Evolution of land subsidence and comparative study on multi-source monitoring methods in New Airlines City of Beijing
-
摘要:
为查明北京新航城地区地面沉降演化规律,结合基岩标-分层标和水准测量对新航城地区地面沉降特征进行了分析,并结合不同监测方法进行了对比研究评价。研究发现:①近十年新航城地区浅部地层中沉降量和沉降比例越来越小,沉降比例由2009年67.62%下降到2019年19.69%,而中部地层和深部地层则随着时间沉降量和沉降比例越来越大,中部地层沉降比例由2009年21.39%增加到2019年35.83%,深部地层沉降比例则由2009年10.99%增加到2019年44.48%;浅部地层含水层水位呈现周期性往复变化,中部和深部地层含水层在周期性变化中持续下降,地层在水位周期性往复变化中持续压缩。②根据历年水准测量和地下水动态监测成果,研究区自北向南累计沉降量逐渐减小。地面沉降和地下水位数据拟合后发现二者具有一定的相关性,相关性随着水位降幅的增大,相关性也随之增大,二者成正相关。③基岩标—分层标静力水准测量系统与人工水准测量系统对同一监测点和不同深度数据互校后的误差值非常接近,符合正态分布规律,不同深度的监测数据相关系数为0.993 6;对比2种方法各有优势与不足,应根据实际情况,多方面获取沉降信息与数据,满足地区级地面沉降监测与防治的不同需求。
Abstract:To reveal the evolution law of land subsidence in the New Airlines City of Beijing, the characteristics of land subsidence in this area are analyzed by combining bedrock standard-layered standard and leveling survey, and the comparative study and evaluation are carried out with different monitoring methods. The results show that: ①In recent ten years, the amount and proportion of subsidence in the shallow stratum of the Xinhangcheng area are smaller and smaller, the proportion of subsidence decreased from 67.62% in 2009 to 19.69% in 2019, while the amount and proportion of subsidence in the middle stratum and deep stratum are increasing with time, the proportion of middle stratum subsidence increased from 21.39% in 2009 to 35.83% in 2019, and the proportion of deep stratum subsidence increased from 10.99% in 2009 to 44.48% in 2019;the water level of the shallow aquifer changes periodically, while that of the middle stratum and deep aquifer decreases continuously, the strata continue to compress in the periodic change of water level. ②According to the results of the level survey and groundwater dynamic monitoring over the years, the accumulated settlement from north to south in the research area gradually decreases. After fitting the data of land subsidence and groundwater level, it is found that there is a certain correlation between them, the correlation increases with the increase of water level drop, and there is a positive correlation between them. ③The error value of the static leveling system of bedrock standard layered standard and artificial leveling system after mutual correction of the same monitoring point and different depth data is very close, which conforms to the normal distribution law, and the correlation coefficient of monitoring data of different depth is 0.993 6; comparing the two methods has advantages and disadvantages, it is suggested to obtain the settlement information and data in many aspects based on the actual situation, to meet the regional requirements different demands of the monitoring and prevention of the grade land subsidence.
-
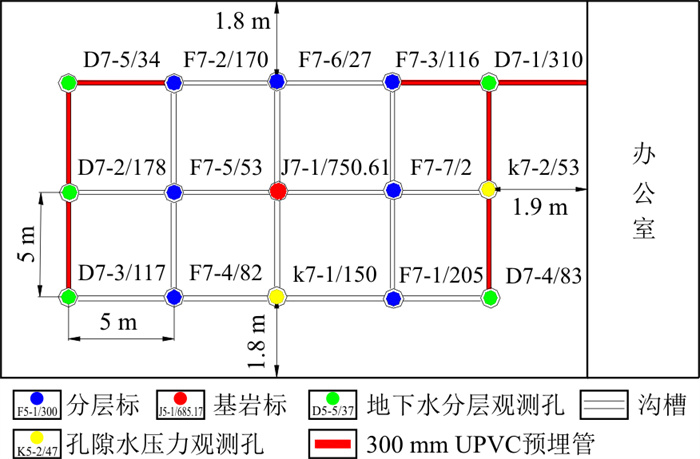
表 1 榆垡地层贡献量表
Table 1. Summary of the Yufa stratigraphic contribution
地层时代 底界埋深/m 沉降比例/% 全新世、晚更新世 46 27.24 中更新世 120 18.35 早更新世 343 54.41 表 2 针对同一监测点采用不同监测方法与一等水准测量互校后的差值
Table 2. List of differences after mutual calibration of different monitoring methods and leveling for the same monitoring point
监测方法对比 2种监测方法互校后的差值/mm 基岩标-分层标与一等水准测量对比 2.830 0.763 0.612 0.619 1.314 0.437 7.265 -0.654 -4.547 -0.682 -0.753 -0.381 1.507 0.144 2.283 0.792 5.821 14.743 2.992 1.192 3.361 表 3 榆垡站各监测层位(2019年)水准测量与分层标测量值
Table 3. Leveling and layer mark measurements of each monitoring horizon (2019) at Yufa station
分层标编号 F7-2 F7-3 F7-4 F7-5 F7-6 F3-7 水准测量/mm -5.090 -8.790 -5.650 -2.715 -3.435 -2.595 分层标测量/mm -4.235 -8.479 -4.912 -2.154 -3.508 -1.696 差值 -0.855 -0.311 -0.738 -0.561 0.073 -0.899 表 4 2种监测方法优缺点对比
Table 4. Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of each monitoring method
监测技术 优势 不足 水准测量 仪器简捷、方法可靠、精度准确 时间长、不能实时监测、占用劳动力 基岩标- 分层标监测 监测准确、实时、分层监测等 费用高、需占地,无法大面积推广 -
[1] 刘明坤, 贾三满, 褚宏亮. 北京市地面沉降监测系统及技术方法[J]. 地质与资源, 2012, 21(2): 244-249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2012.02.012Liu M K, Jia S M, Chu H L. Land subsidence monitoring system and technical method in Beijing[J]. Geology and Resources, 2012, 21(2): 244-249(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2012.02.012 [2] 雷坤超, 马凤山, 罗勇, 等. 北京平原区地面沉降水准监测网参考基准稳定性研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(5): 1757-1769. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201905008.htmLei K C, Ma F S, Luo Y, et al. Study on stability of reference datum of land subsidence leveling monitoring network in Beijing Plain[J]. Advances in Geophysics, 2019, 34(5): 1757-1769(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201905008.htm [3] 雷坤超, 罗勇, 陈蓓蓓, 等. 北京平原区地面沉降分布特征及影响因素[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(6): 2216-2228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201606029.htmLei K C, Luo Y, Chen B B, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of land subsidence in Beijing Plain[J]. Chinese Geology, 2016, 43(6): 2216-2228(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201606029.htm [4] 成建梅, 柳璨, 李敏敏, 等. 城市化进程下北京平原渗流场与地面沉降发展演化模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 43-52. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0105Cheng J M, Liu C, Li M M, et al. Simulation of development and evolution of seepage field and land subsidence in Beijing Plain under the process of urbanization[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 43-52(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0105 [5] 田芳, 罗勇, 周毅, 等. 北京地面沉降与地下水开采时空演变对比[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2017, 15(2): 163-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201702025.htmTian F, Luo Y, Zhou Y, et al. Comparison of temporal and spatial evolution between land subsidence and groundwater exploitation in Beijing[J]. South to North Water Transfer and Water Conservancy Technology, 2017, 15(2): 163-169(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201702025.htm [6] 杨艳, 王荣, 罗勇. 北京典型地面沉降区土体压缩特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(3): 716-722. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.03.023Yang Y, Wang R, Luo Y, et al. Study on soil compression characteristics in typical land subsidence area of Beijing[J]. Modern Geology, 2016, 30(3): 716-722(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.03.023 [7] 于海若, 宫辉力, 陈蓓蓓, 等. 京津冀地区地面沉降研究进展与思考[J]. 测绘科学, 2020, 45(4): 125-133, 141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHKD202004019.htmYu H R, Gong H L, Chen B B, et al. Research progress and thinking on land subsidence in Beijing Tianjin Hebei region[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2020, 45(4): 125-133, 141(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHKD202004019.htm [8] 刘立, 李长安, 高俊华, 等. 基于北斗与InSAR的地质灾害监测关键问题探讨[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6): 141-149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906017.htmLiu L, Li C A, Gao J H, et al. Discussion on key problems of geological disaster monitoring based on Beidou and InSAR[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 141-149(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906017.htm [9] 周春梅, 王勇, 程月. 武汉地区盾构穿过粉细砂层时地表沉降规律分析及施工参数优化[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(5): 222-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201805031.htmZhou C M, Wang Y, Cheng Y, et al. Analysis of ground settlement law and optimization of construction parameters when shield passes through silty fine sand layer in Wuhan[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(5): 222-228(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201805031.htm [10] 贾三满, 王海刚, 赵守生, 等. 北京地面沉降机理研究初探[J]. 城市地质, 2007, 2(1): 20-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDZ200701005.htmJia S M, Wang H G, Zhao S H, et al. Preliminary study on the mechanism of land subsidence in Beijing[J]. Urban Geology, 2007, 2(1): 20-27(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDZ200701005.htm [11] 刘予, 叶超, 贾三满. 北京市平原地面沉降区含水岩组和可压缩层划分[J]. 城市地质, 2007, 2(1): 10-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDZ200701003.htmLiu Y, Ye C, Jia S M, et al. Division of water bearing rock formation and compressible layer in plain land subsidence area of Beijing[J]. Urban Geology, 2007, 2(1): 10-15(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDZ200701003.htm [12] 张云, 薛禹群, 叶淑君, 等. 地下水位变化模式下含水砂层变形特征及上海地面沉降特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2006, 17(3): 103-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200603026.htmZhang Y, Xue Y Q, Ye S J, et al. Analysis of deformation characteristics of water bearing sand layer and land subsidence characteristics in Shanghai under groundwater level change mode[J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazards and Prevention, 2006, 17(3): 103-108(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200603026.htm [13] 施小清, 薛禹群, 吴吉春, 等. 常州地区含水层系统土层压缩变形特征研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2006(3): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200603000.htmShi X Q, Xue Y Q, Wu J C H, et al. Study on soil layer compression deformation characteristics of aquifer system in Changzhou area[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2006(3): 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200603000.htm [14] 魏子新. 上海市第四承压含水层应力-应变分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2002(5): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200201000.htmWei Z X. Stress-strain analysis of the fourth confined aquifer in Shanghai[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2002(5): 1-4(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200201000.htm [15] 贺国平, 周东, 杨忠山, 等. 北京市平原区地下水资源开采现状及评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2005(2): 45-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200502009.htmHe G P, Zhou D, Yang Z S, et al. Exploitation status and evaluation of groundwater resources in plain area of Beijing[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2005(2): 45-48(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200502009.htm [16] 杨艳, 贾三满, 王海刚. 北京平原区地面沉降现状及发展趋势分析[J]. 上海地质, 2010, 30(4): 23-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD201004007.htmYang Y, Jia S M, Wang H G. Analysis on present situation and development trend of land subsidence in Beijing Plain[J]. Shanghai Geology, 2010, 30(4): 23-28(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD201004007.htm [17] 薛禹群, 张云, 叶淑君, 等. 我国地面沉降若干问题研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2006, 12(2): 153-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200602000.htmXue Y Q, Zhang Y, Ye S J, et al. Study on some problems of land subsidence in China[J]. Journal of Geology of Colleges and Universities, 2006, 12(2): 153-160(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200602000.htm -





 下载:
下载: