Real-time detection algorithm of tunnel cracks based on GRU-CNN
-
摘要:
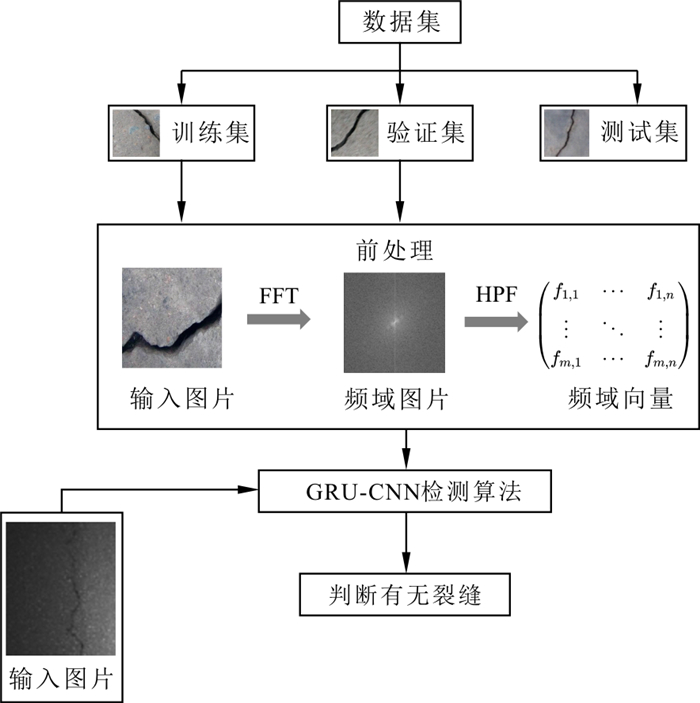
隧道裂缝严重损害隧道的使用寿命以及行车安全, 而传统人工检测方法无法对长隧道中的大量裂缝进行高效精确识别。提出了一种隧道表面裂缝实时检测算法, 该方法创新性地将用于文本学习、信号分析的门控循环单元(GRU)模型应用于图像分类中, 用于提升隧道裂缝检测速度并保证检测精度。为提高训练效率, 首先对裂缝进行预处理将其转换至频域中提取隧道裂缝的关键信息并矩阵重构为一维向量, 再利用一维卷积神经网络提取一维向量的深度特征并输入循环神经网络学习深度特征中的序列依存关系, 最终实现对隧道裂缝的检测。测试结果表明该模型不仅能降低模型训练参数量和硬件配置需求, 同时该模型在精度上能达到99.0%, 检测单张图片速度能达到2.1 s, 相较于主流的分类检测模型其准确率保持不变, 训练时间和预测速度显著提升。最后针对大尺寸隧道裂缝图像开发了检测框架, 可实现对大尺寸图像中裂缝信息的有效提取。
Abstract:Objective Tunnel cracks seriously damage the corresponding life time and traffic safety. However, traditional manual detections cannot efficiently and accurately identify a large number of cracks in long tunnels.This paper proposes a real-time detection algorithm for tunnel surface cracks.
Methods It innovatively applies the Gate Recurrent Unit (GRU) model for text learning and signal analysis to image classification, improving detection speed and ensuring detection accuracy of tunnel cracks. To enhance training efficiency, the cracks are preprocessed and converted into the frequency domain to extract the key information of tunnel cracks, and the matrix is reconstructed into one-dimensional vectors. Then, one-dimensional convolutional neural network is used to extract the vector depth feature, and recurrent neural networks can learn corresponding sequential dependencies to realize tunnel cracks detection.
Results Test results show that this model can reduce the number of training parameters and hardware configuration requirements. At the same time, the detection accuracy can reach 98.8%, and the detection speed for single image can reach in 2.1 s. Comparing with the mainstream classification detection algorithms, its accuracy remains unchanged, with significantly improvements of both training efficiency and prediction rate respectively.
Conclusion Finally, a detection framework is developed for large-scale tunnel cracks to extract corresponding crack information effectively.
-
Key words:
- tunnel crack /
- real-time detection /
- classification detection /
- frequency domain
-
表 1 GRU-CNN模型框架及参数
Table 1. Framework and parameters of GRU-CNN
层类型 类型 输出形态 参数量 Layer 1 Conv1d-1 [-1, 32, 4 096] 128 BatchNorm1d-2 [-1, 32, 4 096] 64 ReLU-3 [-1, 32, 4 096] 0 MaxPool1d-4 [-1, 32, 2 047] 0 Layer 2 Conv1d-5 [-1, 64, 2 047] 6 208 BatchNorm1d-6 [-1, 64, 2 047] 128 ReLU-7 [-1, 64, 2 047] 0 MaxPool1d-8 [-1, 64, 1 022] 0 Layer 3 Conv1d-9 [-1, 128, 1 022] 24 704 BatchNorm1d-10 [-1, 128, 1 022] 256 ReLU-11 [-1, 128, 1 022] 0 MaxPool1d-12 [-1, 128, 255] 0 Layer 4 Conv1d-13 [-1, 256, 255] 98 560 BatchNorm1d-14 [-1, 256, 255] 512 ReLU-15 [-1, 256, 255] 0 MaxPool1d-16 [-1, 256, 63] 0 Layer 5 Conv1d-17 [-1, 256, 63] 196 864 BatchNorm1d-18 [-1, 256, 63] 512 ReLU-19 [-1, 256, 63] 0 MaxPool1d-20 [-1, 256, 15] 0 Layer 6 GRU-21 [[-1, 256, 256], [4, -1, 256]] 1 393 920 Layer 7 Dropout-22 [-1, 256] 0 Linear-23 [-1, 256] 65 792 ReLU-24 [-1, 256] 0 Linear-26 [-1, 2] 514 总参数: 张量(1 788 162) 表 2 评价指标混淆矩阵表示
Table 2. Evaluation for confusion matrix representation
混淆矩阵 真实值 裂缝 无裂缝 预测值 裂缝 TP FP 无裂缝 FN TN 表 3 主流模型对比实验结果
Table 3. Comparison of experimental result of mainstream models
模型 准确率/% 训练时间/s 预测速度/(s·per-1) VGG 99.1 29 596 3.94 GoogLeNet 99.5 11 580 2.65 ResNet 97.5 17 582 3.01 GRU-CNN 99.0 8 859 2.21 表 4 循环神经网络消融和替换实验
Table 4. Ablation and replacement of recurrent neural networks
模型 准确率/% 训练时间/s 预测速度/(s·per-1) 参数量 1D-CNN 98.5 8 305 2.21 858 882 LSTM-CNN 98.7 10 711 2.34 2 252 802 GRU-CNN 99.0 8 859 2.21 1 788 162 -
[1] 王剑非, 刘昆珏, 周文皎, 等. 香丽高速公路昌格洛滑坡-隧道工程病害三维数值分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 34-43. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0009Wang J F, Liu K J, Zhou W J, et al. Three-dimensional numerical analysis of the Changgeluo landslide-tunnel engineering disaster on Shangri-La to Lijiang Highway[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 34-43(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0009 [2] 李喜, 殷坤龙, 陈标典, 等. 武汉白沙洲长江两岸岩溶塌陷易发性评价与地铁建设过程中的防治对策[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 121-130. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0612Li X, Yin K L, Chen B D, et al. Evaluation of susceptibility to karst collapse on both sides of the Yangtze River in Baishazhou, Wuhan and preventive measures in the process of metro construction[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 121-130(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0612 [3] Li P, Wang C, Li S M, et al. Research on crack detection method of airport runway based on twice-threshold segmentation[C]// Anon. International Conference on Instrumentation and Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control(IMCC). Qinhurydao: IEEE, 2015: 1716-1720. [4] 杨心蕊, 许辰扬, 郑玉莹, 等. 基于遗传算法的阈值分割桥梁裂缝检测算法研究[J]. 广东土木与建筑, 2021, 28(10): 5-9.Yang X R, Xu C Y, Zheng Y Y, et al. Research on threshold segmentation algorithm of bridge crack detection based on genetic algorithm[J]. Guangdong Architecture Civil Engineering, 2021, 28(10): 5-9(in Chinese with English abstract). [5] Wang W X, Wang M F, Li H X, et al. Pavement crack image acquisition methods and crack extraction algorithms: A review[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering: English Edition, 2019, 6(6): 535-556. doi: 10.1016/j.jtte.2019.10.001 [6] 赵芳, 周旺辉, 陈岳涛, 等. 改进的Canny算子在裂缝检测中的应用[J]. 电子测量技术, 2018, 41(20): 107-111.Zhao F, Zhou W H, Chen Y T, et al. Application of improved Canny operator in crack detection[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2018, 41(20): 107-111(in Chinese with English abstract). [7] 董安国, 宋君, 张仙艳, 等. 基于图像的桥梁裂缝检测算法[J]. 自动化仪表, 2013, 34(8): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYB201308001.htmDong A G, Song J, Zhang X Y, et al. Image-based bridge crack detection algorithm[J]. Process Automation Instrumentation, 2013, 34(8): 1-4(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYB201308001.htm [8] 武旭娟, 郭骞, 宋捷. 公路隧道衬砌裂缝检测方法研究[J]. 北方交通, 2017(2): 81-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNJT201702023.htmWu X J, Guo Q, Song J. Research on detection method of cracks in highway tunnel lining[J]. Northern Communications, 2017(2): 81-83(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNJT201702023.htm [9] 刘彦锋, 张文彪, 段太忠, 等. 深度学习油气藏地质建模研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 235-241. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0417Liu Y F, Zhang W B, Duan T Z, et al. Progress of deep learning in oil and gas reservoir geological modeling[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 235-241(in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0417 [10] Yang X, Wei S Y, Bao Y Q, et al. Automatic seismic damage identification of reinforced concrete columns from images by a region-based deep convolutional neural network[J]. Structural Control & Health Monitoring, 2019, 26(3): e2313. [11] Cha Y J, Choi W, Suh G, et al. Autonomous structural visual inspection using region: Based deep learning for detecting multiple damage types[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2018, 33(9): 731-747. [12] Protopapadakis E, Voulodimos A, Doulamis A, et al. Automatic crack detection for tunnel inspection using deep learning and heuristic image post-processing[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2019, 49(7): 2793-2806. doi: 10.1007/s10489-018-01396-y [13] Ren Y P, Huang J S, Hong Z Y, et al. Image-based concrete crack detection in tunnels using deep fully convolutional networks[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 234: 117367. [14] Kim B, Cho S. Image-based concrete crack assessment using mask and region-based convolutional neural network[J]. Structural Control & Health Monitoring, 2019, 26(8): e2381. [15] Dong Y A, Wang J, Wang Z F, et al. A deep-learning-based multiple defect detection method for tunnel lining damages[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 182643-182657. [16] 常惠, 饶志强, 李益晨, 等. 基于改进残差网络的铁路隧道裂缝检测算法研究[J]. 东北师大学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 53(3): 56-63.Chang H, Rao Z Q, Li Y C, et al. Research on crack detection algorithm of railway tunnel based on improved residual network[J]. Journal of Northeast Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2021, 53(3): 56-63(in Chinese with English abstract). [17] Zhang Q, Barri K, Babanajad S K, et al. Real-time detection of cracks on concrete bridge decks using deep learning in the Frequency Domain[J]. Engineering, 2021, 7(12): 1786-1796. [18] Zhao X Y, Huang P, Shu X B. Wavelet-attention CNN for image classification[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2022, 28(3): 915-924. [19] Watanabe T, Wolf D F. Image classification in frequency domain with 2SReLU: A second harmonics superposition activation function[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 112: 107851. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568494621007730 [20] Brosch T, Tam R. Efficient training of convolutional deep belief networks in the frequency domain for application to high-resolution 2D and 3D images[J]. Neural computation, 2015, 27(1): 211-227. [21] 庞庆华, 董显蔚, 周斌, 等. 基于情感分析与TextRank的负面在线评论关键词抽取[J]. 情报科学, 2022, 40(5): 111-117.Pang Q H, Dong X W, Zhou B, et al. Keyword extraction of negative online reviews based on sentiment analysis[J]. Information Science, 2022, 40(5): 111-117(in Chinese with English abstract). [22] 李冉冉, 刘大明, 刘正, 等. 融合笔画特征的胶囊网络文本分类[J]. 计算机工程, 2022, 48(3): 69-73, 80.Li R R, Liu D M, Liu Z, et al. Text classification using capsule network integrating stroke features[J]. Computer Engineering, 2022, 48(3): 69-73, 80(in Chinese with English abstract). [23] Zou J Z, Yang J X, Wang G P, et al. Bridge structural damage identification based on parallel CNN-GRU[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 626: 012017. [24] 王亚飞, 韩静, 郭凰, 等. 基于Bi-LSTM的结构变形预测[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2021, 30(11): 304-309.Wang Y F, Han J, Guo H, et al. Prediction of structural deformation based on Bi-LSTM[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2021, 30(11): 304-309(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] Cho K, Merrienboer B, Gulcehre C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[J]. CoRR, 2014. doi: org/ 10.48550/arXiv.1406.1078. -





 下载:
下载: