Occurrence characteristics and influencing factors of movable fluid in the medium- and low-permeability reservoirs of the Es32+3 submember of the Gao3102 fault block in the Gaoshangpu Oilfield
-
摘要:
为了明确中低渗透储层可动流体赋存特征, 以期更好地指导油田增储上产, 以高尚堡油田高3102断块沙三2+3亚段中低渗透砂岩储层为研究对象, 基于薄片资料、全岩衍射分析、高压压汞曲线、密闭取心核磁共振资料、扫描电镜以及油水相渗曲线, 开展了不同孔隙结构储层可动流体的赋存特征及其影响因素研究。结果表明: ①不同孔隙结构储层可动流体饱和度差异较大。Ⅰ类中孔中喉型储层核磁共振
T 2谱呈左低右高双峰型, 可动流体饱和度平均61.14%;Ⅱ类中小孔细喉型储层核磁共振T 2谱呈左高右高双峰型, 可动流体饱和度平均45.24%;Ⅲ类细孔微喉型储层核磁共振T 2谱呈左高右低双峰型, 可动流体饱和度平均30.45%;Ⅳ类微孔微喉型储层核磁共振T 2谱呈左高单峰型, 可动流体饱和度平均13.86%;②储层宏观物性、微观孔隙结构、黏土矿物含量以及储层润湿性共同控制可动流体赋存特征。其中微观孔隙结构是可动流体赋存的关键因素, 孔喉半径越大, 储层渗流能力越好, 黏土矿物含量越低, 储层润湿性越弱, 可动流体饱和度越高。该研究结果对高尚堡油田沙三2+3亚段储层高效注水开发提供合理科学依据。Abstract:Objective In order to clarify the occurrence characteristics of movable fluids in medium- and low-permeability reservoirs, so as to better guide the increase in oil reserves and production in the oilfield.
Methods This study focuses on the medium- and low-permeability sandstone reservoirs in the E
s 32+3 submember of the Gao3102 fault block in the Gaoshangpu Oilfield. Based on thin section data, whole-rock diffraction analysis, high-pressure mercury injection curves, closed core nuclear magnetic resonance data, scanning electron microscopy, and oil-water phase permeability curves, the occurrence characteristics and influencing factors of movable fluids in reservoirs with different pore structures were conducted.Results The results show that (1) the movable fluid saturation of reservoirs with different pore structures varies greatly. The
T 2 spectrum of the nuclear magnetic resonance of the class Ⅰ medium porosity and medium throat reservoir is bimodal with left low and right thigh, and the average saturation of movable fluid is 61.14%. TheT 2 spectrum of the nuclear magnetic resonance of the class Ⅱ medium and small pore fine throat reservoir shows a double peak type with left high and right high, and the average of movable fluid saturation is 45.24%. TheT 2 spectrum of the nuclear magnetic resonance of the class Ⅲ fine porous micro throat reservoir shows a double peak type of left high and right low, and the average of movable fluid saturation is 30.45%. TheT 2 spectrum of the nuclear magnetic resonance of the class Ⅳ microporous micro throat reservoir shows a left high single peak, and the average saturation of movable fluid is 13.86%. (2) The macroscopic physical properties, microscopic pore structure, clay mineral content and reservoir wettability of the reservoir jointly control the occurrence characteristics of the movable fluid. Among them, the microscopic pore structure is a key factor in the occurrence of movable fluid. The larger the pore throat radius is, the better the reservoir seepage capacity, the lower the clay mineral content is, the weaker the reservoir wettability is, and the higher the movable fluid saturation is.Conclusion The results of this research can provide a reasonable scientific basis for high-efficiency water injection development of the E
s 32+3 reservoir in the Gaoshangpu Oilfield.-
Key words:
- Gaoshangpu Oilfield /
- Es32+3 submember /
- microscopic pore structure /
- movable fluid
-
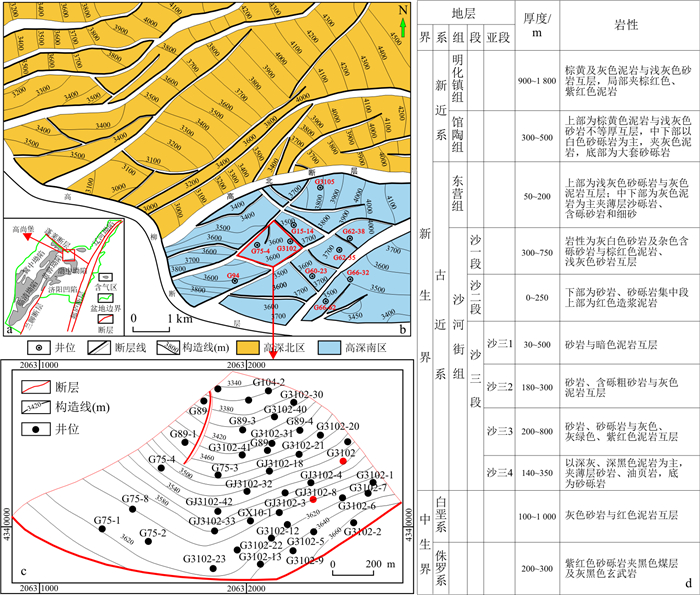
图 1 高3102断块构造位置图及地层综合柱状图[25]
a.渤海湾盆地构造格局;b.高尚堡深层Es32+3亚段油藏构造图;c.高3102断块Es32+3亚段Ⅲ油组顶面构造图; d.地层划分柱状图
Figure 1. Structural location map and comprehensive histogram of the Gao 3102 fault block in the study area
图 4 高尚堡油田高3102断块沙三2+3亚段储层微观孔隙特征相片
a.长石岩屑砂岩,发育粒间孔,粒间溶孔,GJ3102-8井,蓝色铸体薄片(单偏光),3 499.04 m;b.长石岩屑砂岩,残余粒间孔为主,GJ3102-8井,蓝色铸体薄片(单偏光),3 519.12 m;c.岩屑砂岩,发育粒内溶孔,GJ3102-8井,蓝色铸体薄片(单偏光),3 490.76 m;d.长石砂岩,铸模孔,颗粒溶孔,GJ3102-8井,蓝色铸体薄片(单偏光),3 513.96 m;e.绿泥石晶间微孔,GJ3102-8井,扫描电镜, 3 490.76 m;f.微裂缝,GJ3102-8井,铸体薄片(单偏),3 429.46 m
Figure 4. Microscopic pore characteristic photos of the Es32+3 submember in the Gao3102 fault block of the Gaoshangpu Oilfield
表 1 高3102断块沙三2+3亚段储层不同孔隙结构特征参数
Table 1. Characteristic parameters table of different pore structures in the Es32+3 submember of the Gao3102 fault block
代表样品编号 孔隙结构分类 排驱压力/MPa 平均孔喉半径/μm 最大孔喉半径/μm 均质系数 分选系数 退汞效率/% 最大进汞饱和度/% 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 GJ-45 Ⅰ类 0.010 8.446 73.640 0.115 9.155 51.57 90.79 18.30 116.00 GJ-38 Ⅰ类 0.032 6.780 65.230 0.320 5.320 39.62 80.05 16.60 101.60 GJ-393 Ⅱ类 0.049 6.640 16.840 0.480 4.849 35.12 82.91 13.90 66.30 GJ-409 Ⅱ类 0.073 3.490 10.010 0.370 3.250 41.87 74.20 16.40 35.70 GJ-314 Ⅲ类 0.301 1.540 3.389 0.236 0.588 31.50 63.34 13.68 7.59 GJ-197 Ⅲ类 0.308 0.550 2.390 0.230 1.220 33.55 52.33 14.60 2.86 GJ-204 Ⅳ类 0.550 0.246 1.442 0.180 0.321 80.20 27.03 7.50 0.85 GJ-206 Ⅳ类 2.068 0.069 0.356 0.187 0.063 21.10 20.26 7.20 2.06 表 2 高3102断块沙三2+3亚段储层核磁共振T2谱及渗流参数
Table 2. NMR T2 spectrum and seepage parameters of the reservoir in the Es32+3 submember of the Gao3102 fault block
代表样品编号 样品深度/m 岩性 孔隙结构类型 T2谱类型 可动流体饱和度/% T2截止值/ms Swx/% Krwm/% Wi GJ-45 3 431.24 粗粒岩屑长石砂岩 Ⅰ类 左低右高双峰 61.14 12.30 47.20 55.3 20.31 GJ-38 3 430.36 巨-粗粒长石岩屑砂岩 Ⅰ类 左低右高双峰 63.66 11.20 51.00 42.0 29.50 GJ-393 3 511.48 中粒岩屑长石砂岩 Ⅱ类 左高右高双峰 45.24 6.57 53.50 20.2 87.60 GJ-409 3 513.78 粗粒长石岩屑砂岩 Ⅱ类 左高右高双峰 40.04 8.10 51.70 13.1 116.92 GJ-314 3 499.04 不等粒岩屑长石砂岩 Ⅲ类 左高右低双峰 30.45 3.66 50.50 13.6 119.93 GJ-197 3 483.12 细粒岩屑长石砂岩 Ⅲ类 左高右低双峰 22.11 3.22 51.70 10.0 181.50 GJ-204 3 483.84 巨粒长石岩屑砂岩 Ⅳ类 左高单峰型 13.86 3.20 65.30 5.0 601.00 GJ-206 3 484.18 含碳酸盐砂质砾岩 Ⅳ类 左高单峰型 14.87 2.13 64.65 6.1 449.20 注:Swx为油水相渗交点处含水饱和度;Krwn为最大含水饱和度下水相相对渗透率;Wi为润湿指数 表 3 高3102断块沙三2+3亚段储层典型岩心样品的黏土矿物X射线分析结果
Table 3. X-ray analysis results of clay minerals of typical core samples from the in Es32+3 sub member reservoir in the Gao3102 fault block
样品编号 孔隙结构类型 黏土矿物相对质量分数/% 伊/蒙混层比/% 黏土矿物绝对质量分数/% 绿泥石 伊蒙混层 高岭石 伊利石 GJ-45 Ⅰ类 53.8 13.4 28.0 4.8 54 3.8 GJ-38 Ⅰ类 42.1 21.3 27.7 8.9 55 4.4 GJ-393 Ⅱ类 51.7 21.3 20.5 6.5 51 4.9 GJ-409 Ⅱ类 65.5 12.9 18.7 2.9 50 4.0 GJ-314 Ⅲ类 66.9 14.3 16.5 2.3 68 4.8 GJ-197 Ⅲ类 56.7 16.5 20.8 6.0 55 5.8 GJ-204 Ⅳ类 43.2 27.8 23.4 5.6 54 4.7 GJ-206 Ⅳ类 22.3 53.6 15.2 8.9 78 7.5 -
[1] 邹才能, 陶士华, 侯连华. 非常规油气地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011: 103-117.Zou C N, Tao S H, Hou L H. Unconventional oil and gas geology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011: 103-117(in Chinese). [2] Xiao Z K, Ding W L, Hao S Y, et al. Quantitative analysis of tight sandstone reservoir heterogeneity based on rescaled range analysis and empirical mode decomposition: A case study of the Chang 7 reservoir in the Dingbian Oilfield[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 182: 106326. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106326 [3] 刘凯, 石万忠, 王任, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区盒1段致密砂岩孔隙结构分形特征及其与储层物性的关系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 57-68. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0102Liu K, Shi W Z, Wang R, et al. Pore structure fractal characteristics and its relationship with reservoir properties the First Member of Lower Shihezi Formation tight sandstone in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 57-68(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0102 [4] 何娟, 孙立春, 倪军娥, 等. 伊拉克M油田Asmari组B段混积岩储层特征及储层非均质性对开发的影响[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(4): 127-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201804015.htmHe J, Sun L C, Ni J E, et al. Characteristics and heterogeneity of the diamictite reservoir in B Member of Asmari Formation in M oilfield, Iraq and their impacts on development[J]. China offshore oil and gas, 2018, 30(4): 127-134(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201804015.htm [5] 李玉喜, 何建华, 尹帅, 等. 页岩油气储层纵向多重非均质性及其对开发的影响[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(2): 118-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602014.htmLi Y X, He J H, Yin S, et al. The multi-anisotropy of shale oil and gas reservoirs in vertical and its influence on oil-gas development[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(2): 118-125(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602014.htm [6] 马淼, 孙卫, 刘登科, 等. 低渗透砂岩储层可动流体赋存特征及影响因素研究: 以姬塬油田长6储层为例[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2016, 30(6): 64-68, 72, 129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201606015.htmMa M, Sun W, Liu D K, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of movable fluid in low permeability sandstone reservoir: By taking Chang 6 reservoir in Jiyuan Oilfield of Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2016, 30(6): 64-68, 72, 129(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201606015.htm [7] 张世铭, 王建功, 张小军, 等. 酒西盆地间泉子段储层流体赋存及渗流特[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(8): 1111-1119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201808006.htmZhang S M, Wang J G, Zhang X J, et al. Studies on the reservoir characteristics and the fluid flow in Jianquanzi Member of the Jiuxi Basin, Northwest China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(8): 1111-1119(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201808006.htm [8] 卜淘, 曹廷宽. ZJ气田沙溪庙组储层微观孔隙结构及渗流特征研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2018, 38(3): 104-112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201803013.htmPu T, Cao Y K. Study of pore structure and seepage characteristics of Shaximiao Formation reservoir in ZJ Gasfield[J]. Mineral rock, 2018, 38(3): 104-112(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201803013.htm [9] 卢振东, 刘成林, 臧起彪, 等. 高压压汞与核磁共振技术在致密储层孔隙结构分析中的应用: 以鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 300-310. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0256Lu Z D, Liu C L, Zang Q B, et al. Application of high pressure mercury injection and nuclear magnetic resonance in analysis of the pore structure of dense sandstone: A case study of the Heshui area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 300-310(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0256 [10] 韩进, 孙卫, 白云云, 等. 基于真实砂岩微观水驱油实验的低渗透储层流体渗流特征及驱油效率影响因素研究: 以姬塬油田王盘山长6储层为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(6): 89-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201806011.htmHan J, Sun W, Bai Y Y, et al. Fluid seepage characteristics of low permeability reservoir based on the real sandstone microscopic water flooding experiment: Taking the Chang 6 reservoir in Wangpanshan as an example[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(6): 89-95(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201806011.htm [11] Qu Y Q, Sun W, Wu H N, et al. Impacts of pore-throat spaces on movable fluid: Implications for understanding the tight oil exploitation process[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2022, 137: 105509. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105509 [12] Li P, Jia C Z, Jin Z J, et al. The characteristics of movable fluid in the Triassic lacustrine tight oil reservoir: A case study of the Chang 7 Member of Xin'anbian Block, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 102: 126-137. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.11.019 [13] Hui W, Wang Y S, Ren D Z, et al. Effects of pore structures on the movable fluid saturation in tight sandstones: A He8 formation example in Sulige Gasfield, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 192: 107295. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107295 [14] 王剑超, 余瑜, 林良彪, 等. 川西坳陷须家河组四段致密砂岩储层可动流体饱和度影响因素[J]. 矿物岩石, 2023, 43(2): 95-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS202302010.htmWang J C, Yu Y, Lin L B, et al. Influencing factors of mobile fluid saturation in the tight sandstone reservoir in the 4th Member of Xujiahe Formation(T3x4), western Sichuan Basin[J]. Mineral Rock, 2023, 43(2): 95-107(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS202302010.htm [15] Horkowitz J P, Hartman D E, Clerke E A, et al. Residual oil saturation measurements in carbonates with pulsed NMR logs[J]. Log Analyst, 1997, 38(2): 73-83. [16] Gao H, Li H Z. Determination of movable fluid percentage and movable fluid porosity in ultra-low permeability sandstone using nuclear magnetic resonance(NMR) technique[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2015, 133: 258-367. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2015.06.017 [17] Wang W R, Yue D L, Eriksson K A, et al. Qualitative and quantitative characterization of multiple factors that influence movable fluid saturation in lacustrine deep-water gravity-flow tight sandstones from the Yanchang Formation, southern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 121: 104625. [18] Zang Q B, Liu C L, Awan R S, et al. Occurrence characteristics of the movable fluid in heterogeneous sandstone reservoir based on fractal analysis of NMR data: A case study of the Chang 7 Member of Ansai Block, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 214: 110499. [19] Li P, Sun W, Wu B L, et al. Occurrence characteristics and influential factors of movable fluids in pores with different structures of Chang 6(3) reservoir, Huaqing Oilfield, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 97: 480-492. [20] 李海波, 郭和坤, 王学武, 等. 岩心润湿性对核磁共振可动流体T2截止值的影响[J]. 西安石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 30(5): 43-47, 8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201505007.htmLi H B, Guo H K, Wang X W, et al. Influence of core wettability on NMR T2 cutoff value of movable fluid[J]. Journal of Xi'an Petroleum University: Natural Science Edition, 2015, 30(5): 43-47, 8(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201505007.htm [21] 郝国丽, 柳广弟, 谢增业, 等. 广安气田上三叠统须家河组致密砂岩储层气水分布特征[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 34(3): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201003003.htmHao G L, Liu G D, Xie Z Y, et al. Gas water distribution characteristics of tight sandstone reservoir of Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Guang'an Gasfield[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Natural Science Edition, 2010, 34(3): 1-7(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201003003.htm [22] 李冰, 周妍, 许万坤, 等. 渤海东部疏松砂岩油藏水驱渗流特征及控制因素分析[J]. 复杂油气藏, 2020, 13(2): 47-50, 55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ202002012.htmLi B, Zhou Y, Xu W K, et al. Analysis on water drive seepage characteristics and control factors of unconsolidated sandstone reservoir in eastern Bohai Sea[J]. Complex reservoir, 2020, 13(2): 47-50, 55(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ202002012.htm [23] 游秀玲, 金彦君, 常学军. 高尚堡油田沙三段二、三亚段沉积体系与沉积相[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1997, 18(1): 17-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT701.002.htmYou X L, Jin Y J, Chang X J. Sedimentary system and facies of Es32+3 submembers in Gaoshangbao Oilfield[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 1997, 18(1): 17-22(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT701.002.htm [24] 徐珂, 戴俊生, 商琳, 等. 高尚堡油田深层油藏南区现今地应力场预测及应用[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 42(6): 19-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201806003.htmXu K, Dai J S, Shang L, et al. Prediction of current in-situ stress filed and its application of southern area of deep reservoir in Gaoshangpu Oilfield[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2018, 42(6): 19-29(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201806003.htm [25] 冉启佑, 常学军, 刘翠荣. 高尚堡油田沙三段扇三角洲储层沉积学特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1997, 18(1): 23-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT701.003.htmRan Q Y, Chang X J, Liu C R. Sedimentological characteristics of fan-delta reservoir in Es32+3 submembers, Gaoshangbao Oilfield[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 1997, 18(1): 23-29(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT701.003.htm [26] 宋来明, 杨永强, 彭仕宓, 等. 冀东高尚堡油田Es32+3层序地层学研究[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2005, 35(4): 462-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200504009.htmSong L M, Yang Y Q, Peng S M, et al. Study on sequence stratigraphy of Es32+3 formation in Gaoshangpu Oilfield[J], Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2005, 35(4): 462-468(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200504009.htm [27] 张珂, 姜素华, 岳家彤, 等. 高尚堡油田沙三段二、三亚段微相特征研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 48(5): 86-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY201805011.htmZhang K, Jiang S H, Yue J T, et al. Sedimentary micro-facies of fan delta in Es32+3 sub member, Gaoshangpu Oilfield[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China: Natural Science Edition, 2018, 48(5): 86-94(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY201805011.htm [28] 李海燕, 吴胜和, 岳大力. 高尚堡油田深层沙三2亚段沉积微相及成岩储集相特征[J]. 科技导报, 2012, 30(9): 53-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJDB201209023.htmLi H Y, Wu S H, Yue D L. Characteristics of sedimentary microfacies and diagenetic reservoir facies of deep Es32 sub member in Gaoshangpu Oilfield[J]. Science and Technology Guide, 2012, 30(9): 53-61(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJDB201209023.htm [29] 李业会, 齐立新, 夏秋君, 等. 高尚堡油田沙三3亚段储层发育特征[J]. 中国矿业, 2014, 23(9): 83-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA201409021.htmLi Y H, Qi L X, Xia Q J, et al. Reservoir characteristics of Es33 in Gaoshangpu Oilfield[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2014, 23(9): 83-88(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA201409021.htm [30] 周亮, 谢俊, 姜新雨, 等. 高尚堡油田沙三段二、三亚段成岩作用与岩相划分[J]. 中国科技论文, 2018, 13(21): 2475-2481. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKZX201821013.htmZhou L, Xie J, Jiang X Y, et al. Study on the diagenetic facies classification of Es32+3 sub members in Gaoshangpu Oilfield[J]. Chinese Science Paper, 2018, 13(21): 2475-2481(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKZX201821013.htm [31] 崔树清, 刘雪军. 高尚堡油田沙河街组三段Es32+3亚段储层非均质性研究[J]. 西安石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005, 20(2): 22-24, 45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200502005.htmCui S Q, Liu X J. Study on the heterogeneity of the second and the third sub members of the third member of Shahejie Formation in Gaoshangpu Oilfield[J]. Journal of Xi'an Petroleum University: Natural Science Edition, 2005, 20(2): 22-24, 45(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200502005.htm [32] 张娜, 张紫筠, 王帅栋. 低渗透油藏可动流体饱和度计算及影响因素研究综述[J]. 水利水电技术, 2021, 52(9): 143-155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJWJ202109015.htmZhang N, Zhang Z Y, Wang S D. A review on calculation of movable fluid saturation of low permeability oil reservoir and its influencing factors[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2021, 52(9): 143-155(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJWJ202109015.htm [33] Lyu C H, Ning Z F, Cole D R, et al. Experimental investigation on T2 cutoffs of tight sandstones: Comparisons between outcrop and reservoir cores[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering. 2020, 191: 107184 [34] 师调调, 孙卫, 何生平. 低渗透储层微观孔隙结构与可动流体饱和度关系研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012, 31(4): 81-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201204015.htmShi T T, Sun W, He S P. Relationship between micro-pore structure and movable fluid saturation in low permeability reservoir[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012, 31(4): 81-85(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201204015.htm [35] 黄杰, 杜玉洪, 王红梅, 等. 特低渗储层微观孔隙结构与可动流体赋存特征: 以二连盆地阿尔凹陷腾一下段储层为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(5): 93-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202005010.htmHuang J, Du Y H, Wang H M, et al. Characteristics of micro pore structure and movable fluid of extra-low permeability reservoir: A case study of lower Et1 reservoir in A'er Sag, Erlian Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoir, 2020, 32(5): 93-101(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202005010.htm [36] 黄兴, 李天太, 王香增, 等. 致密砂岩储层可动流体分布特征及影响因素: 以鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬油田延长组长8油层组为例[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(5): 557-567. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201905005.htmHuang X, Li T T, Wang X Z, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of movable fluid in tight sandstone reservoir: A case study from Chang-8 oil layer of Yanchang Formation in Jiyuan Oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum, 2019, 40(5): 557-567(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201905005.htm [37] 白云云, 孙卫, 任大忠. 马岭油田致密砂岩储层可动流体赋存特征及控制因素[J]. 断块油气田, 2018, 25(4): 455-458. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201804010.htmBai Y Y, Sun W, Ren D Z. Characteristics and controlling factors of movable fluid in low-permeability and tight sandstone reservoirs in Maling Oilfield[J]. Fault Block Oil and Gas Field, 2018, 25(4): 455-458(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201804010.htm [38] 杨胜来, 魏俊之. 油层物理学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004.Yang S L, Wei J Z. Reservoir physics[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004(in Chinese). [39] 刘登科, 孙卫, 任大忠, 等. 致密砂岩气藏孔喉结构与可动流体赋存规律: 以鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格气田西区盒8段、山1段储层为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(12): 2136-2146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201612005.htmLiu D K, Sun W, Ren D Z, et al. Features of pore-throat structures and movable fluid in tight gas reservoir: A case from the 8th Member of Permian Xiashihezi Formation and the 1st Member of Permian Shanxi Formation in the western area of Sulige Gasfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(12): 2136-2146(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201612005.htm [40] 刘向君, 熊健, 梁利喜, 等. 川南地区龙马溪组页岩润湿性分析及影响讨论[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(10): 1644-1652. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201410021.htmLiu X J, Xiong J, Liang L X, et al. Analysis of the wettability of Longmaxi Formation shale in the South region of Sichuan Basin and its influence[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(10): 1644-1652(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201410021.htm -





 下载:
下载: