Paleogeomorphological restoration and its control on gravity flow sand bodies: A case study of the Chang 73 submember of the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
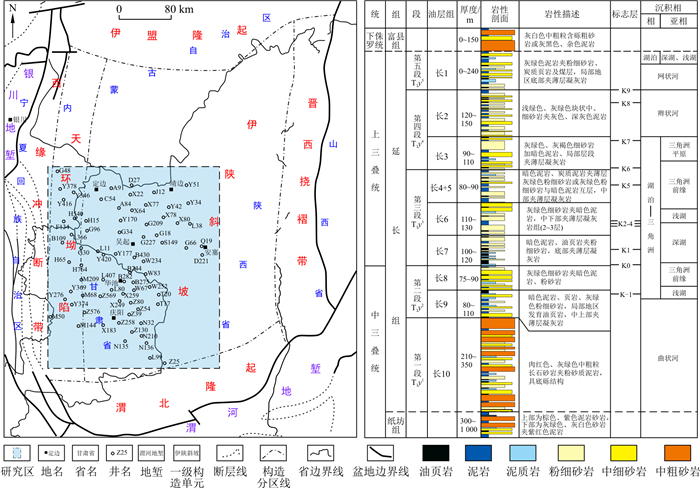
鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长73亚段沉积体系和砂体成因类型及展布特征受湖盆底部形态控制明显,不同地区砂体类型、成因及空间展布各异。根据岩心、钻井、测井等资料运用印模法与沉积学方法精确地恢复了鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长73亚段的古地貌,并对微古地貌单元进行精细刻画,在此基础上分析了古地貌对盆地延长组长73亚段沉积体系和砂体成因类型及展布特征的控制作用。研究表明:长73期古地貌整体呈东缓西陡的不对称坳陷形态,明确了研究区发育高地、坡折带、湖底深洼(凹)、湖底平原、湖底古隆、湖底古脊和古沟道7个微古地貌单元。研究区延长组长73亚段重力流沉积体系受古地貌控制较明显,从湖盆边缘至湖盆中心依次发育三角洲前缘沉积、沟道型重力流沉积、半深湖-深湖沉积,从坡折带至湖盆中央,重力流沉积类型逐渐从砂质碎屑流沉积转换为浊流沉积。古地貌形态控制着研究区延长组长73亚段重力流砂体的整体展布,而高地、坡折带及古沟道等微古地貌单元则进一步控制重力流砂体的物源方向、成因类型、运输方向、横向连通性及展布形态等。
Abstract:The bottom morphology of the lake basin controlled the sedimentary system, genetic types, and distribution characteristics of sand bodies in the Chang 73 submember of the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin. The types, genesis, and spatial distribution of sand bodies in different regions differ. In this study, according to cores, drilling, logging, and other data, the paleogeomorphology of the Chang 73 submember was accurately restored by the impression method and sedimentology method, and the micro paleogeomorphology units were finely characterized. On this basis, the authors analyze the paleogeomorphology control on the sedimentary system, genetic types, and distribution characteristics of sand bodies in the Chang 73 submember. The result shows that the paleogeomorphology of the Chang 73 period is an asymmetrical depression in the east and a steep depression in the west. Seven micro paleogeomorphic units, including the highland, the slope break zone, the lakebed deep depression, the lakebed plain, the lakebed paleouplift, the ancient lakebed ridge, and the ancient channel, are identified in the study area. The paleogeomorphology obviously controlled the gravity flow deposition system of the Chang 73 submember in the study area. From the margin to the center of the lake basin, delta front deposition, channel-type gravity flow deposition, and semideep-deep lake deposition successively developed. From the slope break zone to the center of the lake basin, the gravity flow deposition type gradually changed from sandy debris flow deposition to turbidity flow deposition. The paleogeomorphology controls the overall distribution of the gravity flow sand body in submember 73 in the study area, while the micro paleogeomorphology units such as the highland, the slope break zone, and the ancient channel further control the provenance direction, genetic type, transportation direction, lateral connectivity and distribution pattern of the gravity flow sand bodies.
-
表 1 古地貌恢复部分数据
Table 1. Data on paleogeomorphology restoration
井名 长3顶-长73底现今厚度/m 长3顶-长73底恢复厚度/m 压实厚度/m 压实率 井名 长3顶-长73底现今厚度/m 长3顶-长73底恢复厚度/m 压实厚度/m 压实率 G34 415.30 615.52 200.22 0.33 B282 444.00 680.74 236.74 0.35 G48 395.20 554.03 158.83 0.29 L407 428.20 682.24 254.04 0.37 Y378 402.00 607.68 205.68 0.34 B275 438.00 682.90 244.90 0.36 Y346 440.00 662.17 222.17 0.34 W83 451.00 688.90 237.90 0.35 Y416 413.00 645.92 232.92 0.36 B244 434.00 691.53 257.53 0.37 H540 448.00 669.87 221.87 0.33 B430 456.00 707.00 251.00 0.36 H15 436.00 652.91 216.91 0.33 W234 437.00 673.31 236.31 0.35 A84 426.00 688.04 262.04 0.38 W252 427.00 653.55 226.55 0.35 X22 413.00 595.02 182.02 0.31 X249 459.00 726.88 267.88 0.37 D27 420.80 597.29 176.49 0.30 Z80 436.00 679.40 243.40 0.36 A91 403.00 564.89 161.89 0.29 Z54 420.00 662.36 242.36 0.37 C54 436.00 672.35 236.35 0.35 T17 432.70 645.79 213.09 0.33 X77 414.00 604.82 190.82 0.32 T20 432.70 649.89 217.19 0.33 G209 415.00 618.02 203.02 0.33 Z258 418.00 656.52 238.52 0.36 G18 416.00 608.33 192.33 0.32 M144 439.80 701.33 261.53 0.37 G20 420.00 643.84 223.84 0.35 M50 412.30 663.42 251.12 0.38 G227 408.00 624.24 216.24 0.35 N135 366.70 570.32 203.62 0.36 S149 430.00 644.83 214.83 0.33 Z130 414.00 663.19 249.19 0.38 D235 450.00 633.35 183.35 0.29 N32 409.00 637.60 228.60 0.36 D221 454.00 596.93 142.93 0.24 Z39 409.40 630.25 220.85 0.35 G66 438.00 604.66 166.66 0.28 N210 430.00 665.76 235.76 0.35 Q19 434.00 572.33 138.33 0.24 N136 434.60 654.71 220.11 0.34 X80 410.00 616.89 206.89 0.34 Z25 418.00 582.90 164.90 0.28 X78 395.00 591.01 196.01 0.33 L99 447.90 666.08 218.18 0.33 Y42 409.00 598.40 189.40 0.32 M209 405.00 651.79 246.79 0.38 Y34 425.00 596.44 171.44 0.29 B109 402.20 716.93 314.73 0.44 Y51 409.00 575.16 166.16 0.29 J240 449.00 676.08 227.08 0.34 J12 431.00 609.25 178.25 0.29 Y170 446.00 704.34 258.34 0.37 G96 438.00 739.65 301.65 0.41 X63 436.00 710.58 274.58 0.39 G30 443.00 758.26 315.26 0.42 L366 416.00 709.21 293.21 0.41 L11 434.00 719.69 285.69 0.40 X183 412.00 669.57 257.57 0.38 Y420 436.00 715.50 279.50 0.39 Z576 392.00 637.75 245.75 0.39 Y177 424.00 687.61 263.61 0.38 M68 421.00 698.33 277.33 0.40 H76 425.50 721.97 296.47 0.41 Y276 410.50 683.60 273.10 0.40 H65 449.50 761.28 311.78 0.41 L80 443.00 714.32 271.32 0.38 Y369 427.20 716.06 288.86 0.40 W67 446.00 701.85 255.85 0.36 Y374 462.20 747.89 285.69 0.38 L38 402.00 593.24 191.24 0.32 Z569 419.50 648.20 228.70 0.35 B282 444.00 680.74 236.74 0.35 -
[1] Tony J T. Reservoir characterization, paleoenvironment, and paleogeomorphology of the Mississippian Redwall limestone paleokarst, Hualapai Indian reservation, Grand Canyon area, Arizona[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2000, 84(11): 1875-1880. [2] House M A. Paleogeomorphology of the Sierra Nevada, California, from (U-Th)/He ages in apatite[J]. American Journal of Science, 2001, 301(2): 77-102. doi: 10.2475/ajs.301.2.77 [3] Carr T R, Anderson N L. Paleogeomorphology of the upper Arbuckle karst surface: Implications for reservoir and trap development in Kansas[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1994, 3: 117-120. [4] Wu J, Yang H, Xu D. Introduction to the recovery and technology of palaeogeomorphology in sedimentary basins[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 1073/1076: 2025-2030. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1073-1076.2025 [5] Albani A D, Rickwood P C, Qyilty P G, et al. The morphology and Late Quaternary paleogeomorphology of the continental shelf off Sydney, NSW[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2015, 62(6): 681-694. [6] Wang H, Huang C Y, Zhao S E, et al. Paleogeomorphy, provenance system and sedimentary system of the Dongying Formation in the Qikou Sag[J]. Mining Science and Technology (China), 2009, 19(6): 800-806. doi: 10.1016/S1674-5264(09)60146-0 [7] Yang X, Li H L, Yue Y, et al. The strata and palaeogeomorphology framework at the end of Neoproterozoic and development mode of source rocks at the beginning of Cambrian in Tarim Basin, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 2(5/6): 313-322. [8] Li N, Zhang J L, Shen, W L, et al. Recovery of the erosion thickness and characterization of the paleogeomorphology in the southern Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2020, 19(2): 320-330. doi: 10.1007/s11802-020-3957-8 [9] Uribelarrea D, Domínguez-Rodrigo M, Pérez-González A, et al. Geo-archaeological and geometrically corrected reconstruction of the 1.84 Ma FLK Zinj paleolandscape at Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 322/323: 7-31. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2013.12.023 [10] Fabrício A L, Cláudio E L, Paulo T A C, et al. Paleomorphology of the northwestern of the Quadrilátero Ferrífero (central Brazil): Stratigraphic and geochronological evidence of a Pleistocene alluvial fan system[J]. Quaternary International, 2020, 542: 30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2020.02.025 [11] Chang J, Qiu N S, Liu S, et al. Post-Triassic multiple exhumation of the Taihang Mountains revealed via low-T thermochronology: Implications for the paleogeomorphologic reconstruction of the North China Craton[J]. Gondwana Research, 2018, 68: 34-49. [12] Malyshev A A, Golyeva A A, Spiridonova E A, et al. Paleolandscape reconstruction of the Abrau Peninsula littoral (Krasnodar Territory) based on sediments at the entrance of Lobanova Shchel[J]. Archaeology, Ethnology and Anthropology of Eurasia, 2014, 42(4): 92-105. doi: 10.1016/j.aeae.2015.06.010 [13] 李任远, 梅廉夫, 胡孝林, 等. 缅甸中央盆地北部新生代古地貌重建[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(3): 126-133. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0317Li R Y, Mei L F, Hu X L, et al. Reconstruction of Cenozoic paleogeomorphology in the northern Central Basin of Myanmar[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37 (3): 126-133(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0317 [14] Liu L, Chen H D, Wang J, et al. Geomorphological evolution and sediment dispersal processes in strike-slip and extensional composite basins: A case study in the Liao Bay Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 110: 73-90. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.07.023 [15] 厚刚福, 瞿建华, 朱峰, 等. 古地貌对沉积体系和沉积微相的控制作用分析: 以准噶尔盆地腹部白垩系清水河组为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2018, 47(5): 1038-1045. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201805012.htmHou G F, Qu J H, Zhu F, et al. Analysis on the control of paleogeomorphology on sedimentary system and sedimentary microfacies: Taking the Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in the hinterland of Junggar Basin as an example[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2018, 47(5): 1038-1045(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201805012.htm [16] 刘芬. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组重力流沉积特征及成因机制[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2016.Liu F. Sedimentary characteristics and genetic mechanism of gravity flow of Yanchang Formation in Longdong area, Ordos Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum(Beijing), 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [17] 刘芬, 朱筱敏, 李洋, 等. 鄂尔多斯湖盆西南部晚三叠世深水坡折特征及其对砂体的控制[J]. 高校地质学报, 2015, 21(4): 674-684. doi: 10.16108/j.issn1006-7493.2015051Liu F, Zhu X M, Li Y, et al. Late Triassic deep-water slope break characteristics in the southwestern Ordos Lake Basin and its control on sand bodies[J]. Geological Journal of Universities, 2015, 21(4): 674-684(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16108/j.issn1006-7493.2015051 [18] 崔龙涛, 冯栋, 秦雁群, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地镇北地区延长组长7古地貌与砂体分布特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2013, 25(5): 65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2013.05.011Cui L T, Feng D, Qin Y Q, et al. Paleomorphology and sand body distribution characteristics of Chang 7 in Yanchang Formation, Zhenbei area, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2013, 25(5): 65-69(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2013.05.011 [19] 崔龙涛, 郝帅, 王春平, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地镇原北部三叠系延长组长7-长6油层组古地貌与砂体分布特征[J]. 古地理学报, 2015, 17(6): 805-812. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201506008.htmCui L T, Hao S, Wang C P, et al. The paleogeomorphology and sand body distribution characteristics of the Chang 7-Chang 6 oil-bearing formation in the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the northern Zhenyuan, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Paleogeography, 2015, 17(6): 805-812(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201506008.htm [20] 崔龙涛. 镇北地区延长组长6-长7层序地层与砂体展布规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.Cui L T. Study on the Chang 6-Chang 7 sequence stratigraphy and sandbody distribution law of Yanchang Formation in Zhenbei area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [21] 梁庆韶. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7事件沉积特征及其耦合关系[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2020.Liang Q S. Sedimentary characteristics and coupling relationship of Chang 7 event in Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [22] 童强. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组陇东地区长8沉积相研究[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2018.Tong Q. Study on Chang 8 sedimentary facies in Longdong area of Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Petroleum University, 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [23] 赵重远. 华北克拉通盆地天然气赋存的地质背景[J]. 地球科学进展, 1990(2): 40-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ199002017.htmZhao C Y. Geological background of natural gas occurrence in North China Craton Basin[J]. Progress in Earth Science, 1990(2): 40-42(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ199002017.htm [24] 付金华, 罗顺社, 牛小兵, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长7段沟道型重力流沉积特征研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(1): 29-37, 1. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.01.003Fu J H, Luo S S, Niu X B, et al. Study on the sedimentary characteristics of channel-type gravity flow in Chang 7 Member in Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineral, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(1): 29-37, 1(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.01.003 [25] 吕奇奇, 罗顺社, 李梦杰, 等. 深水碎屑流与浊流混合事件层沉积特征及分布: 以鄂尔多斯盆地西南长7油层组为例[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2020, 44(2): 69-78, 9-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY202002008.htmLü Q Q, Luo S S, Li M J, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and distribution of mixed event layers of clastic flow and turbidity current in deep water: A case study of Chang 7 oil layer formation in southwest Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2020, 44(2): 69-78, 9-10(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY202002008.htm [26] 萧高健, 骆杨, 刘洪平. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部彬长区块延长组长6-长7段深水重力流沉积特征分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 69-82. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0135Xiao G J, Luo Y, Liu H P. Analysis of deep-water gravity flow sedimentary characteristics of Chang 6-Chang 7 Member of Yanchang Formation in Binchang block, southern Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 69-82(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0135 [27] Yuan H, Yin S, Dong L, et al. Restoration of the pre-Jurassic paleogeomorphology and its control on hydrocarbon distribution in western Ordos Basin[J]. Energy Geoscience, 2021, 4(3): 1-5. [28] Yu T, Liu H, Liu B, et al. Restoration of karst paleogeomorphology and its significance in petroleum geology: Using the top of the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation in the northwestern Sichuan Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 208(D): 109638. [29] Han C C, Liu C Y, Wei T, et al. Paleogeomorphology restoration and the controlling effects of paleogeomorphology on karst reservoirs: A case study of an Ordovician-aged section in Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin, China[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2019, 34(1): 31-44. [30] Zhu L W, Wang Z L, Zhang B, et al. Characteristics of paleogeomorphology and paleokarstification and the impact on natural gas accumulation: A case study of upper assemblage of Majiagou Formation in central Sulige Gas Field, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2019, 34(4): 1353-1366. [31] Xiao D, Tan X C, Fan L Y, et al. Reconstructing large-scale karst paleogeomorphology at the top of the Ordovician in the Ordos Basin, China: Control on natural gas accumulation and paleogeographic implications[J]. Energy Science & Engineering, 2019, 7(6): 3234-3254. [32] Tang D H, Xiao D, Tan X C, et al. Restoration of paleokarst landform and its geological significance: A case from Middle Permian Maokou Formation in northwestern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development Online, 2016, 43(5): 751-758. [33] Wang Z C, Jiang H, Wang T S, et al. Paleogeomorphology formed during Tongwan tectonization in Sichuan Basin and its significance for hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development Online, 2014, 41(3): 338-345. [34] Li L A, Jian B H. The Characteristics of palaeogeomorphology in Ek1 and the Lower Part of Es4 of the Paleogene in Dongying Depression and its significance to petroleum geology[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2012, 1792(524/527): 226-230. [35] Wei L, Wang Z L, Wang A G, et al. The detailed palaeogeomorphologic restoration of the Ordovician weathering crust in the northern Jingbian Gas Field: Methods and applications into reservoir properties and gas accumulation[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 2015, 33(4): 471-490. [36] 赵俊兴, 陈洪德, 时志强. 古地貌恢复技术方法及其研究意义: 以鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗纪沉积前古地貌研究为例[J]. 成都理工学院学报, 2001, 32(3): 260-266. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200103008.htmZhao J X, Chen H D, Shi Z Q. Methods and significance of paleogeomorphology restoration: A case study of pre -Jurassic paleogeomorphology in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu Institute of Technology, 2001, 32(3): 260-266(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200103008.htm [37] 刘聪颖. 川中GST构造灯影组顶部岩溶古地貌恢复及其对储层的影响研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2014.Liu C Y. The restoration of karst palaeogeomorphology at the top of Dengying Formation in GST structure in central Sichuan and its influence on reservoir[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [38] 赵俊兴, 陈洪德, 向芳. 高分辨率层序地层学方法在沉积前古地貌恢复中的应用[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2003, 30(1): 76-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200301012.htmZhao J X, Chen H D, Xiang F. Application of high resolution sequence stratigraphy in palaeogeomorphology restoration before sedimentation[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2003, 30(1): 76-81(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200301012.htm [39] Ma H Y, Han T Y, Feng J P, et al. Late Triassic-Early Jurassic paleogeomorphic characteristics and hydrocarbon potential of the Ordos Basin, China: A case of study of the Jiyuan area[J]. Open Geosciences, 2022, 14(1): 44-56. [40] Jin M D, Tan X C, Tong M S, et al. Karst paleogeomorphology of the fourth Member of Sinian Dengying Formation in Gaoshiti-Moxi area, Sichuan Basin, SW China: Restoration and geological significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development Online, 2017, 44(1): 58-68. [41] Xin X L, Ren J Y, Li J P. Control of tectonic-paleogeomorphology on deposition: A case from the Shahejie Formation Sha 3 Member, Laizhouwan Sag, southern Bohai Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development Online, 2013, 40(3): 325-332. [42] Heteren S V, Meekes J A C, Bakker M A J, et al. Reconstructing North Sea palaeolandscapes from 3D and high-density 2D seismic data: An overview[J]. Netherlands Journal of Geosciences-Geologie en Mijnbouw, 2014, 93(1/2): 31-42. [43] 曹志松, 申赵军. 古地貌恢复方法及其优缺点[C]//环球人文地理·理论版. 重庆: 《环球人文地理》编辑部, 2011: 8-9.Cao Z S, Shen Z J. Ancient landform restoration methods and their advantages and disadvantages[C]//Global Human Geography·Theory Edition. Chongqing: Global Human Geography Editorial Office, 2011: 8-9(in Chinese with English abstract). [44] 庞军刚, 李文厚, 陈全红. 陕北地区延长组标志层特征及形成机制[J]. 地层学杂志, 2010, 34(2): 173-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201002012.htmPang J G, Li W H, Chen Q H. Characteristics and formation mechanism of marker layers of Yanchang Formation in northern Shaanxi[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2010, 34(2): 173-178(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201002012.htm [45] 张晓辉, 冯顺彦, 梁晓伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组长7段沉积微相及沉积演化特征[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(3): 957-967. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202003020.htmZhang X H, Feng S Y, Liang X W, et al. Sedimentary microfacies and sedimentary evolution characteristics of Chang 7 Member of Yanchang Formation in Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geological Sciences, 2020, 94(3): 957-967(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202003020.htm [46] 郭秋麟, 米石云, 石广仁, 等. 盆地模拟原理方法[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1998.Guo Q L, Mi S Y, Shi G R, et al. Basin simulation principle and method[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1998(in Chinese). [47] 刘震, 陈凯, 朱文奇, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西峰地区长7段泥岩古压力恢复[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 36(2): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201202000.htmLiu Z, Chen K, Zhu W Q, et al. The paleopressure recovery of Chang 7 mudstone in Xifeng area, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2012, 36(2): 1-7(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201202000.htm [48] 陈树光, 任建业, 吴峰, 等. 渤中坳陷沙北地区古地貌恢复及其应用[J]. 特种油气藏, 2015, 22(2): 52-55, 153.Chen S G, Ren J Y, Wu F, et al. Restoration and application of paleogeomorphology in Shabei area of Bozhong Depression[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2015, 22(2): 52-55, 153(in Chinese with English abstract). [49] 陈延芳, 杜晓峰, 王清斌, 等. 渤海黄河口中洼古地貌对沉积相的控制作用[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2018, 42(5): 35-43, 103, 7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY201805005.htmChen Y F, Du X F, Wang Q B, et al. Controlling effect of paleogeomorphology on sedimentary facies in the middle sag of the Yellow River Estuary in the Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2018, 42(5): 35-43, 103, 7(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY201805005.htm [50] 高盾, 杨少春, 赵永福. 准噶尔盆地车排子地区白垩纪古地貌及其对沉积的控制[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2019, 38(3): 32-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201903005.htmGao D, Yang S C, Zhao Y F. Cretaceous paleogeomorphology and its control on sedimentation in Chepaizi area, Junggar Basin[J]. Daqing Petroleum Geology and Development, 2019, 38(3): 32-39(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK201903005.htm [51] 邢凤存, 陆永潮, 刘传虎, 等. 车排子地区构造-古地貌特征及其控砂机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(1): 78-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200801014.htmXing F C, Lu Y C, Liu C H, et al. Structural-paleogeomorphic features and sand control mechanism in Chepaizi area[J]. Petroleum and Natural Gas Geology, 2008, 29(1): 78-83(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200801014.htm [52] Dou L X, Hou J G, Liu Y M, et al. Sedimentary infill of shallow water deltaic sand bodies controlled by small-scale syndepositional faults related paleogeomorphology: Insights from the paleogene Shahejie formation in the Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 118: 104420. [53] Ji H C, Jia H B, Sun S M, et al. Tectonics-palaeogeomorphology in rift basins: Controlling effect on the sequence architecture[J]. Petroleum Science, 2013, 10(4): 458-465. [54] 熊林芳, 刘池阳, 邱欣卫, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地晚三叠世构造活动及对优质烃源岩发育的影响[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2): 109-114, 136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502016.htmXiong L F, Liu C Y, Qiu X W, et al. Late Triassic tectonic activity in Ordos Basin and its influence on the development of high-quality source rocks[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(2): 109-114, 136(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502016.htm [55] 程逸凡, 董艳蕾, 朱筱敏, 等. 准噶尔盆地春光探区白垩纪古地貌恢复及其控砂机制[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(6): 1127-1142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202006008.htmCheng Y F, Dong Y L, Zhu X M, et al. Restoration of Cretaceous paleogeomorphology and its sand control mechanism in Chunguang exploration area, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Paleogeography, 2020, 22(6): 1127-1142(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202006008.htm -





 下载:
下载: