Sedimentary evolution revealed by aeolian and lacustrine depositions in the southern margin of the Weihe Basin during the Early Pleistocene
-
摘要:
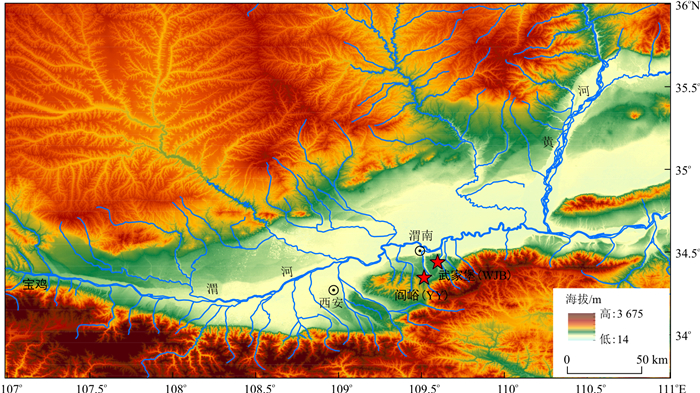
受地球轨道参数诱导的太阳辐射变化和两极冰盖消长的共同影响, 第四纪气候环境演化表现出阶段性变冷及显著的冰期-间冰期波动特征。位于亚洲季风区关键地带的渭河盆地堆积了新生代以来巨厚的河湖相沉积以及风成沉积, 是研究第四纪环境演化的重要区域。盆地堆积的下更新统三门组河湖相地层被认为和古三门湖有密切联系, 但目前对于三门组地层年龄和古三门湖演化及其与区域活动演化是否有联系尚未达成共识。相比单一沉积载体研究, 选取渭河盆地南缘阎峪风成相黄土和武家堡湖相沉积2种沉积载体进行对比分析, 探讨了同期异相沉积记录的粒度和磁化率变化特征, 重建了渭河盆地南缘早更新世(距今2.6~1.6 Ma)沉积环境演化。结果表明, 阎峪记录的黄土-古土壤序列平均粒径和磁化率变化良好地记录了东亚冬、夏季风的盛衰演化历史; 武家堡指示的盆地南缘沉积环境在距今1.95 Ma由湖相转变为风成相沉积, 湖相沉积粒径和磁化率变化呈正相关关系, 敏感响应湖平面高低波动。风成相与湖相记录揭示了渭河盆地边缘早更新世环境演化经历了[2.6, 1.95)Ma的湖盆演化和[1.95, 1.6]Ma的湖盆萎缩-风成相堆积, 湖盆萎缩受黄河贯通影响强烈。
Abstract:The Quaternary climate is characterized by a notable cooling and significant glacial-interglacial fluctuations driven by the influence of orbital-induced insolation and bipolar ice-volume variability. The Weihe Basin, located in the critical zone of the Asian monsoon region, accumulated thick fluvial-lacustrine deposition and aeolian deposition since the Cenozoic, which is a key placeto explore the environmental evolution during the Quaternary period.Objective The fluvial-lacustrine strata of the Sanmen Formation in the Weihe Basin are considered to be closely related to Palaeo-Sanmen Lake. However, the relationship among the stratigraphic age of the Sanmen Formation, the evolution of the palaeolake as well as the evolution of regional tectonics is still under much debated.
Methods In this work, the magnetic susceptibility and grain size records from two sections (Yanyu and Wujiabu) in the southern margin of the Weihe Basin have been generated to investigate sedimentary evolution during the interval of 2.6-1.6 Ma.
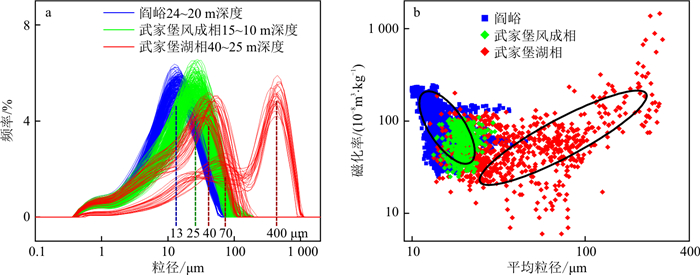
Results The mean grain size (MGS) and magnetic susceptibility (MS) of the Yanyu loess exhibit large-amplitude variations as proxies for the East Asian winter and summer monsoons. The MGS and MS variations in theWujiabu section show that lithology changes from lacustrine to aeolian facies occurred at 1.95 Ma in the southern margin of the Weihe Basin. In lacustrine environments, MGS is positively correlated with MS and is sensitive to fluctuations in lake level linked with monsoonal precipitation.
Conclusion Overall, the climatic characteristics on the margin of the Weihe Basin during the early Pleistocene can be divided into two intervals: ① the lake level frequently fluctuated during 2.6-1.95 Ma, ② the lake shrank from 1.95 to 1.6 Ma. We suggest that the disappearance of Palaeo-Sanmen Lake was affected by the development and integration of the Yellow River.
-
Key words:
- Weihe Basin /
- Early Pleistocene /
- lacustrine deposition /
- aeolian loess /
- Palaeo-Sanmen Lake
-
(所有作者声明不存在利益冲突)
-
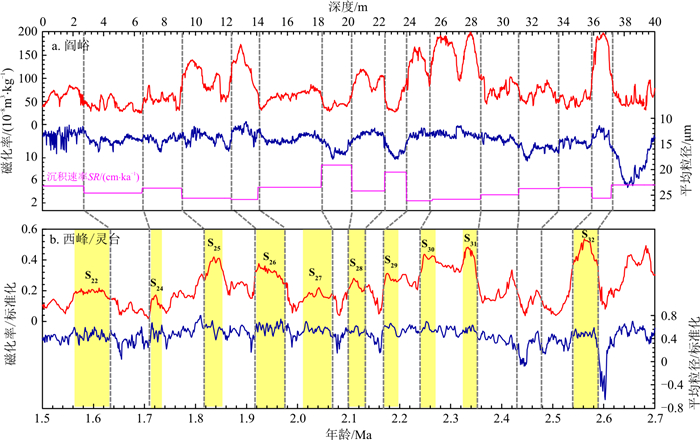
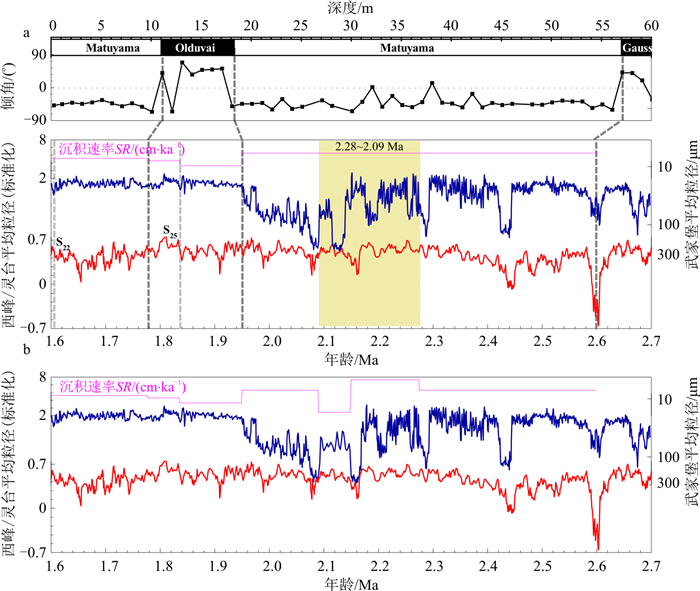
图 5 武家堡剖面的初始(a)和改进(b)年代标尺
a.基于交变退磁结果建立的初始年龄标尺的武家堡平均粒径(蓝色)、沉积速率(橘色)和西峰/灵台平均粒径[17](红色)对比,深灰色竖直虚线表示3个古地磁倒转点,浅灰色竖直虚线表示基于S22及S25增加的年龄控制点,黄色阴影指示年代偏差的阶段;b.基于改进年龄标尺的武家堡平均粒径(蓝色)、沉积速率(橘色)和西峰/灵台平均粒径(红色)对比
Figure 5. Original (a) and improved (b) age models of the Wujiabu section
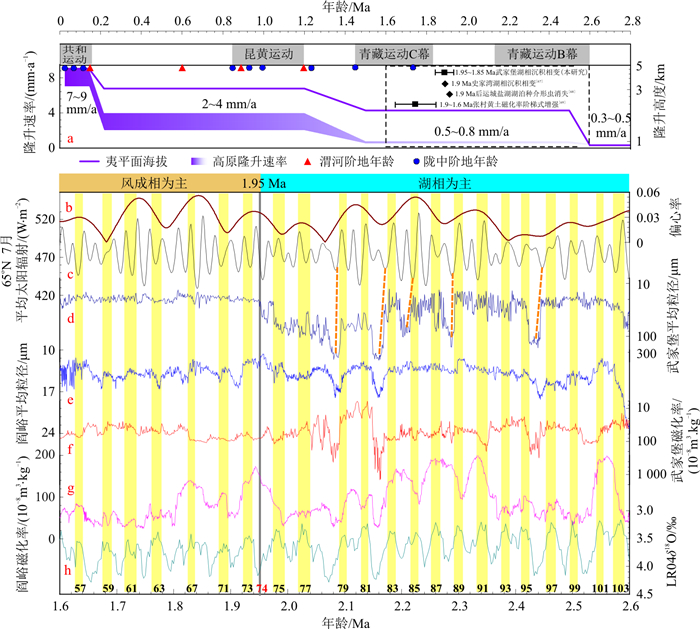
图 7 渭河盆地河流阶地同青藏高原活动的关系以及本研究指标和其他气候记录对比
a.已有研究记录的1.9 Ma前后沉积环境改变[67-69],及渭河盆地阶地年龄[70]、陇中盆地阶地年龄(临夏和兰州)[71]、隆升速率/海拔指示的第四纪青藏高原隆升过程[66],黑色虚线框为本研究涉及的时段;b.偏心率[65];c.65°N地区7月平均太阳辐射[65];d.武家堡平均粒径;e.阎峪平均粒径;f.武家堡磁化率;g.阎峪磁化率;h.全球57个海洋钻孔集成的底栖δ18O记录[6]。黄色阴影表示深海氧同位素阶段中的温暖期,灰色实线表示武家堡在MIS 74冷阶段发生沉积相变、湖盆萎缩
Figure 7. Correlation of the river terraces in the Weihe Basin with uplifting process of Tibetan Plateau, and comparison of the study indicators with other climatic records
-
[1] 刘东生, 郑绵平, 郭正堂. 亚洲季风系统的起源和发展及其与两极冰盖和区域构造运动的时代耦合性[J]. 第四纪研究, 1998, 18(3): 194-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ199803001.htmLiu D S, Zheng M P, Guo Z T. Initiation and evolution of the Asian monsoon system timely coupled with the ice-sheet growth and the tectonic movements in Asia[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1998, 18(3): 194-204(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ199803001.htm [2] An Z S. The history and variability of the East Asian paleomonsoon climate[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2000, 19(1/5): 171-187. [3] An Z S, Wu G X, Li J P, et al. Global monsoon dynamics and climate change[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2015, 43: 29-77. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060313-054623 [4] Zachos J, Pagani M, Sloan L, et al. Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present[J]. Science, 2001, 292: 686-693. doi: 10.1126/science.1059412 [5] Zachos J, Dickens G, Zeebe R. An Early Cenozoic perspective on greenhouse warming and carbon-cycle dynamics[J]. Nature, 2008, 451: 279-283. doi: 10.1038/nature06588 [6] Lisiecki L E, Raymo M E. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records[J]. Paleoceanography, 2005, 20(2): PA2007. [7] Cheng H, Edwards R L, Sinha A, et al. The Asian monsoon over the past 640 000 years and ice age terminations[J]. Nature, 2016, 534: 640-646. doi: 10.1038/nature18591 [8] Sun Y, Yin Q, Crucifix M, et al. Diverse manifestations of the mid-Pleistocene climate transition[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 352. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08257-9 [9] Clemens S C, Murray D W, Prell W L. Nonstationary phase of the Plio-Pleistocene Asian monsoon[J]. Science, 1996, 274: 943-948. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5289.943 [10] An Z S, Kutzbach J E, Prell W L, et al. Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan Plateau since Late Miocene times[J]. Nature, 2001, 411: 62-66. doi: 10.1038/35075035 [11] Clemens S C, Prell W L, Sun Y B, et al. Southern Hemisphere forcing of Pliocene δ18O and the evolution of Indo-Asian monsoons[J]. Paleoceanography, 2008, 23(4): PA4210. [12] Tian J, Xie X, Ma W T, et al. X-ray fluorescence core scanning records of chemical weathering and monsoon evolution over the past 5 Myr in the southern South China Sea[J]. Paleoceanography, 2011, 26: PA4202. [13] Fang X M, An Z S, Clemens S C, et al. The 3.6-Ma aridity and westerlies history over midlatitude Asia linked with global climatic cooling[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2020, 117(40): 24729-24734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922710117 [14] An Z S, Liu T S, Lu Y C, et al. The long-term paleomonsoon variation recorded by the loess-paleosol sequence in central China[J]. Quaternary International, 1990, 7/8: 91-95. doi: 10.1016/1040-6182(90)90042-3 [15] Lu H, Zhang F Q, Liu X, et al. Periodicities of palaeoclimatic variations recorded by loess-paleosol sequences in China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2004, 23(18/19): 1891-1900. [16] Sun Y B, An Z S. An improved comparison of Chinese loess with deep-sea δ18O record over the interval 1.6-2.6 Ma[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(13): L13210. [17] Sun Y B, Clemens S C, An Z S, et al. Astronomical timescale and palaeoclimatic implication of stacked 3.6-Myr monsoon records from the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(1/2): 33-48. [18] Hao Q Z, Wang L, Oldfield F, et al. Delayed build-up of Arctic ice sheets during 400 000-year minima in insolation variability[J]. Nature, 2012, 490: 393-396. doi: 10.1038/nature11493 [19] Sun Y B, Clemens S C, Morrill C, et al. Influence of Atlantic meridional overturning circulation on the East Asian winter monsoon[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(1): 46-49. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1326 [20] Ao H, Dupont-Nivet G, Rohling E J, et al. Orbital climate variability on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau across the Eocene-Oligocene transition[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5249. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18824-8 [21] Rits D S, Prins M A, Troelstra S R, et al. Facies analysis of the Middle and Late Quaternary sediment infill of the northern Weihe Basin, central China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2016, 31(2): 152-165. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2853 [22] 鹿化煜, 张瀚之, 王逸超, 等. 渭河盆地新生代沉积序列与亚洲季风气候起源演化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(5): 1057-1067(in Chinese with English abstract).Lu H Y, Zhang H Z, Wang Y C, et al. Cenozoic depositional sequence in the Weihe Basin (central China): A long-term record of Asian monsoon precipitation from the greenhouse to icehouse Earth[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 38(5): 1057-1067(in Chinese with English abstract). [23] Wang Y C, Lu H Y, Wang K X, et al. Combined high- and low-latitude forcing of East Asian monsoon precipitation variability in the Pliocene warm period[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(46): eabc2414. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abc2414 [24] 陈万川, 陈家弦, 云琼英, 等. 汾渭盆地石油普查阶段地质成果报告[R]. 西安: 国家地质总局第三石油普查勘探大队, 1977.Chen W C, Chen J X, Yun Q Y, et al. Geological report of the petroleum census in the Fenwei Basin[R]. Xi'an: The Third Petroleum Census and Exploration Team, State Bureau of Geology, 1977(in Chinese). [25] Liu T S, Ding Z L, Rutter N. Comparison of Milankovitch periods between continental loess and deep sea records over the last 2.5 Ma[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1999, 18(10/11): 1205-1212. [26] Gao L, Nie J S, Clemens S, et al. The importance of solar insolation on the temperature variations for the past 110 kyr on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 317/318: 128-133. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2011.12.021 [27] 赵景波, 罗小庆, 刘瑞, 等. 西安蓝田S4古土壤剖面中针铁矿富集层与土壤古水分研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(2): 347-353.Zhao J B, Luo X Q, Liu R, et al. Enrichment layer of goethite and paleowater in the section of S4 palaeosol in Xi'an area[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(2): 347-353(in Chinese with English abstract). [28] Thomas E K, Clemens S C, Sun Y, et al. Heterodynes dominate precipitation isotopes in the East Asian monsoon region, reflecting interaction of multiple climate factors[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 455: 196-206. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.09.044 [29] Kang S G, Wang X L, Lu Y C. Quartz OSL chronology and dust accumulation rate changes since the Last Glacial at Weinan on the southeastern Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Boreas, 2013, 42(4): 815-829. doi: 10.1111/bor.12005 [30] Sun J M. Long-termfluvial archives in the Fenwei Graben, central China, and their bearing on the tectonic history of the India-Asia collision system during the Quaternary[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2005, 24(10/11): 1279-1286. [31] 孙文峰, 鹿化煜, 王逸超, 等. 渭河盆地蓝田始新世红河组沉积物特征和古环境记录[J]. 高校地质学报, 2017, 23(3): 533-544.Sun W F, Lu H Y, Wang Y C, et al. Deposits and palaeoenvironmental record of the Eocene Honghe Formation in Lantian, Weihe Basin, central China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2017, 23(3): 533-544(in Chinese with English abstract). [32] Liu J H, Zhang P Z, Lease R O, et al. Eocene onset and Late Miocene acceleration of Cenozoic intracontinental extension in the North Qinling range-Weihe graben: Insights from apatite fission track thermochronology[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 584(S1): 281-296. [33] Chen F H, Yu Z C, Yang M L, et al. Holocene moisture evolution in arid central Asia and its out-of-phase relationship with Asian monsoon history[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2008, 27(3/4): 351-364. [34] Chen F H, Chen J H, Huang W, et al. Westerlies Asia and monsoonal Asia: Spatiotemporal differences in climate change and possible mechanisms on decadal to sub-orbital timescales[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 192: 337-354. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.03.005 [35] 王书兵, 蒋复初, 吴锡浩, 等. 三门组的内涵及其意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24(1): 116-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200401015.htmWang S B, Jiang F C, Wu X H, et al. The connotation and significance of Sanmen Formation[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24(1): 116-123(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200401015.htm [36] 王斌, 郑洪波, 王平, 等. 渭河盆地新生代地层与沉积演化研究: 现状和问题[J]. 地球科学进展, 2013, 28(10): 1126-1135.Wang B, Zheng H B, Wang P, et al. The Cenozoic strata and depositional evolution of Weihe Basin: Progresses and problems[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2013, 28(10): 1126-1135(in Chinese with English abstract). [37] 宋友桂, 兰敏文, 刘慧芳, 等. 关中盆地新生界地层划分对比与第四纪下限[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(2): 24-35. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0204Song Y G, Lan M W, Liu H F, et al. Cenozoic stratigraphic correlation and the lower limit of Quaternary in Guanzhong Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(2): 24-35(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0204 [38] 孙建中, 赵景波, 魏明建, 等. 武家堡剖面古地磁新资料[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 1988, 15(5): 44-48.Sun J Z, Zhao J B, Wei M J, et al. New paleomagnetic records from the Wujiabu section[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 1988, 15(5): 44-48(in Chinese). [39] 刘瑾, 陈兴强, 王平, 等. 渭河-三门峡盆地三门组沉积充填特征、物源区及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(7): 2673-2683. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202007035.htmLiu J, Chen X Q, Wang P, et al. Sedimentary characteristics, provenance and tectonic significance of the Sanmen Formation in Weihe-Sanmenxia Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(7): 2673-2683(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202007035.htm [40] Jiang F, Fu J, Wang S, et al. Formation of the Yellow River, inferred from loess-palaeosol sequence in Mangshan and lacustrine sediments in Sanmen Gorge, China[J]. Quatternary International, 2007, 175(12): 62-70. [41] Zheng H, Huang X, Ji J, et al. Ultra-high rates of loess sedimentation at Zhengzhou since Stage 7: Implication for the Yellow River erosion of the Sanmen Gorge[J]. Geomorphology, 2007, 85(3/4): 131-142. [42] 孙东怀, 安芷生, 苏瑞侠, 等. 古环境中沉积物粒度组分分离的数学方法及其应用[J]. 自然科学进展, 2001, 11(3): 269-276. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJZ200103007.htmSun D H, An Z S, Su R X, et al. Mathematical methods and applications for separation of sediment particle size components in paleoenvironment[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2001, 11(3): 269-276(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJZ200103007.htm [43] Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Rea D K, et al. Grain-size distribution function of polymodal sediments in hydraulic and aeolian environments, and numerical partitioning of the sedimentary components[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 152(3/4): 263-277. [44] Porter S C, An Z S. Correlation between climate events in the North Atlantic and China, during the Last Glaciation[J]. Nature, 1995, 375: 305-308. doi: 10.1038/375305a0 [45] Ding Z L, Ranov V, Yang S L, et al. The loess record in southern Tajikistan and correlation with Chinese loess[J]. Earth And Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 200(3/4): 387-400. [46] Lu H Y, Liu X D, Zhang F Q, et al. Astronomical calibration of loess-palaeosol deposits at Luochuan, central Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1999, 154(3): 237-246. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(99)00113-3 [47] Yang S, Ding Z. Winter-spring precipitation as the principal control on predominance of C3 plants in central Asia over the past 1.77 Myr: Evidence from δ13C of loess organic matter in Tajikistan[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 235(4): 330-339. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.11.007 [48] Prins M A, Vriend M, Nugteren G, et al. Late Quaternary aeolian dust input variability on the Chinese Loess Plateau: Inferences from unmixing of loess grain-size records[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2007, 26(1/2): 230-242. [49] 杨石岭, 丁仲礼. 黄土高原黄土粒度的空间变化及其古环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(5): 934-944.Yang S L, Ding Z L. Spatial changes in grain size of loess deposits in the Chinese Loess Plateau and implications for palaeoenvironment[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2017, 37(5): 934-944(in Chinese with English abstract). [50] An Z H, Kukla G J, Porter S C, et al. Magnetic susceptibility evidence of monsoon variation on the Loess Plateau of central China during the last 130 000 years[J]. Quaternary Research, 1991, 36(1): 29-36. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(91)90015-W [51] Song Y G, Fang X M, King J W, et al. Magnetic parameter variations in the Chaona loess/paleosol sequences in the central Chinese Loess Plateau, and their significance for the Middle Pleistocene climate transition[J]. Quaternary Research, 2014, 81(3): 433-444. [52] Maher B A, Thompson R. Paleorainfall reconstructions from pedogenic magnetic susceptibility variations in the Chinese loess and paleosols[J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(3): 383-391. [53] Maher B A. Palaeoclimatic records of the loess/palaeosol sequences of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 154: 23-84. [54] Campbell C. Late Holocene lake sedimentology and climate change insouthern Alberta, Canada[J]. Quaternary Research, 1998, 49(1): 96-101. [55] Xiao J L, Chang Z G, Wen R L, et al. Holocene weak monsoon intervals indicated by low lake levels at Hulun Lake in the monsoonal margin region of northeastern Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Holocene, 2009, 19(6): 899-908. [56] Fu C F, An Z S, Qiang X K, et al. Magnetostratigraphic determination of the age of ancient Lake Qinghai, and record of the East Asian monsoon since 4.63 Ma[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(8): 875-878. [57] Dearing J A. Sedimentary indicators of lake-level changes in the humid temperate zone: A critical review[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 1997, 18(1): 1-14. [58] 孙千里, 周杰, 肖举乐. 岱海沉积物粒度特征及其古环境意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(1): 93-95.Sun Q L, Zhou J, Xiao J L. Grain-size characteristics of Lake Dahai sediments and its paleoenvironment significance[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(1): 93-95(in Chinese with English abstract). [59] 胡守云, 邓成龙, Appel E, 等. 湖泊沉积物磁学性质的环境意义[J]. 科学通报, 2001, 46(17): 1491-1494.Hu S Y, Deng C L, Appel E, et al. A study of gyroremanent magnetization (GRM) and rotational remanence magnetization (RRM) carried by gregite from lake sediments[J]. Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(17): 1491-1494(in Chinese with English abstract). [60] 刘兴起, 王苏民, 沈吉. 青海湖QH-2000钻孔沉积物粒度组成的古气候古环境意义[J]. 湖泊科学, 2003, 15(2): 112-117(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX200302002.htmLiu X Q, Wang S M, Shen J. The grainsize of the core QH-2000 in Qinghai Lake and its implication for paleoclimate and paleoenvironment[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2003, 15(2): 112-117(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX200302002.htm [61] Zhao Y, Tzedakis P C, Li Q, et al. Evolution of vegetation andclimate variability on the Tibetan Plateau over the past 1.74 million years[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(19): eaay6193. [62] 沈吉, 刘兴起, Matsumoto R, 等. 晚冰期以来青海湖沉积物多指标高分辨率的古气候演化[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2004, 34(6): 582-589.Shen J, Liu X Q, Matsumoto R, et al. High-resolution paleoclimate evolution with multiple proxies in Qinghai Lake sediments since the Late Glacial[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Science, 2004, 34(6): 582-589(in Chinese with English abstract). [63] 沈吉. 湖泊沉积研究的历史进展与展望[J]. 湖泊科学, 2009, 21(3): 307-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX200903003.htmShen J. Progress and prospect of palaeolimnology research in China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2009, 21(3): 307-313(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX200903003.htm [64] Zhou L P, Oldfield F, Wintle A G, et al. Partly pedogenic origin of magnetic variations in Chinese loess[J]. Nature, 1990, 346: 737-739. [65] Laskar J, Robutel P, Joutel F, et al. A long-term numerical solution for the insolation quantities of the Earth[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2004, 428(1): 261-285. [66] 顾家伟. 上新世以来苏北盆地与长江三角洲构造沉降史分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(1): 95-99, 106.Gu J W. Tectonic subsidence analysis of Subei Basin and Yangtze delta from the Pliocene[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(1): 95-99, 106(in Chinese with English abstract). [67] Han J, Fyfe W S, Longstaffe F J, et al. Pliocene-Pleistocene climatic change recorded in fluviolacustrine sediments in central China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1997, 135(1/4): 27-39. [68] Wang Q, Li C G, Tian G Q, et al. Tremendous change of the earth surface system and tectonic setting of salt-lake formation in Yuncheng Basin since 7.1 Ma[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Science, 2002, 45(2): 110-122. [69] Xiao G Q, Pan Q, Zhao Q Y, et al. Early Pleistocene integration of the Yellow River: Ⅱ. Evidence from the Plio-Pleistocene sedimentary record of the Fenwei Basin[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 577: 110550. [70] 岳乐平, 雷祥义, 屈红军. 黄河中游水系的阶地发育时代[J]. 地质论评, 1997, 43(2): 187-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199702013.htmYue L P, Lei X Y, Qu H J. The age of terrace development in the middle reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Geological Review, 1997, 43(2): 187-191(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199702013.htm [71] Li J J, Fang X M, Song C H, et al. Late Miocene-Quaternary rapid stepwise uplift of the NE Tibetan Plateau and its effects on climatic and environmental changes[J]. Quaternary Research, 2014, 81(3): 400-423. [72] Wang S M, Wu X H, Zhang Z K, et al. Sedimentary records of environmental evolution in the Sanmen Lake Basin and the Yellow River running through the Sanmenxia Gorge eastward into the sea[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Science, 2002, 45(7): 596-608. [73] Kong P, Jia J, Zheng Y. Time constraints for the Yellow River traversing the Sanmen Gorge[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2014, 15(2): 395-407. [74] 葛同明, 樊利民, 徐行, 等. 渭南阎村W7孔岩心样品的古地磁学研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1991, 4(11): 59-71.Ge T M, Fan L M, Xu X, et al. Magnetostragraphic study for borehole W7 from Yancun, Weinan[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 1991, 4(11): 59-71(in Chinese with English abstract). [75] 胡巍, 岳乐平, 田新红. 渭南沋河宋家北沟剖面磁性地层学研究[J]. 陕西地质, 1993, 11(2): 26-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXDY199302004.htmHu W, Yue L P, Tian X H. On the magnetostratigraphy of the Songjia-Beigou section, Youhe, Weinan[J]. Geology of Shaanxi, 1993, 11(2): 26-32(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXDY199302004.htm [76] 王迎国, 常宏, 周卫健. 渭河盆地河流阶地演化及其构造—气候意义[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(4): 1033-1049. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202104014.htmWang Y G, Chang H, Zhou W J. Fluvial terrace evolution and its tectonic: Climatic significance in the Weihe Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67(4): 1033-1049(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202104014.htm [77] Liu J, Chen X Q, Shi W, et al. Tectonically controlled evolution of the Yellow River drainage system in the Weihe region, North China: Constraints from sedimentation, mineralogy and geochemistry[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 179: 350-364. [78] Zhang H Z, Lu H Y, Zhou Y L, et al. Heavy mineral assemblages and U-Pb detrital zircon geochronology of sediments from the Weihe and Sanmen Basins: New insights into the Pliocene-Pleistocene evolution of the Yellow River[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 562: 110072. [79] 张信宝, 刘彧, 王世杰, 等. 黄河、长江的形成演化及贯通时间[J]. 山地学报, 2018, 36(5): 661-668. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201805001.htmZhang X B, Liu Y, Wang S J, et al. On the chronology of the Yellow Rivers and the Yangtze Rivers[J]. Mountain Research, 2018, 36(5): 661-668(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201805001.htm [80] Zheng H B, Powell C M, An Z S, et al. Pliocene uplift of the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geology, 2000, 28(8): 715-718. [81] 李吉均. 青藏高原的地貌演化与亚洲季风[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1999, 19(1): 7-17.Li J J. Studies on geomorphological evolution of Tibetan Plateau and Asian monsoon[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 1999, 19(1): 7-17(in Chinese with English abstract). [82] Hu Z B, Pan B T, Bridgland D, et al. The linking of the upper-middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River as a result of fluvial entrenchment[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 166(S1): 324-338. [83] Pan B T, Su H, Hu Z B, et al. Evaluating the role of climate and tectonics during non-steady incision of the Yellow River: Evidence from a 1.24 Ma terrace record near Lanzhou, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2009, 28(27/28): 3281-3290. -





 下载:
下载: