Large-range geological block modeling method
-
摘要:
三维地质建模是一种通过计算机技术将多源地质数据转化为三维地质模型的技术, 它揭示着地下各类地质体之间的空间分布关系, 可以帮助地质工作者更直观地理解地下地质结构, 并为资源勘探、灾害预测和工程建设等工作提供一定支持, 然而复杂的地质环境、有效地质数据的稀缺、巨大的计算量等因素使得大范围地质体的构建成为了三维地质建模发展过程中亟待解决的问题之一。针对该问题, 提出了一种大范围地质体分块建模方法, 该方法基于模型包围盒的水平分布范围将大型建模区域平均划分成若干个相对小型的区块分别进行建模, 引入虚拟钻孔和地层分区自动追踪算法实现了对区块模型顶底部及中间地层分块边界的一致性约束, 同时, 在对每个区块进行建模时, 对其建模数据范围进行一定扩充以确保合并后的区块间地层在分块边界处能够实现平滑过渡。研究结果表明各区块模型能合并成为一个地层衔接连贯、顺滑的完整地质模型, 进而实现大范围地质体建模。以厦门马銮湾新城区的浅层地下模型为例, 构建了厦门马銮湾新城区三维地质模型, 并对该方法的建模效果进行了检验。对该模型剖切得到的地质剖面与真实钻孔进行了对比, 并从建模效率、地层衔接的连贯性和顺滑性等方面进行了分析, 证实了该方法的可行性。
Abstract:Objective 3D geological modelling is a kind of technology that converts multisource geological data into 3D geological models through computer. It reveals the spatial distribution relationship between various underground geological bodies, which helps geologists understand underground geological structures more intuitively, providing certain support for resource exploration, disaster prediction, engineering construction.However, complex geological environment, scarcity of effective geological data, large amount of calculation and other factors make the construction of large-scale complex geological bodies become an urgent problem to be solved in the development of 3D geological modelling.
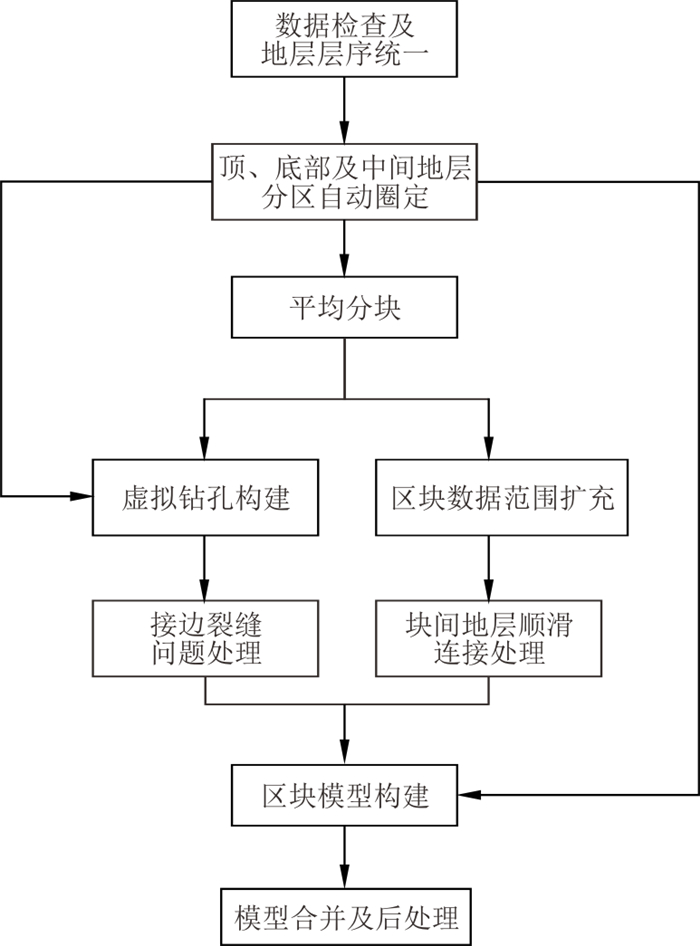
Methods To address these issue, this paper proposes a large range of complex geological body block modelling methods. Based on the model horizontal distribution scope of bounding box, large range of research area will be divided into several relatively smaller ones to perform modelling. At the same time, virtual borehole and stratum partition automatic tracking algorithm will be introduced for the block model at the bottom, top and middle part for the consistency of boundary constraints.At the same time, when modelling each block, the range of modelling data is extended to ensure that the strata between merged blocks can achieve smooth transition at the boundary of block.
Results Each block of model is combined into a complete one with coherent and smooth stara so that a large range of complex three-dimensional geological body modelling can be realized.
Conclusion Taking the shallow underground model of the Xiamen Maluan Bay New urban area as an example, this paper constructed corresponding geological model to test the modelling effect. The model is dissected and compared with the real borehole. The feasibility of proposed method is verified in terms of modelling efficiency, continuity and smoothness of strata connection.
-
表 1 厦门马銮湾新城区钻孔涉及到的标准地层编码及级别编码
Table 1. Standard strata and grade codes for drilling in the new urban area of Maluan Bay, Xiamen
年代地层 岩性 地层编码 级别编码 第四系 水体 G0 1-1-0 杂填土 1-1 1-1-1 素填土 1-2 1-1-2 吹填土 1-3 1-1-3 耕植土 1-4 1-1-4 全新统 淤泥 2-1 1-2-1 淤泥质土 2-2 1-2-2 淤泥 3-1 1-3-1 淤泥质土 3-2 1-3-2 粉砂、细砂 3-3 1-3-3 中砂、粗砂、砾砂 3-4 1-3-4 含淤泥砂 3-5 1-3-5 淤泥质砂 3-6 1-3-6 黏土、粉质黏土、砂质黏土 4-1 1-4-1 粉土 4-2 1-4-2 粉砂、细砂 4-3 1-4-3 中砂、粗砂、砾砂 4-4 1-4-4 角(砾)石 4-5 1-4-5 碎(卵)石 4-6 1-4-6 砂质黏土 5-2 1-5-2 上更新统 黏土、粉质黏土、砂质黏土 8-1 1-6-5 粉砂、细砂 8-3 1-6-7 中砂、粗砂、砾砂 8-4 1-6-8 角(砾)石 8-5 1-6-9 碎(卵)石 8-6 1-6-10 黏土、粉质黏土 10-1 1-8-1 残积砂质黏性土 11-1 1-9-1 残积砾质黏性土 11-2 1-9-2 火山岩残积土 11-3 1-9-3 脉岩残积土 11-4 1-9-4 透镜体 T 1-10-1 填石 Ts 1-11-1 全风化凝灰熔岩 12-1 2-1-1 强风化凝灰熔岩 12-2 2-1-2 中风化凝灰熔岩 12-3 2-1-3 微风化凝灰熔岩 12-4 2-1-4 全风化花岗岩 17-1 2-6-1 土状强风化花岗岩 17-2 2-6-2 碎块状强风化花岗岩 17-3 2-6-3 中风化花岗岩 17-4 2-6-4 微风化花岗岩 17-5 2-6-7 孤石 G 2-9-1 表 2 2种不同建模方法在时间上的横向对比
Table 2. Comparison for two different modeling methods in time
建模范围/km2 网格精度/m 钻孔数量/个 分块参数 模型构建方法 建模耗时/s 20 100
1002 981 5块×3块; 0.95 km×1.4 km
——分块建模
普通方法17.79
29.2920 50 50 2 981 5块×4块; 0.95 km×1.05 km
——分块建模
普通方法14.98
45.9640 100 100 6 489 3块×5块; 1.58 km×0.84 km
——分块建模
普通方法58.64
85.0340 50 50 6 489 4块×7块; 1.19 km×0.6 km
——分块建模
普通方法156.19
无法构建注:分块参数分别指横向块数×纵向块数,长×宽 -
[1] 吴健生, 朱谷昌, 曾新平, 等. 三维GIS技术在固体矿产勘探和开发中的研究与应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2004, 40(1): 68-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200401015.htmWu J S, Zhu G C, Zeng X P, et al. The research and application of three-dimensional GIS technology in solid mineral exploration and development[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2004, 40(1): 68-72(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200401015.htm [2] 张文彪, 段太忠, 刘彦锋, 等. 定量地质建模技术应用现状与发展趋势[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 264-275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903029.htmZhang W B, Duan T Z, Liu Y F, et al. Application status and development trend of quantitative geological modeling[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 264-275(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903029.htm [3] 尚福华, 杨彦彬, 杜睿山. 基于TIN-Octree的三维地质模型构建方法研究[J]. 计算技术与自动化, 2019, 38(4): 121-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJH201904023.htmShang F H, Yang Y B, Du R S. Research on construction method of 3D geological model based on TIN-Octree[J]. Computing Technology and Automation, 2019, 38(4): 121-125(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJH201904023.htm [4] Zhou C Y, Du Z C, Ouyang J W, et al. A 3D geological model and cutting algorithm based on a vertically projected triangulated network[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2020, 143: 104562. [5] Mallet J L. Discrete smooth interpolation in geometric modelling[J]. Computer-aided Design, 1992, 24(2): 178-191. [6] 陈军林, 闫岩, 彭润民. 基于t-SNE降维算法的区域化探数据中地质体空间分布信息可视化: 以英格兰西南部为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(2): 186-196. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0217Chen J L, Yan Y, Peng R M. Visualization of geological spatial distributing information in regional geochemical exploration data based on t-SNE algorithm: A case study of SW England[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(2): 186-196(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0217 [7] Kaufmann O, Martin T. 3D geological modelling from boreholes, cross-sections and geological maps, application over former natural gas storages in coal mines[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2007, 34(3): 278-290. [8] 李健, 刘沛溶, 梁转信, 等. 多源数据融合的规则体元分裂三维地质建模方法[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(4): 1170-1177.Li J, Liu P R, Liang Z X, et al. Three-dimensional geological modeling method of regular voxel splitting based on multi-source data fusion[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(4): 1170-1177(in Chinese with English abstract). [9] 冉祥金. 区域三维地质建模方法与建模系统研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2020.Ran X J. The research of method and system of regional three-dimensional geological modeling[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [10] 陈金龙, 罗文行, 窦斌, 等. 涿鹿盆地三维多裂隙地质模型地温场数值模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 22-33. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0317Chen J L, Luo W X, Dou B, et al. Numerical simulation of geothermal field in a three-dimensional multi-fractured geological model of Zhuolu Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 22-33(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0317 [11] Fouedjio F, Scheidt C, Yang L, et al. A geostatistical implicit modeling framework for uncertainty quantification of 3D geo-domain boundaries: Application to lithological domains from a porphyry copper deposit[J]. Computers and Geosciences, 2021, 157: 104931. [12] Laure P, Robin A, Simon L, et al. Taking better advantage of fold axis data to characterize anisotropy of complex folded structures in the implicit modeling framework[J]. Mathematical Geosciences, 2021, 54(1): 95-130. [13] Li X, Mariethoz G, Lu D T, et al. Patch-based iterative conditional geostatistical simulation using graph cuts[J]. Water Resources Research, 2016, 52(8): 6297-6320. [14] Mahmud K, Mariethoz G, Baker A, et al. Integrating multiple scales of hydraulic conductivity measurements in training image-based stochastic models[J]. Water Resources Research, 2015, 51(1): 465-480. [15] Gonçalves Í G, Kumaira S, Guadagnin F. A machine learning approach to the potential-field method for implicit modeling of geological structures[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2017, 103: 173-182. [16] Bi Z, Wu X, Li Z, et al. DeepISMNet: Three-dimensional implicit structural modeling with convolutional neural network[J]. Geoscientific Model Development Discussions, 2022, 15(17): 6841-6861. [17] 潘懋, 方裕, 屈红刚. 三维地质建模若干基本问题探讨[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2007, 23(3): 1-5.Pan M, Fang Y, Qu H G. Discussion on several foundational issues in three-dimensional geological modeling[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2007, 23(3): 1-5(in Chinese with English abstract). [18] 王威, 周杰, 王水林, 等. 基于径向基函数的三维地层分块建模方法研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(3): 939-944.Wang W, Zhou J, Wang S L, et al. Research on three-dimensional modeling of strata block based on radial basis function[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(3): 939-944(in Chinese with English abstract). [19] 刘小杨. 辽宁鞍山-本溪地区深部地质特征及三维地质建模[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014.Liu X Y. The deep geological characteristics and 3D geological modeling in Anshan-Benxi area, Liaoning Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [20] 薛林福, 李文庆, 张伟, 等. 分块区域三维地质建模方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2014, 44(6): 2051-2058. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201406034.htmXue L F, Li W Q, Zhang W, et al. A method of block-divided 3D geologic modeling in regional scale[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2014, 44(6): 2051-2058(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201406034.htm [21] 王威, 肖云, 葛修润, 等. 基于网格的三维地质体建模方法研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(4): 1275-1280.Wang W, Xiao Y, Ge X R, et al. Grid-based method of three-dimensional geological modeling[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(4): 1275-1280(in Chinese with English abstract). [22] 崔胜辉, 丁晟平, 徐礼来, 等. 1957-2017年厦门市马銮湾国土开发动态规律[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2021, 40(3): 502-510. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TWHX202103015.htmCui S H, Ding S P, Xu L L, et al. Dynamics of land development in Maluan Bay, Xiamen City from 1957 to 2017[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2021, 40(3): 502-510(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TWHX202103015.htm [23] 韦希. 面向实施管理的厦门马銮湾新城城市设计的思考[J]. 城市建筑, 2020, 17(35): 26-31.Wei X. Thoughts on the urban design of Xiameng Maluan Bay New Town for implementation management[J]. Urban Architecture, 2020, 17(35): 26-31(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: