification of runoff in karst drainage system using hydrochemical method[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41(5): 1535-1541(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201105030.htm [27] 李文兴, 郭纯青. 岩溶管道水系统物理模拟: 以岩滩水电站板文地下河系为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 1996, 15(4): 351-357. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR604.006.htmLi W X, Guo C Q. Physical simulation of karst conduit flow system: Taking Banwen underground river in Yantan electric power station for example[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1996, 15(4): 351-357(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR604.006.htm [28] 林加恩, 李亮, 杨慧珠. 管流与渗流耦合流动理论研究初探[J]. 西安石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 22(2): 11-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200702002.htmLin J E, Li L, Yang H Z. Primary investigation of the coupling of channel flow with seepage[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University: Natural Science Edition, 2007, 22(2): 11-15(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200702002.htm [29] 许光祥, 张永兴, 哈秋舲. 粗糙裂隙渗流的超立方和次立方定律及其试验研究[J]. 水利学报, 2003(3): 74-79. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2003.03.014Xu G X, Zhang Y X, Ha Q L. Super-cubic and sub-cubic law of rough fracture seepage and its experiments study[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2003(3): 74-79(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2003.03.014 [30] 沈振中, 陈雰, 赵坚. 岩溶管道与裂隙交叉渗流特性试验研究[J]. 水利学报, 2008, 39(2): 137-145. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2008.02.002Shen Z Z, Chen W, Zhao J. Experimental study on seepage characteristics of the intersection of tubular karst passage and fissure[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2008, 39(2): 137-145(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2008.02.002 [31] 魏加华, 郭亚娇, 王荣, 等. 复杂岩溶介质地下水模拟研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2015, 42(3): 27-34. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2015.03.05Wei J H, Guo Y J, Wang R, et al. Recent advances in simulation approaches of the complex karst medium[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(3): 27-34(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2015.03.05 [32] Hu C H, Hao Y H, J-Yeh T C, et al. Simulation of spring flows from a karst aquifer with an artificial neural network[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2008, 22: 596-604. doi: 10.1002/hyp.6625 [33] Dewandel B, Lachassagne P, Bakalowicz M, et al. Evaluation of aquifer thickness by analysing recession hydrographs: Application to the Oman ophiolite hard-rock aquifer[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2003, 274: 248-269. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00418-3 [34] 束龙仓, 范建辉, 鲁程鹏, 等. 裂隙-管道介质泉流域水文地质模拟试验[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2015, 45(3): 908-917. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201503024.htmShu L C, Fan J H, Lu C P, et al. Hydrogeological simulation test of fissure-conduit media in springs watershed[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2015, 45(3): 908-917(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201503024.htm [35] 刘丽红, 束龙仓, 鲁程鹏. 基于管道流模型的岩溶含水系统降雨泉流量响应规律: 以贵州后寨典型小流域为例[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2010, 40(5): 1083-1089. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201005017.htmLiu L H, Shu L C, Lu C P. Precipitation and discharge response mechanism based on conduit flow model in karstic water system: Application the Houzhai karstic water system of Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2010, 40(5): 1083-1089(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201005017.htm [36] 谢国文. 西南典型岩溶含水介质特征识别方法研究: 以重庆金佛山水房泉流域为例[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2019.Xie G W. A methodological research on the identification of a typical karst aquifer media in Southwest China: A case study of Shuifang spring basin in Jinfo Mountain, Chongqing, China[D]. Chongqing: Southwestern University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [37] Brkiĉž, Kuhta M, Hunjak T. Groundwater flow mechanism in the well-developed karst aquifer system in the western Croatia: Insights from spring discharge and water isotopes[J]. Catena, 2018, 161: 14-26. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.10.011 [38] 王玉凤. 中国南方岩溶区水文过程模拟研究: 以左江流域为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021.Wang Y F. Hydrologic process simulation in karst areas of South China: A case study in Zuo River basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2021(in Chinese with English abstract). [39] Shi P, Zhou M, Qu S, et al. Testing a conceptual lumped model in karst area, Southwest China[J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics, 2013: 1-10. [40] 程根伟. 新安江岩溶水文模型[J]. 水电能源科学, 1991, 9(2): 139-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY199102007.htmCheng G W. Xin'anjiang karst hydrology model[J]. Water Resources and Power, 1991, 9(2): 139-144(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY199102007.htm [41] 袁道先. 中国南方裸露型岩溶峰丛山区岩溶水系统及其数学模型的研究: 以桂林丫吉村为例[M]. 南宁: 广西师范大学出版社, 1996.Yuan D X. Karst water system of a peak cluster catchment in South China's bare karst region and its mathematic model[M]. Nanning: Guangxi Normal University Publishing House, 1996(in Chinese). [42] Beven K, M Kirkby. A physically based, variable contributing area model of basin hydrology[J]. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 1978, 24(1): 43-69. [43] 任启伟. 基于改进SWAT模型的西南岩溶流域水量评价方法研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2006.Ren Q W. Water quantity evaluation methodology based on modified SWAT hydrological modeling in Southwest karst area[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2006(in Chinese with English abstract). [44] 潘欢迎. 岩溶流域水文模型及应用研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2014.Pan H Y. Study and application of hydrologic model in karst basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [45] 张程鹏. 基于SWAT模型的西南岩溶区旱涝特征分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2021.Zhang C P. Analysis the characteristics of drought and flood in karst area of Southwest China based on SWAT model[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2021(in Chinese with English abstract). [46] Malagò A, Efstathiou D, Bouraoui F, et al. Regional scale hydrologic modeling of a karst-dominant geomorphology: The case study of the Island of Crete[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 540: 64-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.05.061 [47] 宋晓晨, 徐卫亚. 裂隙岩体渗流概念模型研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2004, 25(2): 226-232. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX200402015.htmSong X C, Xu W Y. A study on conceptual models of fluid flow in fractured rock[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2004, 25(2): 226-232(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX200402015.htm [48] Hsieh P A, Neuman S P, Stiles G K, et al. Field determination of the three-dimensional hydraulic conductivity tensor of anisotropic media: 2. Methodology and application to fractured rocks[J]. Water Resources Research, 1985, 21(11): 1667-1676. [49] Scanlon B R, Mace R E, Barrett M E, et al. Can we simulate regional groundwater flow in a karst system using equivalent porous media models?Case study, Barton Springs Edwards aquifer, USA[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2003, 276: 137-158. [50] Worthington S R H. Diagnostic hydrogeologic characteristics of a karst aquifer (Kentucky, USA)[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2009, 17: 1665-1678. [51] 朱学愚, 刘建立. 山东淄博市大武水源地裂隙岩溶水中污染物运移的数值研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2001, 8(1): 171-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200101036.htmZhu X Y, Liu J L. Numerical study of contaminants transport in fracture-karst water in Dawu well field, Zibo City Shandong Province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2001, 8(1): 171-178(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200101036.htm [52] 梁腾飞, 成建梅, 张乃俨, 等. 基于数值模拟的汾河二库对晋祠泉岩溶水系统渗漏补给作用研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(2): 147-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202002002.htmLiang T F, Cheng J M, Zhang N Y, et al. Numerical study on surface water leakage replenishment of the Fenhe 2nd reservoir into the Jinci spring system[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(2): 147-153(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202002002.htm [53] Berkowitz B. Characterizing flow and transport in fractured geological media: A review[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2002, 25(8/12): 861-884. [54] 李娜. 香溪河流域岩溶热水成因模式及水文地质参数反演研究: 以湖北省兴山县南阳温泉为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2020.Li N. The formation mechanism and hydrogeological parameters of karst thermal water: A case study of Nanyang thermal spring in Xingshan County of Hubei Province, Xiangxi River basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [55] Kordilla J, Sauter M, Reimann T. Simulation of saturated and unsaturated flow in karst systems at catchment scale using a double continuum approach[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2012, 16(10): 3909-3923. [56] 赵贵清, 陈舟, 周云, 等. 深埋隧洞涌水量预测数值模型研究进展[J]. 工程勘察, 2017, 45(4): 27-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC201704006.htmZhao G Q, Chen Z, Zhou Y, et al. Review of numerical study on groundwater inflow forecasting in deep-buried tunnel construction[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2017, 45(4): 27-34(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC201704006.htm [57] 陈崇希. 岩溶管道-裂隙-孔隙三重空隙介质地下水流模型及模拟方法研究[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 1995, 20(4): 361-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199504000.htmChen C X. Groundwater flow model and simulation method in triple media of karstic tube-fissure-pore[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1995, 20(4): 361-366(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199504000.htm [58] 赵坚, 赖苗, 沈振中. 适于岩溶地区渗流场计算的改进折算渗透系数法和变渗透系数法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(8): 1341-1347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200508015.htmZhao J, Lai M, Shen Z Z. Improved converting permeability coefficient method and variable permeability cofficient method for seepage calculation in karst region[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(8): 1341-1347(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200508015.htm [59] 邹昌喜, 黄勇. 岩溶管道的折算渗透系数取值探讨[J]. 河海大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 48(2): 123-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HHDX202002006.htmZou C X, Huang Y. Discussion on value of converted permeability coefficient in karst conduit[J]. Journal of Hohai University: Natural Sciences, 2020, 48(2): 123-127(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HHDX202002006.htm [60] 郭绪磊, 朱静静, 陈乾龙, 等. 新型地下水流速流向测量技术及其在岩溶区调查中的应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1): 243-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901027.htmGuo X L, Zhu J J, Chen Q L, et al. Flow direction and its application in the investigation of karst area[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(1): 243-249(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901027.htm [61] 叶浩. 单裂隙中水流与溶质运移的试验研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2005.Ye H. Experimental study of water flow and solute transport in a single fracture[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2005(in Chinese with English abstract). [62] 花芳. 水平单裂隙溶质运移弥散系数及其尺度效应实验研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2010.Hua F. Experimental study of dispersion coefficient and scale effect in single horizontal fracture[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2010(in Chinese with English abstract). [63] 腾强, 王明玉, 王慧芳. 裂隙管道网络物理模型水流与溶质运移模拟试验[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2014, 31(1): 54-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKYB201401010.htmTeng Q, Wang M Y, Wang H F. Experiments on fluid flow and solute transport in the fracture network pipe model[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014, 31(1): 54-60(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKYB201401010.htm [64] 刘波, 王明玉, 张敏, 等. 裂隙网络管道模型弥散试验[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2016, 46(1): 230-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201601022.htmLiu B, Wang M Y, Zhang M, et al. Dispersivity experimental investigation based on fracture network pipe model[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2016, 46(1): 230-239(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201601022.htm [65] 张雪梅. 岩溶裂隙-管道水动力弥散特征室内模拟研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2019.Zhang X M. Laboratory simulation study on hydrodynamic dispersion characteristics of karst fissure pipeline[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [66] 闵佳. "渗流-管流耦合模型"的物理模拟及数值模拟[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.Min J. Physical simulation and numerical simulation of "seepage-tube coupling model"[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [67] 季怀松, 罗明明, 褚学伟, 等. 岩溶洼地内涝蓄水量与不同级次裂隙对溶质迁移影响的室内实验与模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 164-172. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0520Ji H S, Luo M M, Chu X W, et al. Laboratory experiment and simulation of solute transport affected by different grades of fissures and water storage of waterlogging in karst depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 164-172(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0520 [68] 张丝诺. 面向修复的裂隙岩溶含水层溶质运移模拟: 以南方某工业污染场地为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021.Zhang S N. Remediation oriented modeling of solute transport in fractured karst aquifer: A case study of an industrial site in the South of China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2021(in Chinese with English abstract). [69] Field S M. Efficient hydrologic tracer-test design for tracer-mass estimation and sample-collection frequency: 1. Method development[J]. Environmental Geology, 2002, 42: 827-838. [70] Stueber A M, Criss R E. Origin and transport of dissolved chemicals in a karst watershed, southwestern Illinois[J]. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 2005, 41(2): 267-290. [71] 李琪. 溶潭容积和管道长度对岩溶管道溶质运移的影响研究[D]. 山东青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2021.Li Q. Study on the influence of pool volume and conduit length on solute transport in karst conduit[D]. Qingdao Shandong: Qingdao University of Technology, 2021(in Chinese with English abstract). [72] 赵小二, 常勇, 吴吉春. 岩溶地下河污染物运移模型对比研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(4): 1250-1259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202004012.htmZhao X E, Chang Y, Wu J C. A comparative study on two contaminant transport models used in karst underground rivers[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(4): 1250-1259(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202004012.htm [73] 罗明明, 陈静, 季怀松, 等. 岩溶管道与裂隙介质间溶质交换研究进展[J/OL]. 地球科学, 2022[2022-05-21]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220119.1649.008.html.Luo M M, Chen J, Ji H S, et al. Review of solute exchange between karst conduit and matrix[J/OL]. Earth Science, 2022[2022-02-21]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220119.1649.008.html(in Chinese with English abstract). [74] 杨杨, 赵良杰, 苏春田, 等. 基于CFP的岩溶管道流溶质运移数值模拟研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(4): 51-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201904008.htmYang Y, Zhao L J, Su C T, et al. A study of the solute transport model for karst conduits based on CFP[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(4): 51-57(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201904008.htm [75] Hill M E, Stewart M T, Martin A. Evaluation of the MODFLOW-2005 conduit flow process[J]. Ground Water, 2010, 48(4): 549-559. [76] Xu Z, Hu B X, Davis H, et al. Simulating long term nitrate-N contamination processes in the Woodville karst plain using CFPv2 with UMT3D[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 524: 72-88. [77] 潘国营, 贾军辉. 焦作矿区岩溶水Cl-污染原因初探[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2002, 29(5): 50-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200205014.htmPan G Y, Jia J H. Reasons of Cl- contamination in karst ground water of Jiaozuo coal mining area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2002, 29(5): 50-51(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200205014.htm [78] 刘娟, 杨国勇, 蒋兆华, 等. FEFLOW在某市岩溶地下水四氯化碳污染中的应用[J]. 地下水, 2011, 33(6): 87-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201106035.htmLiu J, Yang G Y, Jiang Z H, et al. Application of FEFLOW in carbon tetrachloride contamination for a city[J]. Groundwater, 2011, 33(6): 87-91(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201106035.htm [79] 李华, 吴静, 徐世光, 等. 基于GMS的云南德厚水库下游废弃砒霜厂地下水溶质运移模拟[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2014, 25(2): 209-212. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201402045.htmLi H, Wu J, Xu S G, et al. Simulation of solute transport of groundwater at abandoned arsenic factory in downstream of Dehou reservoir in Yunnan based on GMS[J]. Journal of Water Resources Water Engineering, 2014, 25(2): 209-212(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201402045.htm [80] 赵良杰, 夏日元, 杨杨, 等. 基于MODFLOW的岩溶管道水流模拟方法探讨与应用[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(3): 346-351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201703008.htmZhao L J, Xia R Y, Yang Y, et al. Discussion and application of simulation methods for karst conduit flow based on MODFLOW[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(3): 346-351(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201703008.htm [81] 代俊峰, 郭纯青, 方荣杰. 西南岩溶灌区水文特性及其模拟模型的构建[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2011, 22(4): 11-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201104004.htmDai J F, Guo C Q, Fang R J. Hydrologic characteristics in southwest karst irrigated area and construction of simulation model[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2011, 22(4): 11-15(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201104004.htm [82] 赖格英, 易姝琨, 刘维, 等. 基于修正SWAT模型的岩溶地区非点源污染模拟初探: 以横港河流域为例[J]. 湖泊科学, 2018, 30(6): 1560-1575. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX201806008.htmLai G Y, Yi S K, Liu W, et al. Non-point source pollution simulation in karst region based on modified SWAT model: A case study in Henggang River basin[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2018, 30(6): 1560-1575(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX201806008.htm [83] 罗明明, 周宏, 郭绪磊, 等. 峡口隧道间歇性岩溶涌突水过程及来源解析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 246-254. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0054Luo M M, Zhou H, Guo X L, et al. Processes and sources identification of intermittent karst water inrush in Xiakou Tunnel[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 246-254(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0054 [84] 彭红明, 袁有靖, 李铜邦, 等. 青海天峻新关角隧道涌排水水源识别与量化分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 60-70. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0026Peng H M, Yuan Y J, Li T B, et al. Identification and quantitative analysis of groundwater discharged from New Guanjiao Tunnel in Tianjun, Qinghai[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 60-70(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0026 [85] 曾斌, 陈植华, 邵长杰, 等. 基于地下水流系统理论的岩溶隧道涌突水来源及路径分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 99-108. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0006Zeng B, Chen Z H, Shao C J, et al. Analysis of source and path of water inrush in karst tunnel based on the theory of groundwater flow system[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 99-108(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0006 -





 下载:
下载: