Research on anti-seepage grouting in completely weathered granite based on superfine materials
-
摘要:
针对全风化花岗岩地层注浆过程中存在"吃水不吃浆"、可灌性差以及浆液的稳定性问题,提出了一种新的复合注浆材料,以提高完全风化花岗岩的防渗和力学性能。通过一系列室内试验研究了不同水固比、超细膨润土含量和超细硅酸盐水泥含量对注浆材料工程性能和浆液形成机制的影响,确定了水泥浆的最佳配方,采用微观形貌试验揭示了2种超细材料对浆液流动性、稳定性和结石体强度的作用机理,最后通过现场试验验证了注浆材料的可注性和有效性。结果表明,水固比为1.2、超细膨润土和超细硅酸盐水泥掺量分别为10%、普通硅酸盐水泥掺量80%配方的复合浆液具有很好的流动性、稳定性和抗压强度,漏斗黏度为35.5 s,析水率为2.4%,7 d和28 d的抗压强度均大于5 MPa;复合材料中的超细膨润土的掺量对浆液性能起主导作用,超细膨润土含量及其水化胶体的形态与分布决定浆液稳定性,而适量的超细硅酸盐水泥增加了细颗粒含量,使得胶结体更易填充颗粒间隙,改善了浆液可注性和结石体强度;该复合注浆材料在现场试验中表现优异,具有良好的注浆性能,注浆后形成的墙体在防渗效果和加固性能上均满足设计要求。
Abstract:Objective To solve the problems of "draught without slurry", poor groutability and slurry stability in the grouting process of completely weathered granite, a new composite grouting material is proposed in this paper to improve the anti-seepage and mechanical properties of completely weathered granite.
Methods Through a series of laboratory experiments, it investigates the effects of different water-solid ratios, superfine bentonite, and superfine Portland cement content on the engineering properties of grouting materials. The formation mechanism of the slurry were studied, and the optimal formula of the cement slurry was determined. The experiment revealed the action mechanism of the two superfine materials on the fluidity, stability, and stone body strength of the grout. Finally, the castability and effectiveness of the grouting material were verified by a field test.
Results The results show that the composite slurry with a water-solid ratio of 1.2, a content of superfine bentonite and superfine Portland cement of 10%, and a content of ordinary Portland cement of 80% has good fluidity, stability, and resistance. The funnel viscosity was 35.5 s, the water separation rate was 2.4%, and the compressive strengths at 7 d and 28 d were both greater than 5 MPa. The compressive strength and the content of superfine bentonite in the composite material play a leading role in the properties of the slurry. The content of superfine bentonite and the morphology and distribution of its hydrated colloids determine the stability of the slurry, while an appropriate amount of superfine Portland cement increases the content of fine particles, making it easier for the cement to fill the gaps between the particles and improving the injectability of the slurry and the strength of the stone body.
Conclusion The composite grouting material has excellent performance in the field test and good grouting performance. The wall formed after grouting meets the design requirements in terms of the anti-seepage effect and reinforcement performance.
-
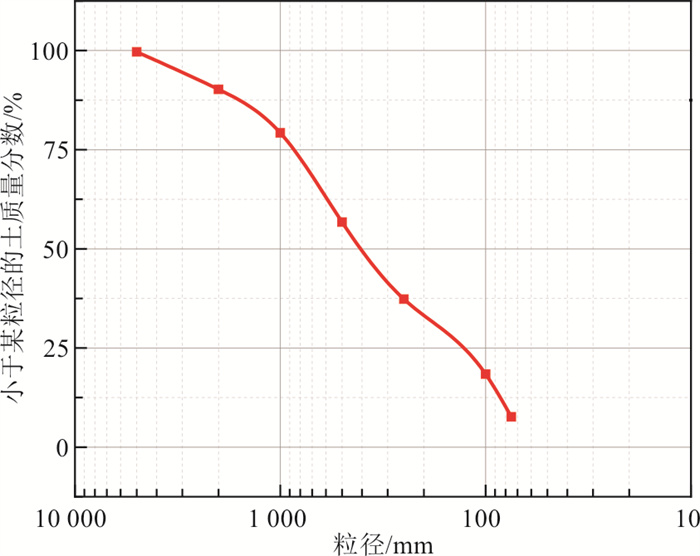
表 1 全风化花岗岩基本物理性质指标
Table 1. Basic physical properties of CWG
密度/(g·cm-3) 含水率/% 干密度/(g·cm-3) 颗粒相对密度 孔隙比 1.73~2.00 13.9~21.7 1.42~1.58 2.618~2.635 0.435~0.852 注:试验按照文献[29]实施 表 2 滤失量测定数据
Table 2. Data of filtration
水固比 SSB掺量wB/% SPC掺量wB/% 0 5 10 15 滤失量/mL 1.2 6 108 106 102 105 1.3 6 118 112 116 112 1.4 6 132 119 109 117 1.2 8 101 93 89 85 1.3 8 113 103 91 101 1.4 8 117 110 104 109 1.2 10 74 72 69 71 1.3 10 75 73 71 74 1.4 10 85 84 82 83 表 3 SCBS流动性和稳定性试验
Table 3. Fluidity and stability test of SCBS
水固比 SSB掺量wB/% SPC掺量wB/% OPC掺量wB/% 漏斗黏度/s 析水率/% 1.2 4 16 80 31.7 16.0 1.2 6 14 80 32.6 9.0 1.2 8 12 80 33.2 6.5 1.2 10 10 80 35.5 2.4 表 4 SCBS性能
水固比 SSB掺量wB/% SPC掺量wB/% OPC掺量wB/% 漏斗黏度/s 析水率/% 1.2 10 10 80 34.8~36.2 2~3 表 5 注浆前后压水试验结果
Table 5. Results of the water pressure test before and after grouting
孔号 透水率/Lu 平均透水率/Lu X1 75.16 48.16 17.44 28.75 16.94 13.16 101.92 5.43 11 28.94 J1 1.74 0 0.58 0.21 0.54 0 0.21 0.11 0.08 0.32 J2 0.69 0.16 0 0.18 0.18 1.39 0 0.05 0.10 0.26 J3 2.08 0 0 0.80 0 0 0.56 / / 0.30 J4 1.02 0.20 0 1.25 0 0.38 0.09 0.15 2.50 0.50 -
[1] 曾利群, 鄢雨南, 陈信峰. 深圳地区风化花岗岩渣土资源化利用试验研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2020, 43(5): 80-83.ZENG L Q, YAN Y N, CHEN X F. Experimental study on resource utilization of weathered granite residue in Shenzhen area[J]. Non-Metallic Mines, 2020, 43(5): 80-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 邓龙洲, 张丽萍, 陈儒章, 等. 侵蚀性风化花岗岩坡地土壤发育特性[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(1): 64-70.DENG L Z, ZHANG L P, CHEN R Z, et al. Characteristics of soil development on the erosive weathered granite slope[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(1): 64-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 齐信, 黎清华, 焦玉勇, 等. 梧州市巨厚层花岗岩风化壳垂直分带标准及工程地质特征研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2022, 30(2): 407-416.QI X, LI Q H, JIAO Y Y, et al. Vertical zoning criteria and engineering geological characteristics of super-thick layer granite weathering crust in Wuzhou City[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(2): 407-416. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 秦效荣, 姚玉增, 何宏平, 等. 广东梅州花岗岩风化壳剖面的可见光-短波红外反射光谱特征及其对风化强度的指示[J]. 地球化学, 2020, 49(4): 422-434.QIN X R, YAO Y Z, HE H P, et al. Visible to shortwave-infrared spectroscopic characteristics and weathering intensity indicators of a weathering-crust-type REE deposit in granite bedrock from Meizhou, Guangdong Province[J]. Geochimica, 2020, 49(4): 422-434. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] 冯文凯, 代洪川, 白慧林, 等. 龙川县花岗岩浅表层抗剪强度试验对比研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(35): 14944-14952.FENG W K, DAI H C, BAI H L, et al. Comparative study on shear strength of granite shallow layer in Longchuan County[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(35): 14944-14952. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 张树坡, 简文星, 蒋天娇, 等. 赣南花岗岩风化带岩土体强度特征及边坡破坏模式分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(15): 6196-6204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.15.044ZHANG S P, JIAN W X, JIANG T J, et al. Strength characteristics of granite weathering zone and analysis of slope failure mode in south Jiangxi Province[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(15): 6196-6204. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.15.044 [7] 周小文, 罗兴财. 全风化花岗岩与花岗岩残积土的判别及物理力学性质对比[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2022, 39(4): 1-7.ZHOU X W, LUO X C. Identification and physical mechanical property comparison between completely decomposed granite and granite residual soil[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2022, 39(4): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 李传懿, 陈志波. 海底强风化花岗岩K0固结三轴试验尺寸效应[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 51(6): 1646-1653.LI C Y, CHEN Z B. Specimen size effect of strongly weathered granite of seabed in triaxial tests under K0-consolidation condition[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology Edition), 2020, 51(6): 1646-1653. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 姚纪华, 宋文杰, 邓仁贵, 等. 溪头水库坝基全风化花岗岩物理力学特性研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2020, 31(6): 208-215.YAO J H, SONG W J, DENG R G, et al. Physical and mechanical properties of completely weathered granite in dam foundation of Xitou Reservoir[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2020, 31(6): 208-215. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] SANDEEP C S, HE H, SENETAKIS K. Experimental and analytical studies on the influence of weathering degree and ground-environment analog conditions on the tribological behavior of granite[J]. Engineering Geology, 2022, 304: 106644. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106644 [11] 陈若, 夏永华, 杨明龙, 等. 基于TLS的全风化花岗岩地区水土保持措施减沙效益研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 59(10): 439-446.CHEN R, XIA Y H, YANG M L, et al. Effect of soil and water conservation measures on sediment reduction in fully weathered granite area based on TLS[J]. Laser and Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 59(10): 439-446. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] QI X, LI Q, JIAO Y, et al. Experimental study on response law and failure process of slopes in fully weathered granites under precipitation infiltration[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2021, 50(4): 531-539. [13] 邓龙洲, 张丽萍, 孙天宇, 等. 南方风化花岗岩坡地产流过程与侵蚀率模拟研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(3): 35-41.DENG L Z, ZHANG L P, SUN T Y, et al. Simulation study on runoff processes and erosion rate on the weathered granite slope in southern China[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(3): 35-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 祝俊, 梁军林, 容洪流, 等. 富水全强风化花岗岩隧道突水突泥灾害机制与帷幕注浆技术[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(26): 10918-10926.ZHU J, LIANG J L, RONG H L, et al. Water and mud inrush disaster mechanism and curtain grouting technology on granite tunnel with rich water and strong weathering[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(26): 10918-10926. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 卓万生. 冲洪积卵石土层分布区滑坡形成机理分析: 以安溪县某安置区边坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(2): 169-177.ZHUO W S. Mechanism of landslides in the alluvial pebble layer distribution area: A case study of the landslope in a resettlement area in Anxi County[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(2): 169-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 刘天乐, 全奇, 蒋国盛, 等. 含CaCl2水基聚合物钻井液沿井周地层渗透规律研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 263-271. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0510LIU T L, QUAN Q, JIANG G S, et al. Study on permeability law of water-based polymer drilling fluid containing CaCl2 in wellbore formation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 263-271. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0510 [17] SHIRLAW J N, HENDERSON T O, HARYONO I S, et al. The effect of altering the slurry circulation system on TBM tunnelling in weathered Kowloon granite[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2022, 124: 104474. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2022.104474 [18] 冯锐, 张鹏, 苏树尧, 等. 大口径长距离钢顶管注浆减阻技术: 以黄浦江上游水源地连通管工程为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 174-180. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0421FENG R, ZHANG P, SU S Y, et al. Resistance reduction by grouting to large diameter and long distance steel pipe jacking: A case study of pipe jacking project in the upstream water source area of Huangpu River[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 174-180. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0421 [19] 盛明强, 邹淳, 乾增珍, 等. 水泥固化剂提高风积沙承载性能试验[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 147-153. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0259SHENG M Q, ZOU C, QIAN Z Z, et al. Experiments on the bearing capacity of aeolian sand stabilized by cement stabilizers[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 147-153. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0259 [20] 苏兴矩, 丘仁科, 邱礼球, 等. 富水全风化花岗岩隧道注浆加固技术研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2021, 17(增刊2): 786-792, 813.SU X J, QIU R K, QIU L Q, et al. Study on grouting reinforcement technology of water rich fully weathered granite tunnel[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2021, 17(S2): 786-792, 813. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] 赵钰, 郑洪, 曹函, 等. 全风化花岗岩地层中高固相离析浆液灌浆机理研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2021, 48(2): 78-88.ZHAO Y, ZHENG H, CAO H, et al. A study of grouting mechanism of high solid phase segregation grout in fully weathered granite[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(2): 78-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] 窦金熙, 张贵金, 陈安重, 等. 全风化花岗岩地层脉动灌浆控制防渗机理研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(2): 309-318.DOU J X, ZHANG G J, CHEN A Z, et al. Mechanism of seepage control of pulsating grouting in completely weathered granite stratum[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(2): 309-318. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] AZADI M R, TAGHICHIAN A, TAHERI A. Optimization of cement-based grouts using chemical additives[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 9(4): 623-637. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.11.013 [24] JIANG H, QIU X. Performance assessment of a newly developed and highly stable grouting material for a completely weathered granite dam foundation[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 299: 123956. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123956 [25] ZHANG C, YANG J, FU J, et al. Recycling of discharged soil from EPB shield tunnels as a sustainable raw material for synchronous grouting[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 268: 121947. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121947 [26] LI Y, ZHANG G, JIANG H, et al. Performance assessment of a newly developed and highly stable sandy cementitious grout for karst aquifers in China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2020, 79(6): 1-11. [27] XU X, XIANG Z, ZOU J, et al. An improved approach to evaluate the compaction compensation grouting efficiency in sandy soils[J]. Geomechanics and Engineering, 2020, 20(4): 313-322. [28] NAEIMI M, HADDAD A. Environmental impacts of chemical and microbial grouting[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(2): 2264-2272. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06614-9 [29] 中华人民共和国水利部. 土工试验方法标准: GB/T 50123-2019[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019.Ministry of Water Resources of the People's Republic of China. Standard for geotechnical testing method: GB/T 50123-2019[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019. (in Chinese) [30] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑砂浆基本性能试验方法标准: JGJ/T 70-2009[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test method of basic properties of construction mortar: JGJ/T 70-2009[S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2009. (in Chinese) [31] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 水泥土配合比设计规程: JGJ/T 233-2011[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2011.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Specification for mix proportion design of cement soil: GB/T 50123-2019[S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2011. (in Chinese) [32] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 水泥基灌浆材料应用技术规范: GB/T 50448-2015[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2015.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Technical code for application of cementitious grout: GB/T 50448-2015[S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2015. (in Chinese) [33] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 岩土工程勘察规范: GB 50021-2001[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Code for investigation of geotechnical engineering: GB 50021-2001[S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2009. (in Chinese) [34] 水电水利规划设计总院. 水电工程钻孔压水试验规程: NB/T 35113-2018[S]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2018.China Renewable Energy Engineering Institute. Specification for water pressure test in borehole of hydropower projects: NB/T 35113-2018[S]. Beijing: China Water and Power Press, 2018. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: