Simulation study on remediation of acid mine drainage by in-situ injection of limestone based sustained release materials
-
摘要:
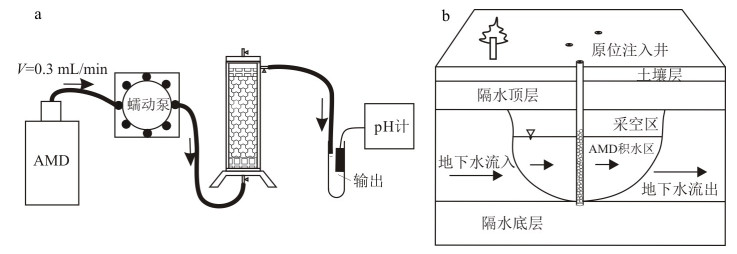
我国岩溶区分布面积广,生态环境脆弱。岩溶区大量矿山开采活动产生的酸性矿山废水(AMD)严重威胁着区域生态环境安全。以岩溶区广泛分布的碳酸盐岩和玉米棒(生物质炭)等为原料,通过改性、造粒、覆膜的方式制备了一种可用于原位注入修复的碱基缓释材料(ASRM),并在室内模拟开展了丰水和枯水交替作用下的原位注入修复实验,以验证和查明ASRM原位修复酸性矿井废水中重金属的能力及去除机制。研究结果表明,碱基缓释材料(ASRM)可有效提高水体pH值,酸性矿山废水(AMD)修复后pH值从2.8提高到5~7,并对Fe2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Pb2+和Cr3+等多种有害重金属有良好去除效果。XRD和SEM分析证明,反应沉淀物主要以FeOOH的形式存在。重金属的去除机制主要包括:①部分金属离子被以反应产生的氢氧化物等沉淀的形式去除;②反应体系产生的大量FeOOH可以吸附去除重金属。本模拟实验研究为利用缓释材料原位高效处理岩溶山区矿山AMD提供了可靠的理论和技术依据。
Abstract:The karst area is widely distributed in China, and the ecological environment is fragile. Acid mine drainage (AMD) produced by mining activities in karst areas seriously threatens the safety of regional ecological environment. In this paper, carbonate rocks and corn cobs (biochar) widely distributed in karst areas were used as raw materials, and an alkaline sustained release material (ASRM) that could be used for in-situ injection and repair was prepared by means of modification, granulation and film coating. In addition, in-situ injection and repair experiments under alternating effects of wet and dry conditions were carried out in the laboratory, to verify and determine the ability and removal mechanism of ASRM in the in-situ remediation of heavy metals in acid mine wastewater. The results showed that ASRM can effectively improve the pH of water, and the pH of AMD can be increased from 2.8 to approximately 5-7, and it had a good removal effect on many harmful heavy metals, such as Fe2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cr3+. XRD and SEM analyses showed that the reaction precipitates mainly existed in the form of FeOOH. The removal mechanism of heavy metals mainly includes: ①some metal ions were removed in the form of precipitation, such as hydroxides produced by the reaction; ②a large amount of FeOOH produced by the reaction system can adsorb and remove heavy metals. This experimental study provides a reliable theoretical and technical basis for the in-situ treatment of AMD in karst mountain mines with high efficiency by using slow-release materials.
-
表 1 模拟酸性矿山废水水质指标(pH=2.8)
Table 1. Water quality index of simulated acid coal mine wastewater (pH=2.8)
成分 模拟AMD质量浓度/(mg·L-1) 配置药品 天然AMD质量浓度/(mg·L-1) Fe2+ 180 FeSO4·7H2O 100~830 Mn2+ 70 MnCl2·4H2O 0.3~160 Zn2+ 13.8 ZnCl2 0.1~22 Cu2+ 30 CuCl2·2H2O 0.01~50 Cd2+ 0.5 CdCl2 0.1~5 Pb2+ 1.5 PbCl2 0.1~30 Cr3+ 1.2 CrCl3·6H2O 0.1~5 -
[1] Tu Z H, Wu Q, He H P, et al. Reduction of acid mine drainage by passivation of pyrite surfaces: A review[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 832: 155116. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155116 [2] Offeddu F G, Cama J, Soler J M, et al. Processes affecting the efficiency of limestone in passive treatments for AMD: Column experiments[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2015, 3(1): 304-316. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2014.10.013 [3] Shim M J, Choi B Y, Lee G, et al. Water quality changes in acid mine drainage streams in Gangneung, Korea, 10 years after treatment with limestone[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 159: 234-242. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.09.015 [4] Shane A, Xu X, Siame J, et al. Removal of copper from acid mine drainage (AMD) or acid rock drainage (ARD)[J]. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 2021, 13(7): 435-454. doi: 10.4236/jwarp.2021.137026 [5] Rivera U Y, Romero F M, Sedoov S, et al. Carbonatos pedogénicos para el tratamiento del drenaje ácido de mina (DAM)[J]. Boletín de la Sociedad Geológica Mexicana, 2020, 72(1): A250919. [6] 徐建平, 万海洮. 利用活性炭处理酸性矿井废水研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2014, 40(3): 57-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLJ201403017.htmXu J P, Wang H Z. Study on the treatment of Acid mine wastewater by activated carbon[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2014, 40(3): 57-59(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLJ201403017.htm [7] Jones S N, Cetin B. Evaluation of waste materials for acid mine drainage remediation[J]. Fuel, 2017, 188: 294-309. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.10.018 [8] Akcil A, Koldas S. Acid mine drainage (AMD): Causes, treatment and case studies[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2006, 14(12/13): 1139-1145. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652605000600 [9] 武强, 李松营. 闭坑矿山的正负生态环境效应与对策[J]. 煤炭学报, 2018, 43(1): 21-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201801004.htmWu Q, Li S Y. Positive and negative environmental effects of closed mines and its countermeasures[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(1): 21-32(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201801004.htm [10] 任虎俊. 废弃煤矿岩溶地下水污染机理及防控研究: 以贵州凯里鱼洞河流域为例[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2021.Ren H J. Investigation on themechanism and control of karst groundwater pollution due to abandoned coal mines: A case study in the Yudong River basin, Kaili City, Guizhou Province, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2021(in Chinese with English abstract). [11] Jiang C, Gao X, Hou B, et al. Occurrence and environmental impact of coal mine goaf water in karst areas in China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 275: 123813. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123813 [12] 宋凯. 前和煤矿开采对岩溶泉域水环境的影响[J]. 现代矿业, 2021, 37(7): 242-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKB202107068.htmSong K. The influence of Qianhe Coal Mining on karst spring water environment[J]. Modern Mining, 2021, 37(7): 242-254(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKB202107068.htm [13] 李冲. 随机森林模型预测岩溶区酸性煤矿井水锰污染[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2021, 33(3): 43-47, 59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT202103009.htmLi C. Prediction of karst region acidic coalmine water manganese pollution based on random forest[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2021, 33(3): 43-47, 59(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT202103009.htm [14] 李曦滨. 煤矿酸性废水污染综合治理技术与展望: 以贵州省鱼洞河流域综合治理技术应用研究为例[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2018, 30(7): 48-53, 93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT201807011.htmLi X B. Coalmine acid wastewater pollution integrated governance technology and expectation: A case study of Yudonghe Valley integrated governance technology application in Guizhou Province[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2018, 30(7): 48-53, 93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT201807011.htm [15] 李星颖, 刘明凤, 吴永贵, 等. 不同碳酸盐岩对铅锌冶炼废渣-黑麦草体系中重金属迁移的影响[J]. 地球与环境, (2021-8-23)[2021-12-20]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/52.1139.P.20211216.1715.002.html.Li X Y, Liu M F, Wu Y G, et al. Effect of different carbonate rocks on the migration and transformation of heavy metals in the lead-zinc smelting slag-plant system[J]. Earth and Environment, (2021-8-23)[2021-12-20]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/52.1139.P.20211216.1715.002.html (in Chinese with English abstract). [16] Kamal N M, Mohammad K, Khan N A, et al. Lab-scale study of passive treatment to treat acidic mine effluent by using limestone and dolomite[C]//AIP Conference Proceedings. [S. l. ]: Aip Publishing LLC, 2019. [17] Silva D, Weber C, Olivwira C. Neutralization and uptake of pollutant cations from acid mine drainage (AMD) using limestones and zeolites in a pilot-scale passive treatment system[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2021, 170: 107000. [18] 张春宇, 管树巍, 吴林, 等. 塔西北地区下寒武统碳酸盐岩地球化学特征及其古环境意义: 以舒探1井为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 99-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202105013.htmZhang C Y, Guan S W, Wu L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and its paleo-environmental significance of the Lower Cambrian carbonate in the northwestern Tarim Basin: A case study of Well Shutan-1[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 99-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202105013.htm [19] 张敏, 胡学玉, 胡晓晓, 等. 硫对地球表层生态系统中镉迁移转化影响的研究进展: 以土壤-植物系统为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 236-245. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0089Zhang M, Hu X Y, Hu X X, et al. Research progress on the effects of sulfur on the migration and transformation of cadmium in the earth surface ecosystem: A case study of soil-plant system[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 236-245(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0089 [20] Wang Y, Sikora S, Townsend T G. Ferrous iron removal by limestone and crushed concrete in dynamic flow columns[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2013, 124: 165-171. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301479713001060 [21] Kairies C L, Capo R C, Watzlaf G R. Chemical and physical properties of iron hydroxide precipitates associated with passively treated coal mine drainage in the Bituminous Region of Pennsylvania and Maryland[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2005, 20(8): 1445-1460. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0883292705001034 [22] Silva A M, Cunha E C, Silvaf D, et al. Treatment of high-manganese mine water with limestone and sodium carbonate[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2012, 29: 11-19. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652612000522 [23] Hallberg K B, Johnson D B. Biological manganese removal from acid mine drainage in constructed wetlands and prototype bioreactors[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2005, 338(1/2): 115-124. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969704006291 [24] 杨绍章, 吴攀, 张瑞雪, 等. 有氧垂直折流式反应池处理煤矿酸性废水[J]. 环境工程学报, 2011, 5(4): 789-794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201104013.htmYang S Z, Wu P, Zhang R X, et al. Treatment of acid mine drainage using aerobic baffled vertical flow reactor[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2011, 5(4): 789-794(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201104013.htm [25] Sracek O, Gzyl G, Frolik A, et al. Evaluation of the impacts of mine drainage from a coal waste pile on the surrounding environment at Smolnica, southern Poland[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2010, 165(1): 233-254. doi: 10.1007/s10661-009-0941-6 [26] Aziz H A, Adlan M N, Ariffin K S. Heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Zn, Ni, Cu and Cr (Ⅲ)) removal from water in Malaysia: Post treatment by high quality limestone[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2008, 99(6): 1578-1583. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960852407003239 [27] Swenlund P J, Webster J G, Miskelly G M. Goethite adsorption of Cu (Ⅱ), Pb (Ⅱ), Cd (Ⅱ), and Zn (Ⅱ) in the presence of sulfate: Properties of the ternary complex[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(6): 1548-1562. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016703708007400 [28] Elghali A, Benzaazoua M, Bouzahzah H, et al. Laboratory study on the effectiveness of limestone and cementitious industrial products for acid mine drainage remediation[J]. Minerals, 2021, 11(4): 413. [29] Genty T, Bussière B, Benzaazoua M, et al. Capacity of wood ash filters to remove iron from acid mine drainage: Assessment of retention mechanism[J]. Mine Water and the Environment, 2012, 31(4): 273-286. doi: 10.1007/s10230-012-0199-z [30] 夏雨, 吴攀, 张瑞雪, 等. 酸性矿山废水对碳酸盐岩侵蚀的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(6): 1702-1707. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201806013.htmXia Y, Wu P, Zhang R X, et al. The effects of acid mine drainage on the erosion of carbonatite in carbonate rocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(6): 1702-1707(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201806013.htm [31] Li W B, Feng Q Y, Liang H Q, et al. Passive treatment test of acid mine drainage from an abandoned coal mine in Kaili Guizhou, China[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2021, 84(8): 1981-1996. [32] Ahammed M M, Meera V. Metal oxide/hydroxide-coated dual-media filter for simultaneous removal of bacteria and heavy metals from natural waters[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 181(1/3): 788-793. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389410006655 -





 下载:
下载: