Analysis of the pore structure of tight sandstone by high-pressure mercury injection combined with fractal theory: A case study of the Heshui area in the Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
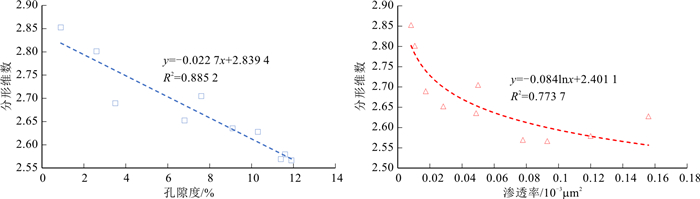
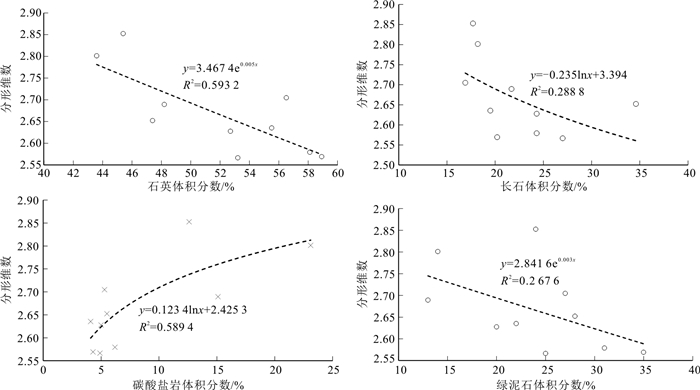
孔隙结构是致密砂岩储层的关键要素,制约油气在储层中的储集与流动,而储层孔隙结构是目前非常规油气勘探开发研究的重点和难点。选取鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区上三叠统延长组长7段10块致密岩心样品,开展高压压汞和X-衍射等实验,运用分形理论研究储层孔喉分形特征,并分析分形维数与储层物性、孔隙结构参数与矿物含量之间的关系。研究结果表明:根据压汞曲线形态和孔隙结构参数将储层分为Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ类,其储集性能和渗流能力依次递减,微观非均质性依次增强。不同类型的储层具有不同的分形特点:根据分形曲线存在的拐点0.05和0.02 μm,将实际情况和IUPAC提出的孔隙大小划分标准结合,Ⅰ类储层孔隙分为大孔(>50 nm)和中孔(50~6 nm);Ⅱ、Ⅲ类储层据拐点分为中孔A段(50~20 nm)和中孔B段(20~6 nm);平均分形维数依次增大,分别为2.619 3,2.745 4,2.852 6,非均质性逐渐增强。较少的大孔贡献了主要的渗透率,分形维数反映的主要是孔隙大小非均质性。分形维数与部分矿物存在较好的相关性,矿物成分及其含量是决定分形维数大小的内在因素,进而影响储层的质量和孔隙结构特征。
Abstract:Pore structure is the key element of tight sandstone reservoirs, which restricts the accumulate and flow of oil and gas in reservoirs. The pore structure is one of the key and difficult point of unconventional oil and gas exploration and development. In this paper, ten dense core samples from the Upper Triassic Yanchang Group 7 section in the Heshui area of the Ordos Basin are selected to carry out experiments, including high-pressure mercury pressure and X-diffraction. Fractal theory is used to analyze the characteristics of pore throats, then the relationship between fractal dimension and reservoir physical properties, pore structure and mineral content is analyzed. The results show that according to the mercury pressure curve and pore structure, the reservoir is divided into categories Ⅰ, Ⅱ and Ⅲ, its reservoir performance and seepage capacity decrease in turn, and the microheterogeneity is enhanced. Different types of reservoirs have different fractal characteristics: according to the inflection points of fractal curves 0.05 and 0.02 μm. The pore size of class Ⅰ reservoirs is divided into large pores (> 50 nm) and medium pores (50-6 nm) by combining the actual situation with the standard of pore size division proposed by IUPAC. According to the inflection point, the reservoirs of classes Ⅱ and Ⅲ can be divided into medium pores a (50-20 nm) and mesoporous B (20-6 nm). The average fractal dimension increased, which was 2.619 3, 2.745 4 and 2.852 6, respectively, and the heterogeneity gradually increased. The main permeability is contributed by fewer large pores, and the fractal dimension mainly reflects the heterogeneity of pore size. The fractal dimension is related to some minerals. Mineral composition and content are the internal factors that determine the fractal dimension and then affect the quality and pore structure of reservoirs.
-
Key words:
- high-pressure mercury injection /
- tight sandstone /
- pore structure /
- fractal dimension /
- heterogeneity
-
基于页岩储层低渗的特征[1],在页岩气生产过程中必须通过注水压裂的方式来联通储层内部的孔裂隙网络,以达到增产的目的。在漫长的地质历史时期以及页岩储层形成的过程中,水分子将在一定的温压和湿度环境下被页岩所吸附,赋存于页岩不同尺度的孔隙空间中。而注水压裂是一个持续加压的过程,高压环境会使页岩吸附水的赋存特征发生变化。此外,结合生产数据来看,重庆焦石坝地区页岩气井压裂液返排率仅为5%~10%,存留地层中的大量压裂液将影响页岩气的流动和解吸[2-4]。因此,明确高压条件对页岩吸附水赋存特征的影响对于指导该地区页岩气的实际生产具有重要意义。目前关于页岩储层水的赋存特征存在如下认识:页岩初期吸水率最快,中期吸水率减慢,最后趋于常数,在蒸馏水中吸水能力最大[5-6];水主要分布在孔裂隙中,主要为毛细水和水膜,其中黏土矿物会影响水分布,当水分子占据页岩黏土孔隙时,吸附态甲烷会减少[7-8];水在不同孔隙中的赋存状态是不同的,微孔中水的赋存由体积充填和表面吸附2种形式共同控制,而介孔中水的赋存随孔径的增大由体积充填转变为表面吸附[9];页岩孔隙和渗透压共同作用使水流动,其吸水过程可以用扩散方程来描述[10];水绝大部分以束缚水的形式存在于岩石孔隙中,少部分为具有流动性质的可动水[11-12]。
尽管前期在页岩中水赋存研究方面取得了一定的认识,但是关于涪陵焦石坝地区页岩储层在注水压裂过程中,高压条件对页岩吸附水赋存特征的影响报道较少。因此,笔者以涪陵焦石坝地区JY11-4井和JY41-5井页岩岩心为研究对象,自主设计了页岩冷冻氮吸附和核磁共振实验流程,利用常压下(相对压力低)冷冻氮吸附结果来类比原始储层状态下(或地质历史时期)吸附水的赋存特征,利用30 MPa饱和水压力下(相对压力高)的核磁共振实验结果类比注水压裂后页岩吸附水的赋存特征,开展高压条件对页岩吸附水赋存特征的影响分析,为进一步掌握页岩气生产过程中压裂液的返排规律提供理论依据。
1. 样品选取与分析方法
1.1 样品选取
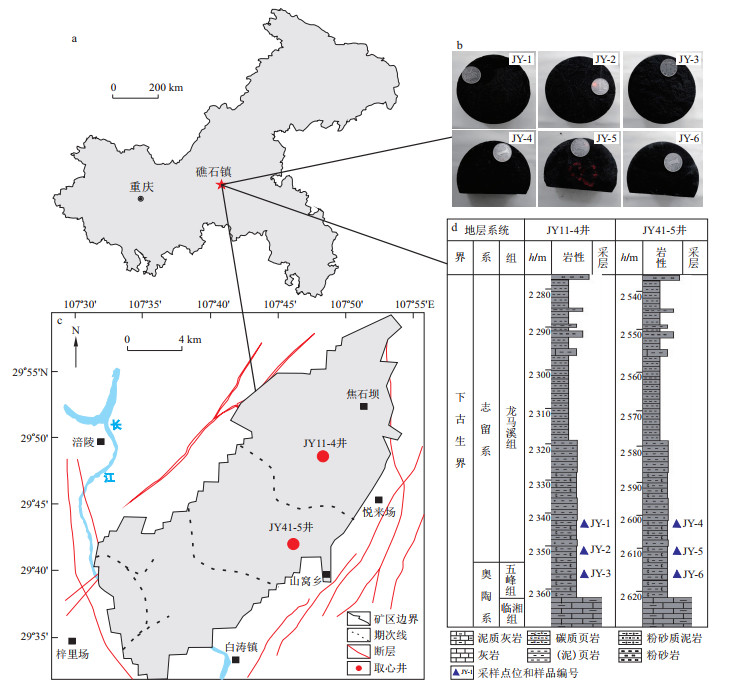
本研究从涪陵焦石坝页岩气矿区(Ⅰ期)JY11-4井和JY41-5井的钻井岩心中共采取6块页岩样品(图 1),样品选自2口钻井中的同一主力页岩气层位,同一钻井采样最大深度和最小深度的差值控制在10 m左右。此外,在实地岩心库取样时,均挑选表面均一完整、无明显裂隙的页岩岩心,最大限度地避免由于样品非均质性对实验造成的影响。实验前,对6块页岩样品依次编号为JY-1、JY-2、JY-3、JY-4、JY-5以及JY-6。
1.2 分析方法
1.2.1 冷冻氮吸附实验
(1) 实验原理
由于常规水吸附实验只能得到水的总吸附占比,无法定量得到水在页岩不同尺度孔隙中的占比。因此,自主设计了一种利用冷冻氮气吸附定量表征页岩吸附水赋存的方法,其基本原理为:当页岩粉末处于一定相对压力时,水蒸气在毛细管力的滞留作用下会进入并侵入页岩孔隙中,当水蒸气吸附达到平衡后,利用液氮将水冷冻在页岩孔隙中,并分别测试得到冷冻前后样品的氮气吸附曲线,再与原始样品对比相同孔隙直径下的体积差值,即为该孔隙直径下孔隙中水的体积,最后根据冷冻前后样品孔体积增量随孔径的变化曲线,即可计算水在不同尺度孔隙中的占比。
(2) 实验方案
冷冻氮吸附实验在中国地质大学(武汉)构造与油气资源教育部重点实验室完成,采用全自动比表面分析仪(型号Micromeritics ASAP 2020)分析测试。基于上述原理设计的实验步骤如下:①将6组页岩样品破碎至粒径为0.25 mm(60目)标准塞以下的粉末;②将样品分别放入烘箱进行烘干处理后,取出样品于全自动比表面分析仪上进行脱气处理,脱气后分别称取每组样品的质量,其中烘干温度为110℃,时间为2 h,脱气温度设置110 ℃,时间为10 h;③将烘干后的6组样品依次置于全自动比表面分析仪中进行氮气吸附测试,得到原始状态(冷冻前)下的氮气吸附曲线;④将分析后的6组样品分别倒入小玻璃皿中,再次烘干后将样品置于密闭干燥皿(近似常压)中进行水蒸气吸附,待吸附平衡后(样品质量不再发生变化),分别称量每组平行样品的平衡质量;⑤将称量完的6组样品立即置入分析用的玻璃管中,然后置于液氮中进行速冻处理,直至液氮不再沸腾时,将样品取出并置于-30 ℃环境中冷藏24 h以上,以防止冷冻后装样内部水分的流失;⑤冷藏处理结束后,取出装有6组样品的玻璃管,将样品依次置于全自动比表面分析仪中进行氮气吸附测试,得到样品冷冻后的氮气吸附曲线。需要注意的是,低压氮气吸附的准备阶段,在升降台未升起的过程中需要使用冰袋包裹玻璃管的玻璃泡防止样品内水分流失。
1.2.2 核磁共振实验
(1) 实验原理
核磁共振(NMR)岩样分析原理在于岩石流体中的自旋氢核(1H)在均匀分布的静磁场下会发生弛豫行为[13]。T2谱曲线可以反映水在岩石孔隙中的分布状态,对于同一岩样,当孔隙内完全饱和水时,孔隙直径越大,对应的T2弛豫时间越长。通过开展高压饱和水页岩岩心的核磁共振测试并获取其T2谱曲线,即可分析水在页岩孔隙中的赋存特征。
(2) 实验方案
核磁共振实验在太原理工大学煤与煤系气地质山西省重点实验室完成,分析仪器采用Macro MR12-150H-1低场核磁共振仪,测试参数如下:频率12.98 MHz,TW(等待时间):2 000 ms,NS(累加次数):64,NECH(回波个数):8 000,TE(回波时间间隔):0.200 ms。实验步骤如下:①钻取直径为25 mm、长度为50 mm的页岩岩心柱,适当清洗岩心柱表面,并将岩心柱置于105 ℃真空干燥箱中干燥至恒重,称量岩心柱干重。②将岩心柱置于样品罐中,注入质量分数为20×10-3的KCl溶液(防止饱和过程中页岩内部黏土膨胀导致样品破碎),使样品在30 MPa的压力下饱和48 h,待样品质量不再发生变化时取出,并称量湿重(由于实际注水压裂所用的压力高达100 MPa以上,现有实验条件无法达到上述真实压力,因此,在保证样品不破碎的前提下采用30 MPa压力进行类比研究)。③将30 MPa饱水岩心柱置于低场核磁共振仪中,进行核磁共振T2测试,反演获得饱和水岩样的T2谱。
2. 实验结果
2.1 常压下页岩水吸附特征
2.1.1 样品孔体积增量(率)随孔径的变化
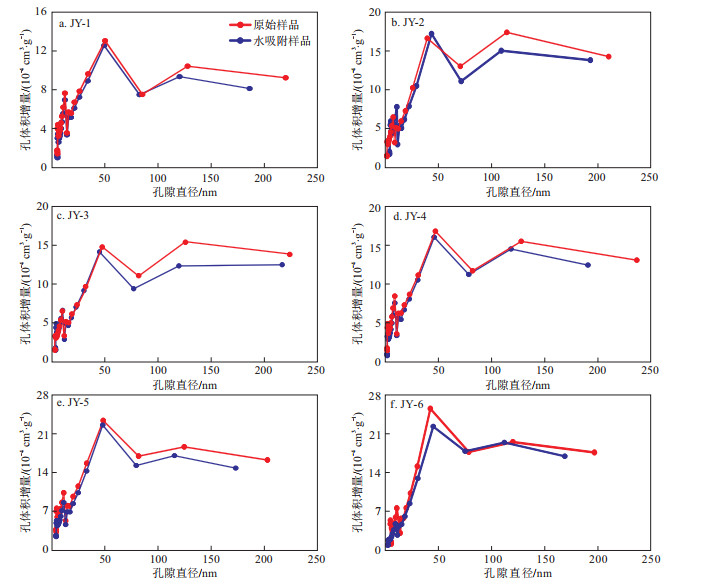
采用IUPAC孔径分类方案[14]对页岩孔隙直径进行划分:微孔([0, 2) nm)、介孔([2, 50] nm、大孔(>50 nm)。此外,由于氮气吸附实验、水吸附实验和核磁共振实验对微孔([0, 2) nm)的表征能力有限,因此在分析时将微孔和介孔([0, 50] nm)联合分析。按照实验方案对6组页岩样品依次进行冷冻氮吸附实验,得到样品的孔体积增量随孔隙直径变化曲线(图 2)。曲线整体形态表现为双峰特征,峰值分别位于[0, 50] nm孔径段和(50, 100] nm孔径段,曲线在[0, 50] nm孔径段迅速上升,在>50 nm孔径段先下降后趋于平稳。此外,从曲线可以看出,6组样品在冷冻前后曲线形态未发生明显改变,仅表现为同一孔径下的孔体积增量降低,这是由于在水吸附过程中,水分子进入页岩内部占据了孔隙空间,使得相同条件下页岩孔隙对N2分子的吸附空间减少。
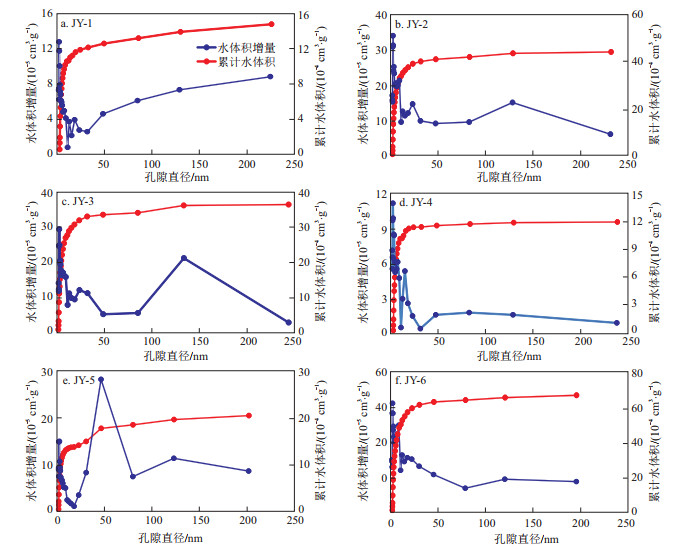
2.1.2 样品水分布曲线
样品冷冻前后孔体积在同一孔隙直径下存在差异,该差值的物理意义即表现为该孔隙直径下水分子占据的体积。因此,分别将6组原始页岩样品与冷冻吸附后的平行样品对应的孔隙体积进行做差处理,得到样品中水体积增量随孔隙直径变化曲线,再对水体积增量进行求和,得到样品的累计水体积随孔隙直径变化曲线(图 3)。曲线显示,样品JY-4和JY-6的水体积增量随着页岩孔隙直径的增大呈现一直降低的趋势,表现为单峰特征,峰值位于孔隙直径1.98 nm处。其余4组样品曲线呈现双峰特征,其峰值对应的孔隙直径存在一定差异,样品JY-1的水体积增量随着页岩孔隙直径的增大呈现先降低后升高的趋势,峰值对应的孔隙直径分别位于1.98,217.00 nm处;样品JY-2和JY-3的水体积增量随着页岩孔隙直径的增大呈现先降低后升高,最后再降低的趋势,峰值对应的孔隙直径位于1.98,122.12 nm处;样品JY-5的水体积增量随着页岩孔隙直径的增大呈现先降低后升高,最后再降低的趋势,峰值对应的孔隙直径位于1.98,47.00 nm处,上述差异的产生可能与样品内部孔隙结构有关。但是,6组样品的累计水体积随孔隙直径的变化特征均表现为:当孔隙直径位于[0, 50] nm时,累计水体积随着孔隙直径的增大急速上升;当孔隙直径>50 nm时,累计水体积随着孔隙直径的增大上升缓慢,最终趋于稳定,这说明水分子大量吸附于孔隙直径[0, 50] nm的孔隙之中,具体解释见后面第3节。
2.1.3 样品冷冻氮吸附结果参数
根据样品水分布曲线,得到样品的水分布参数(表 1)。由表 1可知,原始样品BET比表面积为14.689 6~20.960 1 m2/g,平均值17.119 5 m2/g;BJH总孔体积为0.017 6~0.023 4 cm3/g,平均值0.020 2 cm3/g。冷冻(水)吸附后,由“称重法”计算得到的样品单位质量吸附水体积为0.015 9~0.018 6 mL/g,平均值0.017 3 mL/g;BJH总孔体积为0.013 4~0.021 9 cm3/g,平均值0.016 9 cm3/g。根据冷冻前后BJH孔体积差值计算得到的样品单位质量吸附水体积为0.001 3~0.006 8 mL/g,平均值0.003 5 mL/g。计算得到的不同孔径范围内赋存的水体积参数如下:赋存于孔隙直径为[0, 50] nm孔喉中水体积占比为85.42%~94.26%,平均占比90.94%;单位质量水体积为0.001 2~0.006 4 mL/g,平均值0.003 2 mL/g。赋存在孔隙直径>50 nm中孔喉的水体积占比为5.74%~14.58%,平均占比9.06%;单位质量水体积为0.000 1~0.000 4 mL/g,平均值0.000 3 mL/g。
表 1 样品冷冻氮吸附结果参数Table 1. Results of sample frozen nitrogen adsorption样品号 原始样品 冷冻吸附样品 BET比表面积/(m2·g-1) BJH总孔体积/(cm3·g-1) 干燥质量/mg 平衡质量/mg 单位质量吸附水体积/(mL·g-1) BJH总孔体积/(cm3·g-1) 根据BJH差值计算得到的单位质量吸附水体积/(mL·g-1) 不同孔径范围内水体积占比/% 不同孔径范围内赋存的单位质量水体积/(mL·g-1) [0, 50] nm >50 nm [0, 50] nm >50 nm JY-1 20.960 1 0.023 4 2.571 7 2.619 5 0.018 6 0.021 9 0.002 5 85.42 14.58 0.002 1 0.000 4 JY-2 17.171 8 0.018 5 2.326 0 2.368 6 0.018 3 0.014 0 0.004 5 93.11 6.89 0.004 2 0.000 3 JY-3 14.817 5 0.017 6 2.378 6 2.420 9 0.017 8 0.013 9 0.003 7 92.16 7.84 0.003 4 0.000 3 JY-4 14.689 6 0.019 8 2.361 3 2.399 8 0.016 3 0.018 5 0.001 3 93.08 6.92 0.001 2 0.000 1 JY-5 19.027 4 0.021 5 2.338 2 2.378 2 0.017 1 0.019 4 0.002 2 87.62 12.38 0.001 9 0.000 3 JY-6 16.050 3 0.020 2 2.347 8 2.385 1 0.015 9 0.013 4 0.006 8 94.26 5.74 0.006 4 0.000 4 注:测试单位为中国地质大学(武汉)构造与油气资源教育部重点实验室 2.2 高压条件下页岩吸附水的赋存特征
研究表明[15]:水力压裂后页岩的吸水由两部分控制,一部分为裂缝中保留的流体,在裂缝中以流动水的形式存在;另一部分为页岩基质吸收的流体,这些流体维持于页岩基质孔隙之中,包括毛细管力束缚水和表面力束缚水等。此外,姚艳斌等[16]将孔裂隙分为3类(吸附孔:0.1 ms≤T2≤10 ms;渗流孔:10 ms<T2≤100 ms;裂隙:T2>100 ms)。本研究重点是为了分析高压条件下页岩基质孔隙所吸附的水赋存特征变化,即T2≤10 ms段孔隙内部的水赋存特征,而T2>10 ms段的孔隙为渗流孔和裂隙,非本研究的重点。为此,在数据处理过程中,特将核磁共振实验中T2>10 ms(折算后的孔隙直径>470 nm)的数据进行剔除。
此外,在地层孔隙条件下,忽略流体扩散弛豫的影响,核磁共振实验中横向弛豫时间与岩石孔隙直径大小成正比关系[17],李军等[18]通过实验手段近似得到了四川盆地涪陵地区志留系龙马溪组页岩岩心T2与孔径大小定量关系,即:
Rc=47T2, (1) 式中:Rc为孔隙直径,nm;T2为核磁共振横向弛豫时间,ms。
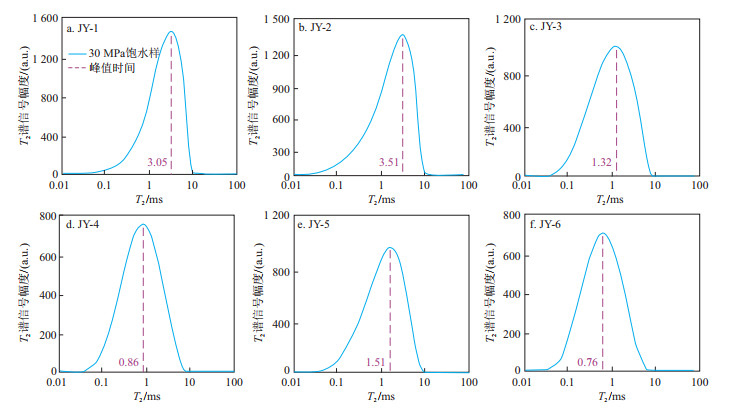
根据上述原理,得到了30 MPa饱和水压力下的样品核磁共振T2谱(图 4)。样品T2谱显示,6组样品的NMR曲线均变现为单峰特征(吸附峰),峰值时间分别为:3.05,3.51,1.32,0.86,1.51,0.76 ms,平均值1.84 ms。再根据式(1)将页岩核磁共振实验中T2与孔隙直径进行换算后,得到了6个页岩样品中吸附水的赋存参数(表 2)。结果表明:高压条件下,样品核磁孔隙度为2.89%~7.29%,平均值4.90%;不同样品吸附的水体积为1.26~1.96 mL,平均吸附的水体积为1.56 mL;单位质量吸附的水体积为0.018 5~0.026 9 mL/g,平均值0.021 6 mL/g。计算得到的不同孔径范围内赋存的水体积参数如下:赋存于孔隙直径为[0, 50]nm孔喉中水体积占比为35.42%~43.15%,平均占比40.26%;单位质量水体积为0.007 9~0.009 5 mL/g,平均值0.008 6 mL/g。赋存在孔隙直径>50 nm孔喉中的水体积占比为56.75%~64.58%,平均占比59.74%;单位质量水体积为0.010 6~0.017 4 mL/g,平均值0.013 1 mL/g。
表 2 样品吸附水赋存参数Table 2. Occurrence parameters of sample adsorbed water样品号 核磁孔隙度/% 干燥质量/g 饱水质量/g 进入样品的水体积/mL 单位质量吸附的水体积/(mL·g-1) 不同孔径范围内赋存的水体积占比/% 不同孔径范围内赋存的单位质量水体积/(mL·g-1) [0, 50] nm >50 nm [0, 50] nm >50 nm JY-1 6.46 60.52 62.19 1.67 0.022 8 39.42 60.58 0.009 0 0.013 8 JY-2 7.29 60.03 61.99 1.96 0.026 9 35.42 64.58 0.009 5 0.017 4 JY-3 5.61 62.33 63.98 1.65 0.021 9 40.66 59.34 0.008 9 0.013 0 JY-4 3.07 65.61 67.12 1.51 0.020 1 40.02 59.98 0.008 0 0.012 1 JY-5 4.09 62.05 63.31 1.26 0.018 5 42.86 57.14 0.007 9 0.010 6 JY-6 2.89 66.12 67.44 1.32 0.019 6 43.15 56.75 0.008 4 0.011 2 注:测试单位为太原理工大学煤与煤系气地质山西省重点实验室;表中“单位质量吸附的水体积”和“不同孔径范围内赋存的水体积占比”采用剔除T2>10 ms段后的数据计算所得 3. 讨论
3.1 高压条件对页岩吸附水赋存特征的影响
为了进一步明确高压条件对页岩吸附水赋存特征的影响,将文中2.1节和2.2节中的结果进行联合分析。冷冻氮吸附实验结果显示,通过样品冷冻前后BJH总孔体积差值计算得到的单位质量吸附水体积(平均值0.003 5 mL/g)明显低于直接采用“称重法”得到的单位质量吸附水体积(平均值0.017 3 mL/g),一种可能的解释为:页岩在水蒸气吸附初期是以表面吸附为主,水分子通过氢键力、范德华力等被吸附在页岩表面上,随着表面吸附点位被逐渐占据后,水分子需要通过内扩散作用进入到孔隙内表面的吸附点位上,开始进行第二阶段的孔隙吸附[19],而实验测得的是孔隙吸附过程中的水分子,因此导致了上述结果(该结果并不影响水体积占比分析)。此外,从不同孔径范围内赋存的水体积参数来看:在实验提供的湿度条件下,绝大部分水分子赋存于微孔和介孔中(孔隙直径为[0, 50]nm),平均占比达90.94%,而赋存于大孔(孔隙直径>50 nm段)中的水分子较少,平均占比仅为9.06%。一般认为,毛细凝聚机制在一定程度上主导着水蒸气的吸附行为,水分子随着孔隙直径的增大而逐渐凝聚充填于孔隙内部的储集空间[20]。相对于大孔而言,微孔和介孔喉道有着更大的毛细管力,这就使得水分子优先吸附进入微孔和介孔之中;当微孔和介孔内表面吸附完成后,水分子在氢键的作用下进入到大孔内壁之中,形成“凝聚态”水膜。然而,由于实验过程中相对压力较小(近似常压),使得水分子无法占据页岩所有孔隙中的吸附位点,这可能导致了水分子大部分凝聚在微孔和介孔中,只有较少的水分子进入大孔之中。此外,也有研究表明[21],富黏土页岩在水吸附过程中,随着相对压力的增大,尺度较小的孔隙会完全被水分子“充填堵塞”,这也可能是微孔和介孔中水体积平均占比明显高于大孔中的原因之一。
30 MPa饱和水压力下的核磁共振实验表明,样品单位质量吸附的水体积为0.018 5~0.026 9 mL/g,平均值为0.021 6 mL/g(该结果是在剔除进入页岩渗流孔和裂隙段的水体积后,利用原始“称重法”结果换算所得),比水蒸气吸附实验中得到的结果(平均值为0.017 3 mL/g)高约25%。计算得到的不同孔径范围内赋存的水体积参数中,赋存于孔隙直径为[0, 50]nm孔喉中水体积平均占比为40.26%,赋存在孔隙直径>50 nm孔喉中的水体积平均占比为59.74%,这说明在高压条件下,赋存在大孔中的水体积要多于赋存在微孔和介孔中的水总体积。对此,也可以利用上文提到的毛细凝聚机制来近似解释:随着相对压力的增大,水分子随着孔隙直径的增大而逐渐凝聚充填于孔隙内部的储集空间中。在这一过程中,高压条件(相对压力高)使得水分子占据微孔和介孔内表面的吸附位点后,仍能被吸附进入大孔中,占据更多大孔内表面的吸附位点,这就导致了赋存在大孔中的水多于赋存在微孔和介孔中的水。此外,由于该实验在水中加入了防膨剂,因此不考虑较小的孔隙会完全被水分子“充填堵塞”的情况。
综上所述,相比于常压条件下的水吸附结果,高压条件会使得水分子在占据微孔和介孔内表面的吸附位点后,仍能在毛细管力的作用下被吸附进入大孔中,占据更多大孔内表面的吸附位点,最终使得页岩单位质量吸附的水体积增加(实验中增加约25%)、大孔中的水体积占比高于微孔和介孔中的水体积总占比。
3.2 关于压裂液返排率低的一种可能性解释
一般认为,产气量高的页岩气藏含水饱和度通常较低,结合水体积分数通常为60%~80%,即页岩储层处于一种“非饱和状态”[15]。根据气-水毛细管理论,超低的含水饱和度使页岩“超干”,形成了毛细管力的潜在趋势,当“高压”压裂液进入页岩储层后,首先会满足页岩孔隙内表面液体的吸附,降低毛细管势能,使得页岩气藏具有较强的水吸附能力[15]。而实际压裂过程的注水压力达100 MPa以上,使得页岩在水吸附过程中的相对压力极高,压裂液可能在毛细管力的作用下进入在之前原始储层压力下未能进入的大孔中来“缓解”原始页岩储层的“非饱和状态”,近似达到一种饱和状态。当压裂作业完成后,储层周围压力逐渐被释放,相对压力逐渐降低,之前在高压条件进入到页岩吸附孔隙中的水可能难以克服其孔喉处的毛管阻力(压裂液返排和吸附是逆过程),造成压裂液滞留在页岩储层之中,从而降低储层中压裂液的返排率。
4. 结论
(1) 常压条件下,由“称重法”计算得到的样品单位质量吸附水体积为0.015 9~0.018 6 mL/g,平均值0.017 3 mL/g;根据冷冻前后BJH孔体积差值计算得到的样品单位质量吸附水体积为0.001 3~0.006 8 mL/g,平均值0.003 5 mL/g。赋存于微孔和介孔中的水体积总占比(平均占比90.94%)明显高于赋存在大孔中的水体积占比(平均占比9.06%),这可能与水吸附过程中相对压力较小,水分子无法占据页岩所有孔隙中的吸附位点,大部分水分子凝聚在微孔和介孔中,只有较少的水分子进入大孔之中有关。此外,富黏土页岩在水吸附过程中,尺度较小的孔隙会完全被水分子“充填堵塞”也可能是其中一个原因。
(2) 30 MPa饱和水压力条件下,由“称重法”计算得到的样品单位质量吸附的水体积为0.018 5~0.026 9 mL/g,平均值为0.021 6 mL/g。赋存于微孔和介孔中水体积总占比(平均占比40.26%)低于赋存在大孔中的水体积占比(平均占比59.74%),这可能与相对压力较高时,水分子在毛细管力的作用下占据微孔和介孔内表面的吸附位点后仍能被吸附进入大孔中,占据更多大孔内表面的吸附位点有关。
(3) 相比于常压,高压条件会使得页岩单位质量吸附的水体积增加(实验中增加约25%),大孔中的水体积占比高于微孔和介孔中的水体积总占比。
(4) 压裂液进入页岩储层后,储层相对压力显著升高,压裂液可能会在毛细管力的作用下进入在之前原始储层压力下未能进入的大孔隙中来“缓解”原始页岩储层的“非饱和状态”。当压裂作业完成后,储层周围压力逐渐被释放,原先在高压条件下进入到页岩吸附孔隙中的水分子可能难以克服其孔喉处的毛管阻力(压裂液返排和吸附是逆过程),导致压裂液滞留在页岩储层之中而难以返排。
-
表 1 岩样基本物性参数
Table 1. Basic physical parameters of rock samples
岩样编号 深度/m 直径/m 长度/cm 岩样密度/(g·cm-3) 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 L23_1 1 645.40 2.515 2.320 2.380 10.30 0.156 L23_2 1 672.03 2.508 2.346 2.460 7.60 0.055 L205_1 1 636.90 2.524 2.304 2.420 9.10 0.049 L205_2 1 645.20 2.525 2.317 2.340 11.90 0.093 N181_1 1 613.60 2.525 2.270 2.570 3.50 0.017 N181_2 1 659.66 2.520 2.415 2.590 2.60 0.011 Z143_1 1 842.67 2.525 2.320 2.480 6.80 0.028 Z143_2 1 835.57 2.520 2.339 2.340 11.60 0.119 Z225_1 1 772.90 2.525 2.320 2.350 11.40 0.078 Z225_2 1 775.04 2.525 2.323 2.650 0.90 0.008 表 2 研究区砂岩储层岩石学特征
Table 2. Petrological characteristics of sandstone reservoirs in the study area
岩样编号 石英 钾长石 斜长石 方解石 白云石 黏土矿物 黏土矿物相对含量/% wB/% 伊利石 绿泥石 伊蒙混层 L23_1 52.7 8.1 16.2 2.4 2.6 18.0 38.0 20.0 42.0 L23_2 56.5 2.9 14.0 2.8 2.5 20.7 33.0 27.0 40.0 L205_1 55.5 4.9 14.6 1.2 2.9 18.6 34.0 22.0 44.0 L205_2 53.2 13.4 13.6 1.4 3.5 10.9 44.0 25.0 31.0 N181_1 48.2 6.0 15.7 11.6 3.5 15.0 32.0 13.0 55.0 N181_2 43.6 6.4 11.8 14.4 8.7 12.1 45.0 14.0 41.0 Z143_1 47.4 6.3 28.3 1.6 3.9 11.9 48.0 28.0 24.0 Z143_2 58.1 14.5 9.8 3.7 2.5 10.7 38.0 31.0 31.0 Z225_1 58.9 6.0 14.2 2.6 1.7 16.2 38.0 35.0 27.0 Z225_2 45.4 4.1 13.6 2.7 9.9 23.5 37.0 24.0 39.0 平均值 52.0 7.3 15.2 4.4 4.2 15.8 38.7 23.9 37.4 表 3 鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区孔隙结构特征参数
Table 3. Characteristic parameters of pore structure in the Heshui area of the Ordos Basin
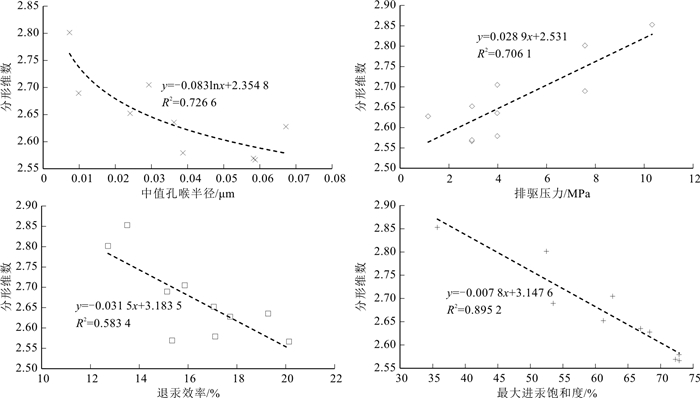
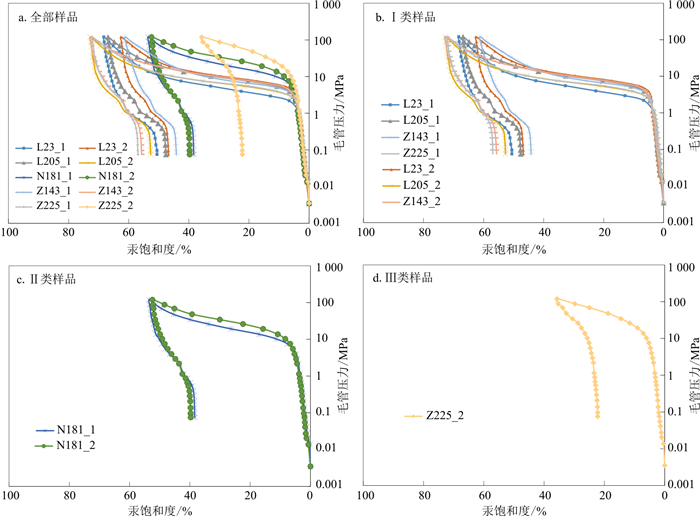
岩样编号 分类 中值孔隙半径/μm 最大进汞饱和度/% 排驱压力/MPa 分选系数 歪度 L23_1 Ⅰ 0.067 68.302 1.148 1.563 0.280 L23_2 Ⅰ 0.029 62.615 3.983 1.494 0.102 L205_1 Ⅰ 0.036 66.904 3.977 1.837 0.038 L205_2 Ⅰ 0.059 72.844 2.939 1.319 0.324 Z143_1 Ⅰ 0.010 61.204 2.947 2.361 0.032 Z143_2 Ⅰ 0.007 72.820 3.979 1.556 0.053 Z225_1 Ⅰ 0.024 72.267 2.943 2.604 0.140 均值 0.045 68.137 3.131 1.819 0.078 N181_1 Ⅱ 0.010 53.509 7.573 3.269 0.612 N181_2 Ⅱ 0.007 52.459 7.571 2.369 0.402 均值 0.009 52.984 7.572 2.819 0.507 Z225_2 Ⅲ / 35.717 10.323 2.463 0.551 表 4 Ⅰ类样品分形维数计算结果
Table 4. Fractal dimension of class Ⅰ samples
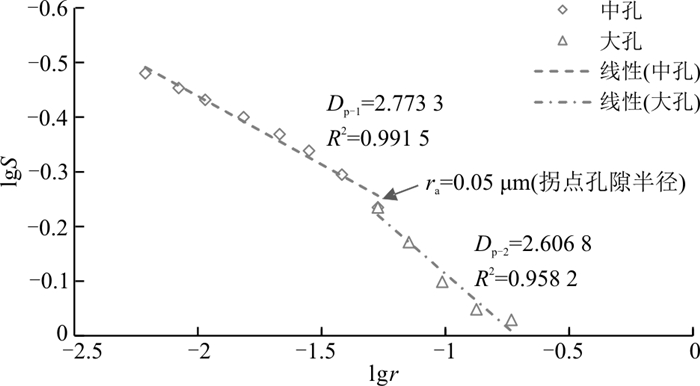
样品编号 大孔 中孔 Dp ra/μm Dp-1 Ф1/% K1/10-3μm2 R2 Dp-2 Ф2/% K2/10-3μm2 R2 L23_1 2.598 7 9.01 0.156 0.993 7 2.830 8 1.29 0.000 08 0.999 6 2.627 7 0.05 L23_2 2.687 5 6.29 0.050 0.919 9 2.787 6 1.31 0.000 25 0.974 8 2.704 8 0.05 L205_1 2.606 8 7.53 0.049 0.958 2 2.773 3 1.57 0.000 22 0.991 5 2.635 4 0.05 L205_2 2.534 6 10.31 0.093 0.979 3 2.772 6 1.59 0.000 18 0.994 3 2.566 5 0.05 Z143_1 2.614 5 5.51 0.028 0.986 6 2.814 2 1.29 0.000 10 0.999 6 2.652 2 0.05 Z143_2 2.533 6 9.28 0.119 0.973 0 2.761 6 2.32 0.000 74 0.999 6 2.579 2 0.05 Z225_1 2.533 6 9.62 0.078 0.973 0 2.761 6 1.78 0.000 19 0.996 0 2.569 2 0.05 平均值 2.587 0 8.22 0.082 0.969 1 2.786 0 1.59 0.000 25 0.993 6 2.619 3 0.05 注:Dp为样品的平均分形维数;Dp-1为大孔段的分形维数;Dp-2为中孔段的分形维数;Φ1为大孔的孔隙占比;Φ2为中孔的孔隙占比;K1为大孔的渗透率贡献值;K2为中孔的渗透率贡献值;ra为拐点孔隙半径 表 5 Ⅱ类分形维数计算结果
Table 5. Calculation results of class Ⅱ fractal dimension
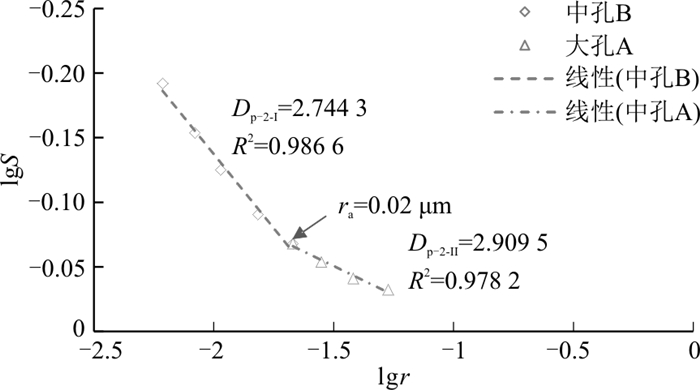
样品编号 中孔A段(50~20 nm) 中孔B段(20~6 nm) Dp ra/μm Dp-2-Ⅰ Φ3/% K3/10-3μm2 R2 Dp-2-Ⅱ Φ4/% K4/10-3μm2 R2 N181_1 2.670 5 1.72 0.002 0.991 8 2.826 0 0.24 0.000 03 0.979 7 2.689 4 0.02 N181_2 2.822 5 1.58 0.002 0.958 1 2.697 5 0.32 0.000 05 0.987 7 2.801 3 0.02 均值 2.746 5 1.65 0.002 0.974 9 2.761 8 0.28 0.000 04 0.983 7 2.745 4 0.02 注:Dp-2-Ⅰ为中孔A段的分形维数;Dp-2-Ⅱ为中孔B段的分形维数;Φ3为中孔A段的孔隙占比;Φ4为中孔B段的孔隙占比。K3为中孔A段的渗透率贡献值;K4为中孔B段的渗透率贡献值 表 6 Ⅲ类分形维数计算结果
Table 6. Calculation results of class Ⅲ fractal dimension
样品编号 中孔A段(50~20 nm) 中孔B段(20~6 nm) Dp ra/μm Dp-2-Ⅰ Φ3/% K3/10-3μm2 R2 Dp-2-Ⅱ Φ4/% K4/10-3μm2 R2 Z225_2 2.9095 0.46 0.001 0.9813 2.7443 0.24 0.00010 0.9866 2.8526 0.02 表 7 孔隙度频率分布与渗透率贡献率
Table 7. Porosity frequency distribution and permeability contribution rate
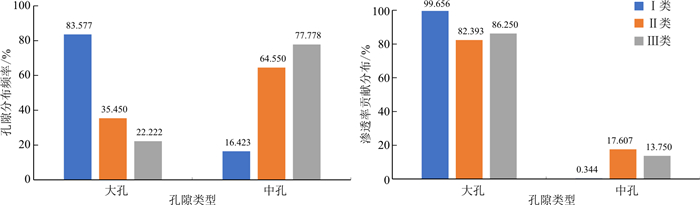
样品编号 分类 大孔(>50 nm) 中孔(50~6 nm) 孔隙频率分布/% 渗透率贡献率/% 孔隙频率分布/% 渗透率贡献率/% L23_1 Ⅰ 87.476 99.949 12.524 0.051 L23_2 Ⅰ 82.763 99.502 17.237 0.498 L205_1 Ⅰ 82.747 99.553 17.253 0.447 L205_2 Ⅰ 86.639 99.807 13.361 0.193 Z143_1 Ⅰ 81.029 99.644 18.971 0.356 Z143_2 Ⅰ 80.000 99.382 20.000 0.618 Z225_1 Ⅰ 84.386 99.757 15.614 0.243 均值 83.577 99.656 16.423 0.344 N181_1 Ⅱ 44.100 86.121 55.900 13.879 N181_2 Ⅱ 26.800 78.665 73.200 21.335 均值 35.450 82.393 64.550 17.607 Z225_2 Ⅲ 22.222 86.250 77.778 13.750 -
[1] 付金华, 郭正权, 邓秀芹. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南地区上三叠统延长组沉积相及石油地质意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2005, 7(1): 34-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2005.01.004Fu J H, Guo Z Q, Deng X Q. Sedimentary facies and petroleum geological significance of Yanchang Formation of Upper Triassic in southwest Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Paleogeography, 2005, 7(1): 34-44(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2005.01.004 [2] 杨华, 李士祥, 刘显阳. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密油、页岩油特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201301000.htmYang H, Li S X, Liu X Y. Characteristics and resource prospects of tight oil and shale oil in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(1): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201301000.htm [3] 邹才能, 赵政璋, 杨华, 等. 陆相湖盆深水砂质碎屑流成因机制与分布特征: 以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(6): 1065-1075. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200906007.htmZou C N, Zhao Z Z, Yang H, et al. Genetic mechanism and distribution of sandy debris flows in terrestrial lacustrine basin: Taking Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(6): 1065-1075(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200906007.htm [4] 白斌, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 非常规油气致密储层微观孔喉结构表征新技术及意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2014, 19(3): 78-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2014.03.010Bai B, Zhu R K, Wu S T, et al. New micro-throat structural characterization techniques for unconventional tight hydrocarbon reservoir[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2014, 19(3): 78-86(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2014.03.010 [5] 周江羽, 袁艳斌, 李星. 地学分形研究中值得注意的几个问题[J]. 地质科技情报, 1999, 18(2): 93-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.1999.02.023Zhou J Y, Yuan Y B, Li X. Some noticeable problems in the study of geoscience fractal[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1999, 18(2): 93-96 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.1999.02.023 [6] 何琰, 吴念胜. 确定孔隙结构分形维数的新方法[J]. 石油实验地质, 1999, 21(4): 372-375. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.1999.04.018He Y, Wu N S. A new method for determining the fractal dimension of pore structure[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 1999, 21(4): 372-375(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.1999.04.018 [7] 杨海, 孙卫, 明红霞, 等. 分形几何在致密砂岩储层微观孔隙结构研究中的应用: 以苏里格气田东南部上石盒子组盒8段为例[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2015, 29(6): 103-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201506028.htmYang H, Sun W, Ming H X, et al. Application of fractal geometry in the study of micro pore structure of tight sandstone reservoir: Taking He8 member of upper Shihezi Formation in the southeast of Sulige gas field as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2015, 29(6): 103-107(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201506028.htm [8] 王瑞飞, 陈明强, 孙卫. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组超低渗透砂岩储层微观孔隙结构特征研究[J]. 地质论评, 2008, 54(2): 270-277. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.02.015Wang R F, Chen M Q, Sun W. The research of micro-pore structure in super-low permeability sandstone reservior of the Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2008, 54(2): 270-277(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.02.015 [9] 尹志军, 盛国君, 王春光. 基于压汞法的煤岩各段孔隙的分形特征[J]. 金属矿山, 2011(9): 54-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201109018.htmYin Z J, Sheng G J, Wang C G. Fractal dimension of varied pore within coal based Mercury intrusion method[J]. Metal Mines, 2011(9): 54-57(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201109018.htm [10] 杨峰, 宁正福, 孔德涛, 等. 高压压汞法和氮气吸附法分析页岩孔隙结构[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(3): 450-455. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201303002.htmYang F, Ning Z F, Kong D T, et al. Analysis of shale pore structure by high pressure mercury injection method and nitrogen adsorption method[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(3): 450-455(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201303002.htm [11] 刘凯, 石万忠, 王任, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区盒1段致密砂岩孔隙结构分形特征及其与储层物性的关系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 57-68. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0102Liu K, Shi W Z, Wang R, et al. Pore structure fractal characteristics and its relationship with resevior properties of the first member of lower Shihezi Formation tight sandstone in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 57-68(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0102 [12] Sing K S W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity(Recommendations 1984)[M]. [S. l. ]: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 1990. [13] 杨胜来. 油层物理学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004.Yang S L. Reservoir physics[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004(in Chinese). [14] 王伟, 宋渊娟, 黄静, 等. 利用高压压汞实验研究致密砂岩孔喉结构分形特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 22-30. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0402Wang W, Song Y J, Huang J, et al. Fractal characteristics of pore-throat structurein tight sandstone using high-pressure mercury intrusion pososimetry[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 22-30(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0402 [15] Haber J. Manual on catalyst characterization(Recommendations 1991)[J]. Pure & Applied Chemistry, 1991, 63(9): 1227-1246. [16] Mandelbrot B B. On the geometry of homogeneous turbulence, with stress on the fractal dimension of the iso-surfaces of scalars[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1975, 72(3): 401. [17] 王欣, 齐梅, 胡永乐, 等. 高压压汞法结合分形理论分析页岩孔隙结构[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2015, 34(2): 165-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201502033.htmWang X, Qi M, Hu Y L, et al. Analysis of shale pore structure by high pressure mercury injection combined with fractal theory[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2015, 34(2): 165-169(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201502033.htm [18] 张全培, 吴文瑞, 刘丽萍, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地镇北地区延长组超低渗透储层孔隙结构及其分形特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(3): 20-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202003004.htmZhang Q P, Wu W R, Liu L P, et al. Pore structure and fractal characteristics of ultra-low permeability reservoir of Yanchang Formation inZhenbei area of Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(3): 20-31(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202003004.htm [19] 吴浩, 刘锐娥, 纪友亮, 等. 致密气储层孔喉分形特征及其与渗流的关系: 以鄂尔多斯盆地下石盒子组盒8段为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(1): 151-162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201701015.htmWu H, Liu R E, Ji Y L, et al. Pore throat fractal characteristics of tight gas reservoir and its relationship with seepage: Taking He 8 member of Lower Shihezi Formation in Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(1): 151-162(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201701015.htm [20] 曾联波, 高春宇, 漆家福, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区特低渗透砂岩储层裂缝分布规律及其渗流作用[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2008, 38(增1): 41-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2008S1005.htmZeng L B, Gao C Y, Qi J F, et al. Fracture distribution law and seepage effect of ultra-low permeability sandstone reservoir in Longdong area of Ordos Basin[J]. Chinese Science : Geoscience, 2008, 38(S1): 41-47(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2008S1005.htm [21] Zhang Z, Weller A. Fractal dimension of pore-space geometry of an Eocene sandstone formation[J]. Geophysics, 2014, 79(6): D377-D387. [22] Lai J, Wang G, Wang Z, et al. A review on pore structure characterization in tight sandstones[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 177: 436-457. [23] 黄金亮, 董大忠, 李建忠, 等. 陆相页岩储层孔隙分形特征: 以四川盆地三叠系须家河组为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(9): 1611-1618. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201609007.htmHuang J L, Dong D Z, Li J Z, et al. Reservoir fractal characteristics of continentalshale: An example from Triassic Xujiahe Formation shale, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(9): 1611-1618(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201609007.htm [24] 贺伟钟, 孚勋, 贺承祖, 等. 储层岩石孔隙的分形结构研究和应用[J]. 天然气工业, 2000, 20(2): 67-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200002024.htmHe W Z, Fu X, He C Z, et al. Research and application of fractal structure of reservoir rock pores[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2000, 20(2): 67-70(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200002024.htm [25] 纪发华, 张一伟. 分形几何学在储层非均质性描述中的应用[J]. 石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 1994, 18(5): 161-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX405.030.htmJi F H, Zhang Y W. Application offractal geometry in reservoir heterogeneity description[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum : Natural Science Edition, 1994, 18(5): 161-168 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX405.030.htm [26] 马新仿, 张士诚, 郎兆新. 储层岩石孔隙结构的分形研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2003, 12(9): 46-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA200309013.htmMa X F, Zhang S C, Lang Z X. Fractal research on pore structure in reservoir rock[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2003, 12(9): 46-48(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA200309013.htm [27] 赵会涛, 郭英海, 杜小伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地高桥地区本溪组砂岩储层微观孔隙多重分形特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 175-184. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0614Zhao H T, Guo Y H, Du X W, et al. Micro-pore multifractal characteristics of Benxi Formation sandstone reservoir in Gaoqiao area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 175-184(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0614 [28] Rouquerol J, Avnir D, Fairbridge C W, et al. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1994, 66(8): 1739-1758. [29] 王域辉. 分形在石油勘探开发中的应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 1993, 12(1): 101-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ199301023.htmWang Y H. Application of fractal in petroleum exploration and development[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1993, 12(1): 101-104 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ199301023.htm -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载: