A new method for restoration of sedimentary paleogeomorphology based on lithofacies and geochemistry: A case study of the Qixia Formation in central Sichuan
-
摘要:
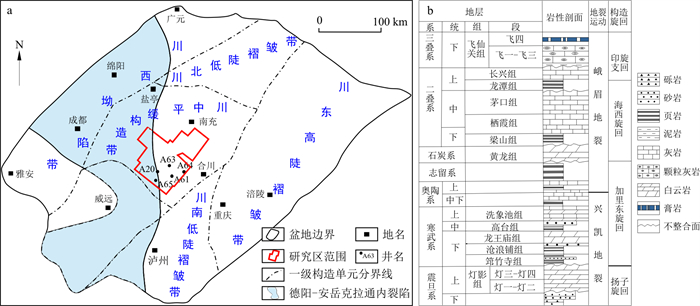
四川盆地二叠系栖霞组沉积古地貌对碳酸盐岩储层的展布和演化具有一定的控制作用。恢复并刻画川中高石梯地区沉积古地貌, 可以进一步认识该区域有利沉积相展布规律、预测优质储层的分布。在明确了三级层序划分的基础上, 利用地球化学元素比值、岩石学标志和测井标志在层序内建立了高分辨率层序地层格架, 识别出两种沉积微相: 滩核和滩翼; 计算了层序内地层厚度差异, 识别出不同类型的沉积序列, 计算了滩核/滩翼厚度比值以及Fe/Mn比值、MgO/Al2O3比值等地球化学参数。分析上述参数在平面上的特征并进行叠合, 恢复了研究区栖霞组沉积时期的古地貌特征。研究结果表明: 栖一段古地貌在西北部和南部较高, 在中部较低, 古地貌落差明显; 栖二段古地貌高地分布在研究区中部, 西部古地貌较低, 古地貌整体差异不大。根据古地貌恢复结果, 高石梯-磨溪地区在北东-南西方向形成浅水环带区, 发育颗粒滩, 南部发育局部微正向构造, 同样发育颗粒滩, 但微正向构造分布有限, 颗粒滩延伸范围因此受限, 未来勘探开发应围绕北东-南西方向的颗粒滩发育区域进行。
Abstract:Objective The sedimentary palaeogeomorphology of the Permian Qixia Formation in Sichuan Basin has key influence over the distribution and evolution of carbonate reservoirs. Restoring and characterizing the sedimentary palaeogeomorphology of Gaoshiti area can gain further understanding of the distribution of favorable sedimentary facies and predict the distribution of high-quality reservoirs.
Methods Based on the division of the third-order sequence, the high-resolution sequence stratigraphic framework was established by using geochemical proxies, petrological markers and logging markers. Two kinds of sedimentary microfacies, i.e. beach core and beach wing, were also identified. In addition, this study has calculated the difference of layer thicknesses in the sequence, and has identified different types of sedimentary sequences. A number of values including the beach core/beach wing value, Fe/Mn and MgO/Al2O3 ratios and other geochemical parameters were also calculated. The characteristics of the above parameters on the plane are analyzed and re-evaluated, which are all used to restore the palaeogeomorphic characteristics of the sedimentary period of the Qixia Formation in the study area.
Results The result of research shows that the palaeogeomorphic characteristics of the 1st Member of Qixia are higher in the northwest and south, lower in the middle, and the palaeogeomorphic drop is obvious. Our new results show that the palaeogeomorphic highlands of the 2nd Member of Qixia are distributed in the middle of the study area, that the western palaeogeomorphology is low, and that the overall difference of palaeogeomorphology is small.
Conclusion According to the results of ancient landform restoration, Gaoshiti-Moxi area forms a shallow water ring zone in the northeast-southwest direction where granular shoals are developed. Local micro-positive structures and granular shoals are developed in the south. However, the distribution of micro-positive structures is so limit that the extension range of granular shoals is limit. This study highlights that future exploration and development should focus on the development area of granular shoals in the northeast-southwest direction.
-
Key words:
- sedimentary paleogeomorphology /
- Qixia Formation /
- sedimentary sequences /
- lithofacies /
- geochemistry
-
表 1 川中高石梯-磨溪地区沉积相划分
Table 1. Classification of sedimentary facies in Gaoshiti-Moxi, central Sichuan
沉积相 沉积亚相 沉积微相 岩石类型 碳酸盐岩缓坡 中-浅水缓坡 颗粒滩 晶粒白云岩、颗粒白云岩、亮晶砂屑灰岩、微亮晶球粒灰岩 滩间海 深灰色泥晶生屑灰岩 深水缓坡 缓坡灰泥 泥晶灰岩、硅质灰岩 表 2 高石梯地区部分井栖霞组地层厚度
Table 2. Stratigraphic thickness of parts of the Qixia Formation in Gaoshiti area
地层厚度/m 井名 栖一段 栖二段 栖霞组 A66 61.614 44.921 106.535 A67 60.589 43.411 104.000 A68 57.842 41.080 98.922 A69 65.570 44.040 109.610 A70 62.076 40.966 103.042 A71 50.913 40.030 90.943 A72 52.696 40.522 93.218 A73 60.680 45.320 106.000 A74 63.595 43.460 107.055 A75 64.966 42.162 107.128 A76 65.996 42.976 108.972 A77 62.840 45.160 108.000 A78 60.933 43.067 104.000 A79 63.685 42.915 106.600 A80 64.555 42.845 107.400 A81 63.583 41.361 104.944 A82 66.900 44.000 110.900 A83 67.001 44.799 111.800 表 3 高石梯地区部分井栖霞组滩核、滩翼厚度及其厚度比值
Table 3. Thickness and relative ratios of core and wing of parts of the Qixia Formation in Gaoshiti area
井号 栖一滩核厚度/m 栖一滩翼厚度/m 栖一段滩核/滩翼厚度比值 栖二滩核厚度/m 栖二滩翼厚度/m 栖二段滩核/滩翼厚度比值 A50 17.405 24.993 0.696 13.200 29.818 0.443 A51 18.795 28.826 0.652 17.100 29.351 0.583 A56 24.155 29.022 0.832 13.830 29.476 0.469 A57 17.779 20.456 0.869 14.941 25.000 0.598 A58 23.048 25.200 0.915 17.968 28.256 0.636 A59 28.994 29.826 0.972 13.748 28.544 0.482 A61 26.612 24.568 1.083 13.516 34.103 0.396 A64 16.455 23.680 0.695 23.460 34.410 0.682 A66 21.865 29.064 0.752 15.665 29.256 0.535 A67 29.860 20.469 1.459 15.220 28.191 0.540 A72 19.100 25.051 0.762 14.450 26.072 0.554 A74 25.165 27.695 0.909 16.475 26.985 0.611 A77 28.630 23.270 1.230 17.300 27.860 0.621 A80 34.675 17.445 1.988 11.690 31.155 0.375 A90 33.168 42.708 0.777 17.576 4.024 4.368 A105 33.538 16.062 2.088 23.369 20.210 1.156 A111 16.990 34.623 0.491 22.372 16.315 1.371 A112 20.565 26.465 0.777 9.435 32.332 0.292 表 4 高石梯-磨溪地区部分井Fe/Mn比值
Table 4. Fe/Mn ratio of some wells in the Gaoshiti-Moxi area
井号 层位 Fe/Mn 井号 层位 Fe/Mn A59 栖一段 32.35 A63 栖二段 57.96 A63 栖一段 20.00 A67 栖二段 50.72 A67 栖一段 30.57 A68 栖二段 95.58 A68 栖一段 28.01 A72 栖二段 33.98 A73 栖一段 46.27 A73 栖二段 56.03 A105 栖一段 65.60 A112 栖二段 31.89 表 5 高石梯-磨溪地区部分井MgO、Al2O3分析数据及m值
Table 5. MgO, Al2O3 data and m value of some wells in Gaoshiti-Moxi area
井号 层位 深度/m MgO Al2O3 m wB/% A59 4 313 0.741 0.137 540.9 A63 4 236 0.630 0.153 411.8 A67 4 131 1.776 0.187 949.7 A68 栖一段 4 100 0.972 0.167 582.0 A69 3 950 1.628 0.262 621.4 A73 4 116 1.472 0.461 319.3 A105 4 150 1.134 0.943 120.3 A63 4 179 1.520 0.680 223.5 A67 4 064 0.602 0.154 390.9 A67 4 048 0.585 0.342 171.1 A72 栖二段 5 158 1.117 0.218 512.4 A73 4 051 1.462 0.651 224.6 A105 4 100 2.073 0.238 871.0 A112 4 142 0.671 0.217 309.2 注:检测方法为GB/T 3286 (1-9)-1998:石灰石、白云石化学分析方法;检测仪器为电感耦合等离子体质谱仪,Aglient Technologies7700 Series ICP-MS;检测单位为成都市东方矿产开发技术研究所。m=100×w(MgO)/w(Al2O3) -
[1] 王建国, 蒋传杰, 常森, 等. 克拉通盆地微古地貌恢复的构造趋势面转换法[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(1): 77-83, 104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201701008.htmWang J G, Jiang C J, Chang S, et al. Structural trend surface conversion method for micro-amplitude paleotopographic restoration of Cratonic basins[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(1): 77-83, 104(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201701008.htm [2] 王建民, 王佳媛, 郭德勋, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东部奥陶系风化壳岩溶古地貌与储层特征[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2013.Wang J M, Wang J Y, Guo D X, et al. Karst landform and reservoir characteristics of Ordovician weathering crust in the eastern part of Ordos Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2013(in Chinese). [3] 汪晶, 王华, 陈思, 等. 酒泉盆地青西凹陷鸭西地区古地貌对沉积体系空间展布的控制作用[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2012, 28(3): 25-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201203006.htmWang J, Wang H, Chen S, et al. Control of paleogeomorphology on sedimentary system distribution: An example from Yaxi area in Qingxi Depression, Jiuquan Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2012, 28(3): 25-33(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201203006.htm [4] 赵俊兴, 陈洪德, 向芳. 高分辨率层序地层学方法在沉积前古地貌恢复中的应用[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2003, 33(1): 76-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2003.01.013Zhao J X, Chen H D, Xiang F. The possibility of rebuilding paleogeomorphology before basin deposition by high-resolution sequence stratigraphy[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science & Technology Edition, 2003, 33(1): 76-81(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2003.01.013 [5] 王敏芳, 焦养泉, 任建业, 等. 沉积盆地中古地貌恢复的方法与思路: 以准噶尔盆地西山窑组沉积期为例[J]. 新疆地质, 2006, 28(3): 326-330. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200603024.htmWang M F, Jiao Y Q, Ren J Y, et al. Method and thinking of paleogeomorphologic reconstruction in sedimentary basin: Example from depression stage of Xishanyao Formation in Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2006, 28(3): 326-330(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200603024.htm [6] 何文军, 郑孟林, 费李莹, 等. 陆相坳陷盆地边缘沉积区古地貌恢复: 以准噶尔盆地玛湖地区三叠系百口泉组为例[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(5): 803-816. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201905008.htmHe W J, Zheng M L, Fei L Y, et al. Ancient landform restoration of marginal sedimentary area in the continental depression basin: A case study of the Triassic Baikouquan Formation in Mahu area of Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography: Chinese Edition, 2019, 21(5): 803-816(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201905008.htm [7] 左丽群. 古地貌恢复方法综述[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2019, 33(3): 12-16, 21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201903004.htmZuo L Q. Review on methods of paleo-geomorphologic restoration[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2019, 33(3): 12-16, 21(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201903004.htm [8] 赵永刚, 王东旭, 冯强汉, 等. 油气田古地貌恢复方法研究进展[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2017, 39(4): 516-529. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201704005.htmZhao Y G, Wang D X, Feng Q H, et al. Review on palaeomorphologic reconstruction methods in oil and gas fields[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2017, 39(4): 516-529(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201704005.htm [9] 杨俊杰, 张伯荣, 曾正全. 陕甘宁盆地侏罗系古地貌油田的油藏序列及勘探方法[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 1984, 3(1): 74-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK198401006.htmYang J J, Zhang B R, Zeng Z Q. Oil pool sequence and exploration methods of Jurassic paleogeomorphologic oil fields in Shaanxi-Gansu-Ningxia Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 1984, 3(1): 74-84(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK198401006.htm [10] 袁珍, 李文厚, 朱静, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区侏罗系古地貌恢复及其对石油聚集的影响[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(11): 1806-1814. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201311013.htmYuan Z, Li W H, Zhu J, et al. The restoration of Pre-Jurassic paleogeomorphology and its influence on oil accumulation in Longdong area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(11): 1806-1814(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201311013.htm [11] 邓宏文, 王红亮, 王敦则, 等. 古地貌对陆相裂谷盆地层序充填特征的控制: 以渤中凹陷西斜坡区下第三系为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2001, 22(4): 293-296, 303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200104001.htmDeng H W, Wang H L, Wang D Z, et al. Control of paleo-morphology to stratigraphic sequence in continental rift basin: Take Lower Tertiary of western slope in Bozhong Depression as an example[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2001, 22(4): 293-296, 303(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200104001.htm [12] 张银德, 周文, 邓昆, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地高桥构造平缓地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩岩溶古地貌特征与储层分布[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(3): 757-767. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201403015.htmZhang Y D, Zhou W, Deng K, et al. Paleo-geomorphology and reservoir distribution of the Ordovician karstified carbonate rocks in the structurally-gentle Gaoqiao area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(3): 757-767(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201403015.htm [13] 李树同, 张海峰, 王多云, 等. 聚油古地貌成因类型及其有利成藏条件分析: 以鄂尔多斯盆地上里塬地区前侏罗纪古地貌为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2011, 29(5): 962-969. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201105017.htmLi S T, Zhang H F, Wang D Y, et al. Genetic type of oil-gas accumulation paleogeomorphology and favorable conditions for petroleum accumulation: Taking the paleogeomorphology of Pre-Jurassic in Shangliyuan area, Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(5): 962-969(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201105017.htm [14] 李笑天, 潘仁芳, 鄢杰, 等. 四川盆地灯四段岩溶古地貌精细刻画及油气勘探意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(3): 191-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201803025.htmLi X T, Pan R F, Yan J, et al. Karst paleogeomorphology features of the Fourth Menber of Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin and the significance of oil and gas exploration[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(3): 191-195(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201803025.htm [15] 付晓燕, 杨勇, 黄有根, 等. 苏里格南区奥陶系岩溶古地貌恢复及对气藏分布的控制作用[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2014, 37(3): 1-5, 18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT201403002.htmFu X Y, Yang Y, Huang Y G, et al. Palaeomorphologic reconstruction of Ordovician karst in southern Sulige Gasfield and its effect on reservoir distribution[J]. Natural Gas Exploration & Development, 2014, 37(3): 1-5, 18(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT201403002.htm [16] 刘永涛, 刘池洋, 周义军, 等. 双界面地震层拉平的古地貌恢复技术及应用: 以鄂尔多斯盆地天环坳陷为例[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2019, 54(3): 656-666, 489-490. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ201903020.htmLiu Y T, Liu C Y, Zhou Y J, et al. Paleo-geomorphology restoration with double-interface seismic layer leveling: An example of Tianhuan Depression in Ordos Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2019, 54(3): 656-666, 489-490 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ201903020.htm [17] 庞军刚, 杨友运, 李文厚, 等. 陆相含油气盆地古地貌恢复研究进展[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2013, 33(4): 424-430. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXB201304008.htmPang J G, Yang Y Y, Li W H, et al. Study development of palaeogeomorphology reconstructions in continental facies hydrocarbon basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2013, 33(4): 424-430(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXB201304008.htm [18] 杨雪飞, 王兴志, 杨跃明, 等. 川中地区下寒武统龙王庙组白云岩储层成岩作用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(1): 35-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201501006.htmYang X F, Wang X Z, Yang Y M, et al. Diagenesis of the dolomite reservoir in Lower Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(1): 35-41(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201501006.htm [19] 梅庆华, 何登发, 文竹, 等. 四川盆地乐山-龙女寺古隆起地质结构及构造演化[J]. 石油学报, 2014, 35(1): 11-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201401002.htmMe Q H, He D F, Wen Z, et al. Geologic structure and tectonic evolution of Leshan-Longnvsi paleo-uplift in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2014, 35(1): 11-25(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201401002.htm [20] 赵宗举, 周慧, 陈轩, 等. 四川盆地及邻区二叠纪层序岩相古地理及有利勘探区带[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(增刊2): 35-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2012S2003.htmZhao Z J, Zhou H, Chen X, et al. Sequence lithofacies paleogeography and favorable exploration zones of the Permian in Sichuan Basin and adjacent areas, China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(S2): 35-51(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2012S2003.htm [21] 魏国齐, 杨威, 朱永刚, 等. 川西地区中二叠统栖霞组沉积体系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2010, 31(4): 442-448. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201004012.htmWei G Q, Yang W, Zhu Y G, et al. Depositional system of the Middle Permian Qixia Formation in the western Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2010, 31(4): 442-448(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201004012.htm [22] 张春宇, 管树巍, 吴林, 等. 塔西北地区下寒武统碳酸盐岩地球化学特征及其古环境意义: 以舒探1井为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 99-111. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0508Zhang C Y, Guan S W, Wu L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and its paleo-environmental significance of the Lower Cambrian carbonate in the northwestern Tarim Basin, A case study of Well Shutan-1[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 99-111(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0508 [23] 陈少伟, 刘建章. 含油气盆地微观裂缝脉体期次、成因与流体演化研究进展及展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 81-92. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0426Chen S W, Liu J Z. Research progress and prospects of the stages, genesis and fluid evolution of micro-fracture veins in petroliferous basins[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 81-92(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0426 [24] 杨万芹, 朱德顺, 银燕, 等. 古水深的地球化学恢复方法及在层序地层划分中的应用[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(增刊1): 756-757. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2015S1357.htmYang W Q, Zhu D S, Yin Y, et al. Geochemical restoration method of paleowater depth and its application in sequence stratigraphic division[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(S1): 756-757(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2015S1357.htm [25] 经雅丽, 张克信, 林启祥, 等. 浙江长兴煤山下三叠统和龙山组、南陵湖组沉积地球化学特征与古环境意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2005, 24(1): 35-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200501007.htmJing Y L, Zhang K X, Lin Q X, et al. Sedimentology geochemistry characteristics and paleoenvironmental meaning of Helongshan Formation and Nanlinhu Formation in Meishan, Changxing County, Zhejiang Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2005, 24(1): 35-40(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200501007.htm [26] 杨振宇, 沈渭洲, 郑连弟. 广西来宾蓬莱滩二叠纪瓜德鲁普统-乐平统界线剖面元素和同位素地球化学研究及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(1): 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200901001.htmYang Z Y, Shen W Z, Zheng L D. Elements and isotopic geochemistry of Guadalupian-Luopingian boundary profile at the Peanglaitan section of Laibin, Guangxi, and its geological implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(1): 1-15(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200901001.htm [27] 田洋, 赵小明, 王令占, 等. 重庆石柱二叠纪栖霞组地球化学特征及其环境意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(6): 1035-1045. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201406005.htmTian Y, Zhao X M, Wang L Z, et al. Geochemical characteristics and its paleoenvironmental implication of Permian Qixia Formation in Shizhu, Chongqing[J]. Acta Sedimentology Sinica, 2014, 32(6): 1035-1045(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201406005.htm [28] 柏道远, 蒋启生, 李彬, 等. 湘东北冷家溪群沉积岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 1-13. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0017Bo D Y, Jiang Q S, Li B, et al. Geochemistry and tectonic implication of the sedimentary rocks in Lengjiaxi Group in northeastern Hunan[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 1-13(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0017 [29] 魏国齐, 杨威, 万怡平, 等. 扬子地块西北缘二叠系-中三叠统层序地层与沉积相展布[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(3): 741-748. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201103014.htmWei G Q, Yang W, Wan Y P, et al. Stratigraphic sequence and sedimentary facies distributions of the Permian-Middle Triassic in the northwestern margin of the Yangtze Block[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(3): 741-748(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201103014.htm [30] 陈思聪. 川中南部二叠系栖霞组层序及沉积特征研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016.Chen S C. The study of sedimentary and sequence stratigraphy characteristics for Permian Qixia Formation of the mid-south part of Sichuan Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [31] 周进高, 姚根顺, 杨光, 等. 四川盆地栖霞组-茅口组岩相古地理与天然气有利勘探区带[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(4): 8-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201604004.htmZhou J G, Yao G S, Yang G, et al. Lithofacies palaeogeography and favorable gas exploration zones of Qixia and Maokou Fms in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(4): 8-15(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201604004.htm [32] 李凤杰, 陈荣林. 四川盆地东北地区中-下二叠统层序地层特征研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2008, 34(5): 472-477. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200805012.htmLi F J, Chen R L. Study on the Middle-Lower Permian sequence stratigraphy in northeastern area, the Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2008, 34(5): 472-477(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200805012.htm [33] 白晓亮, 郗诚, 和源, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统栖霞组层序地层特征及沉积演化模式[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2020, 44(6): 33-42, 6-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY202006004.htmBai X L, Xi C, He Y, et al. Sequence stratigraphy characteristics and sedimentary evolution model of the Middle Permian Qixia Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Northeastern Petroleum University, 2020, 44(6): 33-42, 6-7(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY202006004.htm [34] 陈辉. 川东地区下二叠统茅口组沉积古地貌恢复及岩溶储层研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2020.Chen H. The restoration of sedimentary paleogeomorphology of Maokou Formation of Lower Permian in East Sichuan and karst reservoir research[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology(in Chinese with English abstract). [35] Yu T, Liu H, Liu B W, et al. Restoration of karst paleogeomorphology and its significance in petroleum geology: Using the top of the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation in the northwestern Sichuan Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 208: 109638. -





 下载:
下载: