Quantitative well logging evaluation of diagenetic facies of deep and ultra deep tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of Bozi-Dabei area in Kuqa Depression
-
摘要:
博孜-大北地区巴什基奇克组为深层、超深层致密砂岩储层, 岩性致密, 亟需揭示储层品质主控因素, 建立相配套的有利储层测井评价方法。为单井定量评价其成岩相, 充分利用岩心、常规薄片、铸体薄片、扫描电镜等资料, 对博孜-大北地区巴什基奇克组致密储层的岩石学、物性、成岩作用类型和强度、成岩矿物等特征进行了研究, 并在视压实率、视胶结率、溶蚀孔隙含量和成岩综合系数等参数定量计算的基础上, 根据成岩作用强度及其组合特征对储层成岩相分类命名, 划分出中等压实弱溶蚀相、碳酸盐胶结相及压实致密相等不同的成岩相类型。通过薄片等资料与测井资料拟合分析, 建立了成岩综合系数
C g的测井计算模型, 以及定量识别储层成岩相的方法。对X1、Y1等井的测井资料进行了处理, 并通过识别结果与物性分析、铸体薄片等的匹配关系, 验证了方法模型的可靠性。成岩相测井定量表征方法的建立可为有利储层预测提供指导。Abstract:Bashijiqike Formation in Bozi-Dabei area develops deep and ultra deep tight sandstone reservoirs. It is urgent to reveal the main controlling factors of reservoir quality and establish a matching well logging evaluation method for high quality reservoirs. In order to quantitatively evaluate the diagenetic facies, based on the data of core, thin section, cast thin section and scanning electron microscope and etc., the petrology, physical properties, diagenesis types and intensity, diagenetic minerals and other characteristics of the tight reservoir of Bashijiqike Formation in Bozi-Dabei area were studied. Based on quantitative calculation of ompaction rate, cementation rate, dissolution pore content and comprehensive diagenetic coefficient, the diagenetic facies were classified according to characteristics of diagenesis intensity and its combination. The reservoirs can be divided into three types of diagenetic facies, i.e., medium compaction weak dissolution facies, carbonate cemented facies and compaction dense facies. Through the fitting analysis of thin section data and well logging data, the well logging calculation model of diagenetic comprehensive coefficient
C g was established, and the method of quantitative identification of reservoir diagenetic facies were established. The well logging data of Well X1, Well Y1 and etc were processed.The reliability of the model was verified by matching the identification results with physical property analysis and casting thin section. The establishment of well logging quantitative characterization method of diagenetic facies can provide guidance for "sweet spot" prediction. -
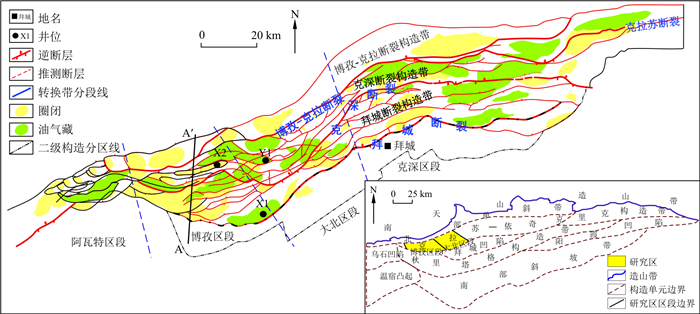
图 1 库车坳陷博孜-大北地区构造区划及研究区构造图(据文献[9]修改)
Figure 1. Top structural map of Cretaceous Bashijiqike Formation in Bozi-Dabei area, Kuqa Depression
图 3 巴什基奇克组储层镜下成岩特征
a.中粒长石岩屑砂岩,箭头指向岩屑、石英及长石颗粒,长石、岩屑具溶蚀特征,方解石胶结染色,Y1井,4 846.76 m;b.中细粒岩屑长石砂岩,箭头指向粒间充填的方解石胶结物、岩屑及石英颗粒,X3井,6 795.66 m;c.原生粒间孔发育,颗粒以点-线接触为主,箭头指向原生粒间孔及粒间溶孔,X4井,8 083.12 m;d.原生粒间孔发育,以点-线接触为主,具有少量溶蚀,箭头指向粒间溶孔及粒内溶孔,X1井,7 689.91 m;e.原生粒间孔,粒间溶孔,另有1条微裂缝贯穿整个视域,部分被铁方解石充填,箭头指向粒间溶孔及微裂缝,Y2井,6 349.34 m;f.石英次生加大显著,胶结致密,见粒内溶孔,箭头指向石英次生加大及粒内溶孔,Y3井, 5 174.42 m
Figure 3. Photomicrographs showing the microscopic diagenetic features of Bashijiqike Formation reservoirs
图 5 博孜9井巴什基奇克组孔隙演化与热埋藏史配置图(据文献[12]修改)
Figure 5. Pore evolution and thermal burial history of Bashijiqike Formation in Well 9 of Bozi
图 7 巴什基奇克组储层成岩相铸体薄片特征
a.极细砂与细砂混杂、线-点接触,可见孔隙极少,视压实率=82.5%,视胶结率=91.8%,溶蚀孔体积分数=0.4%,Cg=0.47%,压实致密相,X1井,7 686.68 m;b.方解石胶结致密,视压实率=71.25%,视胶结率=95.65%,溶蚀孔体积分数=1.6%,Cg=0.89%,碳酸盐胶结相,X5井,6 253.2 m;c.颗粒点-线接触,压实作用中等,胶结作用弱,另有少量粒间溶孔,视压实率=74.5%,视胶结率=35.3%,溶蚀孔体积分数=1.3%,Cg=4.3%,中等压实弱胶结相,X4井,8 079.14 m;d.颗粒点-线接触,压实作用中等,胶结作用弱,另有少量粒间及粒内溶孔,视压实率=72.9%,视胶结率=28.5%,溶蚀孔体积分数=2.4%,Cg=4.6%,中等压实弱胶结相,X4井,8 083.12 m
Figure 7. Cast thin section characteristics of diagenetic facies in Bashijiqike Formation
表 1 博孜-大北地区成岩相划分
Table 1. Division of diagenetic facies of Bozi-Dabei area
成岩相 镜下特征 视压实率/% 视胶结率/% 溶蚀孔体积分数/% 成岩综合系数Cg/% 压实致密相 颗粒粒度细或泥沙混杂,可见孔隙极少 > 75 > 60 < 0.5 < 0.5 碳酸盐胶结相 方解石和白云石胶结粒间孔 < 75 > 75 < 0.5 [0.5, 1] 中等压实弱胶结相 原生粒间孔发育,胶结作用弱 < 75 < 75 > 0.5 > 1 -
[1] 孙龙德, 邹才能, 朱如凯, 等. 中国深层油气形成、分布与潜力分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(6): 641-649. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201306001.htmSun L D, Zou C N, Zhu R K, et al. Formation, distribution and potential of deep hydrocarbon resources in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(6): 641-649(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201306001.htm [2] 张荣虎, 杨海军, 王俊鹏, 等. 库车坳陷超深层低孔致密砂岩储层形成机制与油气勘探意义[J]. 石油学报, 2014, 35(6): 1057-1069. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201406004.htmZhang R H, Yang H J, Wang J P, et al. The formation mechanism and exploration significance of ultra-deep, low-porosity and tight sandstone reservoirs in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2014, 35(6): 1057-1069(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201406004.htm [3] 张光亚, 马锋, 梁英波, 等. 全球深层油气勘探领域及理论技术进展[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(9): 1156-1166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201509015.htmZhang G Y, Ma F, Liang Y B, et al. Domain and theory-technology progress of global deep oil & gas exploration[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(9): 1156-1166(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201509015.htm [4] 朱光有, 曹颖辉, 闫磊, 等. 塔里木盆地8 000 m以深超深层海相油气勘探潜力与方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(6): 755-772. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201806002.htmZhu G Y, Cao Y H, Yan L, et al. Petroleum exploration potential and favorable areas of ultra-deep marine strata deeper than 8 000 meters in Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(6): 755-772(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201806002.htm [5] Lai J, Wang G W, Wang S, et al. Review of diagenetic facies in tight sandstones: Diagenesis, diagenetic minerals, and prediction via well logs[J]. Earth-Science Review, 2018, 185: 234-258. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.06.009 [6] 田军, 王清华, 杨海军, 等. 塔里木盆地油气勘探历程与启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(3): 272-282. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202103004.htmTian J, Wang Q H, Yang H J, et al. Petroleum exploration history and enlightenment in Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(3): 272-282(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202103004.htm [7] 赵文智, 沈安江, 胡安平, 等. 塔里木、四川和鄂尔多斯盆地海相碳酸盐岩规模储层发育地质背景初探[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(11): 3495-3508. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201511024.htmZhao W Z, Shen A J, Hu A P, et al. A Discussion on the geological background of marine carbonate reservoirs development in Tarim, Sichuan and Ordos Basin, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(11): 3495-3508(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201511024.htm [8] 徐春春, 邹伟宏, 杨跃明, 等. 中国陆上深层油气资源勘探开发现状及展望[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(8): 1139-1153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201708001.htmXu C C, Zou W H, Yang Y M, et al. Status and prospects of exploration and exploitation of the deep oil & gas resources onshore China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(8): 1139-1153(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201708001.htm [9] 田军, 杨海军, 吴超, 等. 博孜9井的发现与塔里木盆地超深层天然气勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(1): 11-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001004.htmTian J, Yang H J, Wu C, et al. Discovery of Well Bozi 9 and ultra-deep natural gas exploration potential in the Kelasu tectonic zone of the Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(1): 11-19(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001004.htm [10] 王翠丽, 李红波, 陈东, 等. 克深气田巴什基奇克组致密砂岩储层孔隙结构特征及影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 7(5): 70-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201805010.htmWang C L, Li H B, Chen D, et al. Porosity structure characteristics and influencing factors analysis of Basijiqike tight sandstone reservoir in Keshen Gasfield[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 7(5): 70-77(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201805010.htm [11] 戴金星, 倪云燕, 吴小奇. 中国致密砂岩气及在勘探开发上的重要意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(3): 257-264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201203002.htmDai J X, Ni Y Y, Wu X Q, et al. Tight gas in China and its significance in exploration and exploitation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(3): 257-264(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201203002.htm [12] 曾庆鲁, 莫涛, 赵继龙, 等. 7 000 m以深优质砂岩储层的特征、成因机制及油气勘探意义: 以库车坳陷下白垩统巴什基奇克组为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(1): 38-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001009.htmZeng Q L, Mo T, Zhao J L, et al. Characteristics, genetic mechanism and oil & gas exploration significance of high-quality sandstone reservoirs deeper than 7 000 m: A case study of the Bashijiqike Formation of Lower Cretaceous in the Kuqa Depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(1): 38-47(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001009.htm [13] Lai J, Fan X C, Liu B C, et al. Qualitative and quantitative prediction of diagenetic facies via well logs[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 120: 104486. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104486 [14] 赖锦, 王贵文, 庞小娇, 等. 测井地质学前世、今生与未来: 写在《测井地质学·第二版》出版之时[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(6): 1804-1828. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202106023.htmLai J, Wang G W, Pang X J, et al. The past, present and future of well logging geology: To celebrate the publication of second edition of "Well Logging Geology"[J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67(6): 1804-1828(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202106023.htm [15] 邹才能, 陶士振, 周慧, 等. 成岩相的形成、分类与定量评价方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2008, 35(5): 526-540. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200805004.htmZou C N, Tao S Z, Zhou H, et al. Genesis, classification and evaluation method of diagenetic facies[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2008, 35(5): 526-540(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200805004.htm [16] 杨升宇, 张金川, 黄卫东, 等. 吐哈盆地柯柯亚地区致密砂岩气储层"甜点"类型及成因[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(2): 272-282. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201302010.htmYang S Y, Zhang J C, Huang W D, et al. "Sweet spot" types of reservoirs and genesis of tight sandstone gas in Kekeya area, Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(2): 272-282 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201302010.htm [17] 邹才能, 陶士振, 朱如凯, 等. "连续型"气藏及其大气区形成机制与分布: 以四川盆地上三叠统须家河组煤系大气区为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2009, 36(3): 307-319. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200903010.htmZou C N, Tao S Z, Zhu R K, et al. Formation and distribution of "continuous" gas reservoirs and their giant gas province: A case from the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation giant gas province, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2009, 36(3): 307-319(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200903010.htm [18] 李渭, 白薷, 李文厚. 鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区长6储层成岩作用与有利成岩相带[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012, 31(4): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201204005.htmLi W, Bai R, Li W H. Diagenesis and favorable diagenetic facies of the chang 6 reservoir in Heshui area, Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012, 31(4): 22-28(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201204005.htm [19] 石玉江, 肖亮, 毛志强, 等. 低渗透砂岩储层成岩相测井识别方法及其地质意义: 以鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区长8油层组储层为例[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(5): 820-827. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201105013.htmShi Y J, Xiao L, Mao Z Q, et al. An identification method for diagenetic facies with well logs and its geological significance in low-permeability sandstones: A case study on Chang 8 reservoirs in the Jiyuan region, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(5): 820-827(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201105013.htm [20] 张响响, 邹才能, 朱如凯, 等. 川中地区上三叠统须家河组储层成岩相[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(2): 257-264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201102011.htmZhang X X, Zou C N, Zhu R K, et al. Reservoir diagenetic facies of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the central Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(2): 257-264(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201102011.htm [21] 张海涛, 时卓, 石玉江, 等. 低渗透致密砂岩储层成岩相类型及测井识别方法: 以鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格气田下石盒子组8段为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2012, 33(2): 256-264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201202015.htmZhang H T, Shi Z, Shi Y J, et al. Diagenetic facies types and logging identification methods for low -permeability tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study on the 8th Member of Xiashihezi Formation in Sulige Gas Field, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2012, 33(2): 256-264(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201202015.htm [22] 赖锦, 王贵文, 信毅, 等. 库车坳陷巴什基奇克组致密砂岩气储层成岩相分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(7): 1019-1032. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201407009.htmLai J, Wang G W, Xin Y, et al. Diagenetic facies analysis of tight sandstone gas reservoir of Bashijiqike Formation in Kuqa Depression[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(7): 1019-1032(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201407009.htm [23] 赖锦, 王贵文, 黄龙兴, 等. 致密砂岩储集层成岩相定量划分及其测井识别方法[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(1): 128-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201501021.htmLai J, Wang G W, Huang L X, et al. Quantitative classification and logging identification method for diagenetic facies of tight sandstones[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(1): 128-138(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201501021.htm [24] 雷刚林, 谢会文, 张敬洲, 等. 库车坳陷克拉苏构造带构造特征及天然气勘探[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2007, 28(6): 816-820, 835. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200706018.htmLei G L, Xie H W, Zhang J Z, et al. Structural features and natural gas exploration in the Kelasu structural belt, Kuqa Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2007, 28(6): 816-820, 835(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200706018.htm [25] Nian T, Jiang Z X, Wang G W, et al. Characterization of braided river-delta facies in the Tarim Basin Lower Cretaceous: Application of borehole image logs with comparative outcrops and cores[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 97: 1-23. [26] 张惠良, 张荣虎, 杨海军, 等. 超深层裂缝-孔隙型致密砂岩储集层表征与评价: 以库车前陆盆地克拉苏构造带白垩系巴什基奇克组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(2): 158-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201402005.htmZhang H L, Zhang R H, Yang H J, et al. Characterization and evaluation of ultra-deep fracture-pore tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of Cretaceous Bashijiqike Formation in Kelasu tectonic zone in Kuqa foreland basin, Tarim, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(2): 158-167(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201402005.htm [27] 刘伟, 窦齐丰, 黄述旺, 等. 成岩作用的定量表征与成岩储集相研究: 以科尔沁油田交2断块区九佛堂组(J3jf)下段为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2002, 31(5): 399-403. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD200205014.htmLiu W, Dou Q F, Huang S W, et al. Quantitative characterization of diagenesis and diagenesis reservoir facies: The case study of lower member of J3jf of Jiao 2 Block in Kerqin Oilfield[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2002, 31(5): 399-403(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD200205014.htm [28] 赖锦, 王贵文, 王书南, 等. 碎屑岩储层成岩相研究现状及进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2013, 28(1): 39-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201301006.htmLai J, Wang G W, Wang S N, et al. Research status and advances in the diagenetic facies of clastic reservoirs[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2013, 28(1): 39-50(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201301006.htm [29] 付晶, 吴胜和, 付金华, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组储层定量成岩相研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(2): 86-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201302013.htmFu J, Wu S H, Fu J H, et al. Research on quantitative diagenetic facies of the Yanchang Formationin Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(2): 86-97(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201302013.htm [30] 杨宁, 王贵文, 李潮流, 等. 塔里木盆地大北地区巴什基奇克组成岩相测井识别[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 38(5): 18-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201405004.htmYang N, Wang G W, Li C L, et al. Reservoir diagenetic facies of Bashijiqike Formation in Dabei gas field compartmentalization and quantitative evaluation[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2014, 38(5): 18-24(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201405004.htm [31] 王昌勇, 王成玉, 梁晓伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区上三叠统延长组长8油层组成岩相[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(4): 596-614. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201104007.htmWang C Y, Wang C Y, Liang X W, et al. Diagenetic facies of the Chang 8 oil bearing layer of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Jiyuan area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(4): 596-614(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201104007.htm [32] 兰叶芳, 邓秀芹, 程党性, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区长6油层组砂岩成岩相及储层质量评价[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2014, 33(1): 51-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201401004.htmLan Y F, Deng X Q, Cheng D X, et al. Diagenetic facies and reservoir quality evaluation of Chang 6 sandstone reservoir in the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation of Huaqing area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2014, 33(1): 51-63(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201401004.htm [33] 白烨, 薛林福, 石玉江, 等. 测井成岩相自动识别及其在鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格地区的应用[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 37(1): 35-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201301005.htmBai Y, Xue L F, Shi Y J, et al. An automatic identification method of log diagenetic facies and its application in Sulige area, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2013, 37(1): 35-41(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201301005.htm [34] 马淼, 孙卫, 白云云, 等. 姬塬地区长6储层成岩相特征及测井响应[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(3): 177-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201803023.htmMa M, Sun W, Bai Y Y, et al. Characteristics of diagenetic facies of Chang 6 reservoir and logging response in Jiyuan area[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(3): 177-184(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201803023.htm [35] Wu D, Liu S B, Chen H D, et al. Investigation and prediction of diagenetic facies using well logs in tight gas reservoirs: Evidences from the Xu-2 member in the Xinchang structural belt of the western Sichuan Basin, Western China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 192: 107326. [36] 杨宁, 王贵文, 赖锦, 等. 岩石物理相的控制因素及其定量表征方法研究[J]. 地质论评, 2013, 59(3): 563-574. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201303019.htmYang N, Wang G W, Lai J, et al. Researches of the control factors and the quantitatively characterization method of reservoir petrophysical facies[J]. Geological Review, 2013, 59(3): 563-574(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201303019.htm [37] 曾联波, 刘国平, 朱如凯, 等. 库车前陆盆地深层致密砂岩储层构造成岩强度的定量评价方法[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(12): 1601-1609. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202012012.htmZeng L B, Liu G P, Zhu R K, et al. A quantitative evaluation method of structural diagenetic strength of deep tight sandstone reservoirs in Kuqa foreland basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(12): 1601-1609(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202012012.htm [38] Li Y, Guo S, Wang X, et al. Stratification model of an ultra-deep tight sandstone fracture reservoir under tectonic stress: A case study of a Cretaceous reservoir in the Kuqa foreland thrust belt of the Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2017, 45: 53-64. [39] 张荣虎, 曾庆鲁, 王珂, 等. 储层构造动力成岩作用理论技术新进展与超深层油气勘探地质意义[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(10): 1278-1292. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202010013.htmZhang R H, Zeng Q L, Wang K, et al. New progress in the theory and technology of tectonic diagenesis on reservoir and the geological significance of ultra-deep oil and gas exploration[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(10): 1278-1292(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202010013.htm [40] Liu G Z, Hu G C, Shi X Z, et al. Carbonate cementation patterns and digenetic reservoir facies of the Triassic Yanchang Formation deep-water sandstone in the Huangling area of the Ordos Basin, Northwest China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 203: 108608. [41] Li Y, Chang X C, Yin W, et al. Quantitative identification of diagenetic facies and controls on reservoir quality for tight sandstones[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 102: 680-694. -





 下载:
下载: