Dispersion potential of asphaltene in live oil by nanoparticles
-
摘要:
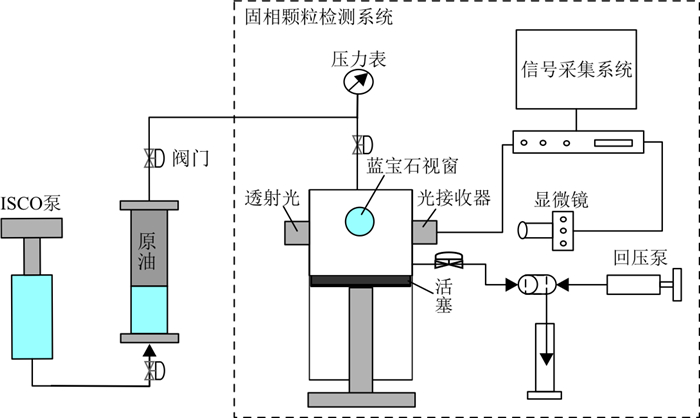
为明确纳米颗粒在高温高压下抑制地层活油中沥青质沉淀的效果及机理, 通过开展高温高压固相颗粒检测实验, 分别采用激光探测、高压显微镜和高温高压过滤等方法, 研究了纳米颗粒二氧化硅(SiO2)(改性)和四氧化三钴(Co3O4)作用下地层活油中沥青质的聚集和沉淀特征, 结合电镜扫描和热重分析实验, 揭示了纳米颗粒抑制沥青质沉淀机理。实验结果表明, 目标储层地层原油中添加SiO2纳米颗粒后, 沥青质沉淀起始压力(
AOP )由原来的59.2 MPa下降至53.4 MPa, 衰竭至35 MPa压力下, 沥青质颗粒的平均粒径由8.82μ m减小至5.53μ m, 沉淀量占比由66.4%降至46.4%。而添加Co3O4纳米颗粒后, 在泡点压力之上未出现明显沥青质沉淀, 35 MPa压力下沥青质颗粒平均粒径仅为1.65μ m, 沉淀量占比仅为13.6%。纳米颗粒能够抑制沥青质分子的析出、减缓沥青质颗粒的聚集速度、降低AOP 及沥青质的沉淀量。与SiO2纳米颗粒相比, Co3O4纳米颗粒具有更高的沥青质吸附亲和力, 抑制效果更好。研究成果为防治沥青质沉积及改善沉积伤害提供了依据。Abstract:Objective In order to clarify the effect and mechanism of nanoparticles on inhibiting asphaltene precipitation in formation live oil formation under high temperature and high pressure.
Methods In this study, by carrying out high-temperature and high-pressure solid particle detection experiment, the aggregation and precipitation characteristics of asphaltene in formation live oil under the action of SiO2 and Co3O4 nanoparticles were studied by means of laser detection, high-pressure microscopy and high-temperature and high-pressure filtration. Combined with the electron microscope scanning and thermogravimetric analysis experiments, the mechanism of nanoparticles inhibiting asphaltene precipitation was revealed.
Results The results show that the initial pressure of asphaltene precipitation (
AOP ) decreases from 59.2 MPa to 53.4 MPa after adding SiO2 nanoparticles to the crude oil of the target reservoir.When the pressure was reduced to 35 MPa, the average particle size of asphaltene particles decreases from 8.82μ m to 5.53μ m, and the proportion of precipitation decreased from 66.4% to 46.4%. After adding Co3O4 nanoparticles, there is no obvious asphaltene precipitation above the bubble point pressure.The average particle size of asphaltene particles is only 1.65μ m under 35 MPa pressure, and the proportion of precipitation is only 13.6%. Nanoparticles can inhibit the precipitation of asphaltene molecules, slow down the aggregation rate of asphaltene particles, and reduceAOP and precipitation. Compared with SiO2, Co3O4 nanoparticles have higher asphaltene adsorption affinity and better inhibition effect.Conclusion The research results provide a basis for preventing asphaltene deposition and improving deposition damage.
-
Key words:
- nanoparticle /
- asphaltene molecule /
- precipitation /
- adsorbent /
- initial pressure
-
表 1 地层原油基本高压物性参数
Table 1. Basic high-pressure physical parameters of the formation crude oil
参数类型 数值 地层原油组分C1~C7 xB/% 75.83 地层原油组分C8~C12xB/% 15.18 地层原油组分C12+xB/% 6.22 地层原油相对分子质量/(g·mol-1) 78 脱气原油相对分子质量/(g·mol-1) 224 泡点压力/MPa 30.6 溶解气油比/(m3·m-3) 275.4 地层原油密度/(g·cm-3)(71.6 MPa,128.7℃) 0.731 6 地层原油黏度/(mPa·s)(71.6 MPa,128.7℃) 2.78 原油中饱和烃xB/% 65.5 原油中芳香烃xB/% 23.3 原油中胶质xB/% 8.7 原油中沥青质xB/% 2.5 胶体不稳定指数 2.12 表 2 纳米颗粒的孔隙结构参数
Table 2. Pore structure parameters of nanoparticles
纳米颗粒类型 BJH模型 BET模型 平均纳米颗粒粒径/nm 孔隙体积/(10-3mL·g-1) 平均孔径/nm 孔隙体积/(10-3mL·g-1) 平均孔径/nm 比表面积/(m2·g-1) SiO2 395.4 18.85 402.6 19.06 75.82 28.69 Co3O4 133.2 20.28 131.8 24.16 21.35 47.62 -
[1] 李新文, 张国威. 沥青质沉积对原油渗流特征的影响[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 15-23. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0602Li X W, Zhang G W. Influence of asphaltene deposition on oil seepage characteristics[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 15-23(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0602 [2] Fakher S, Khlaifat A, Hossain M E, et al. A comprehensive review of sucker rod pumps' components, diagnostics, mathematical models, and common failures and mitigations[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 2021, 11(10): 3815-3839. doi: 10.1007/s13202-021-01270-7 [3] 雷浩. 低渗储层CO2驱油过程中沉淀规律及防治对策研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2017.Lei H. Deposition mechanisms and reservoir protection countermeasures of a low-permeability formation in CO2 flooding process[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum(Beijing), 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [4] 王志坚. 深层-超深层异常高压油藏工艺技术对策[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(5): 126-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202005016.htmWang Z J. Technological strategies for deep and ultra-deep reservoirs with abnormally high pressure[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(5): 126-132(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202005016.htm [5] 刘磊, 曹畅, 程汝镇, 等. 顺北沥青质分子结构和析出沉积规律研究[J]. 复杂油气藏, 2020, 13(4): 86-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ202004020.htmLiu L, Cao C, Cheng R Z, et al. Study on molecular structure and precipitation rules of Shunbei asphaltenes[J]. Complex Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 2020, 13(4): 86-91(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ202004020.htm [6] 王云飞, 魏建光. 减氧空气与轻质原油低温氧化反应特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 207-213. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0181Wang Y F, Wei J G. Reaction characteristics of low temperature oxidation of light crude oil with disoxidation air[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 207-213(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0181 [7] Kalantari F, Farahbod F. Mixing of crude oil with organic ZnO nano-particles from rice bran to improve physical properties of crude oil: A novel agent for enhanced oil recovery[J]. Natural Resources Research, 2019, 28(3): 1183-1196. doi: 10.1007/s11053-018-9443-y [8] 叶航, 刘琦, 彭勃, 等. 纳米颗粒抑制CO2驱过程中沥青质沉积的研究进展[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(5): 86-94.Ye H, Liu Q, Peng B, et al. Inhibition of nanoparticles on asphaltene deposition during CO2 flooding: A review[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(5): 86-94(in Chinese with English abstract). [9] Kazemzadeh Y, Eshraghi E, Kazemi K, et al. Behavior of asphaltene adsorption onto the metal xxide nanoparticle surface and its effect on heavy oil recovery[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(1): 233-239. [10] Taborda E A, Franco C A, Lopera S H, et al. Effect of nanoparticles/nanofluids on the rheology of heavy crude oil and its mobility on porous media at reservoir conditions[J]. Fuel, 2016, 184: 222-232. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.07.013 [11] Shojaati F, Riazi M, Mousavi S H, et al. Experimental investigation of the inhibitory behavior of metal oxides nanoparticles on asphaltene precipitation[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2017, 531: 99-110. [12] Alemi F M, Dehghani S A M, Rashidi A, et al. Potential application of Fe2O3 and functionalized SiO2 nanoparticles for inhibiting asphaltene precipitation in live oil at reservoir conditions[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(7): 5908-5924. [13] Eskin D, Omid M, Kamran A, et al. Reservoir impairment by asphaltenes: A critical review[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 94(6): 1202-1217. doi: 10.1002/cjce.22476 [14] Uetani T. Wettability alteration by asphaltene deposition: A field example[C]//Anon. Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference, 10-13 November. Abu Dhabi, UAE: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2014. [15] Papadimitriou N I, Romanos G E, Charalambopoulou G C, et al. Experimental investigation of asphaltene deposition mechanism during oil flow in core samples[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2007, 57(3/4): 281-293. [16] 郑希谭, 孙雯悦, 李实, 等. GB/T 26981-2011: 油气藏流体物性分析方法[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2010.Zheng X T, Sun W Y, Li S, et al. GB/T 26981-2011: Test method for reservoir fluid physical properties[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2010(in Chinese). [17] 王翠红, 罗爱兰, 王子军. NB/SH/T 0509-2010: 石油沥青质四组分测定方法[S]. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 2010.Wang C H, Luo A L, Wang Z J. NB/SH/T 0509-2010: Test method for separation of asphalt into four fractions[S]. Beijing: SINOPEC Press, 2010(in Chinese). [18] 卢振东, 刘成林, 臧起彪, 等. 高压压汞与核磁共振技术在致密储层孔隙结构分析中的应用: 以鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 300-310. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0256Lu Z D, Liu C L, Zang Q B, et al. Application of high pressure mercury injection and nuclear magnetic resonance in analysis of the pore structure of dense sandstone: A case study of the Heshui area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 300-310(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0256 [19] 岳长涛, 李术元, 许心怡, 等. 宜宾地区页岩微孔特征及吸附解吸特性研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 40(5): 84-94.Yue C T, Li S Y, Xu X Y, et al. Micropore characteristics and adsorption and desorption properties of shales in the Yibin region[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University: Science & Technology Edition, 2018, 40(5): 84-94(in Chinese with English abstract). [20] Fard S R, Khadar R H. The effect of inhibitors asphaltene precipitation due to a natural depletion mechanism in crude oil[J]. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 2012, 34(20): 1868-1875. doi: 10.1080/15567036.2011.615003 [21] Firoozinia H, Abad K F H, Varamesh A. A comprehensive experimental evaluation of asphaltene dispersants for injection under reservoir conditions[J]. Petroleum Science, 2016, 13(2): 280-291. doi: 10.1007/s12182-016-0078-5 [22] Lyu C, Ning Z, Wang Q, et al. Application of NMR T2 to pore size distribution and movable fluid distribution in tight sandstones[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(2): 1395-1405. [23] Maity S K, Blanco E, Ancheyta J, et al. Early stage deactivation of heavy crude oil hydroprocessing Catalysts[J]. Fuel, 2012, 100: 17-23. [24] Hosseinpour N, Mortazavi Y, Bahramian A, et al. Enhanced pyrolysis and oxidation of asphaltenes adsorbed onto transition metal oxides nanoparticles towards advanced in-situ combustion EOR processes by nanotechnology[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2014, 477: 159-171. -





 下载:
下载: