A machine learning lithologic identification method combined with vertical reservoir information
-
摘要:
测井资料中包含丰富的岩性信息, 相比于取心资料, 具有连续性强、成本低等优点。用机器学习方法探索测井曲线与实际取心段样本岩性之间的关系, 实现储层岩性的自动识别, 降低岩性识别成本, 提高识别效率和准确性, 可以为储层评价提供有效手段。基于岩性分类依据选择适合样本的分类方案, 选取适合岩性分类问题的机器学习方法设计试验方案, 提出了融合储层纵向信息的机器学习岩性识别方法, 利用深度窗对常规测井数据和已知岩性数据进行了序列采样, 生成了训练样本。用逻辑回归、支持向量机、随机森林、卷积神经网络和Stacking集成学习5种不同方法分别建立模型, 对新疆某油田的强非均质岩层原始样本进行了岩性识别。结果表明, 当深度窗宽度与岩层厚度相匹配时, 在原始样本具有强非均衡性的情况下, 用本方法对其进行预处理之后, 各个机器学习方法获得的岩性识别准确率均有较大提高。深度窗的宽度决定了方法识别岩层厚度的精度, 深度窗越小, 识别精度越高;深度窗越大能够保留的纵向信息越多, 对相应厚度的岩层识别准确率越高。本文的融合储层纵向信息的机器学习岩性识别方法能提升测井资料岩性识别的准确性, 给非均质薄岩层的自动有效识别提供了经济有效的参考方案。
Abstract:Compared with coring data, well logging data contain much lithologic information with the advantages of strong continuity and low cost. The machine learning method is applied to explore the correlation between the log curves and the lithology of the actual coring samples, realize the automatic identification of the lithology of the reservoirs, reduce the lithologic identification cost, improve the identification efficiency and accuracy and provides an effective tool for the evaluation of the reservoirs. Based on the lithology classification standard, the sample classification scheme is approximately selected and a machine learning lithologic identification method combined with the vertical reservoir information is proposed to design an experimental scheme. The depth window is used to carry out the sequence sampling of the conventional logging data and the known lithologic data to generate training samples. Logistic regression, support vector machine, random forest, convolutional neural networks and stacking ensemble learning are used to build machine learning models to identify the lithology of original samples of strongly heterogeneous rock formations in an oilfield in Xinjiang. The results show that when the width of the depth window matches the thickness of the rock layer well, the accuracy of lithologic identification obtained by each machine learning method is greatly improved after preprocessing the original strong non-equilibrium sample with the method in this paper. The width of the depth window determines the identification accuracy of the rock layer thickness. A thinner depth window can identify a thinner rock layer, while a thicker depth window contains more vertical information, which can obtain higher identification accuracy at the corresponding rock thickness. The machine learning lithologic identification method combined with vertical reservoir information is proposed, which provides an economical and effective reference solution for the automatic and effective identification of heterogeneous thin rock layers.
-
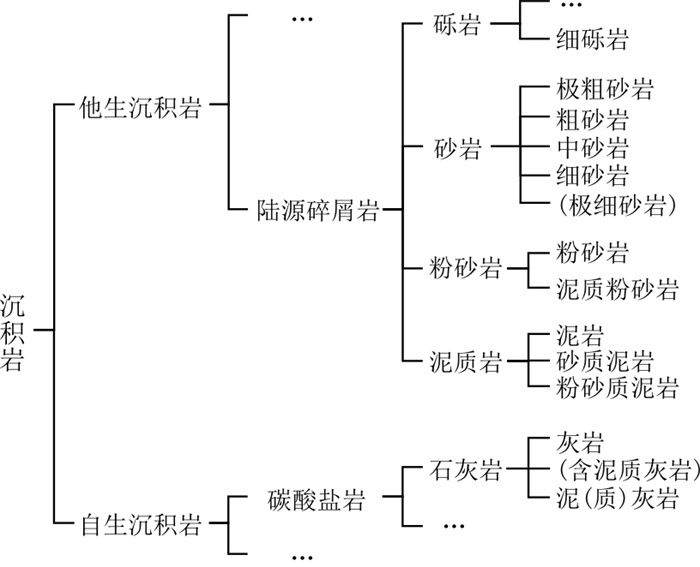
图 1 岩石类别划分方案(据文献[21]修改)
Figure 1. Rock classification scheme
图 3 卷积神经网络基本思想示意图[23]
Figure 3. Basic sketch map of convolutional neural network
图 5 不同厚度地层的自然伽马曲线[31]
Figure 5. Natural Gamma Ray curves of strata with different thickness
表 1 评价标准计算公式
Table 1. Formula of performance evaluation
评价标准 公式 准确率 $\text { accuracy }=(\mathrm{TP}+\mathrm{TN}) /(\mathrm{TP}+\mathrm{TN}+\mathrm{FP}+\mathrm{FN})$ 马修斯相关系数 $\text { Matthews corelation }=\frac{\mathrm{TP} \times \mathrm{TN}-\mathrm{FP} \times \mathrm{FN}}{\sqrt{(\mathrm{TP}+\mathrm{FP})(\mathrm{FN}+\mathrm{TP})(\mathrm{FN}+\mathrm{TN})(\mathrm{FP}+\mathrm{TN})}}$ F1分数 $\begin{gathered} \text { precision }=\mathrm{TP} /(\mathrm{TP}+\mathrm{FP}), \text { recall }=\mathrm{TP} /(\mathrm{TP}+\mathrm{FN}) \\ \text { F1 score }=2 \text { precision } \times \text { recall } / \text { (precision }+ \text { recall }) \end{gathered}$ 注:岩性识别预测结果用混合矩阵进行分类。得到的分类类别可归为4种, 即真正例(true positive, 简称TP)、假正例(false positive, 简称FP)、真反例(true negative, 简称TN)、假反例(false negative, 简称FN)。atturacy.准确率; Matthews correlation.马修斯相关系数;precision.查准率; recall.召回率 表 2 超参数选择结果
Table 2. Results of hyper-parameter selection
分类器 超参数 逻辑回归 penalty=‘l2’;solver=‘saga’;max_iter=700 支持向量机 C=2;Kernel=‘rbf’;Gamma=10 随机森林 n_estimators=500;criterion=‘gini’ Stacking集成学习 基分类器:逻辑回归、支持向量机、随机森林;元分类器:逻辑回归 -
[1] 李政宏, 刘永福, 张立强, 等. 数据挖掘方法在测井岩性识别中的应用[J]. 断块油气田, 2019, 26(6): 713-718. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201906008.htmLi Z H, Liu Y F, Zhang L Q, et al. Application of data mining method in lithology identification using well log[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2019, 26(6): 713-718(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201906008.htm [2] 李宁, 徐彬森, 武宏亮, 等. 人工智能在测井地层评价中的应用现状及前景[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(4): 508-522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202104008.htmLi N, Xu B S, Wu H L, et al. Application status and prospects of artificial intelligence in well logging and formation evaluation[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(4): 508-522(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202104008.htm [3] 张丽华, 张国斌, 齐艳萍, 等. 准噶尔盆地西泉地区石炭系火山岩岩性测井识别[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2017, 38(4): 427-431. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201704009.htmZhang L H, Zhang G B, Qi Y P, et al. Lithology identification of Carboniferous volcanic rock with logging data in Xiquan area, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2017, 38(4): 427-431(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201704009.htm [4] 曾棒, 刘小平, 刘国勇, 等. 陆相泥页岩层系岩相测井识别与预测: 以南堡凹陷拾场次洼为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 69-79. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0103Zeng B, Liu X P, Liu G Y, et al. Logging identification and prediction of lithofacies of lacustrine shale system in Shichang Sub-sag, Nanpu Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 69-79(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0103 [5] 周正龙, 王贵文, 冉冶, 等. 致密油储集层岩性岩相测井识别方法: 以鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区三叠系延长组7段为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(1): 61-68, 83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201601008.htmZhou Z L, Wang G W, Ran Y, et al. A logging identification method of tight oil reservoir lithology and lithofacies: A case from Chang 7 Member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Heshui area, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(1): 61-68, 83(in Chinese with English abstract https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201601008.htm [6] 祗淑华, 沈华, 安纪星, 等. 束鹿凹陷沙河街组致密油复杂岩性测井识别技术[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(增刊1): 40-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2015S1005.htmDi S H, Shen H, An J X, et al. Logging identification technology of tight-oil complex lithology of the Shahejie Formation in Shulu Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(S1): 40-49(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2015S1005.htm [7] 马陇飞, 萧汉敏, 陶敬伟, 等. 基于梯度提升决策树算法的岩性智能分类方法[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(1): 21-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202201003.htmMa L F, Xiao H M, Tao J W, et al. Intelligent lithology classification method based on GBDT algorithm[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(1): 21-29(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202201003.htm [8] 谷宇峰, 张道勇, 鲍志东, 等. 利用GS-LightGBM机器学习模型识别致密砂岩地层岩性[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 224-234. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0416Gu Y F, Zhang D Y, Bao Z D, et al. Lithology prediction of tight sandstone formation using GS-LightGBM hybrid machine learning model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 224-234(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0416 [9] Zhang G, Wang Z, Mohaghegh S, et al. Pattern visualization and understanding of machine learning models for permeability prediction in tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 200: 108142. [10] 刘伟男, 张超谟, 朱林奇, 等. 页岩气水平井TOC测井评价新方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(2): 423-431. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202102019.htmLiu W N, Zhang C M, Zhu L Q, et al. A new method for TOC logging evaluation in shale gas for horizontal well[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2): 423-431(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202102019.htm [11] Nguyen-Sy T, To Q D, Vu M N, et al. Predicting the electrical conductivity of brine-saturated rocks using machine learning methods[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2021, 184: 104238. [12] Rostamian A, Heidaryan E, Ostadhassan M. Evaluation of different machine learning frameworks to predict CNL-FDC-PEF logs via hyperparameters optimization and feature selection[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 208: 109463. [13] Ahmadi K, Riahi M A, Anzehaee M M. Well logs reconstruction by DCT based IPRM and genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 195: 107846. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920410520309062 [14] Zeng L, Ren W, Shan L. Attention-based bidirectional gated recurrent unit neural networks for well logs prediction and lithology identification[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 414: 153-171. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231220311334 [15] Zheng W, Tian F, Di Q, et al. Electrofacies classification of deeply buried carbonate strata using machine learning methods: A case study on Ordovician paleokarst reservoirs in Tarim Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 123: 104720. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817220305031 [16] Belozerov B, Bukhanov N, Egorov D, et al. Automatic well log analysis across priobskoe field using machine learning methods[C]//Anon. SPE Russian Petroleum Technology Conference. [S. l. ]: OnePetro, 2018. [17] 段友祥, 徐冬胜, 孙歧峰, 等. DBN在测井解释中的研究与应用[J]. 应用科学学报, 2018, 36(4): 689-697. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYKX201804012.htmDuan Y X, Xu D S, Sun Q F, et al. Research and application on DBN for well log interpretation[J]. Journal of Applied Sciences, 2018, 36(4): 689-697(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYKX201804012.htm [18] 杨笑, 王志章, 周子勇, 等. 基于参数优化AdaBoost算法的酸性火山岩岩性分类[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(4): 457-467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201904007.htmYang X, Wang Z Z, Zhou Z Y, et al. Lithology classification of acidic volcanic rocks based on parameter-optimized AdaBoost algorithm[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(4): 457-467(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201904007.htm [19] Ao Y, Li H, Zhu L, et al. The linear random forest algorithm and its advantages in machine learning assisted logging regression modeling[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 174: 776-789. [20] 赖强, 魏伯阳, 吴煜宇, 等. 基于随机森林的K-近邻算法划分火成岩岩性[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(6): 62-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202106008.htmLai Q, Wei B Y, Wu Y Y, et al. Classification of igneous rock lithology with K-nearest neighbor algorithm based on random forest(RF-KNN)[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(6): 62-69(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202106008.htm [21] Ren Q, Zhang D, Zhao X, et al. A novel hybrid method of lithology identification based on K-means ++ algorithm and fuzzy decision tree[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 208: 109681. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920410521013103 [22] 桑隆康, 马昌前. 岩石学[M]. 第二版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012.Sang L K, Ma C Q. Petrology[M]. 2nd Edition. Beijing: Geology Press, 2012(in Chinese). [23] 冯梓岩, 殷文, 钟云滔, 等. 基于常规测井的火成岩岩性识别方法: 以准噶尔盆地西北缘红车断裂带石炭系火成岩储层为例[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2021, 45(5): 95-108, 11-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY202105010.htmFeng Z Y, Yin W, Zhong Y T, et al. Lithologic identification of igneous rocks based on conventional log: A case study of Carboniferous igneous reservoir in Hongche Fault Zone in northwestern Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2021, 45(5): 95-108, 11-12(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY202105010.htm [24] 郑阳. 基于深度学习的岩性识别研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2017.Zheng Y. Research on lithology recognition based on deep learning[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum(Beijing), 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] 路成辉. 异构机器学习集成在测井曲线复原和岩性识别中的应用研究[D]. 黑龙江大庆: 东北石油大学, 2020.Lu C H. Application study of heterogeneous machine learning integration in logging curve recovery and lithology recognition[D]. Daqing Heilongjiang: Northeast Petroleum University, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [26] Pavlyshenko B. Using stacking approaches for machine learning models[C]//Anon. 2018 IEEE Second International Conference on Data Stream Mining & Processing(DSMP). [S. l. ]: IEEE, 2018: 255-258. [27] 谷宇峰, 张道勇, 鲍志东. 利用混合模型CRBM-PSO-XGBoost识别致密砂岩储层岩性[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(5): 1210-1222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202105019.htmGu Y F, Zhang D Y, Bao Z D. Lithology identification in tight sandstone reservoirs using CRBM-PSO-XGBoost[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(5): 1210-1222(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202105019.htm [28] Lopes D M R, Andrade A J N. Lithology identification on well logs by fuzzy inference[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 180: 357-368. [29] 洪有密. 测井原理与综合解释[M]. 北京: 中国石油大学出版社, 1998.Hong Y M. Well logging principle and comprehensive interpretation[M]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum Press, 1998(in Chinese). [30] 高春云, 周立发, 路萍. 测井曲线标准化研究进展综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(5): 1777-1783. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ202005018.htmGao C Y, Zhou L F, Lu P. Review of the development of well log normalization[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020, 35(5): 1777-1783(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ202005018.htm [31] 苏艳丽. 提高测井曲线分辨率的方法研究及应用[D]. 武汉: 长江大学, 2012.Su Y L. Study and application of the improvement on the definition of log curves[D]. Wuhan: Yangtze University, 2012(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: