Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and controlling factors of deep-water sediments in the Beikang Basin since the Late Miocene, southern South China Sea
-
摘要:
南海南部北康盆地是我国海域油气研究的重点区域, 前人对该区域沉积地层的研究集中在古近系烃源岩和中中新世碳酸盐岩储层, 有关晚中新世以来深水沉积发育及分布特征的研究仍很薄弱。为此, 研究用2D地震数据资料识别北康盆地晚中新世以来沉积单元, 揭示深水沉积单元分布特征及其控制因素。基于地震反射特征, 研究识别了北康盆地晚中新世以来的主要沉积体类型, 包括披覆沉积、块体流沉积和浊流沉积, 其中浊流沉积可进一步分为限制型浊积体和三角洲前缘浊积体。披覆沉积在北康盆地前隆区域大面积发育, 沉积厚度从南向北递减。块体流沉积则主要分布在研究区隆后盆地, 厚度自西南向东北递减。结果表明北康盆地晚中新世以来的深水沉积受到物源供给、地形、构造活动和海平面变化的控制。其中, 物源供给是控制研究区沉积体发育位置和厚度变化的主要因素。地形对重力流沉积(块体流沉积和三角洲前缘浊积体)和半远洋沉积的分布范围进行控制。研究成果可为深水沉积发育及其控制因素研究提供理论依据。
Abstract:Objective The Beikang Basin, located in the southern South China Sea, is a significant area for offshore oil and gas exploration in China. Previous studies in this region have primarily focused on the Palaeogene source rock and the Middle Miocene carbonate reservoirs, neglecting the investigation of deep-water sediments since the Late Miocene.
Methods Therefore, this study aims to explore the spatiotemporal distribution, characteristics, and controlling factors of deep-water sediments in the Beikang Basin since the Late Miocene, utilizing 2D seismic data.
Results Three types of sedimentary deposits have been identified in the Beikang Basin since the Late Miocene: draping strates, mass-transport deposits (MTDs), and turbidites. Turbidites can be further classified into confined turbidites and delta-front ones. The study reveals that the draping state is predominantly developed in the forebulge tectonic regions of the Beikang Basin, with a decreasing thickness from South to North. MTDs, on the other hand, are mainly distributed in the Backbulge zone, with a thickness that decreases from Southwest to Northeast. The findings indicate that the development and distribution of sediments in the Beikang Basin are influenced by various factors, including sedimentary supply, geomorphic features, tectonic activity, and eustatic sea level changes. The location and thickness of deep-water sediments are primarily controlled by the supply of materials. Additionally, the distribution range of gravity flow deposits and draping states is influenced by the topography of the area.
Conclusion These results provide a theoretical foundation for understanding the development and controlling factors of deep-water sediments in the Beikang Basin.
-
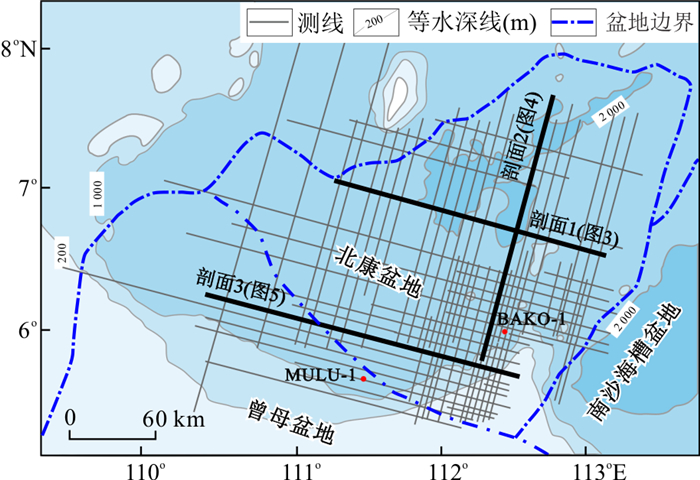
图 3 北康盆地典型地震剖面1的解释(剖面1位置见图 1)
Figure 3. Interpretation of typical seismic Profile 1 in the Beikang Basin
图 4 北康盆地典型地震剖面2的解释(剖面2位置见图 1)
Figure 4. Interpretation of typical seismic Profile 2 in the Beikang Basin
图 5 北康盆地典型地震剖面3的解释(剖面3位置见图 1)
Figure 5. Interpretation of typical seismic Profile 3 in the Beikang Basin
图 7 南海南部海域水深图(海山与海丘的名称据文献[27])(a)与研究区晚中新世以来沉积体系分布图(b)
Figure 7. Bathymetric map of the southern South China Sea (a) and regional sedimentary distribution since the Late Miocene in the study area(b)
表 1 研究区地震相的分类及特征
Table 1. Classification and characteristics of seismic facies in the study area

-
[1] Pickering K, Hiscott R. Deep marine systems: Processes, deposits, environments, tectonics and sedimentation[M]. Washington, DC, USA: Wiley & American Geophysical Union, 2016. [2] Huneke H, Mulder T. Deep-sea sediments[M]. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier, 2011. [3] Rebesco M, Camerlenghi A. Contourites[M]. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier, 2008: 457-489. [4] 孙国桐. 深水重力流沉积研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(3): 30-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201503005.htmSun G T. A review of deep-water gravity-flow deposition research[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(3): 30-36(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201503005.htm [5] 解习农, 任建业, 王振峰, 等. 南海大陆边缘盆地构造演化差异性及其与南海扩张耦合关系[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1): 77-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501009.htmXie X N, Ren J Y, Wang Z F, et al. Difference of tectonic evolution of continental marginal basins of South China Sea and relationship with SCS spreading[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 77-87(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501009.htm [6] Banerjee A, Salim A M A. Seismic attribute analysis of deep-water dangerous grounds in the South China Sea, NW Sabah Platform region, Malaysia[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 83: 103534. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2020.103534 [7] 何玉林, 匡增桂, 徐梦婕. 北康盆地第四纪块体搬运沉积地震反射特征及成因机制[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(4): 258-268. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0435He Y L, Kuang Z G, Xu M J. Seismic reflection characteristics and triggering mechanism of mass transport deposits of Quaternary in Beikang Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(4): 258-268(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0435 [8] Liu S, Hernández-Molina F J, Lei Z Y, et al. Fault-controlled contourite drifts in the southern South China Sea: Tectonic, oceanographic, and conceptual implications[J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 433: 106420. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2021.106420 [9] Hutchison C S. Marginal basin evolution: The southern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21(9): 1129-1148. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.07.002 [10] Madon M, Ly K C, Wong R. The structure and stratigraphy of deepwater Sarawak, Malaysia: Implications for tectonic evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 76(S1): 312-333. [11] 王龙樟, 姚永坚, 张莉, 等. 中中新世以来南海南部前隆的迁移: 来自北康盆地的证据[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(1): 123-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201901013.htmWang L Z, Yao Y J, Zhang L, et al. Forebulge migration since the Mid-Miocene in the southern South China Sea: Evidences from the Beikang Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(1): 123-132(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201901013.htm [12] Banerjee A, Salim A M A. Stratigraphic evolution of deep-water dangerous grounds in the South China Sea, NW Sabah Platform Region, Malaysia[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 201: 108434. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108434 [13] 黄维, 汪品先. 南海沉积物总量的统计: 方法与结果[J]. 地球科学进展, 2006, 21(5): 465-473. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200605003.htmHuang W, Wang P X. The statistics of sediment mass in the South China Sea: Method and result[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2006, 21(5): 465-473(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200605003.htm [14] 雷振宇, 张莉, 苏明, 等. 南海南部北康盆地中中新世深水沉积体类型、特征及意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(6): 110-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201706013.htmLei Z Y, Zhang L, Su M, et al. Middle Miocene deep-water sediments in the Beikang Basin, southern South China Sea: Types, characteristics and implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(6): 110-118(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201706013.htm [15] 王宏斌, 姚伯初, 梁金强, 等. 北康盆地构造特征及其构造区划[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(2): 49-54.Wang H B, Yao B C, Liang J Q, et al. Tectonic characteristics and division of the Beikang Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(2): 49-54(in Chinese with English abstract). [16] 张莉, 王嘹亮, 易海. 北康盆地的形成与演化[J]. 中国海上油气地质, 2003, 17(4): 23-26.Zhang L, Wang L L, Yi H. The formation and evolution of Beikang Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2003, 17(4): 23-26(in Chinese with English abstract). [17] 骆帅兵, 王笑雪, 张莉, 等. 南海南部北康-曾母盆地早中新世层序内部优质砂岩精细刻画[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(2): 111-123.Luo S B, Wang X X, Zhang L, et al. Study of high-quality sandstone in Early Miocene sequence of Beikang-Zengmu Basin, the southern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(2): 111-123(in Chinese with English abstract). [18] 姚永坚, 杨楚鹏, 李学杰, 等. 南海南部海域中中新世(T3界面)构造变革界面地震反射特征及构造含义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(4): 1274-1286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201304024.htmYao Y J, Yang C P, Li X J, et al. The seismic reflection characteristics and tectonic significance of the tectonic revolutionary surface of Mid-Miocene(T3 seismic interface) in the southern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013, 56(4): 1274-1286(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201304024.htm [19] Koša E. Sea-level changes, shoreline journeys, and the seismic stratigraphy of Central Luconia, Miocene-present, offshore Sarawak, NW Borneo[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 59: 35-55. [20] Madon M, Redzuan A H. West Luconia Province//Anon. The petroleum geology and resources of Malaysia[M]. Kuala Malaysia, Malaysia: Petroliam Nasional Berhad, 1999: 427-436. [21] Petronas. The petroleum geology and resources of malaysia[M]. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: Petronas, 1999. [22] Mitchum R M J, Vail P R, Sangree J B. Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level: Part 6. Stratigraphic interpretation of seismic reflection patterns in depositional sequences[M]//Payton C E. Seismic stratigraphy: Applications to hydrocarbon exploration. Tulsa, USA: AAPG Memoir, 1977: 17-133. [23] Madon M. North Luconia Province//Anon. The petroleum geology and resources of Malaysia[M]. Kuala Lumpur: Petroliam Nasional Berhad, 1999: 441-454. [24] Omosanya K O. Episodic fluid flow as a trigger for Miocene-Pliocene slope instability on the Utgard High, Norwegian Sea[J]. Basin Research, 2018, 30(5): 942-964. [25] Masson D G, Hyggett Q J, Brunsden D. The surface texture of the Saharan debris flow deposit and some speculations on submarine debris flow processes[J]. Sedimentology, 1993, 40(3): 583-598. [26] Steventon M J, Jackson C A L, Hodgson D M, et al. Strain analysis of a seismically imaged mass-transport complex, offshore Uruguay[J]. Basin Research, 2019, 31(3): 600-620. [27] 朱本铎, 关水贤, 黄文星, 等. 南海地质地球物理图系(1∶200万)[CM]. 广州: 中国航海图书出版社, 2015.Zhu B D, Guan S X, Huang W X, et al. Atlas of geology and geophysics of South China Sea(1∶2 000 000)[CM]. Guangzhou: China Navigation Publication Press, 2015(in Chinese). [28] Stow D, Smillie Z. Distinguishing between deep-water sediment facies: Turbidites, contourites and hemipelagites[J]. Geosciences, 2020, 10(2): 68. [29] Stow D, Tabrez A R. Hemipelagites: Processes, facies and model[M]. United Kingdom: Geological Society of London Special Publications, 1998: 317-337. [30] Takano S, Ito M, Nakano T, et al. Sequence-stratigraphic signatures of hemipelagic siltstones in deep-water successions: The Lower Pleistocene Kiwada and Otadai Formations, Boso Peninsula, Japan[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2004, 170(3/4): 189-206. [31] 雷振宇, 张莉, 王龙樟, 等. 南海南部北康盆地晚渐新世-中中新世物源变化[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(5): 1855-1864.Lei Z Y, Zhang L, Wang L Z, et al. The provenance migration in the Beikang Basin of the southern South China Sea during the Oligocene to the Mid-Miocene[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(5): 1855-1864(in Chinese with English abstract). [32] 张晋, 李安春, 万世明, 等. 南海南部表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(2): 1-10.Zhang J, Li A C, Wan S M, et al. Grain size distribution of surface sediments in the southern South China Sea and influencing factors[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(2): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). [33] Wang P, Prell W L, Blum P, et al. Proceedings of the ocean drilling program, Initial Reports 184[R]. Texas: Texas A & M University, 2000. [34] Ding W, Franke D, Li J, et al. Seismic stratigraphy and tectonic structure from a composite multi-channel seismic profile across the entire dangerous grounds, South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 582: 162-176. [35] Huang J, Jiao W, Liu J, et al. Sediment distribution and dispersal in the southern South China Sea: Evidence from clay minerals and magnetic properties[J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 439: 106560. [36] 张厚和, 刘鹏, 廖宗宝, 等. 南沙海域主要盆地地质特征与油气分布[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2018, 23(1): 62-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201801007.htmZhang H H, Liu P, Liao Z B, et al. Geological characteristics and hydrocarbon distribution in major sedimentary basins in Nansha sea areas[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2018, 23(1): 62-70(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201801007.htm [37] Abdul M M, Robert H, Wong F. Seismic sequence stratigraphy of the Tertiary sediments, offshore Sarawak deep-water area, Malaysia[J]. Geology Society of Malaysia Bulletin, 1995, 57: 545-561. [38] Xu J, Ren J, Luo P. The evolution of a gravity-driven system accompanied by diapirism under the control of the prograding West Luconia Deltas in the Kangxi Depression, southern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2019, 40(2): 199-221. [39] 王华, 陈思, 刘恩涛, 等. 南海北部莺-琼盆地典型重力流沉积特征与物源体系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 5-18. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0245Wang H, Chen S, Liu E T, et al. Typical gravity flow sedimentary features and provenance system in Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 5-18(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0245 [40] 裴健翔, 张成, 王亚辉, 等. 南海南部陆缘盆地裂陷-漂移-前陆期构造演化及沉积响应: 以礼乐盆地为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(2): 42-53. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0205Pei J X, Zhang C, Wang Y H, et al. Tectonic evolution and depositional response in southern continental marginal basins of South China Sea during period of rift-drift-foreland: A case study from the Liyue Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(2): 42-53(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0205 [41] 周蒂, 吴世敏, 陈汉宗. 南沙海区及邻区构造演化动力学的若干问题[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2005, 29(3): 339-345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200503008.htmZhou D, Wu S M, Chen H Z. Some remarks on the tectonic evolution of Nansha and its adjacent regions in southern South China Sea[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2005, 29(3): 339-345(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200503008.htm [42] Hall R. Reconstructing Cenozoic SE Asia[J]. Geological Society, 1996, 106: 153-184. [43] 孙珍, 赵中贤, 周蒂, 等. 南沙海域盆地的地层系统与沉积结构[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2011, 36(5): 798-806.Sun Z, Zhao Z X, Zhou D, et al. The stratigraphy and the sequence achitecture of the basins in Nansha Region[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2011, 36(5): 798-806(in Chinese with English abstract). [44] 雷振宇, 刘晓峰, 张莉, 等. 南海南部北康盆地构造样式及构造演化[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(5): 861-874.Lei Z Y, Liu X F, Zhang L, et al. Structural styles and evolution of Beikang Basin, southern South China Sea[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(5): 861-874(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: