Experimental study on the change law of internal erosion and seepage characteristics of inverse grading sand accumulation
-
摘要:
反粒序堆积体常见于高速远程滑坡的流通区和堆积区。针对其粒径上大下小的特殊结构和较强透水性而诱发堆积体不稳定的问题, 采用自制的渗流侵蚀试验装置对颗粒粒径为0.075~20 mm的7组连续及间断颗粒级配反粒序土样进行了试验, 研究了反粒序砂土体渗流侵蚀过程中参数变化和细颗粒迁移模式及规律。结果表明:在反粒序堆积土样中, 细颗粒含量和不均匀系数对反粒序砂土体的渗流侵蚀有重要影响, 细颗粒含量越高, 不均匀系数越大, 则起始渗流系数越小。反粒序砂土体发生管涌颗粒跃层后, 底层颗粒流失量最多, 且粒径为0.075~0.125 mm的颗粒流失比最大。反粒序堆积体整体的渗流能力主要取决于底部的细颗粒含量, 细颗粒含量越高, 临界水力梯度越大。在连续级配土样中, 水力梯度与渗流系数呈二次函数关系;在间断级配反粒序土样中, 细颗粒含量超过45%时, 土样趋于稳定。反粒序堆积体发生管涌后, 其颗粒呈现剥离-沉淀-剥离-沉淀中下层颗粒交替侵蚀的运移模式。研究结果对于该类灾害形成机理与防治研究具有理论和实际应用意义。
Abstract:Inverse grading deposits are commonly found in circulation and accumulation areas of high-speed and long-distance landslides. Due to its special structure of large particle size at the top and small at the bottom and strong permeability, the accumulation is highly susceptible to unstable failure. In this study, using a self-designed device, seepage erosion tests were conducted on seven sets of inverse grading soil samples with continuous and discontinuous particle gradation of particle size 0.075-20 mm to investigate the parameter changes and fine particle migration patterns and laws during seepage erosion of inverse grading sand mass. The results show that the fine particle content and nonuniformity coefficient have an important influence on the seepage erosion of the inverse grading soil samples. The higher the fine particle content, the greater the nonuniformity coefficient and the lower the initial seepage coefficient. After the occurrence of cross-layer tube surge particles, the bottom layer of particle loss is the most, and the particle size of 0.075-0.125 mm particle loss ratio is the largest.The seepage capacity of the inverse grading sand mass depends mainly on the content of fine particles at the bottom. The higher the content of fine particles is, the greater the critical hydraulic gradient will be.In continuous graded soil samples, the relationship between the hydraulic gradient is quadratically related to the percolation coefficient.Soil samples with discontinuous particle gradation are stabilized when the content of fine particles exceeds 45%.After tube gushing occurred in the reverse grain sequence accumulation body, the particles show a migration pattern of stripping-precipitation-stripping-precipitation alternately eroded particles in the middle and lower layers. The study has theoretical and practical significance for the formation mechanism and prevention of such disasters.
-
Key words:
- inverse grading /
- sand accumulation /
- fine particle content /
- particle migration /
- piping /
- seepage and erosion
-
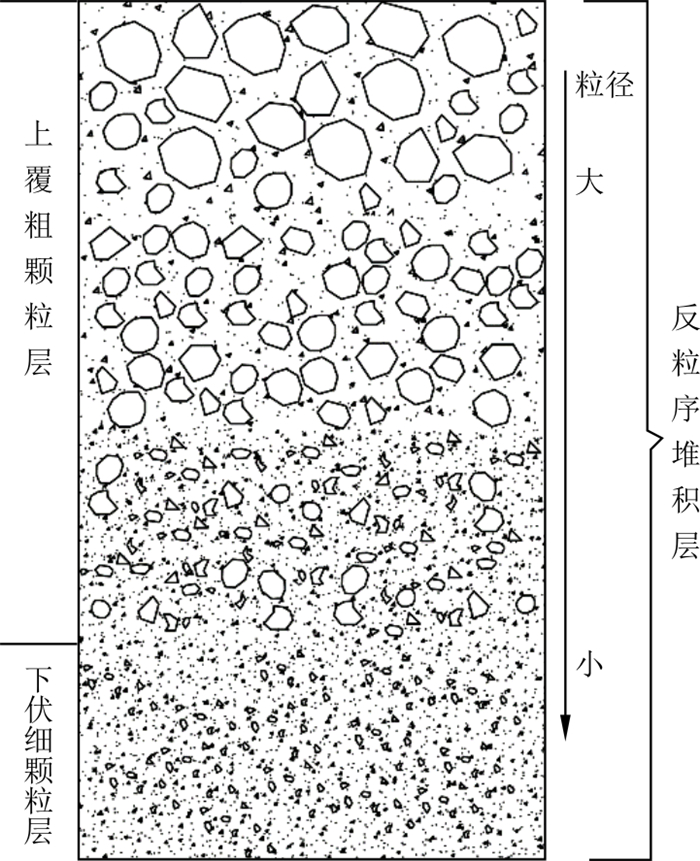
许多学者对高速远程滑坡-碎屑流进行了研究[1-4], 发现其在运动过程中具有流动性异常高、运动速度非常快、运动距离超长的特点, 并因受到碰撞碾压[5]、振动筛分[6]和大粒径颗粒的消散压力作用, 使得堆积体颗粒呈现上粗下细的反粒序堆积结构[7], 如图 1所示。在各类沉积物中也发现了这种反粒序结构[8-10]。
 图 1 反粒序堆积结构示意图[3]Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the structure of inverse grading accumulation
图 1 反粒序堆积结构示意图[3]Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the structure of inverse grading accumulation众多学者已经对各类普通砂土的渗透变形特性和渗透破坏过程做了大量研究并取得了丰富的成果[11-17]。王志兵等[11]通过自下而上渗流对2种分散性不同的土样进行了室内土柱自滤试验, 探讨了土柱不同部位因颗粒运移对土样渗透性的影响。袁涛等[12]利用自主研发的加载式大型渗透变形仪对不同级配粗粒土试样进行了渗透变形试验, 发现细小颗粒的流失会影响土体颗粒结构组成, 从而改变土体力学参数, 形成渗透损伤。朱秦等[13]利用自制大型渗透仪对不同D15/d85(D15为粗粒组中小于该粒径的颗粒质量分数为15%的粒径;d85为细粒组中小于该粒径的颗粒质量分数为85%的粒径; 表 1与之类推)值的宽级配土进行了渗流试验, 提出了3种宽级配土的细颗粒迁移模式。Xiao等[14]利用改进的三轴仪进行了间断级配土样的渗流试验, 发现间断级配土样的渗透性随着侵蚀的进行而降低, 且渗透率的降低在很大程度上取决于内部发生的颗粒堵塞。常东升等[15]通过对收集的167种土的室内渗透侵蚀试验结果的分析得出, 当间断级配土细粒质量分数超过35%时土体的渗透稳定性很好。
表 1 颗粒级配特征Table 1. Particle gradation characteristics试样名称 有效粒径d10/ mm d30/ mm 限制粒径d60/ mm 不均匀系数Cu 曲率系数Cc CA A1 0.161 0.707 2.516 15.63 1.23 A2 0.109 0.499 1.813 16.63 1.26 A3 0.096 0.356 1.189 12.39 1.11 CB B1 0.213 0.851 2.802 13.15 1.21 B2 0.148 0.603 2.060 13.92 1.19 B3 0.122 0.434 1.371 11.24 1.13 CC C1 0.265 0.994 3.100 11.70 1.20 C2 0.187 0.720 2.320 12.41 1.19 C3 0.148 0.512 1.553 10.49 1.14 CD D1 0.330 1.150 3.387 10.26 1.18 D2 0.239 0.851 2.568 10.74 1.18 D3 0.187 0.603 1.735 9.28 1.12 DE E1 0.830 6.620 12.100 14.58 4.36 E2 0.407 2.000 10.676 26.23 0.92 E3 0.196 1.232 9.069 46.27 0.85 DF F1 0.830 6.620 12.100 14.58 4.36 F2 0.407 2.000 10.676 26.23 0.92 F3 0.158 1.000 8.258 52.27 0.77 DG G1 0.830 6.620 12.100 14.58 4.36 G2 0.407 2.000 10.676 26.23 0.92 G3 0.137 0.854 7.344 53.69 0.73 此外, 国内外学者也对高速滑坡堆积体中的反粒序砂土体地质结构进行了较为详细的堆积特征描述和粒组统计分析[3, 18-23], 如最典型的西藏易贡藏布江左岸扎木弄沟形成的易贡滑坡堆积体[20]和四川省汶川县映秀镇牛圈沟滑坡堆积体[3]。但并未有人对反粒序砂土体进行系统的渗流侵蚀试验研究。在反粒序结构中, 粒径较大的块体主要分布于堆积体的表层, 而粒径较小的碎石、角砾及细颗粒主要分布于下部堆积层, 这种特殊的结构使得其上部孔隙率相对较大且透水性能相对更强, 在降雨或流水等作用下, 水的渗透作用对细颗粒可能产生较强的拖拽力, 进而使细颗粒在砂土粗颗粒构成的孔隙中移动, 造成渗流导致堆积体的不稳定问题, 甚至可能引发二次滑动或泥石流等灾害, 因此开展反粒序砂土体渗流侵蚀试验研究其渗流特性变化规律,可为此类灾害的形成机理研究提供理论支持, 同时为防治此类灾害的发生提供科学的建议, 具有重要的理论价值和实际应用意义。
本研究借助自行研发的渗流侵蚀试验装置, 以易贡滑坡和牛圈沟滑坡形成的反粒序堆积体为研究对象, 并制备相应的4种连续级配和3种间断级配的反粒序土样进行渗流侵蚀试验。通过对细颗粒流失量、渗流系数、水力梯度等参数变化的分析, 研究反粒序土样中细颗粒运移、流失对土体渗透性的影响, 探明反粒序堆积体结构内部的颗粒运移现象, 进而揭示反序粒堆积体侵蚀破坏规律和机理。
1. 渗流试验方案
1.1 试验装置
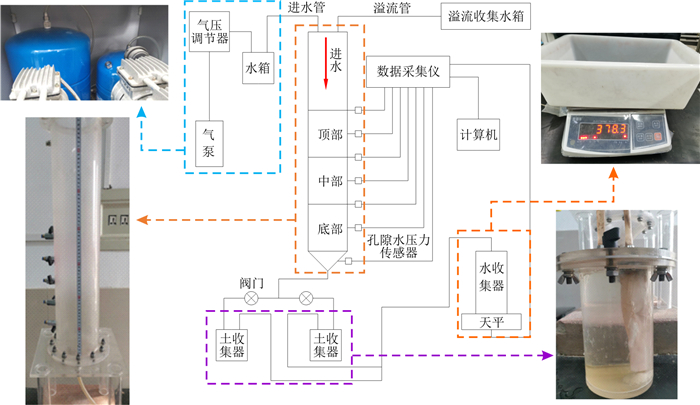
整个试验装置系统由刚性壁渗流室、数据采集系统与加压进水系统3个部分构成。
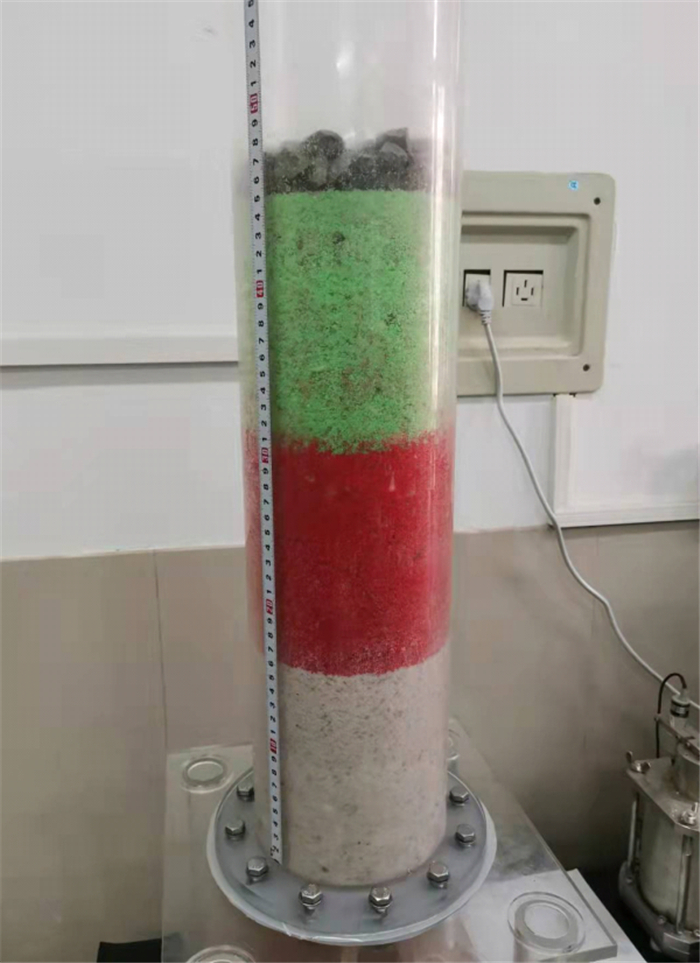
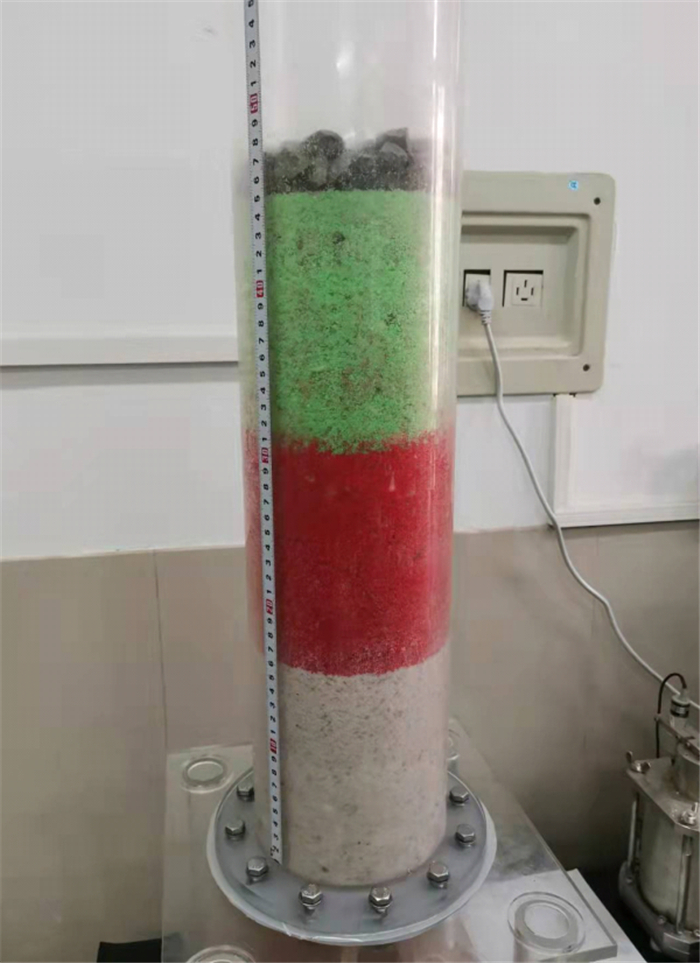
刚性壁渗流室主要由顶部密封盖、有机玻璃圆筒以及漏斗底座组成。圆筒为透明亚克力材质, 以便于在试验过程中观察土样变化。圆筒高75 cm, 内径12.5 cm, 壁厚1 cm。底座上放置孔径4 mm的筛网以允许所有细颗粒流失。数据采集系统主要包括计算机、称重天平、孔隙水压力传感器和DH3818N静态应变测试系统等部分。在有机玻璃圆筒和漏斗底座处安装传感器用于监测渗流过程中土样各位置处孔隙水压力的变化情况。有机玻璃圆筒侧壁上每隔75 mm安装一个孔隙水压力传感器, 共6个, 漏斗侧壁安装一个孔隙水压力传感器, 孔隙水压力传感器与DH3818N静态应力-应变测试分析系统相连。渗流过程中细颗粒由于侵蚀作用冲出渗流室, 进入固液分离的收集器中, 土颗粒进入土收集器, 水进入水收集器。称重天平称出土的质量并将实时质量输递至计算机中, 结合孔隙水压力信息进行断面平均渗透系数的计算。加压系统由气泵、气压调节器、供水管路以及水箱组成, 通过加设阀门与气压调节器,实现压力的控制与稳定。试验装置如图 2所示。
1.2 工程原型及试验材料
本研究以易贡滑坡和牛圈沟滑坡形成的反粒序堆积体为研究对象, 并制备相应的4种连续级配和3种间断级配的反粒序土样进行渗流侵蚀试验。根据不同的颗粒级配, 研究在不同水力梯度条件下进行渗流时土颗粒迁移、流失和形成管涌的过程。但由于滑坡原型颗粒尺寸过大, 无法进行室内试验, 故采用连续级配土的级配方程, 根据原滑坡形状及试验装置尺寸, 确定室内试验所需的砂土颗粒级配曲线。根据有机玻璃圆筒筒径的大小确定试验砂土颗粒最大粒径为20 mm, 细颗粒粒径范围为0.075~2 mm。其中间断级配缺失粒径范围为2~5 mm。砂土颗粒为石英砂, 颗粒形状以棱角形为主, 颗粒密度为2.65×103 kg/m3。
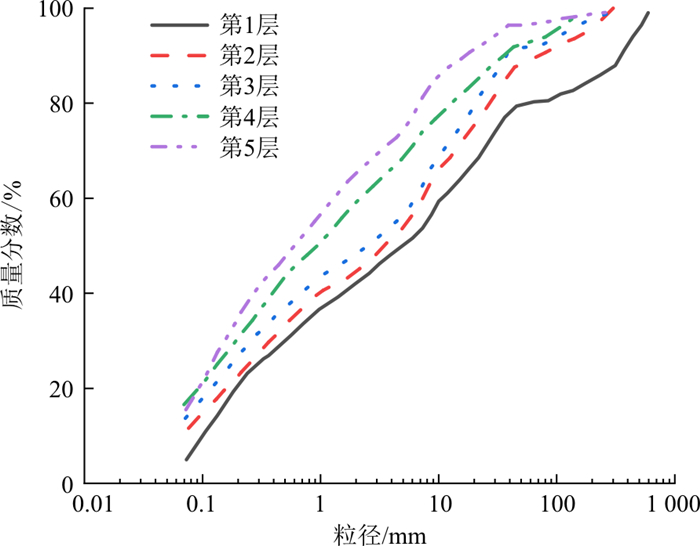
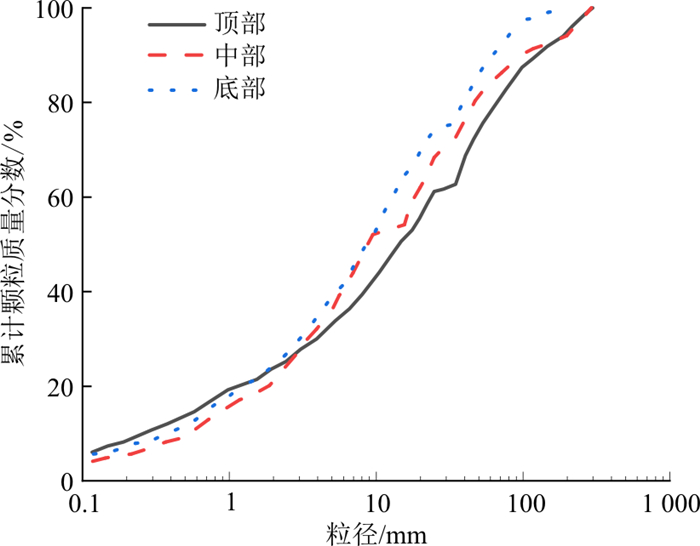
林小龙[20]在对易贡滑坡堆积区主体层纵剖面粒径组成分析中, 发现了反粒序结构, 竖向上自下而上粒径变化范围较大, 呈现出随深度减小粒径增大的规律, 通过筛分得到了易贡滑坡的典型反粒序剖面粒径级配曲线, 如图 3所示,可以发现易贡滑坡堆积体颗粒级配曲线呈现凸型连续状。
 图 3 易贡滑坡堆积体竖向级配曲线[20]Figure 3. Vertical grading curve of the Yigong landslide accumulation body
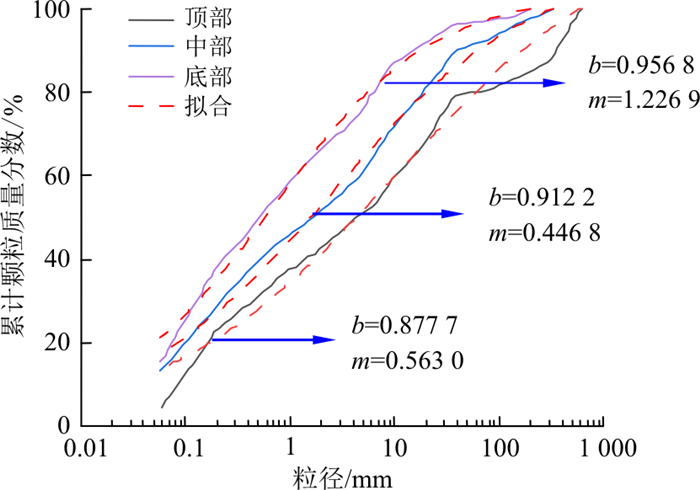
图 3 易贡滑坡堆积体竖向级配曲线[20]Figure 3. Vertical grading curve of the Yigong landslide accumulation body朱俊高等[24]提出了一个描述连续级配土的级配方程, 研究了方程的基本性质、对不同土体级配曲线的反映能力, 并根据方程参数分析得知级配曲线参数b主要决定级配曲线的形状。
P=dm(1−b)dmmax+bdm×100% (1) 式中: P为粒径为d的颗粒质量分数;dmax为最大粒径;b,m为级配曲线参数。
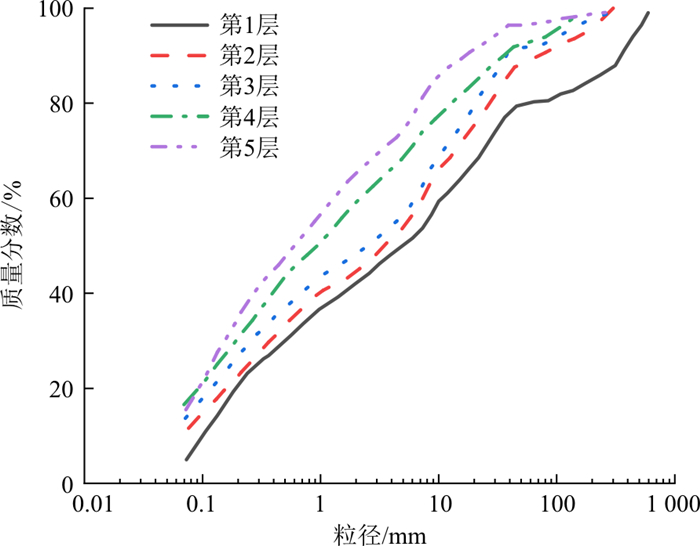
由图 3可知易贡滑坡堆积体级配曲线第2层与第3层、第4层与第5层颗粒级配曲线接近, 故将其两两合并, 为了使对比更直观方便, 将易贡滑坡级配曲线简化为3层。
采用自编最优化程序, 得出易贡滑坡曲线级配方程对应的参数b和m, 如图 4所示。由于参数b决定曲线形状, 为了更好地还原此类凸型级配曲线堆积体, 故对参数b不作改变, 而是通过改变参数m, 进而改变曲线斜率, 达到改变细颗粒含量的目的, 得到4组连续级配颗粒曲线。4组连续颗粒级配试样简称为CA组、CB组、CC组和CD组, CA-CD组中每层的细颗粒含量均随着参数m的增大依次减小。
 图 4 连续级配方程拟合的易贡滑坡堆积体级配曲线[20]Figure 4. Grading curve of the Yigong landslide accumulation body fitted by the continuous gradation equation
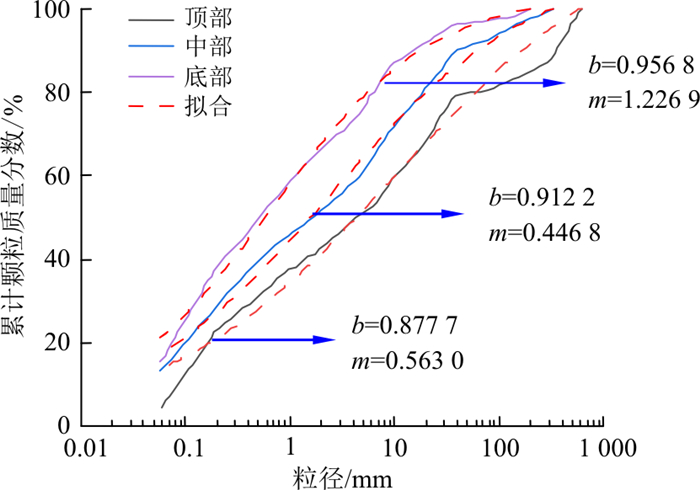
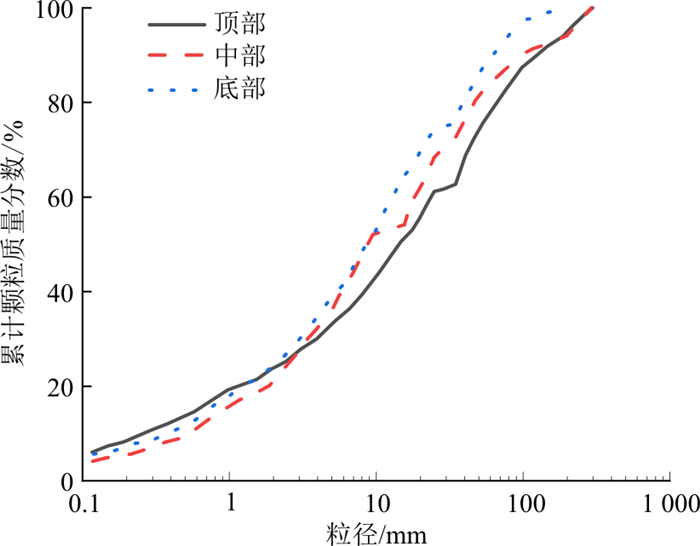
图 4 连续级配方程拟合的易贡滑坡堆积体级配曲线[20]Figure 4. Grading curve of the Yigong landslide accumulation body fitted by the continuous gradation equation王玉峰等[3]在对牛圈沟滑坡进行统计时, 发现牛圈沟堆积体的粒度组成比较均匀, 上中下3条曲线相差虽然不大, 但仍定量化地反映了滑坡堆积体中特有的反粒序结构,如图 5所示,由颗粒级配曲线可以看出, 牛圈沟滑坡堆积物呈现间断特征。
 图 5 牛圈沟滑坡碎屑堆积体竖向级配曲线[3]Figure 5. Vertical grading curve of the debris accumulation body in the Niu Juangou landslide
图 5 牛圈沟滑坡碎屑堆积体竖向级配曲线[3]Figure 5. Vertical grading curve of the debris accumulation body in the Niu Juangou landslide于际都等[25]在研究间断级配粗粒土的压实特性时提出了以下描述间断级配土的级配方程:
M(d)M={ωd3−Dd3−Di,d∈(0,di]ω,d∈(di,dj]1−(1−ω)d3−Dmax−d3−Dd3−Dmax−d3−Djd∈(dj,dmax] (2) 式中: d为粒径; D为分形维数; M(d)为粒径小于d的颗粒质量; M为颗粒总质量; ω为细料质量分数。
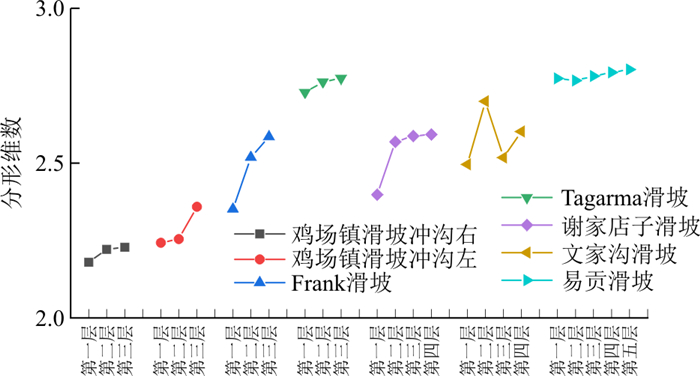
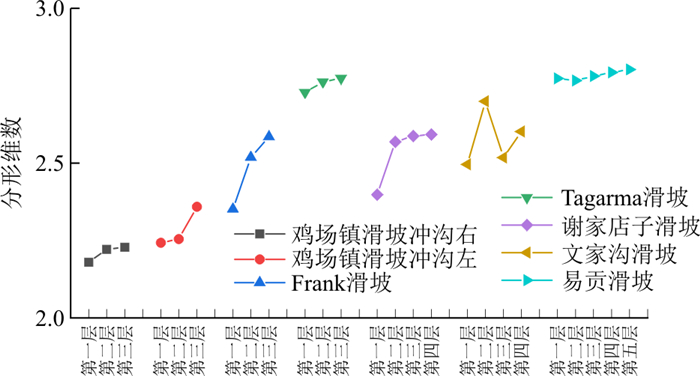
通过对几个反粒序滑坡堆积体分形维数的统计(图 6), 发现反粒序堆积体的分形维数主要集中于2.1~2.8范围内, 且自上层到下层分形维数逐渐增大。故在间断级配曲线设计中, 分形维数自上而下分别取2.2,2.3,2.4,进而得到试验所需的3类间断级配曲线。3类间断颗粒级配试样简称为DE组、DF组、DG组。由于间断级配试样中顶部和中部的细颗粒含量较少, 故仅对间断级配底部细颗粒的含量进行研究, DE组、DF组、DG组底部细颗粒质量分数分别为40%,45%,50%。
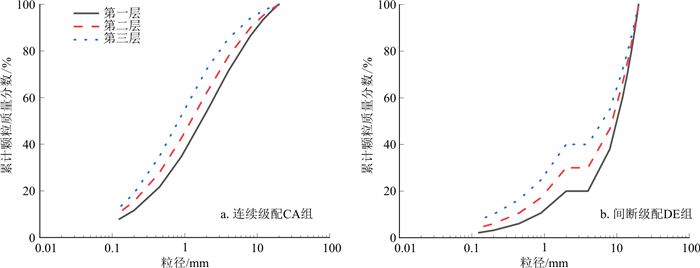
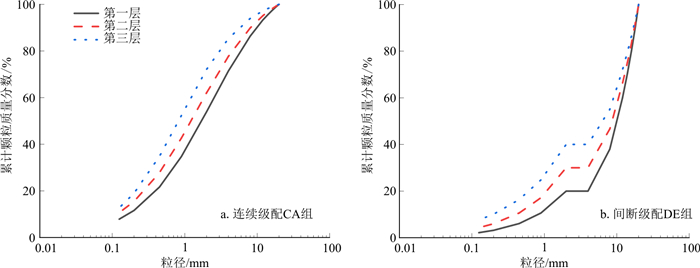
图 7给出了连续级配CA和间断级配DE试样级配曲线图。本研究共有7组试样,每组试样分为三层:第一层顶部, 第二层中部和第三层底部, 为叙述方便, 每层简称为A1、A2、A3, B1、B2、B3, C1、C2、C3, D1、D2、D3, E1、E2、E3, F1、F2、F3, G1、G2、G3(表 1)。各组试样装样完毕后的堆积分层如图 8所示。表 1中列出了试验所用的颗粒级配特征。
1.3 试验原理
水力梯度是影响颗粒侵蚀的关键因素[26]。在试验过程中通过气压调节器调节入渗水头的方式来改变水力梯度。有机玻璃圆筒上安置的孔隙水压力传感器可以实时观测各位置孔隙水压力的变化,故可以得到试验过程中上中下及整体的水力梯度及渗流系数, 计算公式[27]如下:
i=(Hm−Hn)L (3) 式中: i为水力梯度;Hm和Hn分别为两观测点m和n处的压力;L为两观测点间的距离。
k=vi=QA⋅t⋅i (4) 式中: k为渗流系数;Q为水收集器中收集到的流量;A为有机玻璃筒的截面积;t为收集渗流液的时间间隔;v为渗流速度。
1.4 试验过程
将烘干的各粒径土颗粒按照试验设计配制相应的土样, 制备试样时采用分层湿振捣法[28], 分层装样夯实以得到混合搅拌均匀的试样。经现场调查, 堆积体孔隙率主要集中在0.3~0.4, 故保证试样的孔隙率均值为0.35, 并在有机玻璃圆筒内壁涂抹凡士林, 用以减小边界效应对渗流的影响。在装好的试样上方铺一层碎石使入水均匀。饱和时采用自下而上缓慢进水, 尽可能排出土体中的气泡, 最后静置12 h。渗流时采用自上而下进水, 试验共设置2个土颗粒收集器, 渗流过程中只开一个收集器进水阀门, 试验使用气泵逐级加压, 压力调至电脑控制界面中的水压一栏达到试验方案设计压力并保持稳定时停止调节, 根据水收集器和水压, 每级水力梯度渗流过程进行0.5 h, 0.5 h后视觉观察到侵蚀流体明显清澈且无细颗粒流失后, 计算5 min内的渗流系数, 若渗流系数接近, 则将收集器的进水阀门关闭, 打开另一个收集器阀门, 提升下一级水头, 若0.5 h后细颗粒仍在流失或渗流系数未接近, 则继续渗流至稳定。收集每一级水头下收集系统中的流失颗粒质量和渗流量, 将土颗粒收集器中的流失颗粒烘干并称量计算流失率, 将水收集器中收集到的渗流量与对应的水力梯度进行计算, 得到渗流系数。试验结束后, 关闭压力水源, 将渗流室中的水缓慢放掉, 静置12 h, 待土样沥干后分层挖出并烘干, 对烘干后的每层土样进行级配筛分并称重。
2. 试验结果及分析
如图 9所示, 试验后, 连续级配土样未发生管涌破坏, 层间界限依然明显, 而间断级配土样已出现细颗粒的运移跃层现象, 管涌导致中上层土体向下层土体的细颗粒涌入和堆积。
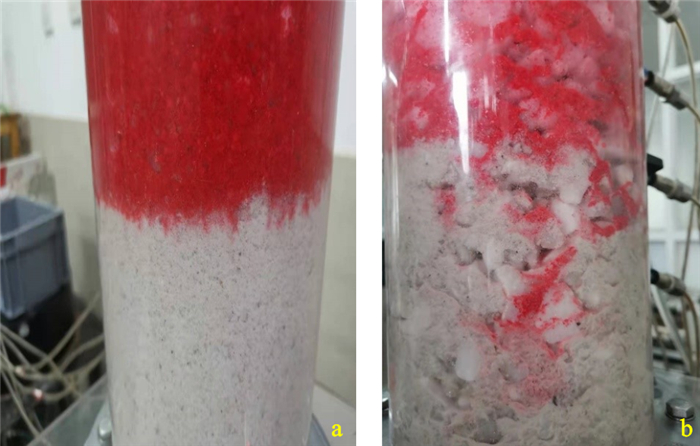
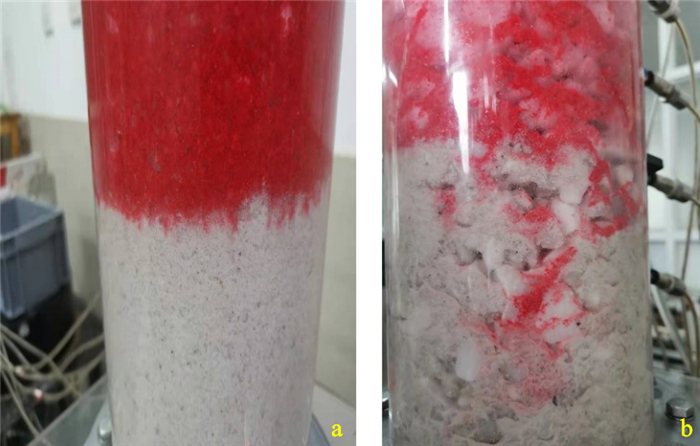
连续级配土样在渗流试验初始阶段, 收集管内水流清澈。随着水头增大, 各试样分别在不同水力梯度下开始出现细颗粒逸出现象, 收集管内水流出现浑浊, 如图 10-a所示;水头继续增大, 细颗粒继续流失, 且流失量高于上一级水头流失量。间断级配土样则在到达临界水力梯度之后, 收集管迅速变浑浊, 大量细砂涌出, 如图 10-b所示, 试样发生管涌破坏。
2.1 颗粒流失量分析
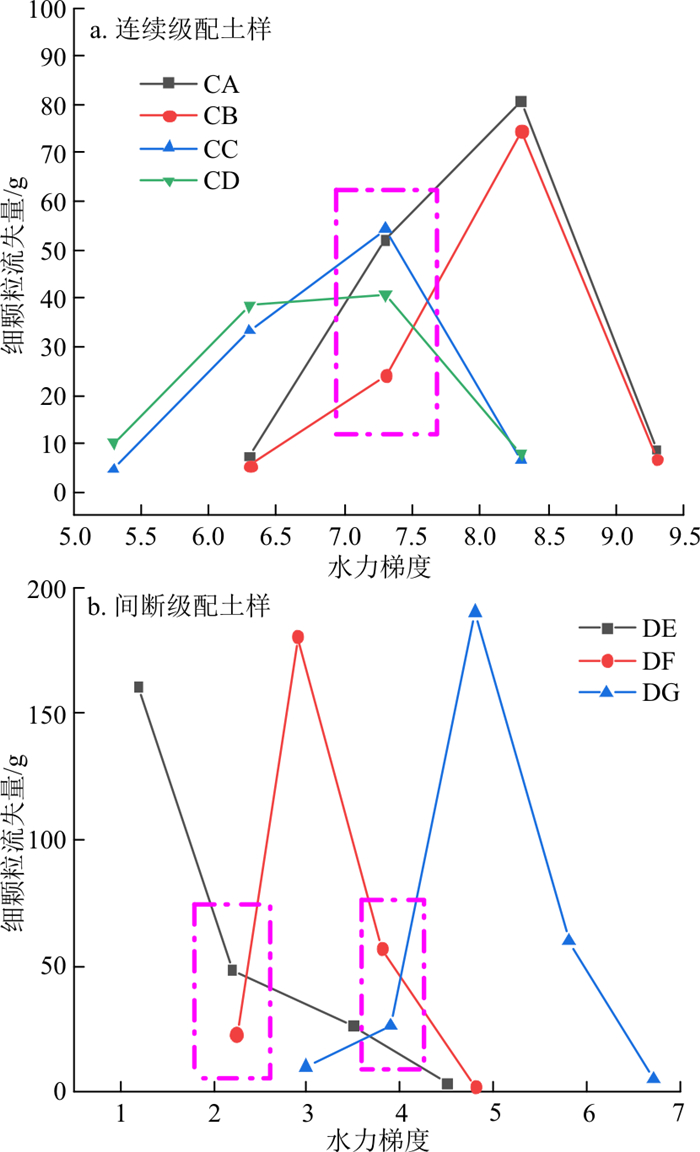
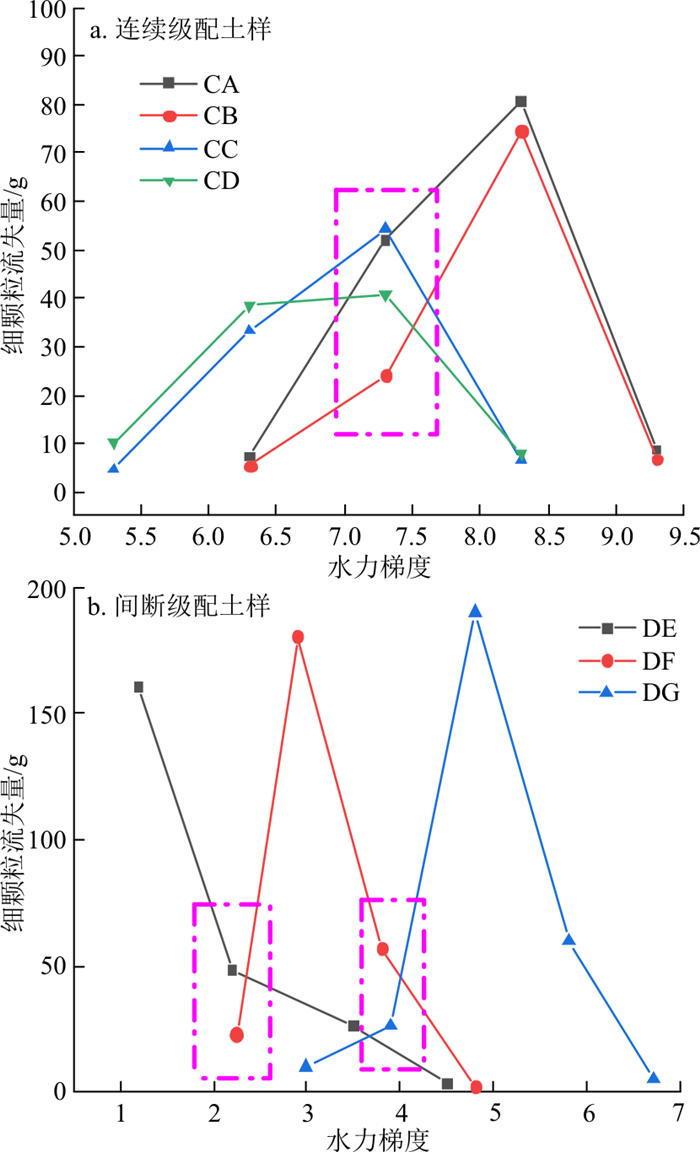
试验结束后对收集筒内的各组颗粒流失情况进行了统计, 图 11-a为CA、CB、CC、CD 4组连续级配土样在各水力梯度下细颗粒流失量的对比图;图 11-b为DE、DF、DG 3组间断级配土样在各水力梯度下细颗粒流失量的对比图。
由图 11可知, 在未发生管涌的连续级配土样中, 试样CA发生局部侵蚀的水力梯度为7.3, 试样CD为5.3。发生管涌的间断级配土样中, 试样DG发生管涌的临界水力梯度为4.9, 试样DF为2.9, 试样DE为1.2。随着细颗粒总含量和不均匀系数的减小, 侵蚀总量也在不断减少, 发生侵蚀的水力梯度也在变小。
由图 11-a可以发现, 当水力梯度为7.3时, 试样CA与CB刚开始侵蚀, 而试样CC、CD已到了侵蚀过程末尾, 由于起始时间的不同, 当水力梯度为7.3时, 各试样的侵蚀情况也不同。试样CA、CB由于细颗粒含量高于试样CC、CD, 试样CA、CB颗粒间接触面积相较试样CC、CD更大, 咬合程度更高, 故发生侵蚀的水力梯度比细颗粒含量少的试样CC、CD更高。而试样CA由于细颗粒含量略高于试样CB, 故当水力梯度为7.3时, 侵蚀开始阶段试样CA的颗粒流失量也高于试样CB。
图 11-b中, 由于试样DG和DF的细颗粒含量高于试样DE, 在水力梯度为2.3左右时, 试样DG和DF刚开始发生侵蚀, 故颗粒流失量相较于水力梯度为2.9管涌发生时少, 而试样DE在水力梯度为2.5时就已处于管涌中期, 颗粒流失量随着水力梯度的增大呈下降趋势, 虽然细颗粒含量逐渐减小, 但因其发生管涌, 细颗粒流失严重, 故在水力梯度为2.5时, 其流失量高于还未发生管涌的试样DF和DG。试样DG相较于试样DF细颗粒含量更多, 颗粒之间咬合更紧密, 故试样DG比试样DF在水力梯度为2.3时更稳定, 颗粒侵蚀量比试样DF更少。
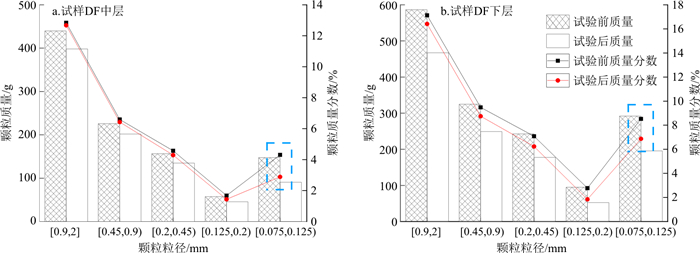
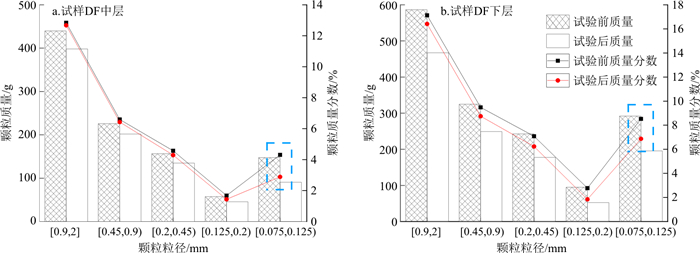
由图 11-a,b对比可知, 发生管涌破坏的间断级配试样的细颗粒流失量明显多于未发生管涌破坏的连续级配试样, 这主要是由于间断级配土样由于粒径缺失, 细颗粒更容易在粗颗粒骨架中移动, 管涌发生后, 底部细颗粒迅速流失而形成管涌通道, 中部细颗粒在水头作用下进入底部, 通过底部管涌通道冲出, 所以流失的细颗粒相对于连续级配试样也会更高。为了进一步研究反粒序砂土体渗流过程中细颗粒流失情况, 试验结束后对土样进行了开挖筛分。由于未发生管涌的连续级配土样未发生颗粒跃层现象, 故不对其进行筛分讨论, 仅对发生管涌的破坏土样进行了筛分, 图 12为试样DF中下层试验前后各粒径颗粒质量流失情况。
反粒序砂土体的颗粒运移情况与普通砂土体有很大差异。普通砂土体由于上下级配较均匀, 其顶部流失区中细颗粒流失量最大, 底部流失区细颗粒流失量次之, 中部均匀区细颗粒流失量最小[29-31]。但是反粒序砂土体由于上层中层的细颗粒含量本身就很少, 尤其上层细颗粒含量占比极少, 故其中层并不能得到上层细颗粒的补充。由图 12可知, 下层细颗粒流失量最多, 因为下层处于渗流下游, 水力梯度更大的作用导致细颗粒更容易流失。无论是中层还是下层, 在流失的颗粒中, 粒径[0.075, 0.125) mm之间的细颗粒为主要流失颗粒, 粒径[0.125, 0.2) mm的流失量次之, 原因在于其粒径越小, 越容易在孔隙中迁移, 故其流失量相较其他粒径也会越多。
2.2 水力梯度和渗流系数分析
以连续级配试样CA、CD和间断级配试样DE、DF、DG为例, 分析试样平均水力梯度和渗流系数的变化规律。
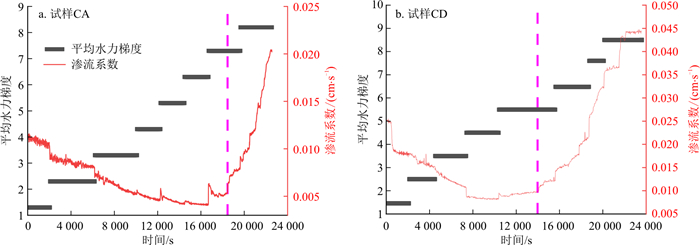
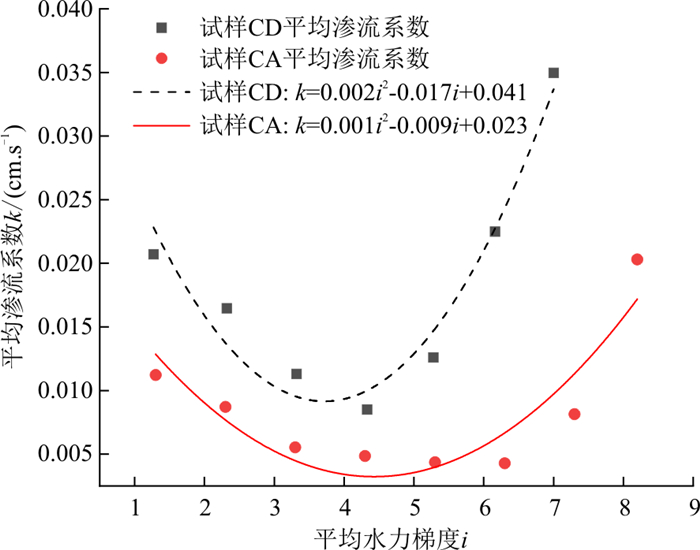
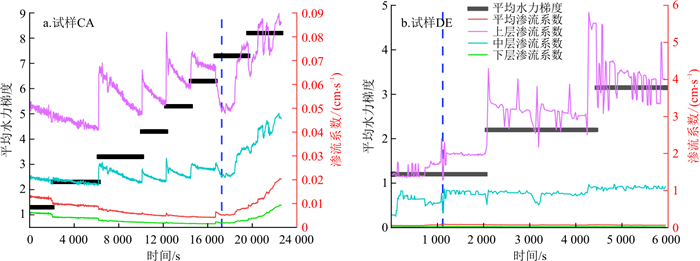
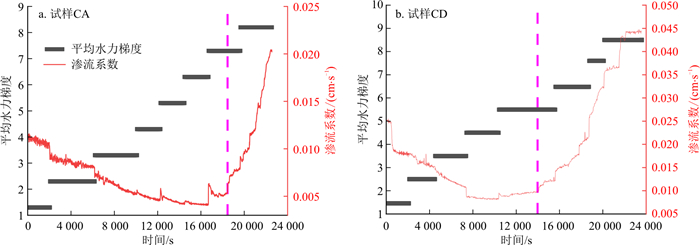
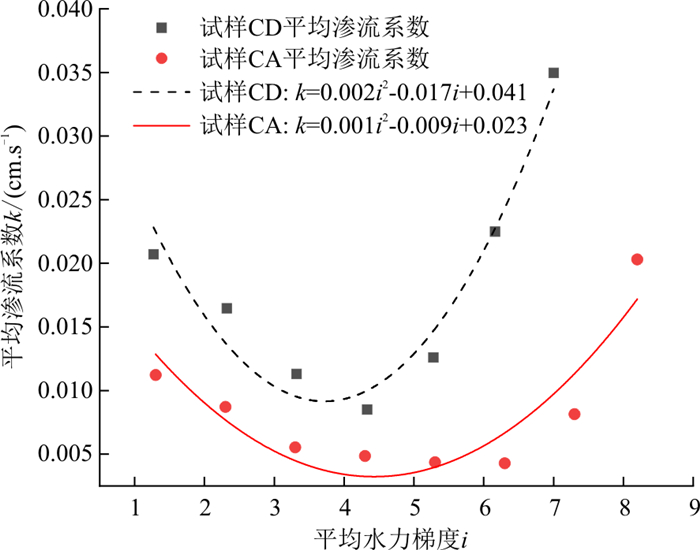
由图 13可知, 两组连续级配试样CA和CD中, 随着水力梯度的不断提高, 试样的渗流系数先呈逐渐减小趋势, 后迅速升高。试样CA于水力梯度i≤5.3时, 渗流系数减小的速率较快, i=6.3时, 渗流系数减小速率逐渐变缓, i=7.3时, 渗流系数开始升高。试样CD于i≤3.3时, 渗流系数减小的速率较快, i=4.3时, 渗流系数减小速率逐渐变缓, i=5.3时, 渗流系数开始升高。由图 14可以看出, 在连续级配试样中, 渗流系数和水力梯度呈现二次函数关系, 临界侵蚀启动的水力梯度为二次函数最低点, 即在临界侵蚀启动的水力梯度之前渗流系数随着水力梯度的增加而下降, 侵蚀启动后渗流系数随着水力梯度的增加而升高。渗流系数出现先减小后增大的原因是在低水力梯度下, 土样内部较为松散, 起始渗流系数较大, 随着时间和水力梯度的增大, 土样孔隙在水压力作用下被压缩, 且细颗粒逐渐将土样内部孔隙堵塞, 土样变得较为密实, 渗流系数逐渐减小。继续提高水头后, 底部细颗粒被侵蚀流出, 土样内部孔隙增大, 渗流系数逐渐增大。
由图 13-a, b和图 14对比可以看出, 试样CA渗流系数开始升高的水力梯度明显大于试样CD, 即试样CA渗流系数和水力梯度的二次函数顶点横坐标大于试样CD。这是由于试样CA因其较高的细颗粒含量, 粗颗粒骨架被细颗粒填充得更密实, 在水力梯度较小的情况下, 水流拖拽力无法使细颗粒发生运移, 故在水力梯度为5.3时, 细颗粒含量较少的试样CD已达到侵蚀启动的水力梯度, 细颗粒侵蚀流失, 渗流系数变大, 而试样CA此时仍处于压缩状态, 渗流系数继续减小, 直到水力梯度为7.3时, 侵蚀启动, 渗流系数开始增大。
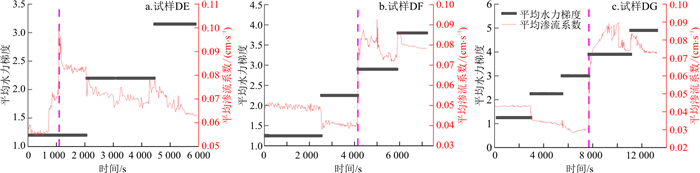
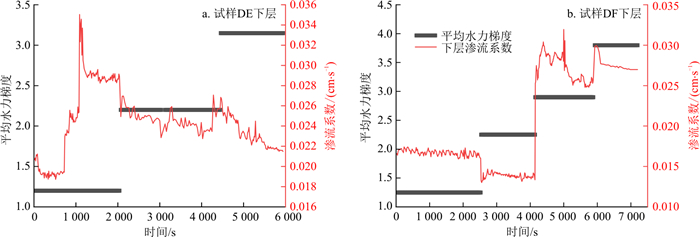
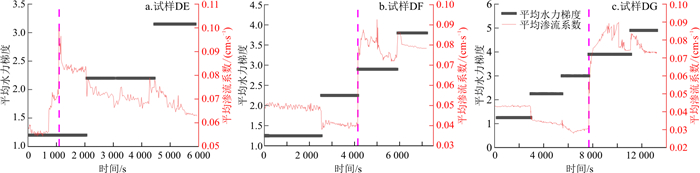
由图 15可知, 3个间断级配试样中, 试样DF和DG随着水力梯度不断提高, 试样的渗流系数仍然呈先逐渐减小趋势, 但试样DF和DG分别在水力梯度i=2.9和i=3.9时, 渗流系数突增, 这是由于底部和中部细颗粒大量涌出, 土体发生管涌破坏, 土体颗粒间孔隙增大, 透水性增强。试样DE在i=1.2时便出现管涌现象, 土体稳定性降低。但随着时间延长和水力梯度的增大, 试样DF和DG的渗流系数在突增后开始下降, 这是因为在水头作用下, 底层管涌通道被中层侵蚀掉落的细颗粒填充, 土体孔隙率开始减小, 透水性变差。
图 15-a与图 15-b,c的区别在于, 图 15-a中, 试样DE渗流系数几乎没有减小便陡增, 但图 15-b, c试样DF和DG的渗流系数仍然呈先减小后增大的变化, 其原因在于, 试样DE因缺乏中间粒径的颗粒且细颗粒含量较少, 细颗粒已无法将土样内部孔隙堵塞, 在水流拖拽力作用下直接被侵蚀带走, 故渗流系数直接增大。由此可见, 在低水头下, 细颗粒含量较少的试样DE相较细颗粒含量较高的试样DF、DG更容易发生颗粒侵蚀。
由图 13和图 15可知, 无论是间断级配试样还是连续级配试样, 随着细颗粒含量和不均匀系数的增加, 渗流系数开始升高时对应的水力梯度也在增大, 其原因在于, 细颗粒含量越多, 土体密实程度越高, 细颗粒能够进行迁移的孔隙直径越小, 故所需要的侵蚀启动的水力梯度越大。
通过渗流系数与土颗粒流失量的统计分析可以发现, 由于试样内部细颗粒迁移堵塞渗流通道或者细颗粒直接被侵蚀流失, 导致孔隙率发生波动变化, 因此渗流系数和细颗粒的侵蚀量也是同步变化的。
2.3 颗粒迁移分析
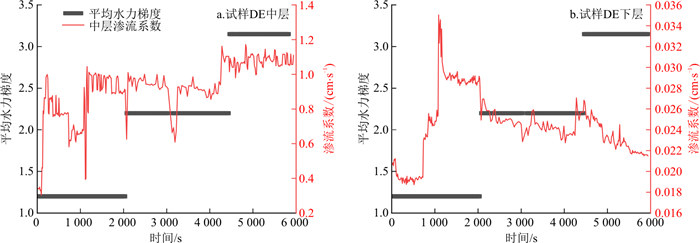
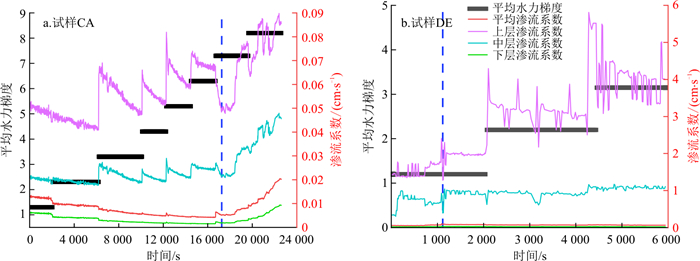
朱秦等[13]认为, 渗流系数增大, 细颗粒主要发生剥离运移;渗流系数减小, 细颗粒主要发生沉淀。为研究土样各层的颗粒迁移情况, 在平均渗流系数的基础上, 引入了局部渗流系数, 根据收集到的上中下3层的孔隙水压力计数值, 计算出上中下3层的局部渗流系数。以连续级配试样CA和间断级配试样DE为例, 得到各层渗流系数与平均渗流系数的变化图(图 16)。
由图 16可知, 侵蚀未发生之前(试样CA为17 200 s之前, 试样DE为1 100 s之前), 各层渗流系数虽然数值不同, 但变化趋势、曲线形状是相同的;侵蚀发生之后, 平均渗流系数与下层渗流系数曲线形状仍然相同, 且逐渐变大;试样上层由于细颗粒含量极少, 侵蚀过程中水流在上层试样中会呈现紊流状态, 故孔隙水压力不稳定, 渗流系数波动变化很大。在连续级配试样CA中, 颗粒发生沉淀-剥离的迁移模式, 沉淀过程中下部细颗粒层孔隙在水头作用下体积不断压缩, 细颗粒在迁移过程中被下层土体孔隙不断截留, 形成致密层, 进而影响整体平均渗流系数。随着水力梯度的不断增大, 到达临界水力梯度时, 细颗粒被侵蚀出土体, 孔隙率增大, 渗流系数不断增大。而在间断级配试样DE中, 颗粒发生剥离的迁移模式, 底部细颗粒在水头作用下被侵蚀出试样下表面, 形成管涌通道, 中部细颗粒于底部管涌通道涌出, 渗流系数不断增大。故在反粒序级配中, 整体平均渗流系数主要取决于底部的渗流能力。
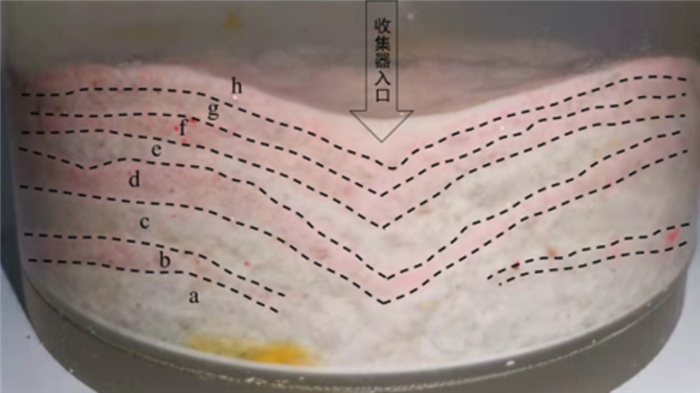
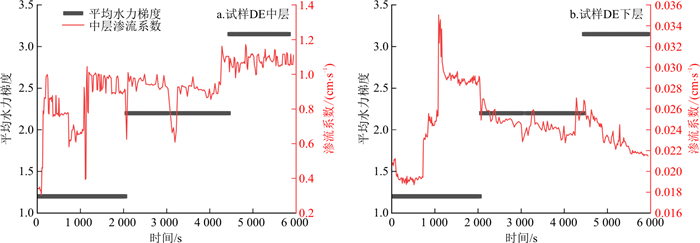
如图 17所示, 发生管涌的间断级配试样, 其各层渗流系数在发生管涌之后呈波动变化, 原因在于, 底部和中部的细颗粒发生剥离-沉淀-剥离-沉淀交替出现的现象, 由收集筒中收集到的颗粒流失情况也可证实这一点(图 18)。
当达到侵蚀启动的水力梯度时, 下层细颗粒最先被侵蚀剥离, 且侵蚀持续时间较长, 故图 18中a层细颗粒收集厚度较其他层更厚, 此时由于底部细颗粒流失, 加之顶部水头作用, 中层细颗粒开始剥离并向下层迁移。中层细颗粒在下层流失颗粒形成的粗孔隙中移动, 当迁移至出口处时, 颗粒进入收集筒内, 如图 18中b层所示, 但因下层此时孔隙较小, 故仅有很少中层细颗粒能够迁移流失。由于中层颗粒填充了部分下层颗粒流失形成的孔隙, 且部分下层孔隙在水头作用下被压缩, 导致下层孔隙体积逐渐减小, 此时土样处于沉淀阶段。随着渗流时间的增加和水流拖拽, 底部细颗粒继续被侵蚀剥离, 继续形成侵蚀通道, 中层细颗粒继续剥离流失, 由于下层细颗粒流失量增加, 细颗粒含量减少, 颗粒间咬合能力减弱, 故此次侵蚀通道形成的时间较短, 通道孔径较上一阶段增大, 所以图 18中c层较a层厚度减小, d层较b层厚度增加。中层流失颗粒继续填充通道, 土样继续沉淀。剥离、沉淀过程重复交替, 直至中层颗粒无法填充侵蚀通道, 继续增加水头无颗粒流失。
间断级配试样DE、DF的区别在于下层颗粒级配不同, 试样DE的细颗粒质量分数为40%, 试样DF细颗粒质量分数为45%。绘制两组下层土体的渗流系数变化曲线(图 19), 发现试样DE渗流系数发生突变的水力梯度要小于细颗粒质量分数为45%的试样DF。当细粒质量分数为45%时, 由于水头作用, 细颗粒在粗颗粒骨架中沉淀, 继续提高水头, 达到临界水力梯度, 细颗粒沉淀阻塞处被冲破贯通, 细颗粒大量涌出, 管涌路径形成, 渗流系数陡增。而当细粒质量分数为40%时, 细颗粒含量较少导致试样的可压缩性不大, 细颗粒不足以填充粗骨架颗粒之间的孔隙, 颗粒之间咬合程度较小, 试样压缩变形已经不能作为阻挡细颗粒流出的主要因素, 在低水头作用下, 水流的拖拽力直接冲破土体的平衡状态, 细颗粒直接发生大量流失, 导致土样不稳定。故下层细颗粒含量是影响反粒序土体内部稳定的重要因素。
与普通砂土体不同的是, 反粒序级配由于细颗粒含量自上而下增加, 上层施加的水头在中上层的水头损失很小, 作用于下层的水头相对也更大, 故与普通间断土样趋于稳定的35%细颗粒质量分数相比, 反粒序级配土样则需要更多的细颗粒含量填充孔隙以承受水流拖拽力, 所以在反粒序砂土体中, 当下层细颗粒质量分数超过45%时, 土样才呈现沉淀再剥离模式, 逐渐趋于稳定。
3. 结论
(1) 在反粒序堆积土样中, 细颗粒含量越多, 不均匀系数越大, 则侵蚀启动的水力梯度越大, 起始渗流系数越小;在连续级配土样中, 水力梯度与渗流系数呈二次函数关系;且细颗粒流失量与渗流系数是同步增长的。
(2) 反粒序砂土体发生管涌颗粒跃层后, 其下层细颗粒流失量最大, 且在流失的细颗粒中, 粒径0.075~0.125 mm的颗粒因其粒径最小, 故流失比最大。
(3) 反粒序堆积体整体渗流能力主要取决于底部的渗流系数, 而底部渗流能力主要取决于底部的细颗粒含量。在间断级配堆积土样中, 当中上层颗粒含量一定、底部颗粒中细颗粒质量分数达到45%以上时, 土样才开始发生沉淀, 趋于稳定。
(4) 反粒序堆积体发生管涌时, 其颗粒内部迁移模式为剥离-沉淀-剥离-沉淀中下层颗粒交替侵蚀过程。
-
图 1 反粒序堆积结构示意图[3]
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the structure of inverse grading accumulation
图 3 易贡滑坡堆积体竖向级配曲线[20]
Figure 3. Vertical grading curve of the Yigong landslide accumulation body
图 4 连续级配方程拟合的易贡滑坡堆积体级配曲线[20]
Figure 4. Grading curve of the Yigong landslide accumulation body fitted by the continuous gradation equation
图 5 牛圈沟滑坡碎屑堆积体竖向级配曲线[3]
Figure 5. Vertical grading curve of the debris accumulation body in the Niu Juangou landslide
表 1 颗粒级配特征
Table 1. Particle gradation characteristics
试样名称 有效粒径d10/ mm d30/ mm 限制粒径d60/ mm 不均匀系数Cu 曲率系数Cc CA A1 0.161 0.707 2.516 15.63 1.23 A2 0.109 0.499 1.813 16.63 1.26 A3 0.096 0.356 1.189 12.39 1.11 CB B1 0.213 0.851 2.802 13.15 1.21 B2 0.148 0.603 2.060 13.92 1.19 B3 0.122 0.434 1.371 11.24 1.13 CC C1 0.265 0.994 3.100 11.70 1.20 C2 0.187 0.720 2.320 12.41 1.19 C3 0.148 0.512 1.553 10.49 1.14 CD D1 0.330 1.150 3.387 10.26 1.18 D2 0.239 0.851 2.568 10.74 1.18 D3 0.187 0.603 1.735 9.28 1.12 DE E1 0.830 6.620 12.100 14.58 4.36 E2 0.407 2.000 10.676 26.23 0.92 E3 0.196 1.232 9.069 46.27 0.85 DF F1 0.830 6.620 12.100 14.58 4.36 F2 0.407 2.000 10.676 26.23 0.92 F3 0.158 1.000 8.258 52.27 0.77 DG G1 0.830 6.620 12.100 14.58 4.36 G2 0.407 2.000 10.676 26.23 0.92 G3 0.137 0.854 7.344 53.69 0.73 -
[1] 程谦恭, 张倬元, 黄润秋. 高速远程崩滑动力学的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 山地学报, 2007, 25(1): 72-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.01.007Cheng Q G, Zhang Z Y, Huang R Q. Study on dynamics of rock avalanches: State of the art report[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2007, 25(1): 72-84(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.01.007 [2] Heim A. Landslides and human lives[M]. Vancouver, B C: Bitech Publishers, 1932: 93-94. [3] 王玉峰, 程谦恭, 朱圻. 汶川地震触发高速远程滑坡-碎屑流堆积反粒序特征及机制分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(6): 1089-1106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.06.002Wang Y F, Cheng Q G, Zhu Q. Inverse grading analysis of deposit from rock avalanches triggered by Wenchuan Earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics Engineering, 2012, 31(6): 1089-1106(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.06.002 [4] Zhou J, Cui P, Yang X. Dynamic process analysis for the initiation and movement of the Donghekou landslide-debris flow triggered by the Wenchuan Earthquake[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 76: 70-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.08.007 [5] Strom A L. Mechanism of stratification and abnormal crushing of rockslide deposits[C]//Anon. Proc. 7th International IAEG Congress. Balkema Rotterdam: [s. n.], 1994: 1287-1295. [6] Bertran P. The rock-avalanche of February 1995 at Claix(French Alps)[J]. Geomorphology, 2003, 54(3): 339-346. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S0169555X03000412&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1470975285&md5=17f573dacfb8e7d07f3ee1d73e522861 [7] Cruden D M, Hungr O. The debris of the frank slide and theories of rockslide-avalanche mobility[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1986, 23(3): 425-432. doi: 10.1139/e86-044 [8] 邹志文, 李辉, 徐洋, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷下三叠统百口泉组扇三角洲沉积特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2): 20-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502004.htmZhou Z W, Li H, Xu Y, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of the Baikouquan Formation, Lower Triassic in the Mahu Depression, Junggar Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(2): 20-26(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502004.htm [9] 刘自亮, 王多云, 李凤杰, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西峰油田主要储层砂体的成因与演化[J]. 地质科技情报, 2008, 27(2): 68-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200802013.htmLiu Z L, Wang D Y, Li F J, et al. Genetic and evolution of main reservoir sand bodies in Xifeng Oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2008, 27(2): 68-72(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200802013.htm [10] 叶茂松, 解习农, 黄灿. 陆相坳陷湖盆斜坡带层序格架下沉积模式及隐蔽圈闭勘探: 以准噶尔盆地车排子凸起春光油田白垩系为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2014, 33(4): 149-158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201404023.htmYe M S, Xie X N, Huang C. Depositional models and subtle trap exploration under sequence stratigraphic framework in slope belt of continental lacustrine depression basin: An example as Chunguang Cretaceous Oilfiled in Chepaizi area, Junggar Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2014, 33(4): 149-158(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201404023.htm [11] 王志兵, 汪稔, 胡明鉴, 等. 颗粒运移对蒋家沟土体渗透性影响的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2011, 32(7): 2017-2024. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.07.017Wang Z B, Wang R, Hu M J, et al. Effects of particle transport characteristics on permeability of soils from Jiangjiagou ravine[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(7): 2017-2024(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.07.017 [12] 袁涛, 蒋中明, 刘德谦, 等. 粗粒土渗透损伤特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(4): 1311-1316, 1336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201804022.htmYuan T, Jiang Z M, Liu D Q, et al. Experiment on the seepage damage coarse grain soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(4): 1311-1316, 1336(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201804022.htm [13] 朱秦, 苏立君, 刘振宇, 等. 颗粒迁移作用下宽级配土渗透性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(1): 125-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202101014.htmZhu Q, Su L J, Liu Z Y, et al. Study of seepage in wide-grading soils with particles migration[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(1): 125-134(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202101014.htm [14] Xiao M, Shwiyhat N. Experimental investigation of the effects of suffusion on physical and geomechanic characteristics of sandy soils[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2012, 35(6): 104594. doi: 10.1520/GTJ104594 [15] 常东升, 张利民. 土体渗透稳定性判定准则[J]. 岩土力学, 2011, 32(增刊1): 253-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2011S1045.htmChang D S, Zhang L M. Internal stability criteria for soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(S1): 253-259(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2011S1045.htm [16] Andrianatrehina L, Hanène Souli, Joël R, et al. Analysis of the internal stability of coarse granular materials according to various criteria[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2015, 20(8): 936-953. doi: 10.1080/19648189.2015.1084385 [17] Chang D S, Zhang L M. A stress-controlled erosion apparatus for studying internal erosion in soils[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2011, 34(6): 579-589. [18] Luzio E D, Bianchi-Fasani G, Esposito C, et al. Massive rock-slope failure in the Central Apennines(Italy): The case of the Campo di Giove rock avalanche[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2004, 63(1): 1-12. [19] 彭双麒. 滑坡-碎屑流堆积体粒度分布研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2020.Peng S L. The study for grain size distribution of rock avalanche deposit[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu Univerisity of Technology, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [20] 林小龙. 高速远程滑坡颗粒组构特征与竖向分带研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2019.Lin X L. Study on debris composition and related effects on vertical grading of rock avalanche deposits[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [21] Hungr D. The debris of the frank slide and theories of rockslide-avalanche mobility[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1986, 23(3): 425-432. [22] Wang Y F, Cheng Q G, Yuan Y Q, et al. Emplacement mechanisms of the Tagarma rock avalanche on the Pamir-western Himalayan syntaxis of the Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17(3): 527-542. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01298-1 [23] Strom A L. Rock avalanches of the Ardon River valley at the southern foot of the Rocky Range, Northern Caucasus, North Osetia[J]. Landslides, 2004, 1(3): 237-241. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000034488404010_f20e.html [24] 朱俊高, 郭万里, 王元龙, 等. 连续级配土的级配方程及其适用性研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(10): 1931-1936. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201510029.htmZhu J G, Guo W L, Wang Y L, et al. Equation for soil gradation curve and its applicability[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(10): 1931-1936(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201510029.htm [25] 于际都, 刘斯宏, 王涛, 等. 间断级配粗粒土压实特性试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(11): 2142-2148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201911024.htmYu J D, Liu S H, Wang T, et al. Experimental research on compaction characteristics of gap-graded coarse-grained soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(11): 2142-2148(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201911024.htm [26] Liang Y, Yeh T, Zha Y, et al. Onset of suffusion in gap-graded soils under upward seepage[J]. Soils and Foundations-Tokyo, 2017, 57(5): 849-860. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040110924210_c00c.html [27] 朱韶茹, 潘梽橼, 杨丽平, 等. 土力学与地基基础[M]. 南京: 东南大学出版社, 2017.Zhu S R, Pang Z Y, Yang L P, et al. Soil mechanics and foundation[M]. Nanjing: Southeast University Press, 2017(in Chinese). [28] Andrianatrehina L, Souli H, Rech J, et al. Analysis of the internal stability of coarse granular materials according to various criteria[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2016, 20(8): 936-953. [29] 田大浪, 谢强, 宁越, 等. 间断级配砂砾石土的渗透变形试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2020, 41(11): 3663-3670. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202011017.htmTian D L, Xie Q, Ning Y, et al. Experimental investigation on seepage deformation of gap-graded sand-gravel soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(11): 3663-3670(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202011017.htm [30] 赵军, 闫文雯, 徐通, 等. 朝阳沟阶地扶杨油层微观孔隙结构及渗流机理分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 194-206. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0111Zhao J, Yan W W, Xu T, et al. Microscopic pore structure and seepage mechanism of Fuyang oil reservoir in Chaoyanggou Terrace[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 194-206(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0111 [31] 唐军峰, 唐雪梅, 肖鹏, 等. 库水位升降与降雨作用下大型滑坡体渗流稳定性分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 153-161. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0409Tang J F, Tang X M, Xiao P, et al. Analysis of seepage stability of large-scale landslide under water-level fluctuation and rainfall[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 153-161(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0409 期刊类型引用(5)
1. 董辉,谭凤鸣,程子华,高乾丰,任佳展. 砂砾土渗流侵蚀中细粒迁移-沉积-滤通的物理水力临界条件. 水文地质工程地质. 2024(01): 69-81 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 杨忠平,李勇华,李诗琪,刘浩宇,高宇豪. 不同含石率土石混合体水力侵蚀分异特征及机制. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2024(01): 133-145 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 朱艳. 邹城地区黏土体-结构面接触渗透下渗流侵蚀试验研究. 广东水利水电. 2024(08): 20-24 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 李诗琪,杨忠平,刘浩宇,高宇豪,刘新荣. 考虑间断级配影响的土石混合体水力侵蚀分异机理. 土木工程学报. 2024(10): 125-134 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 刘世成,王运生,宋良. 四川茂县叠溪堰塞坝溃决的实验研究. 山地学报. 2024(05): 672-684 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载:
















 下载:
下载:





 百度学术
百度学术