-
摘要:
河流地貌学研究河流动力的侵蚀-搬运-堆积过程(源-汇系统)、河流地貌的时空演化,及其与地球内部构造活动和地球表层气候和环境之间的相互关系。介绍了河流地貌学与表层地球系统科学的关系、研究内容和发展趋势、前沿问题和研究机遇。河流侵蚀、搬运和堆积在构造-气候相互作用中起着重要的媒介作用,是地球内部和外部相互作用的重要纽带。随着高精度数字地形模型定量分析、地表侵蚀速率的定量测定、沉积物测年以及地貌演化数值模拟等新技术和新方法的应用,促进了不同时间和空间尺度流域地形、水系发育、河流地貌动力过程、河流地貌空间分布特征及其对构造、气候和人类活动等的响应和反馈的研究。未来除了更深入地理解流域尺度物质和形态的变化规律和机制外,加强河流地貌过程的定量表达,将流域地貌研究与表层地球系统的热点科学问题相联系,进一步开展学科交叉,服务于国家战略,才能提高河流地貌学、乃至地貌学科的竞争力。
Abstract:Significance As an important branch in earth system science, fluvial geomorphology is the study of fluvial erosion-transport-accumulation processes (source-to-sink system), temporal-spatial change in fluvial landscapes, and impact of tectonic, climate and human activities on river evolution. Rivers connect the erosional domain of orogens and the depositional domain of ocean basins, which plays a crucial role in the earth surface system.
Progress On the basis of a sysnthesis of main research progress in fluvial geomorphology in recent decades, this article discusses the new direction of fluvial geomorphology. With the application of high-resolution topographic data, the scope of fluvial geomorphology has expanded and deepened over the past decades, including new methods used to calculate surface erosion rates, innovation in sediment dating techniques, and the development of numerical simulations. Studies on fluvial reorganization and influences of tectonics, climate change, and human activity on river evolution have been greatly advanced.
Conclusion and Prospects In the new era, fluvial geomorphology will focus on the frontiers in earth surface systems and national needs, strengthen the understanding of the mechanics of river formation and reorganization, and address major global and regional social-ecological issues. Furthermore, it needs to carry out the discipline overlap, serve the national strategy, and enhance its role in the research of the earth surface system.
-
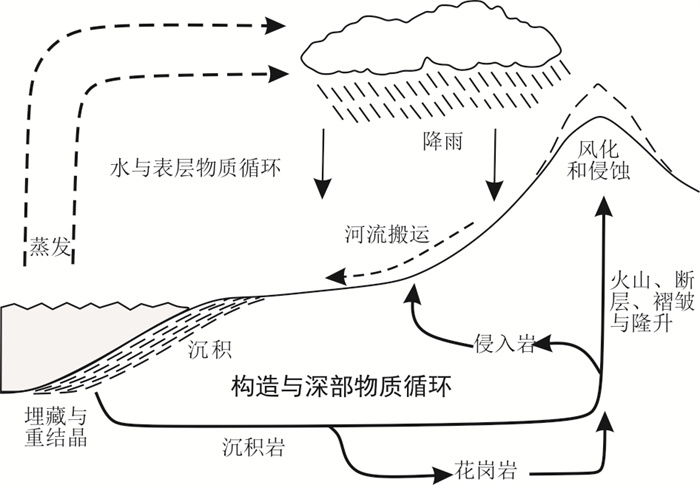
图 2 构造和气候作用下河流动力的侵蚀-搬运-堆积过程和河流地貌演化(改编自文献[27])
Figure 2. Schematic summary of a sediment-routing system and records of landscape evolution
图 4 黄土高原北洛河流域8 000年以来气候和人类活动土地覆盖影响下径流和泥沙量变化的数值模拟[15]
A.8 000 a以来地表径流时空变化模拟结果;B.KK10[73]人类土地利用情景(数据集)下人类土地覆盖面积变化(a)、年均径流变化(b)和年均泥沙量变化(c)模拟结果(圆点表示人类活动影响植被变化情景下模拟值,三角形点表示植被不变情景下模拟值)
Figure 4. Simulation of the discharge and sediments affected by the climate and human activities in the Beiluo River on the Loess Plateau since 8 000 years
-
[1] ZHANG P Z, MOLNAR P, DOWNS W R. Increased sedimentation rates and grain sizes 2-4 Myr ago due to the influence of climate change on erosion rates[J]. Nature, 2001, 410: 891-897. doi: 10.1038/35073504 [2] WHIPPLE K X. The influence of climate on the tectonic evolution of mountain belts[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2009, 2(2): 97-104. doi: 10.1038/ngeo413 [3] WANG P, SCHERLER D, LIU Z J, et al. Tectonic control of Yarlung Tsangpo Gorge revealed by a buried canyon in southern Tibet[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6212): 978-981. doi: 10.1126/science.1259041 [4] WILLETT S D, MCCOY S W, BEESON H W. Transience of the North American High Plains landscape and its impact on surface water[J]. Nature, 2018, 561: 528-532. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0532-1 [5] 刘静, 张金玉, 葛玉魁, 等. 构造地貌学: 构造-气候-地表过程相互作用的交叉研究[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(30): 3070-3088.LIU J, ZHANG J Y, GE Y K, et al. Tectonic geomorphology: An interdisciplinary study of the interaction among tectonic climatic and surface processes[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63: 3070-3088. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] CAVES RUGENSTEIN J K, IBARRA D E, VON BLAN-CKENBURG F. Neogene cooling driven by land surface reactivity rather than increased weathering fluxes[J]. Nature, 2019, 571(7763): 99-102. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1332-y [7] ZHANG H P, ZHANG P Z, CHAMPAGNAC J D, et al. Pleistocene drainage reorganization driven by the isostatic response to deep incision into the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geology, 2014, 42(4): 303-306. doi: 10.1130/G35115.1 [8] ADAMS B A, WHIPPLE K X, FORTE A M, et al. Climate controls on erosion in tectonically active landscapes[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(42): 3166. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz3166 [9] 崔鹏. 中国山地灾害研究进展与未来应关注的科学问题[J]. 地理科学进展, 2014, 33(2): 145-152.CUI P. Progress and prospects in research on mountain hazards in China[J]. Progress in Geography, 2014, 33(2): 145-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 程维明, 周成虎, 申元村, 等. 中国近40年来地貌学研究的回顾与展望[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72: 755-775.CHENG W M, ZHOU C H, SHEN Y C, et al. Retrospect and perspective of geomorphology researches in China over the past 40 years[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72: 755-775. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 傅伯杰, 赵文武. 自然地理学前沿[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021.FU B J, ZHAO W W. Frontier of physical geography[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021. (in Chinese) [12] FAN X M, VAN WESTEN C J, KORUP O, et al. Transient water and sediment storage of the decaying landslide dams induced by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J]. Geomorphology, 2012, 171: 58-68. [13] COOK K L, ANDERMANN C, GIMBERT F, et al. Glacial lake outburst floods as drivers of fluvial erosion in the Himalaya[J]. Science, 2018, 362: 53-57. doi: 10.1126/science.aat4981 [14] LIU W, HE S M. Dynamic simulation of a mountain disaster chain: Landslides, barrier lakes, and outburst floods[J]. Natural Hazards, 2018, 90(2): 757-775. doi: 10.1007/s11069-017-3073-2 [15] CHEN H, WANG X Y, LU H Y, et al. Anthropogenic impacts on Holocene fluvial dynamics in the Chinese Loess Plateau: An evaluation based on landscape evolution modeling[J]. Geomorphology, 2021, 392: 107935. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2021.107935 [16] WU Q L, ZHAO Z J, LIU L, et al. Outburst flood at 1920 BCE supports historicity of China's Great Flood and the Xia dynasty[J]. science, 2016, 353(6299): 579-582. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf0842 [17] 董广辉, 张帆宇, 刘峰文, 等. 喇家遗址史前灾害与黄河大洪水无关[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2017, 48(4): 467-475.DONG G H, ZHANG F Y, LIU F W, et al. Multiple evidences indicate no relationship between prehistoric disasters in Lajia site and outburst flood in upper Yellow River valley, China[J]. Science China(Earth Sciences), 2018, 61: 441-449. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 黄春长, 郭永强, 张玉柱, 等. 青海官亭盆地喇家遗址全新世地层序列与史前灾难研究[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2019, 49(2): 434-455.HUANG C C, GUO Y Q, ZHANG Y Z, et al. Holocene sedimentary stratigraphy and pre-historical catastrophes over the Lajia Ruins within the Guanting Basin in Qinghai Province of China[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2019, 49: 434-455, (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] LU H Y, ZHUO H X, ZHANG W C, et al. Earth surface processes and their effects on human behavior in monsoonal China during the Pleistocene-Holocene epochs[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2017, 27(11): 1311-1324. doi: 10.1007/s11442-017-1437-x [20] YANG X, WANG X Y, VAN BALEN R T, et al. Fluvial terrace formation and its impacts on early human settlement in the Hanzhong Basin, Qinling Mountains, Central China[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2019, 178: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2019.04.007 [21] XIE W T, WANG X Y, ZHANG H Z, et al. Drainage evolution in intermontane basins at the Qinling-Daba Mountains[J]. Science China(Earth Sciences), 2021, 64(11): 1949-1968. doi: 10.1007/s11430-020-9820-y [22] GUPTA S, COLLIER J S, PALMER-FELGATE A, et al. Catastrophic flooding origin of shelf valley systems in the English Channel[J]. Nature, 2007, 448: 342-345. doi: 10.1038/nature06018 [23] HOORN C, WESSELINGH F P, TER STEEGE H, et al. Amazonia through time: Andean uplift, climate change, landscape evolution, and biodiversity[J]. Science, 2010, 330: 927-931. doi: 10.1126/science.1194585 [24] 鹿化煜. 试论地貌学的新进展和趋势[J]. 地理科学进展, 2018, 37(1): 8-15.LU H Y. Progress in geomorphology and future study: A brief review[J]. Progress in Geography, 2018, 37(1): 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] 傅伯杰. 新时代自然地理学发展的思考[J]. 地理科学进展, 2018, 37(1): 1-7.FU B J. Thoughts on the recent development of physical geography[J]. Progress in Geography, 2018, 37(1): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] LYONS N J, VAL P, ALBERT J S, et al. Topographic controls on divide migration, stream capture, and diversification in riverine life[J]. Earth Surface Dynamics, 2020, 8(4): 893-912. doi: 10.5194/esurf-8-893-2020 [27] TOFELDE S, SAVI S, WICKERT A D, et al. Alluvial channel response to environmental perturbations: Fill-terrace formation and sediment-signal disruption[J]. Earth Surface Dynamics, 2019, 7(2): 609-631. doi: 10.5194/esurf-7-609-2019 [28] 李有利, 杨景春. 河西走廊平原区全新世河流阶地对气候变化的响应[J]. 地理科学, 1997, 17(3): 248-252.LI Y L, YANG J C. Response of alluvial terraces to holocene climatic changes in the Hexi Corridor basin, Gansu, China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 1997, 17(3): 248-252. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] 李长安, 殷鸿福, 于庆文. 东昆仑山构造隆升与水系演化及其发展趋势[J]. 科学通报, 1999, 44(2): 211-214.LI C A, YIN H F, YU Q W. Tectonic uplift and water system evolution and development trend of East Kunlun Mountains[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44(2): 211-213. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] 涂继耀, 季建清, 钟大赉, 等. 帕隆藏布江中游地壳剥露特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 292-300. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0260TU J Y, JI J Q, ZHONG D L, et al. Crust erosion characteristics in the middle reach of the Purlung Tsangpo River[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 292-300(in Chinese with English Abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0260 [31] BRIDGLAND D, WESTAWAY R. Climatically controlled river terrace staircases: A worldwide Quaternary phenomenon[J]. Geomorphology, 2008, 98(3/4): 285-315. [32] PAN B T, SU H, HU Z B, et al. Evaluating the role of climate and tectonics during non-steady incision of the Yellow River: Evidence from a 1.24 Ma terrace record near Lanzhou, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2009, 28(27/28): 3281-3290. [33] CRADDOCK W H, KIRBY E, HARKINS N W, et al. Rapid fluvial incision along the Yellow River during headward basin integration[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2010, 3(3): 209-213. doi: 10.1038/ngeo777 [34] 郑洪波, 魏晓椿, 王平, 等. 长江的前世今生[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2017, 47(4): 385-393.ZHENG H B, WEI X C, WANG P, et al. Geological evolution of the Yangtze River[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2017, 47: 385-393. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] VANDENBERGHE J, BRIDGLAND D, WANG X Y. Specific exogenetic(external) and endogenetic(internal) effects on fluvial system evolution[J]. Quaternary, 2018, 1(3): 27. doi: 10.3390/quat1030027 [36] SEYBOLD H, BERGHUIJS W R, PRANCEVIC J P, et al. Global dominance of tectonics over climate in shaping river longitudinal profiles[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2021, 14(7): 503-507. doi: 10.1038/s41561-021-00720-5 [37] PENCK A, BRVCKNER E. Die alpen im Eiszeitalter[M]. [S. l. ]: CH Tauchnitz, 1909. [38] SCHUMM S A. Quaternary paleohydrology[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2015. [39] MACKLIN M G, FULLER I C, LEWIN J, et al. Correlation of fluvial sequences in the Mediterranean basin over the last 200 ka and their relationship to climate change[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, 21(14/15): 1633-1641. [40] HOWARD A J, MACKLIN M G, BAILEY D W, et al. Late-glacial and Holocene river development in the Teleorman Valley on the southern Romanian Plain[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2004, 19(3): 271-280. doi: 10.1002/jqs.805 [41] VELDKAMP A, BAARTMAN J E M, COULTHARD T J, et al. Two decades of numerical modelling to understand long term fluvial archives: Advances and future perspectives[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 166: 177-187. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.10.002 [42] KUKLA G E. Loess stratigraphy of central Europe[C]//Butzer K W, Glynn L. After the Austoralopithecines: Stratigraphy, ecology and culture change in the Middle Pleistocene. Isaac, Berlin, New York: De Cruyter Mouton, 1975: 99-108. [43] PORTER S C, AN Z S, ZHENG H B. Cyclic Quaternary alluviation and terracing in a nonglaciated drainage basin on the north flank of the Qinling Shan, Central China[J]. Quaternary Research, 1992, 38(2): 157-169. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(92)90053-L [44] SCHANZ S A, MONTGOMERY D R, COLLINS B D, et al. Multiple paths to straths: A review and reassessment of terrace genesis[J]. Geomorphology, 2018, 312: 12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.03.028 [45] MADDY D, BRIDGLAND D, WESTAWAY R. Uplift-driven valley incision and climate-controlled river terrace development in the Thames Valley, UK[J]. Quaternary International, 2001, 79(1): 23-36. doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(00)00120-8 [46] PAN B T, BURBANK D, WANG Y X, et al. A 900 ky record of strath terrace formation during glacial-interglacial transitions in Northwest China[J]. Geology, 2003, 31(11): 957-960. doi: 10.1130/G19685.1 [47] YU Y, WANG X Y, YI S W, et al. Late Quaternary aggradation and incision in the headwaters of the Yangtze River, eastern Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2022, 134(1/2): 371-388. [48] CORDIER S, HARMAND D, FRECHEN M, et al. Fluvial system response to Middle and Upper Pleistocene climate change in the Meurthe and Moselle valleys(Eastern Paris Basin and Rhenish Massif)[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(13/14): 1460-1474. [49] WANG X Y, VANDENBERGHE J, YI S W, et al. Climate-dependent fluvial architecture and processes on a suborbital timescale in areas of rapid tectonic uplift: An example from the NE Tibetan Plateau[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2015, 133: 318-329. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2015.09.009 [50] WANG X Y, MA J F, YI S W, et al. Interaction of fluvial and eolian sedimentation processes, and response to climate change since the last glacial in a semiarid environment along the Yellow River[J]. Quaternary Research, 2019, 91(2): 570-583. doi: 10.1017/qua.2018.22 [51] WANG B L, WANG X Y, YI S W, et al. Responses of fluvial terrace formation to monsoon climate changes in the north-eastern Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from pollen and sedimentary records[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 564: 110196. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.110196 [52] WANG X Y, VANDENBERGHE J, LU H Y, et al. Climatic and tectonic controls on the fluvial morphology of the northeastern Tibetan Plateau(China)[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2017, 27(11): 1325-1340. doi: 10.1007/s11442-017-1438-9 [53] SCHEINGROSS J S, LIMAYE A B, MCCOY S W, et al. The shaping of erosional landscapes by internal dynamics[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2020, 1(12): 661-676. [54] DEMOULIN A, MATHER A, WHITTAKER A. Fluvial archives, a valuable record of vertical crustal deformation[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 166: 10-37. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.11.011 [55] BRIDGLAND D R, WESTAWAY R, HU Z. Basin inversion: A worldwide Late Cenozoic phenomenon[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2020, 193: 103260. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2020.103260 [56] 李吉均, 方小敏, 马海洲, 等. 晚新生代黄河上游地貌演化与青藏高原隆起[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 1996, 26(4): 316-322.LI J J, FANG X M, MA H Z, et al. The landscape evolution and uplift of the upper Yellow River in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since the Late Cenozoic[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 1996, 26(4): 316-322. (in Chinese with English abstract) [57] ZHENG H B, CLIFT P D, WANG P, et al. Pre-miocene birth of the Yangtze River[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(19): 7556-7561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216241110 [58] HU Z B, PAN B T, BRIDGLAND D, et al. The linking of the upper-middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River as a result of fluvial entrenchment[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 166: 324-338. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2017.02.026 [59] NIE J S, RUETENIK G, GALLAGHER K, et al. Rapid incision of the Mekong River in the middle Miocene linked to monsoonal precipitation[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2018, 11(12): 944-948. doi: 10.1038/s41561-018-0244-z [60] GUO B H, LIU S P, PENG T J, et al. Late Pliocene establishment of exorheic drainage in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau as evidenced by the Wuquan Formation in the Lanzhou Basin[J]. Geomorphology, 2018, 303: 271-283. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.12.009 [61] REPLUMAZ A, SAN JOSÉ M, MARGIRIER A, et al. Tectonic control on rapid Late Miocene-Quaternary incision of the Mekong River Knickzone, Southeast Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonics, 2020, 39(2): e2019TC005782. doi: 10.1029/2019TC005782 [62] FENG H, LU H Y, CARRAPA B, et al. Erosion of the Himalaya-Karakoram recorded by Indus Fan deposits since the Oligocene[J]. Geology, 2021, 49(9): 1126-1131. doi: 10.1130/G48445.1 [63] LIU Y, WANG X Y, SU Q, et al. Late Quaternary terrace formation from knickpoint propagation in the headwaters of the Yellow River, NE Tibetan Plateau[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2021, 46(14): 2788-2806. doi: 10.1002/esp.5208 [64] VELDKAMP A, VAN DIJKE J J. Simulating internal and external controls on fluvial terrace stratigraphy: A qualitative comparison with the Maas record[J]. Geomorphology, 2000, 33(3/4): 225-236. [65] LU H Y, WANG X Y, AN Z S, et al. Geomorphologic evidence of phased uplift of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since 14 million years ago[J]. Science China(Earth Sciences), 2004, 47: 822-833. doi: 10.1360/03yd0315 [66] ROBERTS G G. Emergent simplicity despite local complexity in eroding fluvial landscapes[J]. Geology, 2021, 49(11): 1322-1326. doi: 10.1130/G48942.1 [67] BRIDGLAND D R, WESTAWAY R. Quaternary fluvial archives and landscape evolution: A global synthesis[J]. Proceedings of the Geologists' Association, 2014, 125(5/6): 600-629. [68] WANG X Y, LU H Y, VANDENBERGHE J, et al. Distribution and forming model of fluvial terrace in the Huangshui catchment and its tectonic indication[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(2): 415-423. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2010.00155.x [69] CAMPFORTS B, SHOBE C M, STEER P, et al. HyLands 1.0: A hybrid landscape evolution model to simulate the impact of landslides and landslide-derived sediment on landscape evolution[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2020, 13(9): 3863-3886. doi: 10.5194/gmd-13-3863-2020 [70] 王晶, 徐亚东, 林晓, 等. 湘江沟头地表和深部地质约束的水系侵蚀能力差异及袭夺预测分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 234-240. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0127WANG J, XU Y D, LIN X, et al. Analysis on difference of erosion capacity and river capture prediction in the head of the Xiangjiang tributary constrainted by surface and deep geological information[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 234-240. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0127 [71] 潘保田, 蔡顺, 耿豪鹏. 山体隆升历史与地貌演化过程的数值模拟约束: 以青藏高原东北缘河西走廊中段的周边年轻上升山地为例[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2021, 51(4), 523-536.PAN B T, CAI S, GENG H P. Numerical simulation of landscape evolution and mountain uplift history constrain: A case study from the youthful stage mountains around the central Hexi Corridor, NE Tibetan Plateau[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2021, 64(3): 412-424. (in Chinese with English abstract) [72] YUAN X P, HUPPERT K L, BRAUN J, et al. Propagating uplift controls on high-elevation, low-relief landscape formation in the southeast Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geology, 2022, 50(1): 60-65. doi: 10.1130/G49022.1 [73] KAPLAN J O, KRUMHARDT K M, ELLIS E C, et al. Holocene carbon emissions as a result of anthropogenic land cover change[J]. The Holocene, 2011, 21(5): 775-791. doi: 10.1177/0959683610386983 [74] YANG R, HERMAN F, LIU T, et al. Enhanced Quaternary exhumation in the Namche Barwa syntaxis, eastern Himalaya[J]. Geology, 2021, 49(8): 958-962. doi: 10.1130/G48595.1 [75] CHEN S A, MICHAELIDES K, GRIEVE S W D, et al. Aridity is expressed in river topography globally[J]. Nature, 2019, 573: 573-577. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1558-8 [76] DETHIER E N, RENSHAW C E, MAGILLIGAN F J. Rapid changes to global river suspended sediment flux by humans[J]. Science, 2022, 376: 1447-1452. doi: 10.1126/science.abn7980 [77] SPRINGER K B, PIGATI J S. Climatically driven displacement on the Eglington fault, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA[J]. Geology, 2020, 48(6): 574-578. doi: 10.1130/G47162.1 [78] COWIE P A, WHITTAKER A C, ATTAL M, et al. New constraints on sediment-flux-dependent river incision: Implications for extracting tectonic signals from river profiles[J]. Geology, 2008, 36(7): 535-538. doi: 10.1130/G24681A.1 [79] JOHNSON J P L, WHIPPLE K X, SKLAR L S, et al. Transport slopes, sediment cover, and bedrock channel incision in the Henry Mountains, Utah[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Earth Surface), 2009, 114(F2): 1-21. [80] JOHNSON J P L, WHIPPLE K X. Evaluating the controls of shear stress, sediment supply, alluvial cover, and channel morphology on experimental bedrock incision rate[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Earth Surface), 2010, 115(F2): 1-21. [81] COOK K L, ANDERMANN C, GIMBERT F, et al. Glacial lake outburst floods as drivers of fluvial erosion in the Himalaya[J]. Science, 2018, 362: 53-57. doi: 10.1126/science.aat4981 [82] SYVITSKI J, ÁNGEL J R, SAITO Y, et al. Earth's sediment cycle during the Anthropocene[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2022, 3(3): 179-196. -





 下载:
下载: