Rock magnetic properties of the Upper Silurian Longmu Co Upper Formation in the North Qiangtang Terrane
-
摘要:
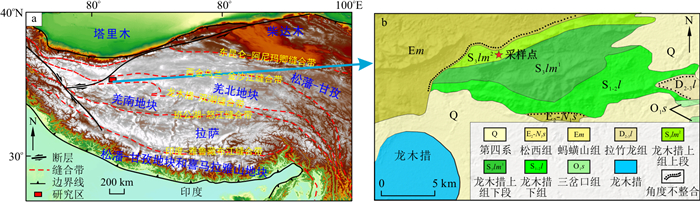
开展羌北地块早古生代古地磁学研究, 定量约束出其古生代以来的古地理位置, 可为研究青藏高原古构造格局、显生宙特提斯演化和古地理重建等提供重要基础和关键制约。在进行古地磁研究之前, 首先进行岩石磁学特征的研究, 明确岩石中载磁矿物的组合类型和特征, 为后续退磁实验方案的选择以及剩磁的原生性的讨论提供岩石磁学基础。对羌北地块上志留统龙木措上组灰岩和砂岩进行岩石磁学特征研究, 包括等温剩磁获得曲线、磁化率随温度变化(
χ -T )曲线、三轴等温系统热退磁实验、低温磁学性质测试以及扫描电镜(SEM)和能谱分析(EDS)等。实验结果表明, 龙木措上组灰岩样品中的磁性矿物以磁铁矿为主, 另外还有少量的磁赤铁矿和磁黄铁矿, 砂岩样品中的磁性矿物较为复杂, 主要为磁铁矿, 可能还含有磁黄铁矿等其他磁性矿物。研究结果表明龙木措上组地层中灰岩样品可以分离出稳定的高温剩磁分量, 适宜开展进一步古地磁学研究。Abstract:Objective Palaeomagnetic study of the early Palaeozoic North Qiangtang Terrane can quantitatively constrain its palaeogeographic location since the Palaeozoic, which serves as an important foundation and key constraint for studying of the palaeotectonic pattern of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the evolution of the Phanerozoic Tethys and palaeogeographic reconstruction.
Methods Prior to palaeomagnetic study, it is essential to investigate the magnetic properties of rocks to identify the types and assemblages of magnetic carriers present in rocks, which will facilitate the selection of demagnetization experimental protocols and discussions on the primary nature of remanent magnetization. This paper focuses on the magnetic properties of limestone and sandstone from the Late Silurian Longmu Co Upper Formation in the North Qiangtang Terrane, through analyses of isothermal remanence acquisition curves, magnetic susceptibility with temperature(
χ -T ) curves, triaxial thermal demagnetization experiments, low-temperature magnetic properties tests, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive spectral (EDS) analysis.Results Results show that magnetite is the predominant magnetic carrier in the limestone samples of the Longmu Co Upper Fm, with small amounts of pyrrhotite. The magnetic assemblage in the sandstone samples is more complex, dominated by magnetite, possibly with other magnetic minerals such as pyrrhotite.
Conclusion Moreover, it demonstrates that stable high-temperature remanent magnetization components can be isolated from the limestone samples in the Longmu Co Upper Formation, making them suitable for further palaeomagnetic researches.
-
-
[1] Hou Z, Yang Z, Lu Y, et al. A genetic linkage between subduction- and collision-related porphyry Cu deposits in continental collision zones[J]. Geology, 2015, 43(3): 247-250. doi: 10.1130/G36362.1 [2] 王成善, 郑和荣, 冉波, 等. 活动古地理重建的实践与思考: 以青藏特提斯为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(5): 849-860.Wang C S, Zheng H R, Ran B, et al. On paleogeographic reconstruction, an example for application in Tibetan Tethys[J]. Acta Sedmentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(5): 849-860(in Chinese with English abstract). [3] 莫宣学, 潘桂堂. 从特提斯到青藏高原形成: 构造-岩浆时间的约束[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(6): 43-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200606007.htmMo X X, Pan G T. From the Tethys to formation of the Qinghai-Tibet Plate: Constrained by tectono-magnatic events[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(6): 43-51(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200606007.htm [4] Yin A, Harrison T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 2003, 28: 211-280. [5] 李德威, 庄育勋. 青藏高原大陆动力学的科学问题[J]. 地质科技情报, 2006, 26(2): 1-10, 18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200602000.htmLi D W, Zhuang Y X. Scientific problems of continental dynamics in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2006, 26(2): 1-10, 18(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200602000.htm [6] 吴福元, 黄宝春, 叶凯, 等. 青藏高原造山带的垮塌与高原隆升[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(1): 1-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200801002.htmWu F Y, Huang B C, Ye K, et al. Collapsed Himalayan-Tibetan orogeny and the rising Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(1): 1-30(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200801002.htm [7] 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李文昌, 等. 青藏高原中的古特提斯体制与增生造山作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(6): 1847-1860.Xu Z Q, Yang J S, Li W C, et al. Paleo-Tethys system and accretionary orogeny in the Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(6): 1847-1860(in Chinese with English abstract). [8] 谭富文, 王剑, 付修根, 等. 藏北羌塘盆地基底变质岩的锆石SHRIMP年龄及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(1): 139-146.Tan F W, Wang J, Fu X G, et al. U-Pb zircon SHRIMP age of metamorphic rocks from the basement of the Qiangtang Basin, northern Tibet, and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(1): 139-146(in Chinese with English abstract). [9] 卢占武, 高锐, 李永铁. 青藏高原羌塘盆地基底结构与南北向变化: 基于一条270 km反射地震剖面的认识[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(11): 3319-3327.Lu Z W, Gao R, Li Y T. Structure of basement and its N-S direction transformation in Qiangtang Basin in Tibet: Discovered by a 270 km seismic reflection profile[J]. Atca Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(11): 3319-3327(in Chinese with English abstract). [10] 胡培远, 李才, 吴彦旺, 等. 藏北羌塘中部存在志留纪洋盆: 来自桃形湖蛇绿岩中斜长花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄证据[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(11): 1651-1661. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201411001.htmHu P Y, Li C, Wu Y W, et al. The Silurian Tethyan Ocean in central Qiangtang, northern Tibet: Constraints from zircon U-Pb ages of plagiogranites within the Taoxinghu ophiolite[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(11): 1651-1661(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201411001.htm [11] 李三忠, 赵淑娟, 李玺瑶, 等. 东亚原特提斯洋(Ⅰ): 南北边界和俯冲极性[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(9): 2609-2627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201706001.htmLi S Z, Zhao S J, Li X Y, et al. Proto-Tehtys Ocean in East Asia (Ⅰ): Northern and southern border faults and subduction polarity[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(9): 2609-2627(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201706001.htm [12] Huang K, Opdyke N D, Peng X J, et al. Paleomagnetic results from the Upper Permian of the eastern Qiangtang Terrane of Tibet and their tectonic implications[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1992, 111(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(92)90164-Q [13] Cheng X, Wu H N, Guo Q, et al. Paleomagnetic results of Late Paleozoic rocks from northern Qiangtang Block in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(1): 67-75. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4287-x [14] Cheng X, Wu H N, Diao Z B, et al. Paleomagnetic data from the Late Carboniferous-Late Permian rocks in eastern Tibet and their implications for tectonic evolution of the northern Qiangtang-Qamdo block[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2013, 56(7): 1209-1220. [15] Song P P, Ding L, Li Z Y, et al. An early bird from Gondwana: Paleomagnetism of Lower Permian lavas from northern Qiangtang(Tibet) and the geography of the Paleo-Tethys[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 475: 119-133. [16] Yang X F, Cheng X, Zhou Y N, et al. Paleomagnetic results from Late Carboniferous to Early Permian rocks in the northern Qiangtang Terrane, Tibet, China, and their tectonic implications[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2017, 60(1): 124-134. [17] 姜南, 吴汉宁, 李玉玉, 等. 羌北地块早-中志留世古地磁学初步研究结果及其构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(3): 1057-1070.Jiang N, Wu H N, Li Y Y, et al. Preliminary Paleomagnetic results of Early-Middle Silurian rocks from North Qiangtang Terrane, Tibet, China, and its tectonic implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(3): 1057-1070(in Chinese with English abstract). [18] 王权, 董挨管, 段春森, 等. 西藏北部拉竹龙地区泥盆纪岩石地层单位划分与时代讨论[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2004, 24(3): 30-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200403004.htmWang Q, Dong A G, Duan C S, et al. Division and ages of the Devonian lithostratigraphic units in Lazhuglung, northern Xizang[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2004, 24(3): 30-37(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200403004.htm [19] 夏军, 钟华明, 童劲松, 等. 藏北龙木错东部三岔口地区下奥陶统与泥盆系的不整合界面[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(1/2): 113-117.Xia J, Zhong H M, Tong J S, et al. Unconformity between the Lower Ordvician and Devonian in the Sanchakou area in the eastern part of the Lungmu Co, northern Tibet, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(1/2): 113-117(in Chinese with English abstract). [20] 夏军, 钟华明, 童劲松, 等. 藏西北三岔口地区泥盆系生物礁特征及其意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2006, 26(2): 34-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200602008.htmXia J, Zhong H M, Tong J S, et al. The Devonian bioherms in Sanchakou, northwestern Xizang and their implications[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2006, 26(2): 34-41(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200602008.htm [21] 夏军, 王陆太, 钟华明, 等. 青藏高原龙木错地区志留纪大型古三角洲沉积体系的识别及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(9): 1267-1275.Xia J, Wang L T, Zhong H M, et al. Discovery of large-scale Silurian ancient delta deposition system in Longmu Co area, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China and its significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(9): 1267-1275(in Chinese with English abstract). [22] Gradstein F M, Ogg G, Schmitz M. The geologic time scale[J]. Newsletters on Stratigraphy, 2012, 45(2): 171-188. [23] 戎嘉余, 王怿, 詹仁斌, 等. 中国志留纪综合地层和时间框架[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 49(1): 93-114.Rong J Y, Wang Y, Zhan R B, et al. Silurian integrative stratigraphy and timescale of China[J]. Science Sinica: Earth Sciences, 2019, 49(1): 93-114(in Chinese with English abstract). [24] Kruiver P P, Dekkers M J, Heslop D. Quantification of magnetic coercivity components by the analysis of acquisition curves of isothermal remanent magnetization[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 189(3/4): 269-276. [25] Stockhausen H. Some new aspects for the modelling of isothermal remanent magnetization acquisition curves by cumulative log Gaussian functions[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1998, 25(12): 2217-2220. [26] Kruiver P P, Passier H F. Coercivity analysis of magnetic phases in sapropel S1 related to variations in redox conditions, including an investigation of the S ratio[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2001, 2: 2001GC000181. [27] Hrouda F. A technique for the measurement of thermal changes of magnetic susceptibility of weakly magnetic rocks by the CS-2 apparatus and KLY-2 Kappabridge[J]. Geophysical Journal Internation, 1994, 118(3): 604-612. [28] Van V A J, Dekkers M J. The incorporation of thermal methods in mineral magnetism of loess-paleosol sequence: A brief overiew[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44: 53-63. [29] 李波, 石显耀, 李学杰, 等. 西菲律宾海西部沉积物磁学特征及其环境意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(5): 34-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201605005.htmLi B, Shi X Y, Li X J, et al. Magnetic properties of sediments from the western West Philippine Sea and their environmental implications[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(5): 34-41(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201605005.htm [30] Hopkinson J. Magnetic and other physical properties of iron at a high temperature[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. A, 1889, 180: 443-465. [31] 敖红, 邓成龙. 磁性矿物的磁学鉴别方法回顾[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(2): 432-442. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200702014.htmAo H, Deng C L. Review in the identification of magnetic minerals[J]. Progress in geophysics, 2007, 22(2): 432-442(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200702014.htm [32] Verwey E J W. Electronicconduction of magnetite (Fe3O4) and its transition point at low temperatures[J]. Nature, 1939, 144(3642): 327-328. [33] Rochette P, Gérard Fillion, Jean-Luc Mattéi, et al. Magnetic transition at 30-34 Kelvin in pyrrhotite: Insight into a widespread occurrence of this mineral in rocks[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1990, 98(3/4): 319-328. [34] Aubourg C, Pozzi J P, Kars M. Burial, claystones remagnetization and some consequences for magnetostratigraphy[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2012, 371(1): 181-188. [35] Bruce M M, Richard B F, Sarah A W, et al. Determination of the preexponential frequency factor for superparamagnetic maghemite particles in magnetoferritin[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1997, 102(B10): 2671-2680. -





 下载:
下载: