Remote sensing interpretation and analysis of key engineering geological problems in the Nalati Mountain crossing section of the Yining-Aksu Railway
-
摘要:
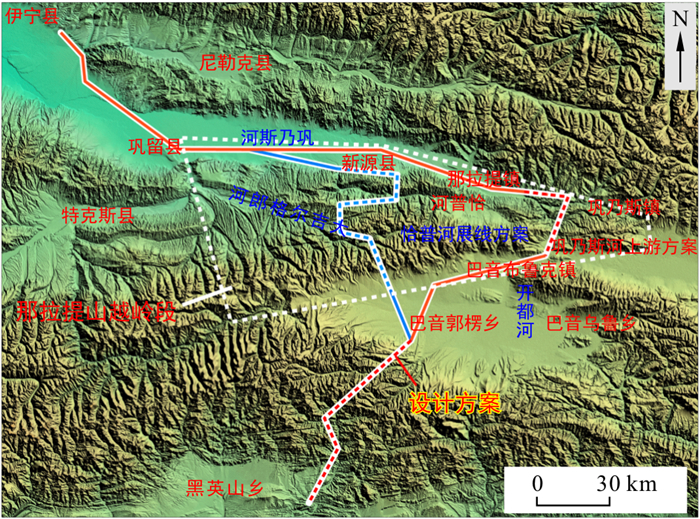
伊宁至阿克苏铁路由北至南需2次翻越天山, 北侧那拉提山越岭段自然气候恶劣、地质环境复杂, 线路方案的设计、选择明显受地质条件的约束, 前期选线勘测需要彻底摸清区内各类地质问题。在分析区域地质构造背景的基础上, 采用高分二号、Landsat8卫星影像和航空高分辨率影像等多源数据, 对区内存在的恰普河中游及巩乃斯镇东滑坡群、近EW-NEE向地震活动断裂带、巩乃斯河上游危岩落石区等关键地质问题开展了详细的解译分析, 结合现场调查, 对其发育位置、规模、形态、稳定性等进行了评价, 为外业工程地质勘察、线路方案比选提供了可靠的基础资料, 充分发挥了遥感技术在复杂山区铁路勘察中的指导作用。
Abstract:The Yining-Aksu Railway needs to cross the Tianshan Mountains twice from north to south. The natural climate and geological environment are harsh and complex at the crossing section of Nalati Mountain on the north side. The design and selection of the route scheme are obviously constrained by geological conditions, and the preliminary route selection survey requires to thoroughly determine all kinds of geological problems in the area. In this study, multisource data(e.g., Gaofen-2 images, Landsat 8 satellite images, and aerial high-resolution images) were used to perform detailed interpretation and analysis of the Nalati mountain crossing section, showing that there are densely developed landslide deformation areas along both banks of the Qiapu River, and the landslide groups on the left bank of the Qiapu River significantly impact the route scheme. The EW-NEE trending seismic-active fault zones in the area are mainly developed in the Meso-Cenozoic soft strata, with the southern margin of the Nalati fault and the Qiapu River fault as the typical ones, all of which have the phenomenon of local 're-movement'; the rockfall hazard regions in the upper reaches of the Gongnai River is mainly distributed in the intersection area of Highway G217 and G218 and its east areas, mainly in the sunny slope area.The results provide reliable basic data for field engineering geological surveys and route scheme comparisons, verifying the guiding function of the remote sensing in railway surveys in complex mountainous areas.
-
Key words:
- remote sensing /
- Yining-Aksu Railway /
- landslide /
- active fault /
- unstable rock
-
表 1 遥感数据一览
Table 1. Summary of remote sensing data
类型 分辨率/m 时相 获取方式及特征 用途 GF-2 1.0 2019/08-2020/06 覆盖全、时相多、性价比高,影像纹理清晰、色彩较单一 地层岩性、断裂构造等解译识别 OLI 15.0 2020/08 存储量多,免费获取,影像色彩丰富、分辨率中等 ALOS PALSAR 12.5 2010/06 DEM数据覆盖全、免费获取 制作地貌图、坡度图,快速识别大范围区域内危岩落石区,效果较好 高空航摄数据 0.1~0.2 2021/02-05 载人固定翼平台(PC-6)搭载DMCII-230数码航摄仪,航高4~6 km高空获取 制作三维真实感大场景立体影像模型,对于滑坡、泥石流、危岩落石等解译分析效果好 低空航摄数据 3~5 cm 2021/05-08 大疆Mavic 2、经纬M300无人机,航高100~300 m获取 对于地表宏观观测、精细化边界解译圈定效果好 -
[1] 孟祥连, 周福军. 真实感场景遥感技术在铁路工程勘察中的应用[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2017, 52(5): 949-955. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.05.015Meng X L, Zhou F J. Application of railway engineering survey based on remote sensing technology for realistic scenes[J], Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(5): 949-955(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.05.015 [2] 卓宝熙. 航测遥感技术在铁路勘测设计中的作用[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2006(增刊1): 9-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC2006S1002.htmZhuo B X. The role of aerial surveying and remote sensing technology in railway survey and design[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2006(S1): 9-14(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC2006S1002.htm [3] 刘桂卫, 李国和, 陈则连, 等. 多源遥感技术在艰险山区铁路地质勘察中应用[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2019, 36(8): 4-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2019.08.002Liu G W, Li G H, Chen Z L, et al. Application of remote sensing technology for geological investigation in mountain railways[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2019, 36(8): 4-8(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2019.08.002 [4] 任晓春, 李伟, 王玮. 高分光学遥感影像在铁路勘察中的应用及展望[J]. 测绘通报, 2019(5): 44-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHTB201905010.htmRen X C, Li W, Wang W. Application and prospect of high-resolution optical remote sensing image in railway survey and design[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2019(5): 44-47(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHTB201905010.htm [5] 黄艺丹, 姚令侃, 谭礼, 等. 喜马拉雅造山带工程效应及中尼铁路工程地质分区[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(2): 421-430. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-513Huang Y D, Yao L K, Tan L, et al. Engineering effect of the Himalayan orogen and engineering geological zoning of China-Nepal Railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(2): 421-430(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-513 [6] 仝德富, 谭飞, 苏爱军, 等. 基于多源数据的谭家湾滑坡变形机制及稳定性评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 162-170. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0432Tong D F, Tan F, Su A J, et al. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of Tanjiawan landslide based on multi-source data[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 162-170(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0432 [7] 王俊虎, 武鼎, 张杰林, 等. 基于多源遥感数据的纳米比亚欢乐谷地区千岁兰断裂带识别及新发现[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 183-190. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0630Wang J H, Wu D, Zhang J L, et al. Identification and new discovery of Qiansuilan fault belt in Gaudeanmus area, Namibia based on the multi-source remote sensing data[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 183-190(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0630 [8] 谢猛. 综合勘察方法在蒙华铁路石膏矿采空区选线勘察中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2021, 32(1): 58-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202101008.htmXie M. Application of comprehensive survey methods in the gypsum mine goaf for Mengxi-Huazhong Railway route selection[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(1): 58-64(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202101008.htm [9] 刘桂卫, 陈则连, 储文静, 等. 包银铁路断裂构造遥感勘察与地质选线[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2018, 35(8): 11-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC201808003.htmLiu G W, Chen Z L, Chun W J, et al. Remote sensing interpretation on the fault structure and geological route selection of Baotou-Yinchuan Railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2018, 35(8): 11-15(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC201808003.htm [10] 张占忠. 铁路大场景立体影像模型制作关键技术及应用[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2020, 37(4): 11-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC202004003.htmZhang Z Z. Key technologies for making large scene stereo model and its application in railway survey and design[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2020, 37(4): 11-16(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC202004003.htm [11] 肖建华, 邬明权, 周世健, 等. "一带一路"重大铁路建设生态与经济影响遥感监测[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(11): 4605-4613. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS202011059.htmXiao J H, Wu M Q, Zhou S J, et al. Remote sensing monitoring of ecological and economic impact of major railway construction in the benguela railway[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(11): 4605-4613(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS202011059.htm [12] 吴传勇, 吴国栋, 陈建波, 等. 天山内部那拉提断裂晚第四纪活动速率[J]. 内陆地震, 2013, 27(2): 97-105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LLDZ201302002.htmWu C Y, Wu G D, Chen J B, et al. The Late Quaternary activity rate of Nalati fault, interior Tianshan[J]. Inland Earthquake, 2013, 27(2): 97-105(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LLDZ201302002.htm [13] 于海峰, 王福君, 梁有为, 等. 西天山那拉提-红柳河缝合带构造组合样式与变形分析[J]. 新疆地质, 2011, 29(2): 130-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201102004.htmYu H F, Wang F J, Liang Y W, et al. Tectonics tyle and deformation analysis of Nalati-Hongliuhe suture zone in western Tianshan Mountains[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2011, 29(2): 130-137(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201102004.htm [14] 曹小红, 孟和, 尚彦军, 等. 伊犁谷地黄土滑坡发育分布规律及成因[J]. 新疆地质, 2020, 38(3): 405-411. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI202003023.htmCao X H, Meng H, Shang Y J, et al. The development and distribution of loess landslides in Yili Alley and its causes[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2020, 38(3): 405-411(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI202003023.htm [15] 李传想, 宋友桂, 王乐民. 伊犁盆地黄土分布、年代及粉尘来源分析[J]. 地球与环境, 2012, 40(3): 314-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201203004.htmLi C X, Song Y G, Wang L M. Distribution, age and dust sources of loess in the Yili Basin[J]. Earth and Environment, 2012, 40(3): 314-320(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201203004.htm [16] 陈奋雄, 聂逢君, 张成勇, 等. 伊犁盆地洪海沟地区西山窑组上段层间氧化带分布特征及其主控因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(3): 105-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201603013.htmChen F X, Nie F J, Zhang C Y, et al. Distribution characteristics of interlayer oxidation zone and its main controlling factors of Upper Xishanyao Formation in Honghaigou area, Yili Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(3): 105-111(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201603013.htm [17] 杨章. 对1944年3月10日新源7 1/4级地震震中位置的讨论[J]. 中国地震, 1992(2): 31-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD199202003.htmYang Z. Discussion on the epicentral position of Xinyuan earthquake with magnitude 7 1/4 on Marth 10, 1944[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 1992(2): 31-39(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD199202003.htm [18] 余宏甸, 陈汉林, 程晓敢, 等. 南天山褶皱冲断带西段变形空间差异性及控制因素[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(6): 1689-1703. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202006003.htmYu H D, Chen H L, Cheng X G, et al. Spatial variation and controlling factors of deformation in the western segment of the southern Tianshan fold-thrust belt[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(6): 1689-1703(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202006003.htm [19] 吴传勇. 西南天山北东东走向断裂的晚第四纪活动特征及在天山构造变形中的作用[D]. 中国地震局地质研究所, 2016.Wu C Y. Late Quaternary activity of the east-northeastern trending faults in the southwestern Tianshan and their role in the tectonic deformation of Tianshan Mountains[D]. Institude of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [20] 李锦轶, 王克卓, 李亚萍, 等. 天山山脉地貌特征、地壳组成与地质演化[J]. 地质通报, 2006(8): 895-909. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200608001.htmLi J Y, Wang K Z, Li Y P, et al. Geomorphological features, crustal composition and geological evolution of the Tianshan Mountains[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006(8): 895-909(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200608001.htm -





 下载:
下载: