Research status of rock sliding specular reflection and its application in shale gas preservation
-
摘要:
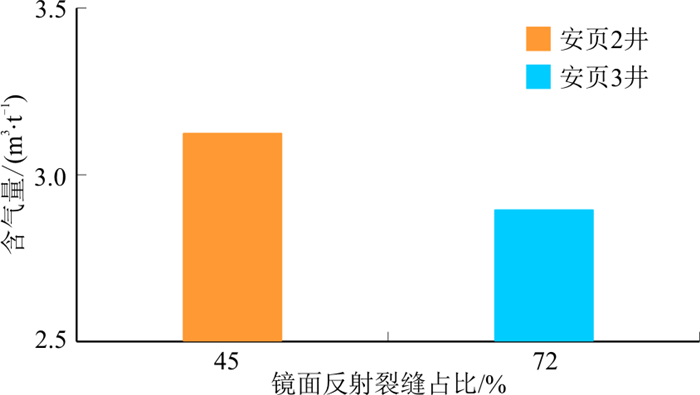
镜面反射是岩层滑动过程中形成的光滑表面, 具有一定的金属和玻璃光泽以及反光特性。在一些断裂带中, 这些光滑的表面也被称为断层镜(FMs)。镜面反射可见于多种类型的岩石中, 在泥岩、砂岩、页岩、煤层、碳酸盐岩、硅酸盐岩等地层中均有发现, 不同岩性的镜面形成机制存在差异, 但镜面的形成均与岩层滑动有关。因此, 与岩层滑动相关的应力、滑动速率、滑移距以及温度等对镜面形成均有重要影响。黔北安场向斜龙马溪组页岩中发育大量镜面反射, 为了查明这些镜面反射形成的影响因素及其与页岩含气性之间的内在联系, 通过大量文献阅读系统总结了镜面反射的发育特征和形成机制及其对流体渗流和页岩气保存条件的影响。结果表明: ①应力、滑动速率、滑动位移和温度对镜面反射的形成具有重要影响; ②镜面反射的形成取决于应力与滑动速率的组合形式, 高速高应力条件下更容易形成镜面反射; 低速低应力条件下, 即使滑动位移很大也不会形成镜面反射; ③相同应力和滑动速率条件下, 总体上滑动位移会促进镜面覆盖率增加, 镜面覆盖率甚至能达100%;④温度促使岩石颗粒由脆性转变成塑性, 在一定程度上能防止岩石颗粒发生脆性破裂, 进而烧结岩石颗粒, 促使镜面反射的形成; ⑤镜面粗糙度极低, 一般处于微米级别, 平均粗糙度振幅仅几个微米; ⑥形成镜面的裂缝以及滑移距, 明显改善了页岩气的渗流, 页岩气的加速散失可能导致其较差的含气性。因此, 在缺乏顶底板条件时, 镜面反射可能是导致页岩含气性较差的重要原因之一。
Abstract:Objective Specular reflection is a smooth surface formed during the sliding process of rock strata, with a certain metallic and glass luster and reflective properties. In some fault zones, these smooth surfaces are also known as fault mirrors (FMs). Specular reflection can be seen in many rock types, such as mudstone, shale, coal seam, carbonate rock, silicate rock and so on. The mechanism of specular reflection is different in different lithologies, but the formation of specular reflection is related to strata sliding. Therefore, the stress, slip rate, slip distance and temperature related to rock strata sliding have important influence on the formation of specularity.
Methods A large amount of specular reflection is developed in the syncline Longmaxi Formation shale in Anchang, northern Guizhou. To find out the factors influencing the formation of specular reflection and the internal relationship between them and the gas content of shale in this paper, the development characteristics and formation mechanism of specular reflection and its effects on fluid flow and shale gas preservation conditions were summarized systematically through a large number of literature reviews.
Results The results show that: (1) Stress, slip rate, slip displacement and temperature have important influence on the formation of specular reflection. (2) The formation of specular reflection depends on the combination form of stress and sliding rate. It is easier to form specular reflection under high-speed and high-stress conditions. Under low-speed and low-stress conditions, the specular reflection will not be formed even if the sliding displacement is large. (3) Under the same stress and sliding rate, the overall sliding displacement will promote the increase of specular coverage, and the specular coverage can even reach 100%. (4) The temperature makes the rock particles change from brittle to plastic, which can prevent the brittle fracture of the rock particles to a certain extent, and then sinter the rock particles, prompting the formation of specular reflection. (5) The specular roughness is very low, usually in the micrometer level, the average roughness range is only a few micrometers. (6) Specular cracks and slip distances are formed, which significantly improve the flow of shale gas, accelerated loss of shale gas may lead to poor gas.
Conclusion Therefore, in the absence of roof and floor conditions, specular refection may be one of the important reasons for the poor gas content of shale.
-
图 2 自然镜面反射面和部分非反射面特征
A.彩虹色赤铁矿镜面[22]; B.石灰岩中微红色的断层镜面[4]; C.电气石断层镜面[7]; D.白云岩断层镜面及200 μm×300 μm小区域数字高程模型[11]; E.汶川科钻岩心中发育的暗色断层镜面(四川龙门山); F.页岩中深褐色断层镜面和非反射面[2]; G, H, L.贵州正安地区安页1-6HF井暗黑色页岩镜面(G.埋深2 339.34 m;H.埋深2 346.57 m;L.埋深2 338.06 m, L中见未被镜面全覆盖时的不连续光亮斑块)
Figure 2. Features of natural specular reflective surface and partial non-reflective surface
图 4 低应力条件下岩石表面最高温度(a)和镜面覆盖率(b)与滑动速率的关系(据文献[4]修改, vc为临界滑动速率)
Figure 4. Relationship between maximum temperature on rock surface (a) and specular coverage (b) and slip rate under low stress conditions
图 5 镜面覆盖率与滑移距的关系(黑色点代表在17.3 MPa和1 m/s条件下运行; 红色点(S526)代表在26 MPa, 1 m/s的条件下运行(据文献[11]修改))
Figure 5. Relationship between mirror coverage and slip distance (The black dots represent operations at 17.3 MPa and 1 m/s; The red dot (S526) represents operation at 26 MPa, 1 m/s(according to reference[11] amendments))
图 6 流量与三维分形维数的关系(据文献[43]修改; b为裂缝开度)
Figure 6. Relationship between flow and three-dimensional fractal dimension
图 7 等效渗透系数与粗糙度系数关系[38]
Figure 7. Relationship between equivalent permeability coefficient and roughness coefficient
图 8 渗透率与滑移距的关系[40] (不同颜色曲线代表在不同裂隙面中的渗流实验)
Figure 8. Relationship between permeability and slip distance (different color curves represent seepage experiments in different fracture surfaces)
表 1 天然镜面类型统计
Table 1. Natural mirror type statistics
位置 镜面类型 成因 资料来源 美国瓦萨奇断层带 赤铁矿镜面 穿层滑动 文献[1] 美国科罗纳高地断层 硅酸盐镜面 穿层滑动 文献[5] 意大利厄尔巴岛 电气石镜面 穿层滑动 文献[7] 四川盆地 页岩镜面 顺层滑脱 文献[8-9, 14] 南阿尔卑斯山 碳酸盐镜面 穿层滑动 文献[11] 黔北 页岩镜面 顺层滑脱 文献[15] 藏南嘉黎断裂 片麻岩镜面 穿层滑动 文献[16] 中扬子宜昌地区 泥岩镜面 顺层滑脱 据文献[17] 秦岭构造带 黄铁矿镜面 穿层滑动 文献[18] 湘中龙山金锑矿 绿泥石镜面 穿层滑动 文献[19] 东秦岭-大别山造山带 砂岩镜面 穿层滑脱 文献[20] 华北中南部 煤层镜面 穿层滑动 文献[21] -
[1] Evans J P, Prante M R, Janecke S U, et al. Hot faults: Iridescent slip surfaces with metallic luster document high-temperature ancient seismicity in the Wasatch fault zone, Utah, USA[J]. Geology, 2014, 42(7): 623-626. doi: 10.1130/G35617.1 [2] Li G W, Sheng R S, Suppe J, et al. Fault mirrors in seismically active fault zones: A fossil of small earthquakes at shallow depths[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(5): 1-10. [3] Siman-Tov S, Aharonov E, Sagy A, et al. Nanograins form carbonate fault mirrors[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(6): 703-706. doi: 10.1130/G34087.1 [4] Siman-Tov S, Boneh Y, Reches Z, et al. Fault mirrors along carbonate faults: Formation and destruction during shear experiments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 430: 367-376. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.08.031 [5] Kirkparick J D, Rowe C D, White J C, et al. Silica gel formation during fault slip: Evidence from the rock record[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(9): 1015-1018. doi: 10.1130/G34483.1 [6] Laurich B, Urai J L, Desbois G, et al. Microstructural evolution of an incipient fault zone in Opalinus Clay: Insights from an optical and electron microscopic study of ion-beam polished samples from the main fault in the Mt-Terri Underground Research Laboratory[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2014, 67: 107-128. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2014.07.014 [7] Viti C, Brogi A, Liotta D, et al. Seismic slip recorded in tourmaline fault mirrors from Elba Island (Italy)[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2016, 86: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2016.02.013 [8] 徐壮, 彭女佳, 石万忠, 等. 涪陵地区五峰-龙马溪组页岩气储层裂缝特征及其控制因素[J]. 东华理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 44(3): 267-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ202103008.htmXu Z, Peng N J, Shi W Z, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of shale gas reservoir fractures in Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, Fuling area[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2021, 44(3): 267-279(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ202103008.htm [9] 何贵松. 川南古蔺地区仁页1井五峰组-龙马溪组生物地层及成藏特征[J]. 地层学杂志, 2021, 45(2): 142-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ202102003.htmHe G S. Biostratigraphy and accumulation characteristics ofWufeng-Longmaxi Formations in Well Renye 1, Gulin area, southern Sichuan[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2021, 45(2): 142-150(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ202102003.htm [10] Boneh Y, Sagy A, Reches Z. Frictional strength and wear-rate of carbonate faults during high-velocity, steady-state sliding[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 381: 127-137. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.08.050 [11] Fondriest M, Smith S A F, Candela T, et al. Mirror-like faults and power dissipation during earthquakes[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(11): 1175-1178. doi: 10.1130/G34641.1 [12] Smith S A F, di Toro G, Kim J H, et al. Coseismic recrystallization during shallow earthquake slip[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(1): 63-66. doi: 10.1130/G33588.1 [13] Verberne B A, Pluemper O, Damd W, et al. Superplastic nanofibrous slip zones control seismogenic fault friction[J]. Science, 2014, 346: 1342-1344. doi: 10.1126/science.1259003 [14] 王濡岳, 胡宗全, 周彤, 等. 四川盆地及其周缘五峰组-龙马溪组页岩裂缝发育特征及其控储意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(6): 1295-1306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202106005.htmWang R Y, Hu Z Q, Zhou T, et al. Characteristics of shale fractures and their controlling and reservoir significance in Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations, Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(6): 1295-1306(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202106005.htm [15] 谷阳, 徐晟, 张炜, 等. 黔北地区牛蹄塘组页岩储层裂缝特征[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(9): 3556-3562. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS202109018.htmGu Y, Xu S, Zhang W, et al. Characteristics of shale fractures in Niutitang Formation, northern Guizhou area[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(9): 3556-3562(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS202109018.htm [16] 赵远芳, 公王斌, 江万, 等. 藏南嘉黎断裂古乡-通麦段多期活动特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 35(1): 220-233. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202101025.htmZhao Y F, Gong W B, Jiang W, et al. Multi-stage activity characteristics and tectonic significance of Guxiang-Tongmai member of Jiali fault in south Tibet[J]. Geoscience, 2016, 35 (1): 220-233(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202101025.htm [17] 罗胜元, 陈孝红, 岳勇, 等. 中扬子宜昌地区沉积-构造演化与寒武系页岩气富集规律[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(8): 1052-1068. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202008002.htmLuo S Y, Chen X H, Yue Y, et al. Sedimentary and tectonic evolution and Cambrian shale gas enrichment in Yichang area, Middle Yangtze Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(8): 1052-1068(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202008002.htm [18] 张飞, 曾冠中, 许佳琪. 西秦岭安坝金矿床控矿断裂破碎带地质-地球化学特征[J]. 中国金属通报, 2020(23): 33-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSTB202012018.htmZhang F, Zeng G Z, Xu J Q. Geological and geochemical characteristics of ore-controlling fracture belt in Anba Gold Deposit, west Qinling[J]. China Metal Bulletin, 2020(23): 33-34(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSTB202012018.htm [19] 贾朋远, 宋江涛. 湘中龙山金锑矿断裂构造与成矿关系研究[J]. 世界有色金属, 2020(17): 76-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO202017037.htmJia P Y, Song J T. Research on the relationship between fault structure and mineralization of Longshan Au-antimony Deposit in central Hunan Province[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2020(17): 76-78(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO202017037.htm [20] 徐江红, 郑德顺, 刘思聪, 等. 豫西宜阳南部地区中新生代地质构造特征分析及其演化过程[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(5): 22-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705004.htmXu J H, Zheng D S, Liu S C, et al. Characteristics and evolution of Mesozoic and Cenozoic geological structures in southern Yiyang area, western Henan Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(5): 22-30(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705004.htm [21] 任建刚. 华北中南部中高煤级构造煤瓦斯扩散规律及控制机理研究[D]. 河南焦作: 河南理工大学, 2016.Ren J G. Study on gas diffusion law and control mechanism of middle-high coal grade structure coal in south-central North China[D]. Jiaozuo, Henan: Henan Polytechnic University, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [22] McDermott R G, Ault A K, Evans J P, et al. Thermochronometric and textural evidence for seismicity via asperity flash heating on exhumed hematite fault mirrors, Wasatch fault zone, UT, USA[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 471: 85-93. [23] 张福, 黄艺, 蓝宝锋, 等. 正安地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩储层特征及控制因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 49-56. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0016Zhang F, Huang Y, Lan B F, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of shale reservoir in Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation of the Zheng'an area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 49-56(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0016 [24] 杨锐, 何生, 胡东风, 等. 焦石坝地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩孔隙结构特征及其主控因素[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(5): 105-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201505017.htmYang R, He S, Hu D F, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of shale pore structure in Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, Jiaoshiba area[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(5): 105-113(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201505017.htm [25] Liu R, Hao F, Engelder T, et al. Influence of tectonic exhumation on porosity of Wufeng-Longmaxi shale in the Fuling Gas Field of the eastern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2020, 104(4): 939-959. [26] 王保战. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部延长组长7段生烃潜力研究[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2015, 29(4): 27-30, 154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201504009.htmWang B Z. Hydrocarbon generation potential of Chang 7 Member of Yanchang Formation, southern Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2015, 29(4): 27-30, 154(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201504009.htm [27] 李彦录, 陆诗磊, 夏东领, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部延长组长7油组页岩层系天然裂缝发育特征及主控因素[J]. 地质科学, 2022, 57(1): 73-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202201004.htmLi Y L, Lu S L, Xia D L, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of natural fractures in shale of Chang 7 Member of Yanchang Formation, southern Ordos Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2022, 57(1): 73-87(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202201004.htm [28] 邹辰, 李德华, 杨庆, 等. 滇黔北地区龙马溪组有机质石墨化特征及成因[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(增刊1): 67-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG2021S1010.htmZou C, Li D H, Yang Q, et al. Graphitization characteristics and genesis of organic matter in the Longmaxi Formation, northern Yunnan and Guizhou areas[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(S1): 67-72(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG2021S1010.htm [29] 蒋珊, 王玉满, 王书彦, 等. 四川盆地川中古隆起及周缘下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩有机质石墨化区预测[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(10): 19-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201810004.htmJiang S, Wang Y M, Wang S Y, et al. Prediction of organic matter graphitization area of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi shale in central Sichuan paleo-uplift and its surrounding area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(10): 19-27(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201810004.htm [30] Paola N D, Holdsworth R E, Viti C, et al. Can grain size sensitive flow lubricate faults during the initial stages of e-arthquake propagation?[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 431: 48-58. [31] Verberne B A, deBresser J H P, Niemeijer A R, et al. Nanocrystalline slip zones in calcite fault gouge show intense crystallographic preferred orientation: Crystal plasticity at sub-seismic slip rates at 18-150℃[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(8): 863-866. [32] 李欢, 王清斌, 庞小军, 等. 致密砂砾岩储层裂缝形成及储层评价: 以黄河口凹陷沙二段为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1): 176-185. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901019.htmLi H, Wang Q B, Pang X J, et al. Fracture formation and reservoir evaluation of tight conglomerate reservoir: A case study of the 2nd Member of Shahejie Formation in Huanghekou Sag[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(1): 176-185(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901019.htm [33] 王焕, 李海兵. 断裂带中古地震滑动的岩石记录[J]. 地球学报, 2019, 40(1): 135-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201901010.htmWang H, Li H B. Seismic slip records in fault rock[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2019, 40(1): 135-156(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201901010.htm [34] Rowe C D, Griffith W A. Do faults preserve a record of seismic slip: A second opinion[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2015, 78: 1-26. [35] Sibson R H. Thickness of the seismic slip zone[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2003, 93(3): 1169-1178. [36] Rice J R. Heating and weakening of faults during earthquake slip[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2006, 111(B5): B05311. [37] 任彦锦. 裂隙粗糙度及开度影响砂岩渗流特性研究[D]. 沈阳阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2017.Ren Y J. Study on the effect of fracture roughness and opening on seepage characteristics of sandstone[D]. Fuxin, Shenyang: Liaoning Technical University, 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [38] 王蓉. 基于三维扫描技术的裂隙面重建及其渗流规律研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉轻工大学, 2017.Wang R. Study on fracture surface reconstruction and seepage law based on 3D scanning technology[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Polytechnic University, 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [39] 段玲玲, 邓华锋, 熊雨, 等. 岩体裂隙面形貌特征对其渗流特性的影响研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 2021, 41(1): 110-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK202101013.htmDuan L L, Deng H F, Xiong Y, et al. Study on the influence of morphology of rock mass fracture surface on its seepage characteristics[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2021, 41(1): 110-117(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK202101013.htm [40] Zhang X, Shi W, Hu Q et al. Pressure-dependent fracture permeability of marine shales in the northeast Yunnan area, southern China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2019, 214: 103237. [41] Chen D, Pan Z, Ye Z. Dependence of gas shale fracture permeability on effective stress and reservoir pressure: Model match and insights[J]. Fuel, 2015, 139: 383-392. [42] 杨金保, 冯夏庭, 潘鹏志, 等. 考虑应力历史的岩石单裂隙渗流特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(6): 1629-1635. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201306018.htmYang J B, Feng X T, Pan P Z, et al. Experimental study on seepage characteristics of rock single fracture considering stress history[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(6): 1629-1635(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201306018.htm [43] 王来贵, 张阳, 刘向峰, 等. 单裂隙砂岩渗流特性实验研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2018, 37(5): 1804-1812. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSYT201805054.htmWang L G, Zhang Y, Liu X F, et al. Experimental study on seepage characteristics of sandstone with single fracture[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018, 37(5): 1804-1812(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSYT201805054.htm [44] 段慕白, 李皋, 孟英峰, 等. 不同节理粗糙度系数的裂隙渗流规律研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2013, 24(5): 41-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201305009.htmDuan M B, Li G, Meng Y F, et al. Study on seepage law of fracture with different joint roughness coefficients[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2013, 24(5): 41-44(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201305009.htm [45] 王志良, 申林方, 徐则民, 等. 岩体裂隙面粗糙度对其渗流特性的影响研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2016, 38(7): 1262-1268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201607013.htmWang Z L, Shen L F, Xu Z M, et al. Effect of fracture surface roughness on seepage characteristics of rock mass[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(7): 1262-1268(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201607013.htm [46] Kassis S, Sondergeld C. Fracture permeability of gas shale: Effects of roughness, fracture offset, proppant, and effective stress[C]//Anon. International Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition in China. [S. l. ]: SPE Journal, 2010: 1-17. [47] Guo T, Zhang S, Gao J, et al. Experimental study of fracture permeability for stimulated reservoir volume (SRV) in shale formation[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2013, 98(3): 525-542. [48] 苗凤彬, 彭中勤, 汪宗欣, 等. 雪峰隆起西缘下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩裂缝发育特征及主控因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 31-42. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0204Miao F B, Peng Z Q, Wang Z X, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of shale fractures in the Lower CambrianNiutitang Formation in the western margin of Xuefeng Uplift[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 31-42(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0204 [49] 苟启洋, 徐尚, 郝芳, 等. 基于成像测井的泥页岩裂缝研究: 以焦石坝区块为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 193-200. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0620Gou Q Y, Xu S, Hao F, et al. Study on shale fractures based on imaging logging: A case study of Jiaoshiba block[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 193-200(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0620 [50] 何顺, 秦启荣, 周吉羚, 等. 川东南DS地区龙马溪组页岩裂缝发育特征及期次解析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 101-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902012.htmHe S, Qin Q R, Zhou J L, et al. Development characteristics and epoch analysis of shale fractures in Longmaxi Formation in DS area, southeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2): 101-109(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902012.htm [51] 汤济广, 汪凯明, 秦德超, 等. 川东南南川地区构造变形与页岩气富集[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 11-21. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0502Tang J G, Wang K M, Qin D C, et al. Tectonic deformation and shale gas enrichment in Nanchuan area, southeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 11-21(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0502 -





 下载:
下载: