Logging evaluation of the engineering quality of the Paleogene Funing Formation oil shales in the Subei Basin
-
摘要:
页岩储层通常无自然产能, 需要采用水平井钻井和体积压裂等手段进行商业开采, 基于工程品质测井评价的页岩可压裂层段优选工作显得尤为重要。以苏北盆地古近系阜宁组页岩为例, 应用阵列声波资料计算泊松比、杨氏模量等岩石力学参数, 并与岩心实测资料刻度实现岩石力学参数动静态转换, 以此为基础应用泊-杨法和一维岩石力学模型分别计算脆性指数与三轴地应力。综合考虑单井不同层段的脆性指数以及水平主应力差, 优选了脆性指数以及脆性指数与水平最大、最小主应力差的比值作为工程品质表征参数。结合试油资料表明对于脆性指数越大、水平主应力差越小的储层, 其压裂后产能越高。将苏北盆地阜宁组工程品质划分为两类: Ⅰ类高产(工程品质表征参数>2.2), Ⅱ类中-低产(工程品质表征参数 < 2.2), 并且Ⅰ类工程"甜点"段普遍压裂出油, 表明依据该参数的"甜点"分类效果较好。页岩工程品质测井评价结果, 可为可压裂性层段的优选提供理论依据与技术支撑, 为页岩储层钻井轨迹设计与压裂设计工作提供科学指导。
Abstract:Shale oil reservoirs, characterized by no productivity, are developed by horizontal drilling and volume fracturing, and it is very important to optimize shale fracable intervals based on engineering quality logging evaluation. The Paleogene Funing Formation shale in the Subei Basin is taken as a typical example in this study. A sonic scanner is used to calculate the elastic parameters, including Poisson's ratio and Young's modulus. Dynamic and static parameters are converted through core analysis data. The brittleness index and in situ stress are calculated according to Poisson's ratio and Young's modulus. In addition, a one-dimensional rock mechanics model was constructed with the shear slowness in a single well to calculate three components of in situ stress. Finally, considering the difference in the brittleness index and horizontal stress differences between different layers, brittleness index (
BI ) and (BI /(σ H-σ h)) were selected to describe the engineering quality. According to oil test data, the larger the brittleness index and the smaller the horizontal stress are, the higher the capacity after fracturing. A cross plot of the brittleness index andBI /(σ H-σ h) is established to divide the reservoir types. Consequently, there are two types, including I high productivity(engineering quality characterization parameters >2.2) and Ⅱ medium-low productivity (engineering quality characterization parameters < 2.2), in the Paleogene Funing Formation in the Subei Basin. High productivity produces oil after fracturing, which suggests that the classification results of sweet spots depending on the engineering quality characterization parameters are better. Logging evaluation of the engineering quality of shale oil reservoirs can provide a theoretical basis and technical guidance for optimizing favorable fracability and high productivity layers and provide scientific guidance for drilling and fracturing layer optimization of shale reservoirs.-
Key words:
- shale oil /
- engineering quality /
- brittleness index /
- in situ stress difference /
- logging evaluation /
- Funing Formation /
- Subei Basin
-
图 10 J19井阜二段工程品质测井评价[44]
Figure 10. Logging evaluation of the engineering quality of E1f2 in Well J19
表 1 岩石力学强度测试结果
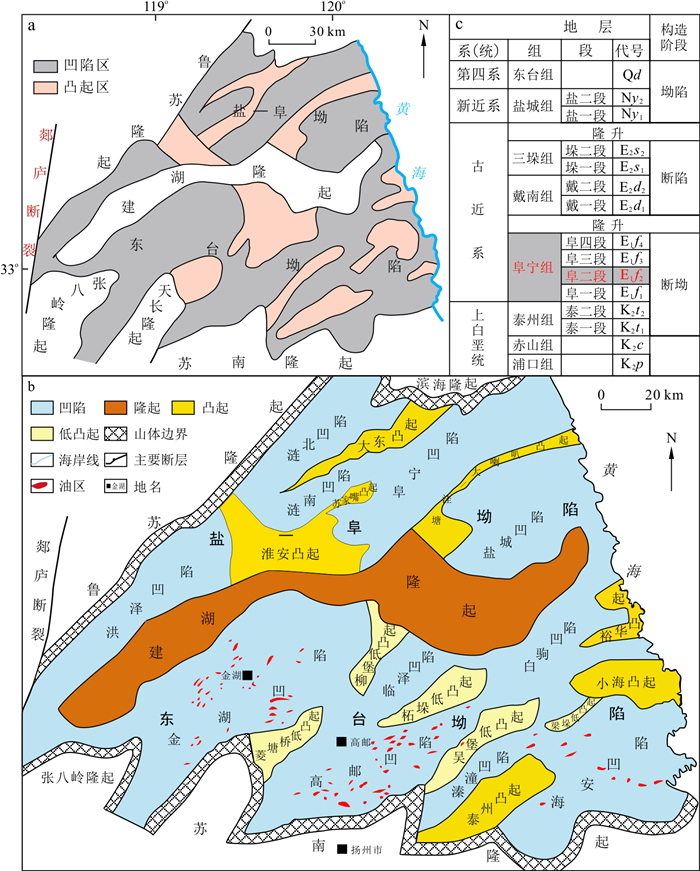
Table 1. Rock mechanical strength test results
编号 直径/mm 长度/mm 杨氏模量/GPa 泊松比 围压/MPa 深度/m 8-62/101 24.40 36.80 30.33 0.22 40.00 3 889.32 8-95/101 24.40 53.40 31.34 0.27 40.00 3 895.00 5-65/90 24.50 32.20 29.52 0.30 40.00 3 853.15 8-29/101 24.40 53.10 32.15 0.35 40.00 3 883.66 2-18/54 24.40 49.70 26.86 0.31 40.00 3 819.66 4-59/61 24.50 49.50 29.00 0.35 40.00 3 842.32 6-58/102 24.60 46.40 32.08 0.30 40.00 3 868.45 9-63/98 24.30 51.40 29.50 0.34 40.00 3 907.50 注:测试单位为中国石油大学(华东)石油工程学院岩石力学参数实验室 -
[1] 金之钧, 王冠平, 刘光祥, 等. 中国陆相页岩油研究进展与关键科学问题[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(7): 821-835. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202107001.htmJin Z J, Wang G P, Liu G X, et al. Research progress and key scientific issues of continental shale oil in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(7): 821-835(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202107001.htm [2] Sonnenberg S A, Pramudito A. Petroleum geology of the giant Elm Coulee field, Williston Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(9): 1127-1153. doi: 10.1306/05280909006 [3] Jarvie D M. Shale resource systems for oil and gas: Part2. Shale-oil resource systems[J]. AAPG Memoir, 2012, 97: 89-119. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284338010_Shale_resource_systems_for_oil_and_gas_Part_2_Shale-oil_resource_systems [4] Liu X, Jin Z, Lai J, et al. Fractal behaviors of NMR saturated and centrifugal T2 spectra in oil shale reservoirs: The Paleogene Funing Formation in Subei Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 129: 105069. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105069 [5] Liu Y, Zeng J, Yang G, et al. An innovative method for the characterization of oil content in lacustrine shale-oil systems: A case study from the Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation in the Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 130: 105112 doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105112 [6] Cao H, Zou Y R, Lei Y, et al. Shale oil assessment for the Songliao Basin, northeastern China, using oil generation-sorption method[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(5): 4826-4842. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039889529810_19ee.html [7] Cui J, Li S, Mao Z. Oil-bearing heterogeneity and threshold of tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study on Triassic Chang 7 Member, Ordos Basin[J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 2019, 104: 180-189. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000042279499399_6805.html [8] Liu X P, Lai J, Fan X C, et al. Insights in the pore structure, fluid mobility and oiliness in oil shales of Paleogene Funing Formation in Subei Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 114: 104228. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104228 [9] 夏一军, 胡向阳, 魏水健. 页岩气勘探开发中地球物理技术的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(4): 1798-1803. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201504037.htmXia Y J, Hu X Y, Wei S J. Application of geophysics in shale gas exploration and exploitation[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(4): 1798-1803(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201504037.htm [10] 陈林, 陈孝红, 张保民, 等. 鄂西宜昌地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩储层特征及其脆性评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 54-61. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0206Chen L, Chen X H, Zhang B M, et al. Reservoir characteristics and brittleness evaluation of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation shale in Yichang area, western Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 54-61(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0206 [11] Rybacki E, Meier T, Dresen G. What controls the mechanical properties of shale rocks?Part Ⅱ. Brittleness[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2016, 144: 39-58. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2016.02.022 [12] Guo Z, Li X Y, Liu C, et al. A shale rock physics model for analysis of brittleness index, mineralogy and porosity in the Barnett Shale[J]. Journal of Geophysics & Engineering, 2013, 10(2): 025006. http://nora.nerc.ac.uk/503215/1/A%20shale%20rock%20physics%20model%20for%20analysis%20of%20brittleness%20index%20mineralogy%20%20%20.pdf [13] 周立宏, 陈长伟, 甘华军, 等. 歧口凹陷沙一下亚段页岩形成环境及页岩油潜力综合评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 19-30. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0233Zhou L H, Chen C W, Gan H J, et al. Shale formation environment and comprehensive evaluation of shale oil potential of the Lower First Member of Shahejie Formation in Qikou Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 19-30(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0233 [14] Boersma Q D, Douma L A N R, Bertotti G, et al. Mechanical controls on horizontal stresses and fracture behaviour in layered rocks: A numerical sensitivity analysis[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2020, 130: 103907. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2019.103907 [15] Beugelsdijk L J L, Pater C, Sato K. Experimental hydraulic fracture propagation in a multi-fractured medium[C]//Anon. SPE Asia Pacific Conference on Integrated Modelling for Asset Management. [S. l.]: [s. n.], 2000. [16] 覃建华, 张景, 蒋庆平, 等. 玛湖砾岩致密油"甜点"分类评价及其工程应用[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(2): 110-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.02.011Qin J H, Zhang J, Jiang Q P, et al. Sweet spot classification evaluation of tight conglomerate reservoir in Mahu Sag and its engineering application[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(2): 110-119(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.02.011 [17] 邹才能, 杨智, 张国生, 等. 常规-非常规油气"有序聚集"理论认识及实践意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(1): 14-25, 27, 26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201401002.htmZou C N, Yang Z, Zhang G S, et al. Conventional and unconventional petroleum "orderly accumulation": Concept and practical significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(1): 14-25, 27, 26(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201401002.htm [18] 陈友飞, 严钦尚, 许世远. 苏北盆地沉积环境演变及其构造背景[J]. 地质科学, 1993, 28(2): 151-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199302006.htmChen Y F, Yan Q S, Xu S Y. Evolution of the sedimentary environments in north Jiangsu Basin and its tectonic setting[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 1993, 28(2): 151-160(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199302006.htm [19] 舒良树, 王博, 王良书, 等. 苏北盆地晚白垩世-新近纪原型盆地分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2005, 11(4): 534-543. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.04.009Shu L S, Wang B, Wang L S, et al. Analysis of Northern Jiangsu Prototype Basin from Late Cretaceous to Neogene[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2005, 11(4): 534-543(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.04.009 [20] 王旭影. 苏北盆地古近系阜三段沉积体系研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.Wang X Y. Study on the sedimentary system of the Third Member of Paleogene Funing Formation in the Subei Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [21] 李维, 朱筱敏, 段宏亮, 等. 苏北盆地高邮-金湖凹陷古近系阜宁组细粒沉积岩纹层特征与成因[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(3): 469-482. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202003007.htmLi W, Zhu X M, Duan H L, et al. Characteristics and forming mechanism of laminae fine-grained sedimentary rock of the Paleogene Funing Formation in Gaoyou and Jinhu Sags, Subei Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2020, 22(3): 469-482(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202003007.htm [22] 王旭影, 姜在兴. 苏北盆地古近系阜三段物源特征及其形成的构造背景分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(2): 376-390. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202102028.htmWang X Y, Jiang Z X. Provenance characteristics and tectonic setting analysis of the 3rd Member of the Paleogene Funing Formation, Subei Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(2): 376-390(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202102028.htm [23] 张廷山, 彭志, 祝海华, 等. 海安凹陷曲塘次凹阜二段页岩油形成条件及勘探潜力[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(2): 177-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201602035.htmZhang T S, Peng Z, Zhu H H, et al. Forming conditions and exploration potential of shale oil from Member 2 of Funing Formation in Qutang Subsag, Hai'an Sag[J]. Geologial Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(2): 177-184(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201602035.htm [24] 许东俊, 耿乃光. 岩体变形和破坏的各种应力途径[J]. 岩土力学, 1986, 7(2): 17-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX198602002.htmXu D J, Geng N G. The various stress paths causing deformation and failure in rocks[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 1986, 7(2): 17-25(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX198602002.htm [25] Liang X, Qiu K, Shu H, et al. Geomechanical evaluations of deep shale gas reservoir in Sichuan Basin, western China[C]//Anon. Unconventional Resources Technology Conference. [S. l.]: [s. n.], 2020: 1797-1816. [26] Zhang H, Qiu K, Fuller J, et al. Geomechanical-evaluation enabled successful stimulation of a high-pressure/high-temperature tight gas reservoir in western China[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2016, 18(4): 157-170. [27] Cheng C H, Johnston D H. Dynamic and static moduli[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1981, 8(1): 39-42. doi: 10.1029/GL008i001p00039 [28] 姜在兴, 张文昭, 梁超, 等. 页岩油储层基本特征及评价要素[J]. 石油学报, 2014, 35(1): 184-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201401027.htmJiang Z X, Zhang W Z, Liang C, et al. Characteristics and evaluation elements of shale oil reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2014, 35(1): 184-196(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201401027.htm [29] Shaver M A, Segret G, Yudhia D P, et al. A geomechanical model and workflow for calibrating elastic moduli and min/max horizontal stress from well logs in the Nahr Umr Shale[C]//Anon. SPE/IADC Middle East Drilling Technology Conference and Exhibition. [S. l.]: [s. n.], 2021. [30] Zhang D, Ranjith P G, Perera M S A. The brittleness indices used in rock mechanics and their application in shale hydraulic fracturing: A review[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2016, 143: 158-170. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920410516300547 [31] Jarvie D M, Hill R J, Ruble T E, et al. Unconventional shale-gas systems: The Mississippian Barnett shale of north-central Texas as one model for thermogenic shale-gas assessment[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4): 475-499. http://www.eesi.psu.edu/seminars-conferences/earthtalks-spring2009-marcellus-supplements/BarnettShGasJarvie.pdf [32] Zhao P Q, Mao Z Q, Huang Z H, et al. A new method for estimating total organic carbon content from well logs[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2016, 100(8): 1311-1327. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039530147210_831f.html [33] 赖锦, 王贵文, 范卓颖, 等. 非常规油气储层脆性指数测井评价方法研究进展[J]. 石油科学通报, 2016, 1(3): 330-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE201603002.htmLai J, Wang G W, Fan Z Y, et al. Research progress in brittleness index evaluation methods with logging data in unconventional oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2016, 1(3): 330-341(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE201603002.htm [34] Rickman R, Mullen M, Petre E, et al. A practical use of shale petrophysics for stimulation design optimization: All shale plays are not clones of the Barnett shale[C]//Anon. SPE Annual Technical Conference & Exhibition. [S. l.]: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2008. [35] Eaton B A. The equation for geopressure prediction from well logs[R]. [S. l.]: SPE, 1975: 5544. [36] 张筠, 林绍文. 利用测井进行地层弹性特征及应力场分析[J]. 测井技术, 2001, 25(6): 467-472, 480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS200106018.htmZhang J, Lin S W. Analysis of formation elastic characteristics and stress field with log data[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2001, 25(6): 467-472, 480(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS200106018.htm [37] Lai J, Li D, Wang G, et al. Earth stress and reservoir quality evaluation in high and steep structure: The Lower Cretaceous in the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 101: 43-54. [38] 王亚超, 窦斌, 喻勇, 等. 不同冷却方式下高温花岗岩巴西劈裂及声发射特性试验研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 200-207. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0028Wang Y C, Dou B, Yu Y, et al. Experimental study on Brazilian split test and acoustic emission characteristics of high temperature granite under different cooling methods[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 200-207(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0028 [39] 沈海超, 程远方, 赵益忠, 等. 靖边气田煤层地应力及井壁稳定研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(增刊2): 123-126, 131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2009S2028.htmShen H C, Chen Y F, Zhao Y Z, et al. Research on in-situ stresses and borehole stability of coal seam in Jingbian Gas Field[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(S2): 123-126, 131(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2009S2028.htm [40] 郭建春, 尹建, 赵志红. 裂缝干扰下页岩储层压裂形成复杂裂缝可行性[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(8): 1589-1596. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201408009.htmGuo J C, Yin J, Zhao Z H. Feasibility of formation of complex fractures under cracks interference in shale reservoir fracturing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(8): 1589-1596(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201408009.htm [41] 赖锦, 王贵文, 庞小娇, 等. 测井地质学前世、今生与未来: 写在《测井地质学·第二版》出版之时[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(6): 1804-1828. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202106023.htmLai J, Wang G W, Pang X J, et al. The past, present and future of Well Logging Geology: To celebrate the publication of second edition of "Well Logging Geology"[J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67(6): 1804-1828(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202106023.htm [42] Stadtmuller M, Lis-Šledziona A, słota-Valim M. Petrophysical and geomechanical analysis of the Lower Paleozoic shale formation, North Poland[J]. Interpretation, 2018, 6(3): 91-106. http://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/interpretation/article-pdf/6/3/SH91/4333018/int-2017-0193.1.pdf [43] 魏周拓, 范宜仁, 陈雪莲. 横波各向异性在裂缝和应力分析中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2012, 27(1): 217-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201201025.htmWei Z T, Fan Y R, Chen X L. Application of shear wave anisotropy in fractures and in-situ stress analysis[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2012, 27(1): 217-224(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201201025.htm [44] 赖锦, 凡雪纯, 黎雨航, 等. 苏北盆地阜宁组页岩油七性关系与三品质测井评价[J/OL]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(2): 751-768.Lai J, Fan X C, Li Y H, et al. Well logging evaluation of seven relationships and three properties of Paleogene Funing Formation oil shales in Subei Basin[J/OL]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(2): 751-768(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: