Assessment of the water-sealed safety of underground crude oil storage based on a three-dimensional refined numerical model
-
摘要:
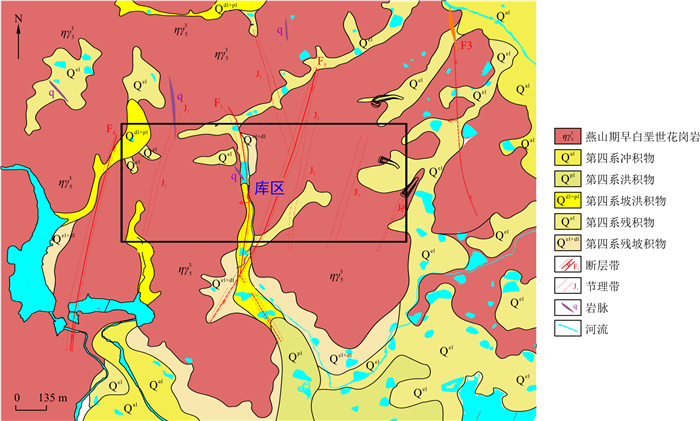
地下水封油库利用"隙存水封"原理实现原油大规模地下储存, 水封安全性是决定地下油库安全经济运行的重要前提。为评价某地下水封油库的水封安全性, 基于精细化工程地质勘察, 获取了洞库围岩、库区内断层带、节理裂隙密集带、破碎带的渗透系数, 综合分析了库址区范围内的渗透系数空间变化规律; 并结合多源高精度勘察信息构建了三维精细化渗流数值模拟模型, 在对比分析三维精细化模型与均匀介质模型的优劣后, 通过数值模拟, 对比分析了有、无水幕条件下洞库的水封可靠性, 并预测了洞库施工和运营期的涌水量。结果表明: 三维精细化数值模型可以精确地反映地质构造对地下水位及水压力的影响, 使得分析结果更加符合实际情况; 水幕系统可以有效提高洞库水封安全性, 具体表现为, 在无水幕条件下进行洞室开挖时, 地下水位明显下降, 部分洞室上方出现疏干区, 而在有水幕条件下进行洞室开挖时, 地下水位下降不明显, 洞室上方具有较厚的含水层, 其厚度足以保证洞室水封安全性; 同时, 洞室涌水量在可控范围内。本研究提出的地下油库水封安全评价方法对类似工程具有借鉴意义。
Abstract:Objective The principle of a "gap storage water seal" is used to realize large-scale underground storage of crude oil, in which water-sealed safety is an important prerequisite for the safe and economical operation of underground oil storage.
Methods To evaluate the water-sealed safety of underground oil storage, based on a refined engineering geological survey, the permeability coefficients of cavern surrounding rock, fault zones, dense joint fracture zones, and broken zones are obtained accurately, and the spatial variation of the permeability coefficient within the reservoir area is comprehensively analysed. Combined with multi-source high-precision survey information, a three-dimensional refined seepage numerical simulation model is constructed. After comparing and analysing both advantages and disadvantages of the three-dimensional refined model and corresponding homogeneous medium model, a numerical simulation is carried out to compare and analyse the reliability of cave storage with or without a water seal, and the water inflow of cavern during construction and operation is also predicted.
Results Results show that the three-dimensional refined model can accurately reflect the influence of geological structures on the groundwater level and water pressure, making analysis more in line with the real situation.The water curtain system can effectively improve the water-sealed safety of underground oil storage. Specifically, when the cavern is excavated without water curtain, the groundwater level drops significantly, and drainage area exists above some caverns. When the cavern is excavated under water curtain, the groundwater level does not drop significantly, and thick aquifer exists above the cavern, ensuring the water-sealed safety of underground oil storage; at the same time, the water inflow of cavern is under control.
Conclusion Assessment of the water-sealed safety of underground crude oil storage provided in this article can be used as a reference for other similar projects.
-
图 10 地下水封油库储油原理示意图[22]
Figure 10. Schematic diagram of oil storage of underground water-sealed oil depot
表 1 洞库各区渗透系数和渗透张量修正结果
Table 1. Permeability coefficient and correction of the permeability tensor in each cavern area
分区 渗透系数主值/(m·d-1) 压水试验渗透系数/(m·d-1) 修正系数 修正后的渗透系数主值/(m·d-1) Ⅰ 3.97×10-4 8.87×10-4 2.27 9.02×10-4 3.53×10-6 8.01×10-6 3.94×10-4 8.94×10-4 Ⅱ 1.02×10-3 9.74×10-4 1.12 1.14×10-3 1.91×10-4 2.15×10-4 8.27×10-4 9.29×10-4 Ⅲ 1.12×10-3 1.95×10-3 2.01 2.25×10-3 6.49×10-4 1.31×10-3 9.79×10-4 1.97×10-3 Ⅳ 1.21×10-3 1.35×10-3 1.40 1.70×10-3 5.56×10-4 7.80×10-4 6.55×10-4 9.19×10-4 表 2 库区优势节理隙宽、结构面间距、倾向及倾角
Table 2. Dominant joint gap width, structural plane spacing, tendency and dip angle in the reservoir area
优势节理 隙宽/mm 结构面间距/m 倾向/(°) 倾角/(°) 西北区域优势节理1 0.09 1.05 250.0 70.0 西北区域优势节理2 0.09 1.22 155.0 70.0 东北区域优势节理1 0.07 0.70 255.0 65.0 东北区域优势节理2 0.08 0.83 70.0 12.5 东北区域优势节理3 0.06 0.61 170.0 67.5 西南区域优势节理1 0.05 0.60 230.0 75.0 西南区域优势节理2 0.05 0.58 155.0 60.0 东南区域优势节理1 0.08 0.91 240.0 70.0 东南区域优势节理2 0.08 0.98 185.0 70.0 表 3 库区断层、节理密集带以及破碎带渗透系数
Table 3. Permeability coefficient of the fault, joint dense zone and fracture zone in the reservoir area
断层 渗透系数/(10-2m·d-1) 节理 渗透系数/(10-3m·d-1) 破碎带 渗透系数/(10-3m·d-1) F1 1.95 J1 5.35 P2 6.45 F4 1.25 J2 9.11 P4 1.15 F5 1.24 J3 6.14 — J4
J57.13
6.77— — 表 4 洞库涌水量计算结果汇总
Table 4. Summary of water inflow calculation of caverns
数值模拟 工况 施工工序 涌水量/(m3·d-1) 施工期 开挖1层 1 785.5 开挖2层 2 017.2 开挖3层 3 380.0 运营期 1 032.0 -
[1] 王者超, 李术才, 乔丽苹, 等. 地下石油洞库水封性评价方法体系及应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2016, 38(11): 2033-2042.Wang Z C, Li S C, Qiao L P, et al. Assessment methods for containment properties of underground crude oil storage caverns and their applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(11): 2033-2042(in Chinese with English abstract). [2] 丁国生, 魏欢. 中国地下储气库建设20年回顾与展望[J]. 油气储运, 2020, 39(1): 25-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCY202001004.htmDing G S, Wei H. Review on 20 years' UGS construction in China and the prospect[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2020, 39(1): 25-31(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCY202001004.htm [3] 王者超, 陆宝麒, 李术才, 等. 地下水封石油洞库施工期安全风险评估研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(6): 1057-1067. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201506015.htmWang Z C, Lu B Q, Li S C, et al. Risk assessment for an underground crude oil storage facility with water-curtaining system during construction phase[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(6): 1057-1067(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201506015.htm [4] 时洪斌. 黄岛地下水封洞库水封条件和围岩稳定性分析与评价[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2010.Shi H B. Analysis and evaluation of water seal condition and surrounding rock stability for Huangdao water sealed underground petroleum storage caverns in rock[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2010(in Chinese with English abstract). [5] 杨明举, 关宝树. 地下水封储气洞库原理及数值模拟分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2001, 20(3): 301-305.Yang M J, Guan B S. Simulation analysis of underground gas storage caverns and numerical principle[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2001, 20(3): 301-305(in Chinese with English abstract). [6] 孙哲, 张彬, 陈大伟, 等. 花岗岩裂隙岩体油水两相渗流可视化试验及数值模拟研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(3): 465-475. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202303032.htmSun Z, Zhang B, Cheng D W, et al. Two-phase oil/water seepage in fracture dgranite rock mass: Insight from seepage visualization experiment and numerical simulation[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(3): 465-475(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202303032.htm [7] 胡成, 陈刚, 曹孟雄, 等. 基于离散裂隙网络法和水流数值模拟技术的地下水封洞库水封性研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 119-126, 136. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0029Hu C, Cheng G, Cao M X, et al. A case study on water sealing efficieny of groundwater storage caverns using discrete fracture network method and flow numerical simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 119-126, 136(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0029 [8] Li S C, Wang Z C, Ping Y, et al. Discrete element analysis of hydro-mechanical behavior of a pilot underground crude oil storage facility in granite in China[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2014, 40: 75-84. [9] 蒋中明, 冯树荣, 赵海斌, 等. 惠州地下水封油库三维非恒定渗流场研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2012, 8(2): 334-338, 344.Jiang Z M, Feng S R, Zhao H B, et al. 3D non-steady seepage simulation of Huizhou water sealed underground caverns for oil storage[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2012, 8(2): 334-338, 344(in Chinese with English abstract). [10] Gao X, Yan E C, Yeh T C J, et al. Reliability analysis of hydrologic containment of underground storage of liquefied petroleum gas[J]. Tunnelling & Underground Space Technology, 2018, 79: 12-26. [11] 张彬, 石磊, 杨森, 等. 新建地下水封油库对附近运行油库水封可靠性影响研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2016, 24(5): 815-822.Zhang B, Shi L, Yang S, et al. Minimum separation distance between existing and newly constructing underground water-sealed oil storages[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(5): 815-822(in Chinese with English abstract). [12] Dai Y, Zhou Z. Steady seepage simulation of underground oil storage caverns based on Signorini type variational inequality formulation[J]. Geosciences Journal, 2015, 19(2): 341-355. [13] Li Z, Wang K, Wang A, et al. Experimental study of water curtain performance for gas storage in an underground cavern[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 1(1): 89-96. [14] 黎照洪, 胡成, 陈刚, 等. 烟台水封能源洞库水幕钻孔布设方案优化[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(6): 212-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201606030.htmLi Z H, Hu C, Cheng G, et al. Seepage analysis of water-sealed petroleum storage caver based on the theory of discrete crack network model[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(6): 212-217(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201606030.htm [15] Lin F, Ren F, Luan H, et al. Effectiveness analysis of water-sealing for underground LPG storage[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2016, 51: 270-290. [16] Zhang B, Shi L, Yu X, et al. Assessing the water-sealed safety of an operating underground crude oil storage adjacent to a new similar cavern: A case study in China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 249: 257-272. [17] 张振刚, 谭忠盛, 万姜林, 等. 水封式LPG地下储库渗流场三维分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2003, 25(3): 331-335. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC200303016.htmZhang Z G, Tan Z S, Wan J L, et al. Three-dimensional seepage analysis of underground LPG storage with water curtain[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2003, 25(3): 331-335(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC200303016.htm [18] 谭忠盛, 万姜林, 张振刚. 地下水封式液化石油气储藏洞库修建技术[J]. 土木工程学报, 2006, 39(6): 88-93, 99.Tan Z S, Wan J L, Zhang Z G. Construction technology of underground water seal liquefied petroleum gas storage[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2006, 39(6): 88-93, 99(in Chinese with English abstract). [19] 宋琨, 孙驰, 安冬, 等. 数字钻孔全景影像中结构面特征智能识别方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 17-22. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0503Song K, Sun C, An D, et al. Intelligent identification method for rock discontinuities properties by digital borehole panoramic images[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 17-22(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0503 [20] Snow D T. Rock fracture spacing, opening and porosities[J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanicsand Foundations Division, 1968, 94(1): 73-92. [21] 张超. 大型地下水封油库水幕系统作用机理与优化研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.Zhang C. Study of mechanism and optimization setting about large underground water oil storage's water curtain system[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [22] Shi L, Zhang B, Wang L, et al. Functional efficiency assessment of the water curtain system in an underground water-sealed oil storage cavern based on time-series monitoring data[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 239: 79-95. -





 下载:
下载: