Coral reef bleaching monitoring based on multitime Landsat-8 remote sensing image series
-
摘要:
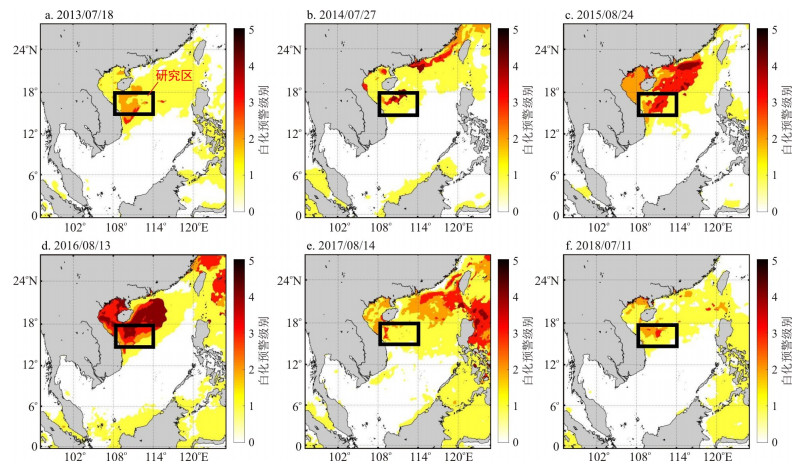
近年来, 受人类活动和全球变暖的双重影响, 我国南海区域珊瑚礁生态系统退化, 发生白化现象。利用遥感技术监测和掌握珊瑚礁的白化情况, 对南海生态环境的保护和治理具有重大价值。首先通过多期海表温度数据获取珊瑚礁白化预警的区域, 选定西沙群岛永乐环礁中的羚羊礁作为研究对象; 然后, 提出了一种新型的珊瑚礁白化监测模型, 分别采取水深校正、珊瑚礁分类、反射率调整以及阈值选择等方式对2013-2018年的Landsat-8遥感影像开展了多时间序列的珊瑚礁白化监测研究。最终的结果显示, 该模型能够较为准确地获取珊瑚礁白化区域, 为南海珊瑚礁白化现象的长时间序列监测提供依据。
Abstract:In recent years, due to the influence of human activities and global warming, the coral reef ecosystem in the South China Sea (SCS) has degraded, and bleaching occurs. Utilizing the remote sensing method to monitor and understand the bleaching status of coral reefs is of great value to the protection and management of the ecological environment in the SCS. This study first obtains coral reef bleaching alert areas (BAAs) through multiperiod sea surface temperature data (SST) and selects the Antelope Reef in the Yongle Atoll of the Paracel Islands as the research area. Then, a new coral reef bleaching monitoring model is proposed, which uses water depth correction, coral reef classification, reflectance adjustment and threshold selection to carry out multitime series coral reef bleaching monitoring research with Landsat-8 remote sensing images from 2013 to 2018. The results show that the model can effectively obtain coral reef bleaching areas and provide a feasible approach for the monitoring of coral reef bleaching in the South China Sea.
-
表 1 珊瑚礁白化预警分级
Table 1. Coral reef bleaching warning classification
珊瑚礁白化预警级别 预警标准 影响 无危险(1) HS≤0 — 白化监视(2) 0<HS<1 — 白化警告(3) HS≥1且0<DHW<4 有可能发生白化 白化警报级别1(4) HS≥1且4≤DHW<8 很可能发生白化 白化警报级别2(5) HS≥1且DHW≥8 可能出现死亡 表 2 2013-2018年羚羊礁区域地物分类结果
Table 2. Substrate classification results of the Antelope Reef area from 2013 to 2018
类型 2013年分类结果 2014年分类结果 2015年分类结果 2016年分类结果 2017年分类结果 2018年分类结果 像元数 百分比/% 像元数 百分比/% 像元数 百分比/% 像元数 百分比/% 像元数 百分比/% 像元数 百分比/% 海洋 44 165 70.66 40 43 690 69.904 0 43 725 69.96 43 711 69.937 6 43 730 69.968 0 43 899 70.238 4 珊瑚礁 8 555 13.688 0 7 981 12.769 6 7 991 12.785 6 9 153 14.644 8 8 788 14.060 8 8 382 13.411 2 沙地 3 197 5.115 2 4 246 6.793 6 4 212 6.739 2 3 501 5.601 6 4 101 6.561 6 3 885 6.216 0 泻湖 6 583 10.532 8 6 583 10.532 8 6 572 10.515 2 6 135 9.816 0 5 881 9.409 6 6 334 10.134 4 表 3 2013-2018年珊瑚礁白化结果
Table 3. Results of coral reef bleaching from 2013 to 2018
类型 2013-2014年白化检测 2014-2015年白化检测 2015-2016年白化检测 2016-2017年白化检测 2017-2018年白化检测 像元数 百分比/% 像元数 百分比/% 像元数 百分比/% 像元数 百分比/% 像元数 百分比/% 海洋 43 690 69.904 0 43 725 69.960 0 43 711 69.937 6 43 730 69.968 0 43 899 70.238 4 珊瑚礁 7 482 11.971 2 4 988 7.980 8 4 375 7.000 0 7 485 11.976 0 7 359 11.774 4 沙地 4 246 6.793 6 4 212 6.739 2 3 501 5.601 6 4 101 6.561 6 3 885 6.216 0 泻湖 6 583 10.532 8 6 572 10.515 2 6 135 9.816 0 5 881 9.409 6 6 334 10.134 4 白化 499 0.798 4 3 003 4.804 8 4 778 7.644 8 1 303 2.084 8 1 023 1.636 8 -
[1] 黄荣永, 余克服, 王英辉, 等. 珊瑚礁遥感研究进展[J]. 遥感学报, 2019, 23(6): 1091-1112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB201906008.htmHuang R Y, Yu K F, Wang Y H, et al. Progress of the study on coral reef remote sensing[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 23(6): 1091-1112(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB201906008.htm [2] Liu G, Heron S, Eakin C, et al. Reef-scale thermal stress monitoring of coral ecosystems: New 5 km global products from NOAA coral reef watch[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(11): 11579-11606. doi: 10.3390/rs61111579 [3] Eakin C M, Lough J M, Heron S F. Climate variability and change: Monitoring data andevidence for increased coral bleaching stress[C]//Lough J, van Oppen M. Coralbleaching: Partterns, processes, causes and consequences. Berlin: Springer, 2009. [4] 孙旋, 蔡玉林, 索琳琳, 等. 基于SST的珊瑚礁白化监测技术综述[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2018, 30(2): 21-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG201802003.htmSun X, Cai Y L, Suo L L, et al. Review of coral reef bleaching monitoring technology based on SST[J]. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 2018, 30(2): 21-28(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG201802003.htm [5] Andréfouët S, Mumby P, McField M, et al. Revisiting coral reef connectivity[J]. Coral Reefs, 2002, 21(1): 43-48. doi: 10.1007/s00338-001-0199-0 [6] Yamano H, Tamura M. Detection limits of coral reef bleaching by satellite remote sensing: Simulation and data analysis[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2003, 90(1): 86-103. [7] Kabiri K, Pradhan B, Shafri H Z M, et al. A novel approach to estimate diffuse attenuation coefficients for Quick Bird satellite Images: A case study at Kish Island, the Persian Gulf[J]. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 2013, 41(4): 797-806. doi: 10.1007/s12524-013-0293-0 [8] 王雪丽, 蔡玉林, 索琳琳, 等. 基于Landsat-8数据的珊瑚礁白化变化监测[J]. 遥感信息, 2019, 34(6): 119-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2019.06.019Wang X L, Cai Y L, Suo L L, et al. Monitoring of coral reef bleaching based on Landsat-8 data[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2019, 34(6): 119-124(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2019.06.019 [9] 潘艳丽, 唐丹玲. 卫星遥感珊瑚礁白化概述[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(9): 5076-5080. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.09.057Pan Y L, Tang D L. General introduction to satellite remote sensing of coral reef bleaching[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2009, 29(9): 5076-5080(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.09.057 [10] Lyzenga D R. Remote sensing of bottom reflectance and water attenuation parameters in shallow water using aircraft and landsat data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1981, 2: 71-82. doi: 10.1080/01431168108948342 [11] 索琳琳, 蔡玉林, 孙旋, 等. 基于Landsat-8数据的西沙群岛珊瑚礁信息提取[J]. 中国科技论文, 2019, 14(3): 347-352. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2019.03.019Suo L L, Cai Y L, Sun X, et al. Mapping coral reefs at Xisha Islands using Landsat-8[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2019, 14(3): 347-352(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2019.03.019 [12] 吴柯, 牛瑞卿, 王毅, 等. 基于PCA与EM算法的多光谱遥感影像变化检测研究[J]. 计算机科学, 2010, 37(3): 282-284, 296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJA201003074.htmWu K, Niu R Q, Wang Y, et al. Change detection of mul ti-spectral remote sensed images based on PCA and EM algorithm[J]. Computer Science, 2010, 37(3): 282-284, 296(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJA201003074.htm [13] 徐京萍, 李方, 孟庆辉, 等. 基于野外实测数据的珊瑚礁不同底质光谱可分性及珊瑚色素影响分析[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2019, 39(8): 2462-2469. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201908028.htmXu J P, Li F, Meng Q H, et al. The analysis of spectral separability of different coral reef benthos and the influence of pigments on coral spectra based on in-situ data[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(8): 2462-2469(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201908028.htm [14] 王伟, 许兆林, 李维振, 等. 基于高斯过程回归和高压压汞测定致密砂岩渗透率: 以鄂尔多斯盆地长7段致密砂岩为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 30-37. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0117Wang W, Xu Z L, Li W Z, et al. Determination of permeability in tight sandstone reservoirs using Gaussian process regression and high-pressure porosimetry: A case study of the Member-7 of Yanchang Formation in the Jiyuan area of Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 30-37(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0117 [15] 李元超, 吴钟解, 梁计林, 等. 近15年西沙群岛长棘海星暴发周期及暴发原因分析[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(33): 3478-3484.Li Y C, Wu Z X, Liang J L, et al. Analysis on the outbreak period and cause of Acanthaster planci in Xisha Islands in recent 15 years[J]. China Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(33): 3478-3484(in Chinese with English abstract). [16] 张振冬, 邵魁双, 杨正先, 等. 西沙珊瑚礁生态承载状况评价研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2018, 37(4): 487-492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYHJ201804003.htmZhang Z D, Shao K S, Yang Z X, et al. Evaluation of the Xisha coral reef ecosystem carrying capacity[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2018, 37(4): 487-492(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYHJ201804003.htm -





 下载:
下载: