A study of petrophysical properties based on digital core technology: A case study of a porous carbonate reservoir in the overseas J Oilfield
-
摘要:
走向海外是解决我国能源安全问题的必由之路。但海外油气藏评价往往缺乏第一手岩心资料, 使得储层孔隙结构和渗流规律认识不清, 影响评价效果。以海外J油田孔隙型碳酸盐岩油藏为例, 应用数字岩心技术开展油气藏孔渗特征研究。①以不同流动单元的铸体薄片图像作为输入数据, 经过中值滤波和阈值分割预处理后, 基于马尔科夫链蒙特卡洛数值重构算法构建数字岩心; ②分析孔喉分布、孔喉连通性、孔隙度特征; ③基于格子玻尔兹曼模拟方法开展单相和油水两相流动模拟, 计算数字岩心的绝对渗透率和相对渗透率曲线。结果表明, 构建的三维数字岩心能够刻画不同流动单元孔隙型碳酸盐岩的孔喉半径分布及孔喉连通程度的差异化特征。数字岩心孔隙度与铸体薄片孔隙度吻合度高, 数字岩心渗透率与真实岩心渗透率存在较好的正相关关系, 且符合真实岩心所属的流动单元。油水两相稳态流动模拟计算的相对渗透率曲线体现了不同流动单元的两相渗流能力差异, 可作为数值模拟输入条件, 以及估算油藏采收率。数字岩心分析与物理实验结果吻合良好, 证明了该方法的可靠性。为岩心资料稀缺条件下油气藏表征和渗流特征分析提供新的思路, 对油气藏精细描述具有重要的参考价值。
Abstract:Developing overseas petroleum exploration and production businesses is a necessary way to guarantee the energy security in China. However, in evaluating overseas reservoirs or designing development plans, due to lack of the first-hand data, the pore structures and seepage mechanisms cannot be well understood and the evaluation effects are influenced. In this study, with the porous carbonate reservoir of the overseas J Oilfield as a case study, the digital core technology is proposed to analyze the pore structure and seepage mechanism. ①With the thin section images of different flow units as the input data, after preprocessing of the medium filtering and threshold segmentation, the digital cores are reconstructed based on the Markov Chain Monte Carlo numerical reconstruction algorithm. ②The bore throat distribution, pore throat connectivity and porosity of the digital cores are analyzed. ③The lattice Boltzmann method is adopted to perform a single phase and two phase oil-water flow simulation in the digital cores, and the absolute permeability and relative permeability curves are calculated based on the simulation results. The reconstructed three-dimensional digital core can describe the differential characteristics of the pore throat radius distribution and pore throat connectivity of porous carbonate rocks in different flow units. The digital core porosity is highly consistent with the porosity of thin section images, and the digital core permeability shows a good positive correlation with the core permeability, thus conforming to the flow unit of the real core. The relative permeability curves of oil-water two-phase flow simulation show differences in the two-phase seepage capacity of different flow units, which can be used as the input of numerical simulation and the estimation of reservoir recovery. The results of digital core analysis are consistent with the results of physical experiments, thus verifying the reliability of the digital core analysis technique. This study provides a new strategy for reservoir evaluation and seepage study in case of data insufficiency and is valuable for reservoir description and effective development.
-
Key words:
- porous carbonate reservoir /
- digital core /
- pore structure /
- rock physics
-
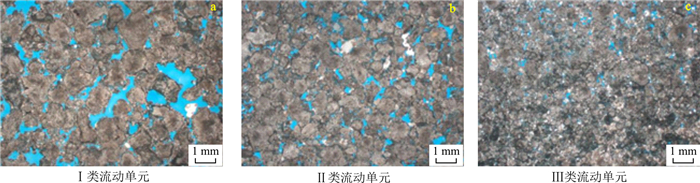
表 1 铸体薄片的基本参数
Table 1. Fundamental parameters of selected thin section images
序号 深度/m 流动单元 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 水平像素数 垂直像素数 图像分辨率/mm 1 5 126 Ⅰ 16.7 432 868 650 0.025 2 5 230 Ⅰ 17.7 830 994 745 0.011 3 5 310 Ⅰ 25.1 3 620 870 652 0.025 4 5 311 Ⅰ 10.9 2 440 1 123 838 0.019 5 5 409 Ⅰ 21.5 3 330 850 636 0.025 6 5 132 Ⅱ 19.1 85.5 868 650 0.013 7 5 162 Ⅱ 14.1 19.0 868 650 0.025 8 5 164 Ⅱ 14.8 32.9 868 650 0.013 9 5 309 Ⅱ 23.4 852 870 652 0.025 10 5 322 Ⅱ 21.3 572 990 739 0.006 11 5 351 Ⅱ 21.8 917 870 652 0.025 12 5 360 Ⅱ 26.4 260 870 652 0.025 13 5 363 Ⅱ 20.2 360 870 652 0.025 14 5 285 Ⅲ 13.3 4.53 850 636 0.025 15 5 306 Ⅲ 14.1 5.35 870 652 0.013 16 5 316 Ⅲ 14.8 2.09 941 702 0.006 -
[1] 王志刚, 蒋庆哲, 董秀成, 等. 中国油气产业发展分析与展望报告蓝皮书(2019-2020)[M]. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 2020.Wang Z G, Jiang Q Z, Dong X C, et al. Blue book of China's oil and gas industry development analysis and prospect report (2019-2020)[M]. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 2020 (in Chinese). [2] Blunt M J, Bijeljic B, Dong H, et al. Pore-scale imaging and modelling[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2013, 51: 197-216. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.03.003 [3] Andhumoudine A B, Nie X, Zhou Q, et al. Investigation of coal elastic properties based on digital core technology and finite element method[J]. Advances in Geo-energy Research, 2021, 5(1): 53-63. doi: 10.46690/ager.2021.01.06 [4] Ambrose R J, Hartman R C, Diaz Campos M, et al. New pore-scale considerations for shale gas in place calculations[C]//Anon. SPE unconventional gas conference, :, 2010. [5] Wildenschild D, Sheppard A P. X-ray imaging and analysis techniques for quantifying pore-scale structure and processes in subsurface porous medium systems[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2013, 51: 217-246. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.07.018 [6] 苏娜, 段永刚, 于春生. 微CT扫描重建低渗气藏微观孔隙结构: 以新场气田上沙溪庙组储层为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(5): 792-796. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201105024.htmSu N, Duan Y G, Yu C S. Reconstruction of microscopic pore structure in low permeability gas reservoir by micro-CT scanning: An example from the Upper Shaximiao Formation in Xinchang Gas Field[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2011, 32(5): 792-796(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201105024.htm [7] 陈浩, 黄继新, 聂志泉, 等. 基于全岩心CT的遗迹化石定量表征新方法: 以加拿大麦凯Ⅲ油砂区块为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 252-259. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0419Chen H, Huang J X, Nie Z Q, et al. Quantitaive characterization of ichnology based on CT scan: A case study of Mackay-III oil sands, Canada[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 252-259(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0419 [8] Liu X, Sun J, Wang H. Reconstruction of 3-D digital cores using a hybrid method[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2009, 6(2): 105-112. doi: 10.1007/s11770-009-0017-y [9] Wang M, Wang J, Pan N, et al. Mesoscopic predictions of the effective thermal conductivity for microscale random porous media[J]. Physical Review E, 2007, 75(3): 036702. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.75.036702 [10] Wu K, Nunan N, Crawford J W, et al. An efficient Markov chain model for the simulation of heterogeneous soil structure[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2004, 68(2): 346-351. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2004.3460 [11] Bryant S, Cade C, Mellor D. Permeability prediction from geologic models[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1993, 77(8): 1338-1350. [12] Dong H, Blunt M J. Pore-network extraction from micro-computerized-tomography images[J]. Physical Review E, 2009, 80(3): 036307. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.80.036307 [13] 朱可丹, 张友, 林彤, 等. 基于CT成像的白云岩储层孔喉非均质性分析: 以塔东古城地区奥陶系GC601井鹰三段为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(4): 862-873. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004019.htmZhu K D, Zhang Y, Lin T, et al. Pore-throat heterogeneity in dolomite reservoirs based on CT imaging: A case study of the 3rd Member of the Ordovician Yingshan Formation in Well GC601 in Gucheng area, eastern Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(4): 862-873(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004019.htm [14] Chen S, Doolen G D. Lattice Boltzmann method for fluid flows[J]. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech., 1998, 30(1): 329-364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fluid.30.1.329 [15] Chen L, Kang Q, Mu Y, et al. A critical review of the pseudopotential multiphase lattice Boltzmann model: Methods and applications[J]. International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 2014, 76(6): 210-236. [16] 吴胜和, 蔡正旗, 施尚明. 油矿地质学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011.Wu S H, Cai Z Q, Shi S M. Oilfield geology[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011(in Chinese). [17] 廉培庆, 高文彬, 汤翔, 等. 基于CT扫描图像的碳酸盐岩油藏孔隙分类方法[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(4): 852-861. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004018.htmLian P Q, Gao W B, Tang X, et al. Workflow for pore-type classification of carbonate reservoirs based on CT scanned images[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(4): 852-861(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004018.htm [18] Sahiner B, Pezeshk A, Hadjiiski L M, et al. Deep learning in medical imaging and radiation therapy[J]. Medical Physics, 2019, 46(1): 1-36. doi: 10.1002/mp.13201 [19] Zhao T, Zhao H, Ning Z, et al. Permeability prediction of numerical reconstructed multiscale tight porous media using the representative elementary volume scale lattice Boltzmann method[J]. International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 2018, 118: 368-377. [20] Otsu N. A Threshold selection method from gray-level histograms[J]. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern, 1979, 9(1): 62-66. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076 [21] Schneider C A, Rasband W S, Eliceiri K W. NIH image to image J: 25 years of image analysis[J]. Nature Methods, 2012, 9(7): 671-675. [22] Wu K, Van Dijke M I, Couples G D, et al. 3D stochastic modelling of heterogeneous porous media: Applications to reservoir rocks[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2006, 65(3): 443-467. [23] Chen L, Zhang L, Kang Q, et al. Nanoscale simulation of shale transport properties using the lattice Boltzmann method: Permeability and diffusivity[J]. Sci. Rep., 2015, 5: 8089. [24] 郭照立, 郑楚光. 格子Boltzmann方法的原理及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.Guo Z L, Zheng C G. Theory and applications of lattice Boltzmann method[M]. Beijing: China Science Press, 2009: (in Chinese). [25] 赵华伟. 致密油储层微观孔隙结构及渗流规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2017.Zhao H W. Study on micro scale pore structure and flow mechanism of tight oil sandstones[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2017 (in Chinese with English abstract). [26] 汪新光, 张冲, 张辉, 等. 基于微观孔隙结构的低渗透砂岩储层分类评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 93-103. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0429Wang X G, Zhang C, Zhang H, et al. Classification and evaluation of low-permeability sand reservoir based on micro-pore structure[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 93-103 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0429 [27] 赵日新, 卢双舫, 薛海涛, 等. 扫描电镜分析参数对定量评价页岩微观孔隙的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(5): 1141-1154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201905019.htmZhao R X, Lu S F, Xue H T, et al. Effect of SEM parameters on quantitative evaluation of shale micropores[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(5): 1141-1154(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201905019.htm [28] 刘彦锋, 张文彪, 段太忠, 等. 深度学习油气藏地质建模研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 235-241. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0417Liu Y F, Zhang W B, Duan T Z, et al. Progress of deep learning in oil and gas geological modeling[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 235-241 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0417 -





 下载:
下载: