Development law of gravity flow sandstone reservoir in the second Member of the Dongying Formation in the northeastern Nanpu Depression
-
摘要:
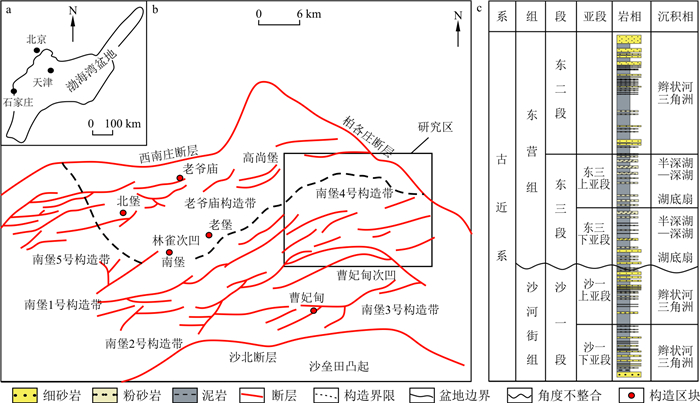
随着勘探程度的提高,深水重力流成因的浊积岩储层已成为我国东部断陷湖盆油气勘探开发的重要目标之一。因为沉积分异不足和成岩破坏,重力流砂岩的储层质量通常整体较差,优质储层的预测成为制约其有效油气勘探的关键地质因素。利用岩心、测井资料及储层物性、岩石薄片分析结果,研究了南堡凹陷东北部东营组二段重力流砂岩的岩相特征、成因类型、储层特征,以探索优质储层的控制因素和发育规律。研究表明,区内重力流沉积可细分为8种岩相,解释为滑动滑塌、砂质碎屑流、泥质碎屑流、浊流4类成因。储层物性参数统计分析证实,本区重力流砂岩储层非均质性强,储层质量受控于砂岩成因、砂-泥结构及其影响的溶蚀强度。从成因看,砂质碎屑流和浊流对重力流砂岩优质储层的发育贡献最大。砂质碎屑流成因的块状砂岩厚度较大、泥岩夹层较少、钙质胶结物的溶蚀程度高,储层质量最好;而浊流成因的砂岩厚度较薄,与泥岩呈互层或夹层产出,成岩环境封闭、钙质胶结物溶蚀程度低,储层质量较差。本研究为湖盆深水重力流砂岩油气的高效勘探开发提供了一种基于成因和结构的储层预测思路。
Abstract:With the improvement of hydrocarbon exploration, turbidite reservoirs formed by deep-water gravity flow have become an important target for oil and gas exploration and development in faulted basins in eastern China. Due to the weak depositional differentiation and diagenesis damage, the overall quality of gravity flow sandstone reservoirs is poor. The prediction of high-quality reservoirs is becoming the key to restricting effective hydrocarbon exploration. In this paper, the authors study the distribution, lithofacies, and reservoir characteristics of gravity flow sandstone in the northeastern Nanpu Depression by cores, well-logging data, reservoir physical properties, and rock slices to explore the key control factor and development law of high-quality reservoirs. The result shows that the gravity flow sediments are mainly composed of eight lithofacies interpreted as slide-slump, sandy debris flow, muddy debris flow, and turbidity current. According to the statistical analyses of reservoir physical property parameters, it is proven that the gravity flow sandstone reservoir is with strong heterogeneity and that its quality depends on sandstone genesis, sand-mud structure, and dissolution intensity. The high-quality reservoirs are mainly from sandy debris flows and turbidity currents. Massive sandstones from sandy debris flows are usually high-quality reservoirs characterized by large single-bed thickness, strong calcareous dissolution of calcareous cement, and few muddy interbeds.In contrast, the sandstones from turbidity currents are of low quality due to small thickness, weak dissolution of calcareous cement, and many interbedded mudstones, and are formed in a closed diagenetic environment. This study provides an effective predictive idea for hydrocarbon exploration on deep-water gravity flow sandstone reservoir in a lacustrine basin based on analyses of sandstone genesis and sand-mud structure.
-
Key words:
- sediment gravity flow /
- sandstone reservoir /
- debris flow /
- turbidity current /
- sand-mud structure
-
图 2 南堡4号构造带东二段重力流砂岩不同岩相的岩心照片
a, b.NP4-31井, 3 968 m,滑塌构造含砾砂岩,砂岩呈撕裂状; c.NP4-65井,4 389.52 m,碎屑支撑砾岩相;d.NP4-65井,4 389.46 m,富含泥岩撕裂屑砂岩相,泥岩撕裂屑延呈层状延层理发育;e.NP43-4830井, 3 843.2 m,正粒序含砾砂岩相;f.NP403x14井,3 436.64 m,爬升波纹层理砂岩相,顶部砂泥互层平行纹层;鲍马序列Tc段向上过渡到鲍马序列Td段;g.NP4-22井,3 650.3 m,平行层理砂岩相,内部可见泥质纹层;h.NP43-x4830,3 839.2 m,砂质透镜体、砂质团块,含砾石
Figure 2. Core photos of the gravity flow sandstone with different lithofacies of the second Member of the Dongying Formation of the No.4 tectonic belt in the Nanpu Depression
图 3 南堡凹陷NP4-87井东二段沉积相组成与重力流发育特征(钻井位置详见图 4)
Figure 3. Sedimentary facies and gravity flow sedimentary characteristics of the second Member of the Dongying Formation in Well NP4-87 in the Nanpu Depression
图 4 南堡凹陷东二段关键时期沉积相展布与重力流分布特征(成图范围详见图 1中研究区)
a.PSS1时期;b.PSS2时期;c.PSS3时期;d.PSS4时期
Figure 4. Sedimentary facies and gravity flow sediment distribution characteristics during the key period of the second Member of the Dongying Formation in the Nanpu Depression
图 5 南堡凹陷东二段重力流砂岩镜下照片与显微结构特征
a.NP2-52井,3 512.3 m,砂岩镜下照片(-);分选差、棱角-次棱角状;方解石胶结物发育而致密,实测孔隙度为5%,泥质碎屑流沉积;b.NP2-52井,3 513.65 m,砂岩镜下照片(-);分选中等-好、次棱角状;粒间孔隙发育(深蓝色为孔隙),实测孔隙度为28%,砂质碎屑流沉积;c.NP2-53井,3 125.3 m,砂岩镜下照片(-);中等-好、次棱角-次圆状;方解石胶结物发育,局部溶解形成次生孔,实测孔隙度约15%,浊流沉积;d.NP2-53井,3 129.3 m,砂岩镜下照片(-);中等-好、次棱角-次圆状;方解石胶结物完全溶解(深蓝色为孔隙),次生孔隙发育,面孔率16%,实测孔隙度为26%,砂质碎屑流沉积
Figure 5. Microstructure characteristics of gravity flow sandstone of the second Member of the Dongying Formation in the Nanpu Depression
表 1 南堡凹陷4号构造带岩相特征
Table 1. Lithofacies of the No.4 tectonic belt in the Nanpu Depression
编号 岩相类型 岩性特征 单层厚度/cm 沉积解释 Ⅰ 滑塌变形碎屑支撑砾岩 大量的塑性泥岩基质支撑,变形构造 20~40 滑动滑塌沉积 Ⅱ 碎屑支撑砾岩 富含泥岩撕裂屑,无粒序特征 20~40 砂质碎屑流 Ⅲ 富撕裂屑块状砂岩 中粗砂岩,无粒序,内部含泥岩撕裂屑 15~100 砂质碎屑流 Ⅳ 正粒序含砾砂岩、粗砂岩 中粗砂岩,正粒序,底部具冲刷面,可见泥岩撕裂屑,底部含叠瓦状砾石 10~40 浊流,鲍马序列Ta段 Ⅴ 波状层理砂岩 中细砂岩,波状层理,爬升波纹层理 10~50 浊流,鲍马序列Tc段 Ⅵ 平行层理砂岩 中细砂岩,平行层理 10 浊流,鲍马序列Tb段 Ⅶ 砂岩-泥岩薄互层 细砂岩、粉砂岩及泥岩薄互层 20 浊流沉积体边缘 Ⅷ 液化变形含砂泥岩 塑性变形泥岩沉积,内部含透镜状砂岩 10~30 泥质碎屑流 -
[1] 鲜本忠, 安思奇, 施文华. 水下碎屑流沉积: 深水沉积研究热点与进展[J]. 地质论评, 2014, 60(1): 39-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201401005.htmXian B Z, An S Q, Shi W H. Subaqueous debris flow: Hotspots and advances of deep-water sedimention[J]. Geological Review, 2014, 60(1): 39-51(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201401005.htm [2] 杨田, 操应长, 田景春. 浅谈陆相湖盆深水重力流沉积研究中的几点认识[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(1): 88-111. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2020.037Yang T, Cao Y C, Tian J C. Discussion on research of deep-water gravity flow deposition in lacustrine basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(1): 88-111(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2020.037 [3] Shanmugam G. High-density turbidity currents: Are they sandy debris flows?[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1996, 66(1): 2-10. doi: 10.1306/D426828E-2B26-11D7-8648000102C1865D [4] Marr J G, Harff P A, Shanmugam G, et al. Experiments on subaqueous sandy gravity flows: The role of clay and water content in flow dynamics and depositional structures[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2001, 113(11): 1377-1386. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2001)113<1377:EOSSGF>2.0.CO;2 [5] Mohrig D, Whipple K X, Hondzo M, et al. Hydroplaning of subaqueous debris flows[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1998(110): 387-394. [6] 杨田, 操应长, 王艳忠, 等. 深水重力流类型、沉积特征及成因机制: 以济阳坳陷沙河街组三段中亚段为例[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(9): 1048-1059. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201509003.htmYang T, Cao Y C, Wang Y Z, et al. Types, sedimentary characteristics and genetic mechanisms of deep-water gravity flows: A case study of the middle submember in Member 3 of Shahejie Formation in Jiyang Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(9): 1048-1059(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201509003.htm [7] 杨田, 操应长, 田景春, 等. 陆相湖盆深水重力流混合事件层沉积及沉积学意义[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(12): 3842-3857. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.12.019Yang T, Cao Y C, Tian J C, et al. Deposition of deep-water gravity-flow hybird event beds in lacustrine basins and their sedimentological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(12): 3842-3857(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.12.019 [8] 陈宇航, 朱增伍, 贾鹏, 等. 重力流沉积砂岩的成因、改造及油气勘探意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(5): 148-155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705020.htmChen Y H, Zhu Z W, Jia P, et al. Genetic mechanism and rework of deep-water sedimentary sand and its significance for petroleum exploration[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(5): 148-155(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705020.htm [9] 孙国桐. 深水重力流沉积研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(3): 30-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201503005.htmSun G T. A review of deep-water gravity-flow deposition research[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(3): 30-36(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201503005.htm [10] 李相博, 刘化清, 潘树新, 等. 中国湖相沉积物重力流研究的过去、现在与未来[J]. 沉积学报, 2019, 37(5): 904-921. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201905003.htmLi X B, Liu H Q, Pan S X, et al. The past, present and future of research on deep-water sedimentary gravity flow in lake basins of China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(5): 904-921(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201905003.htm [11] 刘策, 于炳松, 蒋锐, 等. 湖盆重力流沉积特征及模式[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(5): 133-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705018.htmLiu C, Yu B S, Jiang R, et al. Sedimentary feature and mode of gravity flow in lacustrine basin: Example from Ordos Basin and Luanping Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(5): 133-142(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705018.htm [12] 鲜本忠, 王璐, 刘建平, 等. 东营凹陷东部始新世三角洲供给型重力流-沉积特征与模式[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 40(5): 10-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201605003.htmXian B Z, Wang L, Liu J P, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and model of delta-fed turbidites in Eocene eastern Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2016, 40(5): 10-21(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201605003.htm [13] 符勇, 李忠诚, 万谱, 等. 三角洲前缘滑塌型重力流沉积特征及控制因素: 以松辽盆地大安地区青一段为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(1): 198-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202101018.htmFu Y, Li Z C, Wan P, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and controlling factors of slump gravity flow in delta front: A case study of Qing 1 Member in Da'an area, Songliao Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(1): 198-208(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202101018.htm [14] 王华, 陈思, 巩天浩, 等. 牵引流化重力流沉积过程与堆积机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 95-104. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0111Wang H, Chen S, Gong T H, et al. Sedimentary process and accumulation mechanism of traction fluidization gravity flow: An example from Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 95-104(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0111 [15] 鲜本忠, 万锦峰, 姜在兴, 等. 断陷湖盆洼陷带重力流沉积特征与模式: 以南堡凹陷东部东营组为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(1): 121-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201201015.htmXian B Z, Wan J F, Jiang Z X, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and model of gravity flow deposition in the depressed belt of rift lacustrine basin: A case study from Dongying Formation in Nanpu Depression[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(1): 121-135(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201201015.htm [16] Chen P, Xian B, Li M, et al. A giant lacustrine flood-related turbidite system in the Triassic Ordos Basin, China: Sedimentary processes and depositional architecture[J]. Sedimentology, 2021, 68(7): 3279-3306. [17] Zhang J, Wu S, Hu G, et al. Sea-level control on the submarine fan architecture in a deepwater sequence of the Niger Delta Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 94: 179-197. [18] Pu X, Zhao X, Wang J, et al. Reservoirs properties of slump-type sub-lacustrine fans and their main control factors in first Member of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Binhai area, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(5): 977-989. [19] Yang T, Cao Y, Friis H, et al. Genesis and distribution pattern of carbonate cements in lacustrine deep-water gravity-flow sandstone reservoirs in the third Member of the Shahejie Formation in the Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression, Eastern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 92: 547-564. [20] Chen D, Pang X, Jiang Z, et al. Reservoir characteristics and their effects on hydrocarbon accumulation in lacustrine turbidites in the Jiyang Super-depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(2): 149-162. [21] Zhao X, Pu X, Zhou L, et al. Geologic characteristics of deep water deposits and exploration discoveries in slope zones of fault lake basin: A case study of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Banqiao-Qibei slope, Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(2): 171-182. [22] Talling P J, Masson D G, Sumner E J, et al. Subaqueous sediment density flows: Depositional processes and deposit types[J]. Sedimentology, 2012, 59(7): 1937-2003. [23] Haughton P, Davis C, Mccaffrey W, et al. Hybrid sediment gravity flow deposits: Classification, origin and significance[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(10): 1900-1918. [24] 操应长, 燕苗苗, 葸克来, 等. 玛湖凹陷夏子街地区三叠系百口泉组砂砾岩储层特征及控制因素[J]. 沉积学报. 2019, 37(5): 945-956. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201905006.htmCao Y C, Yan M M, XI K L, et al. The characteristics and controlling factors of glutenite reservoir in the Triassic Baikouquan Formation, Xiazijie area, Mahu Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(5): 945-956(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201905006.htm [25] 管红, 朱筱敏. 南堡凹陷滩海地区古近系砂岩孔隙类型、分布及其控制因素[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 33(4): 22-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200904004.htmGuan H, Zhu X M. Types, distribution of sandstone pore of Paleaogene and its controlling factors in beach area, Nanpu Sag[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2009, 33(4): 22-26(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200904004.htm [26] 吴浩, 纪友亮, 周勇, 等. 南堡凹陷南部古近系深层优质储层成因[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2019, 48(3): 553-569. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201903010.htmWu H, Ji Y L, Zhou Y, et al. Origin of the Paleogene deep burial high-quality reservoirs in the southern Nanpu Sag[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2019, 48(3): 553-569(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201903010.htm [27] 张艺楼, 吴浩, 纪友亮, 等. 南堡凹陷南部不同构造带东二段储层孔隙结构差异及其对储层质量的影响[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2020, 39(1): 85-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW202001007.htmZhang Y L, Wu H, Ji Y L, et al. Characteristics of pore structure differences in the 2th Member reservoir of Oligocene Dongying Formation, southern Nanpu Sag: Implications for reservoir quality[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2020, 39(1): 85-95(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW202001007.htm [28] 王恩泽, 刘国勇, 庞雄奇, 等. 南堡凹陷中深层碎屑岩储集层成岩演化特征及成因机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(2): 321-333. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202002012.htmWang E Z, Liu G Y, Pang X Q, et al. Diagenetic evolution and formation mechanisms of middle to deep clastic reservoirs in the Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(2): 321-333(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202002012.htm [29] 徐波, 廖保方, 张帆, 等. 南堡油田储层构型分级方案建议[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2): 165-170. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502024.htmXu B, Liao B F, Zhang F, et al. Proposal for hierarchical scheme of architectural units to Nanpu Oilfield[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(2): 165-170(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502024.htm [30] 李潇鹏. 南堡凹陷沙一段-东营组强烈断拗背景下扇体的精细刻画及差异性研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2020.Li X P. Characterization of fans and analysis of their variations on the background of strong rifting and depression, 1st Member of Shahejie Formation to Dongying Formation, Nanpu Sag[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [31] Zhang J, Gao J, Wu J, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and seismic geomorphology of the upper third Member of Eocene Dongying Formation in double slope systems of Laoyemiao transverse anticline, Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 109: 36-55. [32] Jia H, Liu T, Ji H, et al. Fan-delta facies architecture, morphological evolution and sediment delivery in the Oligocene Dongying Formation of the Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2021, 68(8): 1201-1214. [33] 童亨茂, 范彩伟, 孟令箭, 等. 中国东-南部裂陷盆地断裂系统复杂性的表现形式及成因机制: 以南堡凹陷和涠西南凹陷为例[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(9): 1753-1765. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201809001.htmTong H M, Fan C W, Meng L J, et al. Manifestation and origin mechanism of the fault system complexity in rift basins in eastern-southern China: Case study of the Nanpu and Weixinan sags[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(9): 1753-1765(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201809001.htm [34] 童亨茂, 龚发雄, 孟令箭, 等. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷边界断层的"跃迁"特征及其成因机制[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2018, 42(3): 421-430(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201803001.htmTong H M, Gong F X, Meng L J, et al. Tectonic model of boundary fault migration and its genetic mechanism in the Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2018, 42(3): 421-430(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201803001.htm [35] 朱光有, 张水昌, 王拥军, 等. 渤海湾盆地南堡大油田的形成条件与富集机制[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(1): 97-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201101007.htmZhu G Y, Zhang S C, Wang Y J, et al. Forming condition and enrichment mechanism of the Nanpu Oilfield in the Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(1): 97-113(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201101007.htm -





 下载:
下载: