Salinity characteristics of paleo-aqueous medium and their controlling factors in the third Member of the Shahejie Formation, Dongying Sag
-
摘要:
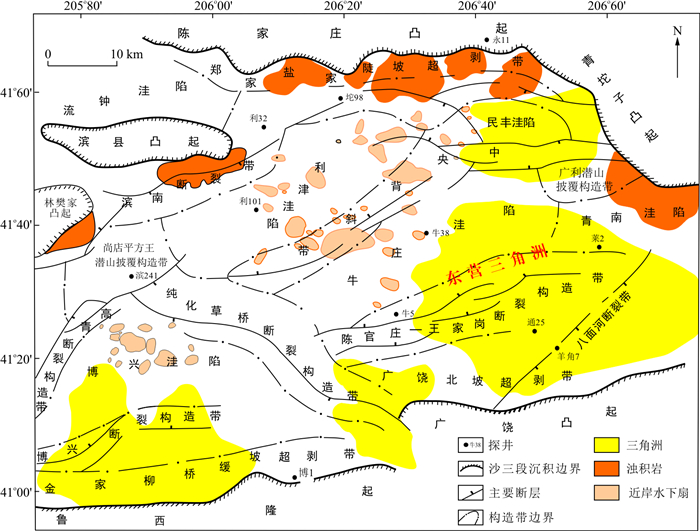
东营凹陷沙三段浊积岩油藏是重要的油气增储领域, 由于沉积期水体富灰特征明显, 严重影响地球物理预测精度及储层的品质, 因此恢复古水介质盐度、研究古盐度分布、寻找淡水稀释区显得尤为重要。综合利用微量元素、黏土矿物、碳-氧同位素等多种测试数据, 探索了不同恢复方法之间的量化联系, 并建立了一套综合表征方法, 用于量化恢复研究区的古盐度并剖析其纵、横向展布规律。在此基础上, 进一步探索了控制古盐度展布规律的成因机制。研究表明:高盐区主要分布于坨-胜断裂区、草北地区、中央背斜带及斜坡带地区, 低盐区主要分布于淡水物源注入区及深洼区;古盐度展布受控于古气候旋回、古物源性质和深部卤水上涌, 其中, 古气候旋回控制了纵向水体盐度旋回, 古物源性质及供应量控制了物源通道附近的平面水体差异, 沙四段深部卤水上涌造成了局部高盐度水体;前三角洲附近的淡水影响区和洼陷中心的淡水稀释区的浊积岩储层品质更高且灰质泥岩的影响更小,因此是重力流砂体下步勘探的有利方向。
Abstract:The turbidite reservoir in the third Member of the Shahejie Formation is an important field for oil and gas accumulation in the Dongying Sag. The obvious carbonate-rich characteristics of the water during the sedimentation period seriously affect the accuracy of geophysical prediction and the quality of the reservoir. Therefore, it is particularly important to carry out studies on salinity reconstruction of the paleo-aqueous medium in the study area. The authors integrated multiple test data of trace elements, clay minerals, carbon and oxygen isotopes, etc. to explore the quantitative links between different reconstruction methods and establish a set of comprehensive characterization methods to quantitatively reconstruct the vertical and horizontal differences of paleosalinity in the study area. On this basis, the authors further explore the mechanisms controlling the distribution pattern of paleosalinity. The study showed that the high salinity areas were mainly distributed in the Tuo-Sheng fault zone, the north slope of the Caoqiao area, the central anticline zone and the slope zone, while the low salinity areas were mainly distributed in the recharge area of freshwater and the deep depressions. The paleoclimate cycle controls the longitudinal water salinity cycle and the nature and supply of the source input control the difference in the plane water body near the source channel. The local high-salinity water body were caused by the upwelling of deep brine from the fourth Member of the Shahejie Formation. The results indicate that the next direction of turbidite exploration should target the freshwater-affected areas around the paleo-delta and the freshwater dilution areas around the sag center.
-
-
[1] 韩佳君, 周训, 姜长龙, 等. 柴达木盆地西部地下卤水水化学特征及其起源演化[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(6): 1454-1464. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201306025.htmHan J J, Zhou X, Jiang C L, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics, origin and evolution of the subsurface brines in western Qaidam Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(6): 1454-1464(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201306025.htm [2] 王焰新, 杜尧, 邓娅敏, 等. 湖底地下水排泄与湖泊水质演化[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 1-10. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0001Wang Y X, Du Y, Deng Y M, et al. Lacustrine groundwater discharge and lake water quality evolution[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0001 [3] 赵伟, 邱隆伟, 姜在兴, 等. 断陷湖盆萎缩期浅水三角洲沉积演化与沉积模式: 以东营凹陷牛庄洼陷古近系沙三段上亚段和沙二段为例[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(6): 1019-1027. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201106010.htmZhao W, Qiu L W, Jiang Z X, et al. Depositional evolution and model of shallow water delta in the rifting lacustrine basins during the shrinking stage: A case study of the Third Member and Second Member of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in the Niuzhuang Subsag, Dongying Sag[J]. Acta Geolocica Sinica, 2011, 85(6): 1019-1027(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201106010.htm [4] 张少敏, 操应长, 王艳忠, 等. 牛庄洼陷西南部沙三中亚段浊积岩储层成岩作用与物性演化[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 41(2): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201702001.htmZhang S M, Cao Y C, Wang Y Z, et al. Diagenesis and physical properties evolution of turbidite reservoirs in Es3z of Niuzhuang Sag, Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2017, 41(2): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201702001.htm [5] 刘鑫金, 刘惠民, 宋国奇, 等. 东营凹陷洼陷斜坡带坡移扇沉积特征及展布模式[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2016, 23(4): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201604001.htmLiu X J, Liu H M, Song G Q, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and distribution pattern of the slope-shifting fan in the low-lying slope zone of Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2016, 23(4): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201604001.htm [6] 李文俊, 岳大力, 何贤科, 等. 地质模式约束的SVR属性融合在浅水三角洲储层描述中的应用: 以西湖凹陷X气田为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 106-113. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0611Li W J, Yue D L, He X K, et al. Application of SVR attribute fusion constrained by geological model in reservoir description of shallow water delta: A case study of X gas field in Xihu Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 106-113(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0611 [7] 曾承, 安芷生, 刘卫国, 等. 湖泊沉积物记录的湖水古盐度定量研究进展[J]. 盐湖研究, 2007, 15(4): 13-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHYJ200704002.htmZeng C, An Z S, Liu W G, et al. Quantitative research progress on palaeo-salinity deduced from lacustrine sediments[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2007, 15(4): 13-19(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHYJ200704002.htm [8] 刘姝君, 操应长, 梁超. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷古近系细粒沉积岩特征及沉积环境[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(3): 479-489. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201903009.htmLiu S J, Cao Y C, Liang C. Lithologic characteristics and sedimentary environment of fine-grained sedimentary rocks of the Paleogene in Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basion[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography: Chinese Edition, 2019, 21(3): 479-489(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201903009.htm [9] Wu H C, Zhang S H, Jiang G Q, et al. The floating astronomical time scale for the terrestrial Late Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation from the Songliao Basin of Northeast China and its stratigraphic and paleoclimate implications[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 278(3): 308-323. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X08007668 [10] 张顺, 陈世悦, 浦秀刚, 等. 断陷湖盆细粒沉积岩岩相类型及储层特征: 以东营凹陷沙河街组和沧东凹陷孔店组为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2016, 45(3): 568-581 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201603020.htmZhang S, Chen S Y, Pu X G, et al. Lithofacies types and reservoir characteristics of fine-grained sedimentary rocks in Paleogene, southern Bohai fault-depressed lacustrine basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2016, 45(3): 568-581(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201603020.htm [11] 于正军. 地震属性融合技术及其在储层描述中的应用[J]. 特种油气藏, 2013, 20(6): 6-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201306002.htmYu Z J. Seismic attribute fusion and its application in reservior[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2013, 20(6): 6-9(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201306002.htm [12] 王海雷, 郑绵平. 青藏高原湖泊水化学与盐度的相关性初步研究[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(10): 1517-1522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201010013.htmWang H L, Zheng M P. Preliminary study of the correlation between hydrochemistry and salinity of lakes in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(10): 1517-1522(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201010013.htm [13] 童乐, 何幼斌, 李华. 陕西富平地区晚奥陶世沉积环境研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2019, 38(4): 748-758. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201904011.htmTong L, He Y B, Li H. Sedimentary environment of Late Ordovician carbonates in the Fuping area, Shaanxi Province[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2019, 38(4): 748-758(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201904011.htm [14] 李进龙, 陈东敬. 古盐度定量研究方法综述[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2003, 10(5): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200305001.htmLi J L, Chen D J. Summary of quanti-fied research method on paleosalinity[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2003, 10(5): 1-3(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200305001.htm [15] Chivas A R, de Deckker P, Shelley J M G. Magnesium content of non-marine ostracod shells: A new palaeosalinometer and palaeothermometer[J]. Palaeogeogr., Palaeoclim., Palaeoecol., 1986, 54: 43-61. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035326188810_9b2d.html [16] 王昌勇, 郑荣才, 刘哲, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长9油层组古盐度特征及其地质意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(1): 159-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201401018.htmWang C Y, Zheng R C, Liu Z, et al. Paleosalinity of Chang 9 reservoir in Longdong area, Ordos Basin and its geological significance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(1): 159-165(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201401018.htm [17] 钱焕菊, 陆现彩, 张雪芬, 等. 东营凹陷沙四段上部泥质烃源岩元素地球化学及其古盐度的空间差异性[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2009, 28(2): 161-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200902008.htmQian H J, Lu X C, Zhang X F, et al. Spatial paleosalinity distribution and element geochemistry of argillaceous source rocks in the upper part of 4th Member of Tertiary Shahejie Formation in Dongying Sag[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2009, 28(2): 161-167(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200902008.htm [18] Couch E L. Calculation of palaeosalinites from boron and clay mineral data[J]. 1971, AAPG Bulletin, 1971, 55: 1829-1839. http://aapgbull.geoscienceworld.org/content/55/10/1829 [19] 黄第藩. 关于松辽和华北中、新生代沉积相的某些问题[J]. 地质论评, 1982, 28(3): 217-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP198203003.htmHuang D F. Some questions on sedimentary facies of Mesozoic and Cenozoic in Songliao Basin and North China[J]. Geological Review, 1982, 28(3): 217-227(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP198203003.htm [20] 王冠民. 古气候变化对湖相高频旋回泥岩和页岩的沉积控制: 以济阳凹陷古近系为例[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2005: 42-80.Wang G M. The sedimentary control to mudstone and shale in lacustrine high-frequency cycle by paleoclimate change: Taking the Eogene in Jiyang Depression as an example[D]. Beijing: Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005: 42-80(in Chinese with English abstract). [21] 赵岩, 刘池洋, 张东东, 等. 宁南盆地古近纪沉积岩地球化学特征对沉积环境的反映[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(5): 27-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201605004.htmZhao Y, Liu C Y, Zhang D D, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Paleogene sedimentary rocks in Ningnan Basin and their implications for sedimentary environments[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(5): 27-33(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201605004.htm [22] 巩雪娇, 王攀, 杨振京, 等. 粒度端元记录的靖边地区MIS3以来的气候变化[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 184-191. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0113Gong X J, Wang P, Yang Z J, et al. Climate change recorded by the grain size end member since MIS3 in Jingbian area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 184-191(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0113 [23] 刘庆. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷烃源岩碳氧同位素组成及地质意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(2): 247-252. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201702014.htmLiu Q. Composition and geologic significance of carbon and oxygen isotopes in hydrocarbon source rocks, Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(2): 247-252(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201702014.htm [24] 刘杰, 操应长, 樊太亮, 等. 东营凹陷民丰地区沙三段中下亚段物源体系及其控储作用[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(4): 1399-1410. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201404029.htmLiu J, Cao Y C, Fan T L, et al. An analysis of the source system and its effect on the reservoir of the middle lower submember of 3rd Member of Shahejie Formation in Minfeng area, Dongying Depression[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(4): 1399-1410(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201404029.htm [25] 刘昊年, 黄思静, 胡作维, 等. 锶同位素在沉积学中的研究与进展[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2007, 19(3): 59-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX200703012.htmLiu H N, Huang S J, Hu Z W, et al. Advances of strontium isotope in sedimentology[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2007, 19(3): 59-65(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX200703012.htm [26] 侯中帅, 陈世悦, 刘惠民, 等. 东营凹陷热液流体活动及其油气地质意义[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2019, 48(5): 1090-1101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201905017.htmHou Z S, Chen S Y, Liu H M, et al. Hydrothermal fluid activity and its hydrocarbon geological significance in Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2019, 48(5): 1090-1101(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201905017.htm [27] 王冠民, 任拥军, 钟建华, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系黑色页岩中纹层状方解石脉的成因探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(6): 834-838. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200506023.htmWang G M, Ren Y J, Zhong J H, et al. Genetic analysis on lamellar calcite veins in Paleogene black shale of the Jiyang Depression[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(6): 834-838(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200506023.htm [28] 钱诗友, 曾溅辉. 东营凹陷沙河街组地层水化学特征及其石油地质意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(4): 603-609. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200904021.htmQian S Y, Ceng J H. Chemical characteristics of Shahejie Formation formation water and their petroleum geological significance, Dongying Sag[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(4): 603-609(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200904021.htm -





 下载:
下载: