Simulation of burial history, thermal evolution history, and hydrocarbon generation history of the Upper Cretaceous Yogou Formation source rocks in the Termit Basin
-
摘要:
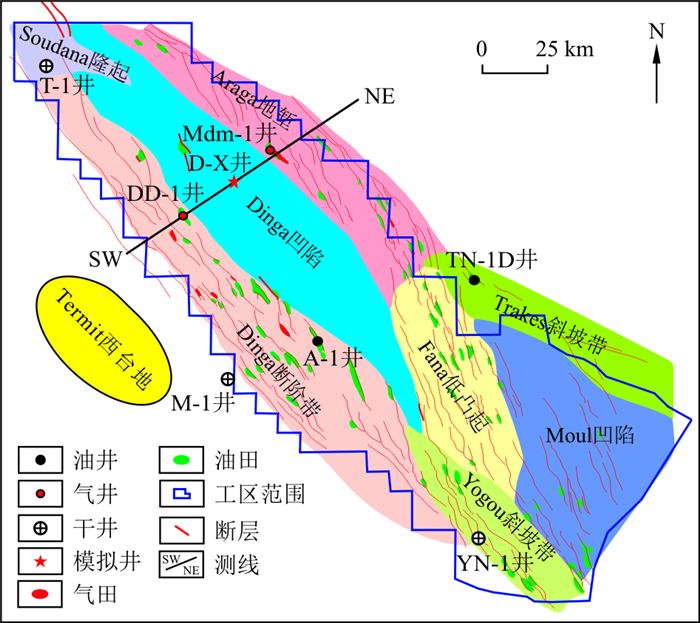
Yogou组烃源岩作为尼日尔Termit盆地晚白垩世重要的烃源岩层系, 然而缺乏对该套地层的埋藏史、热演化史和生烃史的系统研究, 制约了该地区油气成藏规律的认识。结合钻井、地震二维剖面及地球化学等资料, 利用BasinMod盆地模拟软件中生烃动力学模型, 恢复了Termit盆地Yogou组烃源岩热演化史, 分析不同地区烃源岩的热演化特征及其与油气成藏的匹配关系, 为Termit盆地下一步油气勘探提供了重要依据。研究表明, Termit盆地热流值具有明显的两段式演化特征, 初始热流值较低, 古近纪晚期热流值达到最大, 热流值介于64.3~69.2 mW/m2之间; 新近纪以来, 盆地热状态表现为持续冷却, 现今热流值介于60.7~67.4 mW/m2之间。Yogou组顶部烃源岩在55 Ma进入生烃门限(
R o=0.5%), 达到生烃高峰(R o=1.0%)的时间为35 Ma, 在27.5 Ma进入高成熟演化阶段(R o=1.3%)。Yogou组烃源岩存在2期生烃过程, 晚白垩世末期(70~60 Ma)生烃阶段主要存在于盆地深凹陷区, 古近纪(40~20 Ma)是全盆地主要的生烃阶段。盆地不同构造带对比发现, Dinga凹陷烃源岩具有成熟度更高, 生烃时间更早和生烃能力更强等特征, 可为Termit盆地储层提供充足油气来源。古近纪Termit盆地断裂强烈活动, 促使底部烃源岩生成的油气在古近系储层中聚集成藏。研究成果为Termit盆地烃源岩生烃潜力评价提供依据, 并为该盆地油气勘探提供理论指导。Abstract:Objective The Yogou Formation source rock is an important Late Cretaceous source rock series in Termit Basin, Niger. Due to the lack of systematic research on the burial history, thermal evolution history, and hydrocarbon generation history of this set of strata, the understanding of oil and gas accumulation rules in this area is restricted.
Methods In this paper, the thermal evolution history of the Yogou Formation source rocks in Termit Basin is restored by using the hydrocarbon generation dynamics model in BasinMod basin simulation software, combined with drilling wells, two-dimensional seismic profiles, and geochemical data. The thermal evolution characteristics of source rocks in different areas and their matching relationship with hydrocarbon accumulation are analysed, which provides important evidence for the next exploration of the Termit Basin.
Results The results show that the heat flow value of Termit Basin has obvious two-stage evolution characteristics. The initial heat flow value is low and reaches maximum values in the Late Palaeogene (ranging from 64.3 to 69.2 mW/m2). Since the Neogene, the thermal state of the basin has been characterized by continuous cooling, and the current heat flow value is between 60.7 and 67.4 mW/m2. The hydrocarbon generation of the top Yogou Formation began at 55 Ma (
R o=0.5%), and the main hydrocarbon generation window (R o=1.0%) started at 35 Ma and reached a high maturity level (R o=1.3%) at 27.5 Ma. Two stages of hydrocarbon generation are found in the source rocks of the Yogou Formation; in particular, the Late Cretaceous (70-60 Ma) hydrocarbon generation stage mainly exists in the deep area depression of the basin, while the Palaeogene (40-20 Ma) is the main hydrocarbon generation stage of the whole basin. Compared to different tectonic belts show that the source rocks of the Dinga Depression are characterized by high maturity, earlier hydrocarbon generation, and stronger hydrocarbon generation, which are beneficial for providing sufficient hydrocarbons. The strong activity of the Palaeogene faults led to the migration and accumulation of oil and gas generated by the bottom source rocks into the Palaeogene reservoirs.Conclusion The research results can provide a basis for the evaluation of the hydrocarbon generation potential of source rocks in the Termit basin and provide theoretical guidance for oil and gas exploration in the basin.
-
Key words:
- rift basin /
- Termit Basin /
- source rocks /
- basin modeling /
- history of thermal evolution
-
图 2 Termit盆地地层综合柱状图[21]
Figure 2. Stratigraphic composite histogram of the Termit Basin
表 1 Termit盆地单井热流值
Table 1. Single-well heat flow values in the Termit Basin
井名 现今热流值/(mW·m-2) 最大古热流值/(mW·m-2) M-1井 62.5 67.6 YN-1井 60.7 64.3 TN-1D井 67.4 69.2 表 2 Termit盆地底部烃源岩成熟度演化史及生烃史特征
Table 2. Maturity evolution and hydrocarbon generation history characteristics of bottom source rocks in the Termit Basin
井名 烃源岩成熟阶段距今时间/Ma 开始生烃距今时间/Ma 生烃高峰距今时间/Ma Ro=0.5% Ro=0.7% Ro=1.3% Ro=2% M-1井 49.0 15.5 — — 66.0 25.0 YN-1井 64.5 39.5 15.0 — 69.0 29.0 TN-1D井 59.0 24.5 — — 68.0 24.5 D-X井 68.2 67.1 65.2 59.4 67.6 66.2 -
[1] 石广仁. 盆地模拟技术30年回顾与展望[J]. 石油工业计算机应用, 2009, 61(1): 3-6.Shi G R. Review and outlook for the 30th anniversary of basin modelling techniques[J]. Computer Applications of Petroleum, 2009, 61(1): 3-6(in Chinese with English abstract). [2] 郭小文, 何生, 侯宇光. 板桥凹陷沙三段油气生成、运移和聚集数值模拟[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2010, 35(1): 115-124.Guo X W, He S, Hou Y G. Numerical simulation of petroleum generation, migration and accumulation of the Es3 Formation in Banqiao Depression[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010, 35(1): 115-124(in Chinese with English abstract). [3] 段威, 侯宇光, 何生, 等. 澳大利亚波拿巴盆地侏罗系烃源岩热史及成熟史模拟[J]. 地质科技情报, 2011, 30(3): 65-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201103010.htmDuan W, Hou Y G, He S, et al. Jurassic source rock thermal and maturity history modelling in the Bonaparte Basin of Australia[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2011, 30(3): 65-71(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201103010.htm [4] 吴琰杰, 王帅, 何磊, 等. 吐哈盆地小草湖凹陷东缘侏罗系煤系烃源岩埋藏史、热演化史模拟[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(4): 180-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI202104015.htmWu Y J, Wang S, He L, et al. Research on the burial history and the thermal evolution history of the Jurassic coal-measure source rocks in the eastern margin of Xiaocaohu Sag[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(4): 180-191(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI202104015.htm [5] 刘可禹, 刘建良. 盆地和含油气系统模拟(BPSM)研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 石油科学通报, 2017, 2(2): 161-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE201702001.htmLiu K Y, Liu J L. Current status and future development trends of Basin and Petroleum System Modeling (BPSM)[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2017, 2(2): 161-175(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE201702001.htm [6] 曹自成, 唐大卿, 骆满嵩, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北地区中新生界断裂构造特征及演化[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 226-238. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0176Cao Z C, Tang D Q, Luo M S, et al. Structural characteristics and tectonic evolution of Mesozoic-Cenozoic faults in the Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 226-238(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0176 [7] 关德范, 徐旭辉, 李志明, 等. 成盆成烃成藏理论思维与有限空间生烃模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(6): 709-715. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.06.001Guan D F, Xu X H, Li Z M, et al. A study on theories of basin evolution and hydrocarbon generation and accumulation and model of hydrocarbon generation in finite spaces[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2008, 29(6): 709-715(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.06.001 [8] 王亮, 赵红岩, 邱春光, 等. 东非裂谷Turkana坳陷新生代构造演化及动力学[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 151-161. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0512Wang L, Zhao H Y, Qiu C G, et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution and dynamics of Turkana Depression, East African Rift[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 151-161(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0512 [9] 郑晨宇, 赵红岩, 邱春光, 等. 东非裂谷系Albert湖凹陷新生代构造沉降特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 162-172. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0513Zheng C Y, Zhao H Y, Qiu C G, et al. Cenozoic tectonic subsidence characteristics of Albert Lake Depression in East African Rift System[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 162-172(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0513 [10] 周立宏, 苏俊青, 董晓伟, 等. 尼日尔Termit裂谷型叠合盆地油气成藏特征与主控因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(3): 330-339.Zhou L H, Su J Q, Dong X W, et al. Controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation in Termit rift superimposed basin, Niger[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44 (3): 330-339(in Chinese with English abstract). [11] 毛凤军, 刘邦, 刘计国, 等. 尼日尔Termit盆地上白垩统储层岩石学特征及控制因素分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(4): 1257-1268.Mao F J, Liu B, Liu J G, et al. The reservoir characteristics and controlling factors of the Upper Cretaceous sandstones in the Termit Basin, Niger[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(4): 1257-1268(in Chinese with English abstract). [12] 刘邦, 潘校华, 万仑坤, 等. 东尼日尔Termit盆地构造演化及古近系油气成藏主控因素[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(3): 394-403.Liu B, Pan X H, Wan L K, et al. Structural evolution and main controlling factors of the Paleogene hydrocarbon accumulation in Termit Basin, eastern Niger[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(3): 394-403(in Chinese with English abstract). [13] 吕明胜, 薛良清, 万仑坤, 等. 西非裂谷系Termit盆地古近系油气成藏主控因素分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(6): 207-216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201506019.htmLv M S, Xue L Q, Wan L K, et al. Main controlling factors of Paleogene hydrocarbon accumulation of Termit Basin, West African Rift System[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(6): 207-216(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201506019.htm [14] 薛良清, 万仑坤, 毛凤军, 等. 东尼日尔盆地Termit坳陷油气富集规律及Dibeilla-1井发现的意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2012, 17(4): 53-59, 7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201204010.htmXue L Q, Wan L K, Mao F J, et al. Petroleum migration and accumulation in Termit Depression of East Niger Basin and implications for discovery of Well Dibeilla-1[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2012, 17(4): 53-59, 7(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201204010.htm [15] 董晓伟, 刘爱平, 钱茂路, 等. 西非裂谷系尼日尔Termit盆地烃源岩地球化学特征分析与原油分类[J]. 录井工程, 2016, 27(2): 87-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGZ201602023.htmDong X W, Liu A P, Qian M L, et al. Geochemical characteristics of source rocks and crude oil classification in Termit Basin, Niger, West Africa Rift System[J]. Mud Logging Engineering, 2016, 27 (2): 87-92(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGZ201602023.htm [16] Sweeney J J, Burnham A K. Evaluation of a simple model of vitrinite reflectance based on chemical kinetics[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(10): 1559-1570. [17] Genik G. Petroleum geology of Cretaceous Tertiary rift basins in Niger, Chad and Central African Republic[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1993, 77(8): 1405-1434. [18] Guiraud R, Bosworth W, Thierry J, et al. Phanerozoic geological evolution of northern and central Africa: An overview[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2005, 43(1/3): 83-143. [19] 毛凤军, 刘若涵, 刘邦, 等. 尼日尔Termit盆地及其周缘晚白垩世古地理演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(3): 186-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201603027.htmMao F J, Liu R H, Liu B, et al. Palaeogeographic evolution of the Upper Cretaceous in Termit Basin and its adjacent areas, Niger[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(3): 186-197(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201603027.htm [20] Liu J, Zhang G, Li Z, et al. Oil charge history of Paleogene-Eocene reservoir in the Termit Basin (Niger)[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2019, 66(4): 597-606. [21] 吕明胜, 薛良清, 苏永地, 等. 裂谷作用对层序地层充填样式的控制: 以西非裂谷系Termit盆地下白垩统为例[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2012, 42(3): 647-656.Lü M S, Xue L Q, Su Y D, et al. Rifting controls on sequence stratigraphic architecture: A case study in the Lower Cretaceous of Termit Basin, West African Rift System[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2012, 42(3): 647-656(in Chinese with English abstract). [22] 周立宏, 汤戈, 苏俊青, 等. 西非Termit叠合裂谷盆地构造沉积演化及控藏机理[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(2): 129-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201802001.htmZhou L H, Tang G, Su J Q, et al. Tectonic-sedimentary evolution and reservoir controlling mechanism of Termit superimposed rift basin in West Africa[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(2): 129-140(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201802001.htm [23] 郑凤云, 史卜庆, 李早红, 等. 尼日尔Termit盆地古近系构造样式及其对油气聚集的控制作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(2): 72-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201802010.htmZheng F Y, Shi B Q, Li Z H, et al. Paleogene structure styles and their controls on the hydrocarbon accumulation in the Termit Basin, Niger[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(2): 72-82(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201802010.htm [24] 袁圣强, 毛凤军, 郑凤云, 等. 尼日尔Termit盆地上白垩统成藏条件分析与勘探策略[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(2): 42-50.Yuan S Q, Mao F J, Zheng F Y, et al. Analysis of hydrocarbon accumulation condition and exploration tactics of the Upper Cretaceous strata in the Termit Basin, Niger[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(2): 42-50(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] 黄谦, 陈容涛, 彭晓波, 等. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷古近系烃源岩生物标志物特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 180-192. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0085Huang Q, Chen R T, Peng X B, et al. Characteristics and geological significance of biomarkers from the Paleogene sourcerocks in Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 180-192(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0085 [26] 王巍. 利用盆地模拟方法分析莫里青断陷地层压力演化[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(5): 103-109.Wang W. Modelling of pressure evolution in the Moliqing Rift, Yitong Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(5): 103-109(in Chinese with English abstract). [27] 张鑫, 陈红汉, 龙昭, 等. 泌阳凹陷北部缓坡带核桃园组油气运聚成藏过程[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 140-149. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0315Zhang X, Chen H H, Long Z, et al. Hydrocarbon migration and accumulation process of Hetaoyuan Formation in the northern gentle slope zone of Biyang Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 140-149(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0315 [28] Falvey D A, Middleton M F. Passive continental margins: Evidence for a prebreakup deep crustal metamorphic subsidence mechanism[J]. Oceanologica Acta, 1981, 4(S): 103-114. [29] Wan L, Liu J, Mao F, et al. The petroleum geochemistry of the Termit Basin, eastern Niger[J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 2014, 51(2): 167-183. [30] Mckenzie D. Some remarks on the development of sedimentary basins[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1978, 40(1): 25-32. [31] Callies M, Filleaudeau P Y, Dubille M, et al. How to predict thermal stress in hyperextended margins: Application of a new lithospheric model on the Iberia margin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2018, 102(4): 563-585. [32] Suggate R P. Relations between depth of burial, vitrinite reflectance and geothermal gradient[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 1998, 21(1): 5-32. [33] Harouna M, Pigott J D, Philp R P. Burial history and thermal maturity evolution of the Termit Basin, Niger[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 2017, 40(3): 277-297. [34] 于彪, 刘建良, 杨贵丽, 等. 渤海海域东部不同富油凹陷烃源岩生烃特征差异及意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 104-114, 130. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0407Yu B, Liu J L, Yang G L, et al. Hydrocarbon generation characteristics and signification of source rock in different oil-rich depressions in the eastern part of the Bohai Sea[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 104-114, 130(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0407 [35] 郑见超, 李斌, 吴海燕, 等. 基于盆地模拟技术的烃源岩热演化史及油气关系研究: 以塔里木盆地玉尔吐斯组为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2018, 25(5): 39-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201805006.htmZheng J C, Li B, Wu H Y, et al. Study on the thermal history of the source rock and its relationship with hydrocarbon accumulation based on the basin modeling technology: A case of the Yuertusi Formation of Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2018, 25(5): 39-49(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201805006.htm [36] 乔彦国, 李瑞, 左毅, 等. 盆地模拟技术研究Aryskum凹陷侏罗系油气藏生烃史[J]. 计算机与应用化学, 2014, 31(6): 648-654. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSYH201406002.htmQiao Y G, Li R, Zuo Y, et al. Aryskum depression Jurassic hydrocarbon reservoirs history study based on basin modeling techniques[J]. Computers and Applied Chemisry, 2014, 31(6): 648-654(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSYH201406002.htm [37] 周江羽, 吴冲龙, 韩志军. 鄂尔多斯盆地的地热场特征与有机质成熟史[J]. 石油实验地质, 1998, 20(1): 20-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD199801004.htmZhou J Y, Wu C L, Han Z J. Geothermal field and maturing history of organic matter in the Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 1998, 20(1): 20-24(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD199801004.htm [38] 邱楠生, 汪为孝, 谢明举. 沉积盆地中镜质组反射率异常的物理化学环境探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(11): 1760-1769.Qiu N S, Wang W X, Xie M J. Study on the pyhsical and chemical environments of abnormal vitrinite reflectance evolution in the sedimentary basins[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(11): 1760-1769(in Chinese with English abstract). [39] 程克明, 张怡蓉. 中国中、新生代陆相盆地中有机质的热演化[J]. 石油学报, 1981, 2(4): 17-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB1981S1002.htmCheng K M, Zhang Y R. Thermal evolution of organic matter in Meso-Cenozoic continental basins in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1981, 2(4): 17-24(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB1981S1002.htm [40] 关德范, 徐旭辉, 李志明, 等. 烃源岩生排烃理论研究与泥页岩油气[J]. 中外能源, 2012, 17(5): 40-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZW201205008.htmGuan D F, Xu X H, Li Z M, et al. Theory study of hydrocarbon generation and expulsion of source rocks and oil and gas in shale[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2012, 17(5): 40-52(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZW201205008.htm -





 下载:
下载: