Lineament mapping and deposit prospecting in the Gouli area, East Kunlun, Qinghai Province: Using multisource remote sensing data
-
摘要:
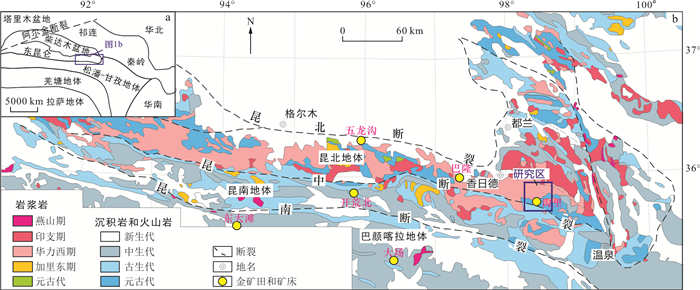
沟里地区是青海东昆仑金及多金属成矿带重要组成部分之一,矿产资源丰富,具有良好的找矿前景,目前区内尚无大面积基于多源遥感卫星数据的线性构造识别及找矿应用方面的研究。选取Landsat8 OLI、GF-2不同空间分辨率遥感数据,运用最佳波段选择、主成分分析、图像融合、线性拉伸、定向滤波等遥感图像处理技术,结合DEM衍生产品和多元地学信息综合研究方法,实现了沟里地区线性构造识别和找矿预测。结果表明:(1)研究区构造格架以卡可特尔-色日德一线为界,可分为南部、北部2个区域,北部区域线性构造以NNE向最为发育,近EW向次之,NW、NE向分布较少,南部区域受昆中断裂带控制作用,线性构造主要发育近EW向和少量NW向、NE向;(2)已知矿床(点)全部位于线性构造内及其附近,构造控矿作用明显;(3)线性构造密集分布和交汇处以及遥感影像上不同色调连接区是寻找金矿化的有利地区。最后根据多元地学信息与遥感解译构造信息综合对比分析,在研究区圈定找矿靶区4处并进行了野外验证。研究结果表明,基于多源遥感卫星数据能够较好地识别地表构造空间结构特征,结果较为客观和准确,能够为该地区和外围找矿预测提供参考和依据。
Abstract:Objective The Gouli area is one of the important gold and polymetallic belt in the East Kunlun Orogen. There is no research on lineament identification and mineral exploration based on multisource remote sensing data in the area.
Methods In this paper, various enhancement techniques were employed on Landsat 8 OLI, GF-2 and DEM data to delineate structural lineaments. Meanwhile, information on geological, mineral and geochemical anomalies was combined to define prospecting targets in the Gouli area.
Results The results show that (1) The tectonic framework of the study area can be divided into two regions by the boundary of Kaketeer-Seride. The lineament in the northern region is most developed in the NNE direction, followed by the near-EW direction, and less distributed in the NW and NE directions. The lineament in the southern region is mainly developed in the near-EW direction, and the NW to NE directions are less distributed. (2) The gold ore is controlled by lineaments. (3) The areas of densely distributed and intersected lineaments, as well as the areas connected by different colors on remote sensing images, are favorable locations for gold mineralization. Finally, based on the comprehensive analysis of multiple geological information and remote sensing interpreted tectonic information, four prospecting targets were identified in the study area and verified in the field.
Conclusion This study proves that multisource remote sensing data can better identify the spatial structure characteristics of surface tectonics, which can provide a reference and basis for prospecting new deposits in the Gouli area.
-
Key words:
- GF-2 /
- high spatial resolution /
- remote sensing /
- lineament /
- Gouli area /
- deposit prospecting
-
表 1 Landsat8 OLI和GF-2数据主要技术参数
Table 1. Main technical parameters of Landsat8 OLI and GF-2 data
卫星名称 波段号 波段名称 光谱范围/μm 空间分辨率/m Landsat8 OLI Band 1 Coastal 0.43~0.45 30 Band 2 Blue 0.45~0.52 30 Band 3 Green 0.53~0.60 30 Band 4 Red 0.63~0.68 30 Band 5 NIR 0.85~0.89 30 Band 6 SWIR 1 1.56~1.66 30 Band 7 SWIR 2 2.10~2.30 30 Band 8 Pan 0.50~0.68 15 Band 9 Cirrus 1.36~1.39 30 GF-2 — Pan 0.45~0.90 1 Band 1 Blue 0.45~0.52 4 Band 2 Green 0.52~0.59 4 Band 3 Red 0.63~0.69 4 Band 4 NIR 0.77~0.89 4 表 2 融合数据波段标准差、均值及相关系数统计
Table 2. Statistics of band standard deviation, average and correlation coefficient of fusion data
统计值 波段 Band2 Band3 Band4 Band5 Band6 Band7 标准差 441.89 621.01 755.79 928.60 1 026.76 888.55 均值 1 088.84 1 608.33 1 934.36 2 832.55 3 109.43 2 524.66 相关系数矩阵 1 0.994 213 1 0.989 288 0.997 255 1 0.881 185 0.706 360 0.692 695 1 0.925 156 0.947 292 0.942 235 0.863 996 1 0.958 154 0.974 140 0.974 103 0.736 571 0.986 125 1 表 3 融合数据多波段组合及OIF值
Table 3. Different band combinations and OIF values of the fusion data
波段组合 OIF 波段组合 OIF 754 1 070.56 654 1 084.93 753 1 008.73 653 1 023.32 752 876.99 652 897.73 表 4 融合数据主成分特征向量矩阵
Table 4. PCA eigenvectors matrix for the fusion data
特征向量 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 百分比/% PC1 -0.220 294 -0.314 994 -0.381 546 -0.466 080 -0.529 065 -0.457 747 82.70 PC2 -0.315 577 -0.358 446 -0.498 597 0.650 092 0.272 462 -0.162 707 12.58 PC3 0.278 662 0.299 848 0.223 719 0.532 057 -0.462 089 -0.534 582 3.72 PC4 -0.767 893 -0.110 960 0.593 397 0.108 054 -0.178 726 0.047 847 0.78 PC5 0.058 847 -0.073 131 -0.229 271 0.250 207 -0.632 746 0.689 675 0.21 PC6 -0.425 566 0.815 307 -0.388 700 -0.052 788 0.004 247 0.016 595 0.01 -
[1] FARUWA A R, QIAN W, AKINSUNMADE A, et al. Aeromagnetic and remote sensing characterization of structural elements influencing iron ore deposits and other mineralization in Kabba, southwestern Nigeria[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 68(8): 3302-3313. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.06.024 [2] 魏俊浩. 初论成矿场与矿产勘查意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 114-129. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0113WEI J H. Preliminary discussion on the theory of ore-forming field and its significant role for mineral exploration[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 114-129 (in Chinese with Englishabstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0113 [3] 隋志龙, 李德威, 黄春霞. 断裂构造的遥感研究方法综述[J]. 地理学与国土研究, 2002, 18(3): 34-37, 44.SUI Z L, LI D W, HUANG C X. Overview of research approach of faults based on remote sensing technology[J]. Geography and Territorial Research, 2002, 18(3): 34-37, 44. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 张宝林, 吕古贤, 余建国, 等. 内蒙古赤峰柴胡栏子金矿及周边地区构造形迹的"米字型"分布及其控矿特征[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(5): 1267-1273.ZHANG B L, LÜ G X, YU J G, et al. Double-cross-shaped distribution and ore-controlling characteristics of structural traces in Chaihulanzi gold deposit and its surrounding area at Chifeng, Northern China[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(5): 1267-1273. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] KEMGANG G F E, KANA J D, Aretouyap Z, et al. Main structural lineaments of the southern Cameroon volcanic line derived from aeromagnetic data[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2022, 186: 104418. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2021.104418 [6] TÖZÜN K A, ÖZYAVA A. Automatic detection of geological lineaments in central Turkey based on test image analysis using satellite data[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 69(9): 3283-3300. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.02.026 [7] NEDJRAOUI K, HAMOUDI M, BEN EL KHAZNADJI R, et al. Structural mapping and interpretation of lineaments related to the In Teria volcanism (southeastern Algeria) using Landsat 8 OLI TIRS images and aeromagnetic data[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2021, 184: 104348. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2021.104348 [8] 姚佛军, 焦鹏程, 赵艳军, 等. 干盐湖区隐伏控卤构造遥感识别研究: 以马海盐湖为例[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(7): 2225-2237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.07.020YAO F J, JIAO P C, ZHAO Y J, et al. Research of remote sensing recognition of concealed brine-controlling structures in dry salt lake area: A case study of Mahai salt lake[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(7): 2225-2237. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.07.020 [9] 鲁泽恩, 田玉刚, 柳庆威, 等. 基于Sentinel-1和DEM数据的南岭高植被覆盖区地形线性特征提取方法[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(4): 1349-1358.LU Z E, TIAN Y G, LIU Q W, et al. Topographical linear feature extraction method based on Sentinel-1 and DEM in areas with high vegetation coverage of Nanling[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(4): 1349-1358. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 王俊虎, 武鼎, 张杰林, 等. 基于多源遥感数据的纳米比亚欢乐谷地区千岁兰断裂带识别及新发现[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 183-190. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0630WANG J H, WU D, ZHANG J L, et al. Identification and new discovery of Qiansxuilan fault belt in Gaudeanmus area, Namibia based on the multi-source remote sensing data[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 183-190. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0630 [11] AHMADI H, PEKKAN E. Fault-based geological lineaments extraction using remote sensing and GIS: A Review[J]. Geosciences, 2021, 11(5): 183. doi: 10.3390/geosciences11050183 [12] JELLOULI A, EL HARTI A, ADIRI Z, et al. Application of optical and radar satellite images for mapping tectonic lineaments in kerdous inlier of the Anti-Atlas belt, Morocco[J]. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 2021, 22: 100509. doi: 10.1016/j.rsase.2021.100509 [13] SHEBL A, CSÁMER Á. Reappraisal of DEMs, radar and optical datasets in lineaments extraction with emphasis on the spatial context[J]. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 2021, 24: 100617. doi: 10.1016/j.rsase.2021.100617 [14] FORSON E D, MENYEH A, WEMEGAH D D. Mapping lithological units, structural lineaments and alteration zones in the southern Kibi-Winneba belt of Ghana using integrated geophysical and remote sensing datasets[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 137: 104271. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104271 [15] OYAWALE A A, ADEOTI F O, AJAYI T R, et al. Applications of remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS) in regional lineament mapping and structural analysis in Ikare area, southwestern Nigeria[J]. Journal of Geology and Mining Research, 2020, 12(1): 13-24. doi: 10.5897/JGMR2019.0310 [16] 杨宝荣, 张里斌, 马忠贤, 等. 青海沟里地区金矿床地质背景研究[J]. 矿产勘查, 2018, 9(10): 1920-1925.YANG B R, ZHANG L B, MA Z X, et al. Study on metallogenic geological background of gold deposits in Gouli area, Qinghai[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2018, 9(10): 1920-1925. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 周红智, 徐崇文, 张松涛, 等. 青海都兰沟里金矿整装勘查区1∶100 000地质矿产数据集[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(增刊1): 93-104.ZHOU H Z, XU C W, ZHANG S T, et al. The 1∶100 000 mineralogical dataset of the Gouli gold deposit integrated exploration area in Dulan County, Qinghai Province[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(S1): 93-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] LI X, FAN H, LIANG G, et al. Texture, trace elements, sulfur and He-Ar isotopes in pyrite: Implication for ore-forming processes and fluid source of the Guoluolongwa gold deposit, East Kunlun metallogenic belt[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 136: 104260. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104260 [19] LIANG G, YANG K, SUN W, et al. Multistage ore-forming processes and metal source recorded in texture and composition of pyrite from the Late Triassic Asiha gold deposit, Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, western China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2021, 220: 104920. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2021.104920 [20] ZHAO X, FU L, WEI J, et al. Generation and structural modification of the giant Kengdenongshe VMS-type Au-Ag-Pb-Zn polymetallic deposit in the East Kunlun Orogen, East Tethys: Constraints from geology, fluid inclusions, noble gas and stable isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 131: 104041. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104041 [21] 毛生录, 杨顺龙, 李善财. 青海省沟里地区金矿成矿规律及找矿方向[J]. 世界有色金属, 2020(15): 71-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2020.15.034MAO S L, YANG S L, LI S C. Metallogenic regularity and prospecting direction of gold deposits in Gouli area, Qinghai Province[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2020(15): 71-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2020.15.034 [22] 岳维好, 周家喜. 青海都兰县阿斯哈石英闪长岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄与Hf同位素特征[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(增刊1): 328-338.YUE W H, ZHOU J X. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic characteristics of the Asiha diorite in Dulan County, Qinghai Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2019, 38(S1): 328-338. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] ZHAO X, FU L, WEI J, et al. Late Permian back-arc extension of the eastern Paleo-Tethys Ocean: Evidence from the East Kunlun Orogen, northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Lithos, 2019, 340/341: 34-48. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.05.006 [24] 赵旭, 付乐兵, 魏俊浩, 等. 东昆仑按纳格角闪辉长岩体地球化学特征及其对古特提斯洋演化的制约[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(2): 354-370.ZHAO X, FU L B, WEI J H, et al. Geochemical characteristics of An'nage hornblende gabbro from East Kunlun Orogenic Belt and its constraints on evolution of Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(2): 354-370. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] CHEN J, WEI J, FU L, et al. Multiple sources of the Early Mesozoic Gouli batholith, Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, northern Tibetan Plateau: Linking continental crustal growth with oceanic subduction[J]. Lithos. 2017, 292/293: 161-178. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.09.006 [26] 陈加杰, 付乐兵, 魏俊浩, 等. 东昆仑沟里地区晚奥陶世花岗闪长岩地球化学特征及其对原特提斯洋演化的制约[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(11): 1863-1882.CHEN J J, FU L B, WEI J H, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Late Ordovician granodiorite in Gouli area, eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Qinghai Province: Implications on the evolution of Proto-Tethys Ocean[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(11): 1863-1882. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 王永锋, 孟文文. 青海瓦勒尕金矿床地质特征及找矿方法[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(7): 1559-1564.WANG Y F, MENG W W. Preliminary analysis on geological features and prospecting methods of Walega gold deposit in Qinghai[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2019, 10(7): 1559-1564. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] 杨经绥, 许志琴, 马昌前. 复合造山作用和中国中央造山带的科学问题[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(1): 1-11.YANG J S, XU Z Q, MA C Q. Compound orogeny and scientific problems concerning the Central Orogenic Belt of China[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(1): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] 黄啸坤, 魏俊浩, 李欢, 等. 东昆仑巴隆地区晚三叠世石英闪长岩成因: U-Pb年代学、地球化学及Sr-Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(6): 2037-2056.HUANG X K, WEI J H, LI H, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronological, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of Late Triassic quartz diorite in Balong region, East Kunlun Orogen[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(6): 2037-2056. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] 王艺龙, 李艳军, 魏俊浩, 等. 东昆仑五龙沟地区晚志留世A型花岗岩成因: U-Pb年代学、地球化学、Nd及Hf同位素制约[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(4): 1219-1236.WANG Y L, LI Y J, WEI J H, et al. Origin of Late Silurian A-type granite in Wulonggou area, East Kunlun Orogen: Zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry, Nd and Hf isotopic constraints[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(4): 1219-1236. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] 赵旭. 东昆仑造山带沟里地区构造岩浆转换与金成矿作用[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2020.ZHAO X. Tectono-magmatic transformation and gold mineralization in the Gouli area, the East Kunlun Orogen[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] 付乐兵, 魏俊浩, 谭俊, 等. 东昆仑沟里整装勘查区脉状金矿床多级构造控矿规律[J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(增刊1): 388-389.FU L B, WEI J H, TAN J, et al. Ore controlling regularity of multistage structure of vein gold deposit in Gouli integrated exploration area, East Kunlun Orogen[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2015, 35(S1): 388-389. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] 张景华, 欧阳渊, 张建龙, 等. 雪峰山西侧地区线性和环状构造特点及其与油气关系探讨[J]. 华北地质, 2021, 44(1): 33-38.ZHANG J H, OUYANG Y, ZHANG J L, et al. Characteristics of linear structure and ring structure and its relationship with oil and gas discuss in the western part of the Xuefeng Mountains[J]. North China Geology, 2021, 44(1): 33-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] 魏永明, 蔺启忠, 肖磉, 等. 新疆西准噶尔地区不同尺度地质构造的遥感标识特征及找矿意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(1): 76-92.WEI Y M, LIN Q Z, XIAO S, et al. Remote sensing identification of geological structures at different scales in western Junggar, Xinjiang and its prospecting significance[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2015, 39(1): 76-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] 姜放, 张国勇. 遥感图像目视解译值得注意的几个问题[J]. 长春工程学院学报(自然科学版), 2002(3): 49-50.JIANG F, ZHANG G Y. Several notable issues on visual interpretation of remote sensing image[J]. Journal of Changchun Institute of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2002(3): 49-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] 李盼盼, 陈国旭, 刘盛东, 等. 基于高分卫星影像的断层构造识别及三维地质建模应用[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 43(5): 680-687.LI P P, CHEN G X, LIU S D, et al. Identification of fault structures in GF-1 remote sensing image and its application in 3D geological modeling[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 43(5): 680-687. (in Chinese with English abstract) [37] 于洪苹, 滕正双. 基于多源遥感影像的吉林敦化塔东铁矿断裂构造解译[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2020, 35(2): 223-229.YU H P, TENG Z S. Multi-source remote sensing image-based interpretation of faults in Tadong iron mining district, Dunhua, Jilin Province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2020, 35(2): 223-229. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] ABDELOUHED F, AHMED A, ABDELLAH A, et al. Lineament mapping in the Ikniouen area (Eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco) using Landsat-8 Oli and SRTM data[J]. Remote Sensing Applications(Society and Environment), 2021, 23: 100606. doi: 10.1016/j.rsase.2021.100606 [39] INNOCENT A J, CHIDUBEM E O, CHIBUZOR N A. Analysis of aeromagnetic anomalies and structural lineaments for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration in Ikom and its environs southeastern Nigeria[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2019, 151: 274-285. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.12.011 [40] HUNG L Q, BATELAAN O, DE SMEDT F. Lineament extraction and analysis, comparison of LANDSAT ETM and ASTER imagery. Case study: Suoimuoi tropical karst catchment, Vietnam[M]. Bellingham, Wash: SPIE, 2005. [41] NOVAK I D, SOULAKELLIS N. Identifying geomorphic features using LANDSAT-5rTM data processing techniques on Lesvos, Greece[J]. Geomorphology, 2000, 34: 101-109. doi: 10.1016/S0169-555X(00)00003-9 [42] ALDHARAB H S, ALI S A, IKBAL J, et al. Spatial analysis of lineaments and their tectonic significance using landsat imagery in Alarasah area, Southeastern Central Yemen[J]. Journal of Geography, Environment and Earth Science International, 2018, 18(2): 1-13. [43] 韩乐乐, 丁伟翠, 陈宣华, 等. 西准噶尔地区多源遥感信息的线性构造提取与定量分析[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(5): 1209-1223.HAN L L, DING W C, CHEN X H, et al. Linear structure extraction and quantitative analysis of multi-source remote sensing information in West Junggar Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(5): 1209-1223. (in Chinese with English abstract) [44] BAHIRU E A, WOLDAI T. Integrated geological mapping approach and gold mineralization in Buhweju area, Uganda[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 777-793. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.09.010 [45] HAN L, LIU Z, NING Y, et al. Extraction and analysis of geological lineaments combining a DEM and remote sensing images from the northern Baoji loess area[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2018, 62(9): 2480-2493. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2018.07.030 [46] 王烜, 王海鹏, 王然, 等. 基于GF2号与Landsat8数据融合的遥感图像地质解译: 以1∶5万瓦房店市幅为例[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(4): 918-928.WANG X, WANG H P, WANG R, et al. Geological interpretation of remote sensing images based on data fusion of GF2 and landsat 8: A case study of the Wafangdian 1∶50 000 quadrangle map[J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(4): 918-928. (in Chinese with English abstract) [47] CHAVEZ P S, BERLIN G L, SOWERS L B. Statistical method for selecting Landsat MSS ratios[J]. Journal of Applied Photographic Engineering, 1982, 8(1): 23-30. [48] CIAMPALINI A, GARFAGNOLI F, ANTONIELLI B, et al. Remote sensing techniques using Landsat ETM+ applied to the detection of iron ore deposits in Western Africa[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2013, 6(11): 4529-4546. doi: 10.1007/s12517-012-0725-0 [49] 田野, 赵春晖, 季亚新. 主成分分析在高光谱遥感图像降维中的应用[J]. 哈尔滨师范大学自然科学学报, 2007, 23(5): 58-60.TIAN Y, ZHAO C H, JI Y X. The principal component analysis applied to hyperspectral remote sensing image dimensional reduction[J]. Natural Science Journal of Harbin Normal University, 2007, 23(5): 58-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) [50] 严红萍, 俞兵. 主成分分析在遥感图像处理中的应用[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2006, 20(2): 168-170.YAN H P, YU B. The principal component analysis for rs image processing[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2006, 20(2): 168-170. (in Chinese with English abstract) [51] 吴志春, 叶发旺, 郭福生, 等. 主成分分析技术在遥感蚀变信息提取中的应用研究综述[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2018, 20(11): 1644-1656.WU Z C, YE F W, GUO F S, et al. A review on application of techniques of principle component analysis on extracting alteration information of remote sensing[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2018, 20(11): 1644-1656. (in Chinese with English abstract) [52] HARALICK R M, STERNBERG S R, ZHUANG X. Image analysis using mathematical morphology[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 1987, 9(4): 532-550. [53] TOUZI R, LOPES A, BOUSQUET P. A statistical and geometrical edge detector for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1988, 26(6): 764-773. doi: 10.1109/36.7708 [54] 刘小利, 李雪, 李井冈, 等. ETM+和DEM数据在断裂解译中的应用[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2012, 32(6): 50-53.LIU X L, LI X, LI J G, et al. Application of etm+ image and dem data in fault interpretation[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2012, 32(6): 50-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) [55] SKAKNI O, HLILA R, POUR A B, et al. Integrating remote sensing, GIS and in-situ data for structural mapping over a part of the NW Rif belt, Morocco[J]. Geocarto International, 2021: 1-28. [56] 李晨伟, 张瑞丝, 张竹桐, 等. 基于多源遥感数据的构造解译与分析: 以西藏察隅吉太曲流域为例[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2018, 33(4): 657-665.LI C W, ZHANG R S, ZHANG Z T, et al. Tectonic interpretation and analysis based on Multi-source remote sensing data: A case study of JitaiRiver in Chayi, Tibet[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2018, 33(4): 657-665. (in Chinese with English abstract) [57] 陈文凯, 张景发, 姜文亮, 等. 基于TM和DEM的茅山地区断裂构造解译[C]//佚名. 地壳构造与地壳应力文集. 北京: 地震出版社, 2007: 67-75.CHEN W K, ZHANG J F, JIANG W L, et al. Active fault interpretation of Mao Mountain area based on the TM image and DEM data[C]//Anon. Bulletin of the institute of crustal dynamics. Beijing: Earthquake Press, 2007: 67-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) [58] 张欣欣. 数字高程模型在活动断层位置及地表变形变位特征提取研究中的应用[J]. 地理科学进展, 2015, 34(10): 1288-1296.ZHANG X X. DEM application in the extraction of active fault location and active fault surface deformation features[J]. Progress in Geography, 2015, 34(10): 1288-1296. (in Chinese with English abstract) [59] 徐世潮, 赵栋. 遥感图像提取断裂构造信息的方法研究进展[J]. 地下水, 2015, 37(1): 247-250.XU S C, Zhao D. Advances in methods of extracting fault structure information from remote sensing images[J]. Ground Water, 2015, 37(1): 247-250. (in Chinese with English abstract) [60] EL GHRABAWY O, SOLIMAN N, TARSHAN A. Remote sensing signature analysis of ASTER imagery for geological mapping of Gasus area, central eastern desert, Egypt[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2019, 12(13). [61] 陈加杰. 东昆仑造山带东端沟里地区构造岩浆演化与金成矿[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018.CHEN J J. Paleozoic-Mesozoic tectono-magmatic evolution and gold mineralization in Gouli area, east end of East Kunlun Orogen[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) [62] 徐俊龙, 温兴平, 余敏, 等. 基于地质统计学原理的会泽铅锌矿遥感线性构造解析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2014, 50(4): 763-771.XU J L, WEN X P, YU M, et al. An analysis of linear structures in the Huize lead-zinc mine based on remote sensing images using the principle of geostatistics[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2014, 50(4): 763-771. [63] 张旺生, 杨巍然. 北祁连山西段遥感构造定量分析与金铜矿化关系[J]. 地质科技情报, 1997, 17(增刊1): 66-68.ZHANG W S, YANG W R. Quantitative analysis of remote sensing structure and its relation to Au-Cu mineralization in the western part of North Qilian Mountains[J]. Geological Science and Technology Informatioin, 1997, 17(S1): 66-68. [64] ZHOU Y, XU D, DONG G, et al. The role of structural reactivation for gold mineralization in northeastern Hunan Province, South China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2021, 145: 104306. [65] CARLOS J, CHERNICOFF J P R E. Crustal lineament control on magmatism and mineralization in northwestern Argentina: Geological, geophysical, and remote sensing evidence[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2002, 21: 127-155. [66] 周灵洁, 张正伟, 程远, 等. 西昆仑北部地区铅锌铜矿带遥感构造蚀变信息提取与成矿预测[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2011, 35(4): 603-611.ZHOU L J, ZHANG Z W, CHENG Y, et al. The comprehensive interpretation of remote sensing information and prospecting for the Pb-Zn-Cu ore belts in the northern part of West Kunlun Orogen[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2011, 35(4): 603-611. (in Chinese with English abstract) [67] 唐洋, 付乐兵, 杨宝荣, 等. 东昆仑东段果洛龙洼脉状金矿床断裂构造控矿规律[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(2): 160-167.TANG Y, FU L B, YANG B R, et al. Ore controlling regularities of fault in the Guoluolongwa lode gold deposit, east segment of eastern Kunlun Orogen[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(2): 160-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: