Depositional system constrained by the high-precision sequence framework and the source to sink systems: A case study from the First Member of the Liushagang Formation in the Weixinan Sag
-
摘要:
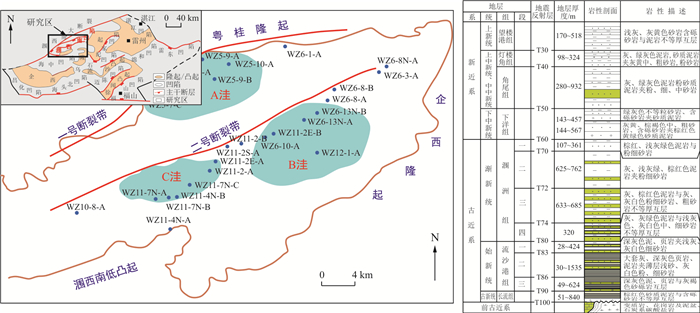
北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷的勘探方向已经从构造圈闭转移到岩性圈闭上,寻找岩性油气藏的核心问题就是明确砂体的展布。以涠西南凹陷流沙港组一段为研究对象,综合利用碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、测井、录井、岩心及地震等资料,对研究区目的层进行了高精度层序划分和沉积体系时空展布研究,明确了涠西南凹陷流沙港组一段沉积相类型及分布规律。研究表明,目的层流沙港组一段可以划分为1个三级层序、3个体系域以及8个准层序组。通过对研究区源-汇体系与沉积相分析,表明涠西南凹陷的沉积物主要来自西北部万山物源、东部企西物源、东南部涠西南物源以及西南部物源。涠西南凹陷流沙港组一段主要发育三角洲、湖泊和湖底扇等3种沉积相类型。低位期主要发育中深湖和湖底扇沉积,发育浊积水道、天然堤和席状朵体等沉积微相;湖扩期主要以深湖泥沉积微相为主;高位期则主要发育三角洲前缘沉积,其中水下分流河道、水下分流河道间较为发育,河口坝、席状砂等沉积微相发育较少。B洼主要发育西部三角洲进积滑塌型、南部近源断坡带型和东部远源缓坡型等3种类型湖底扇,其中,南部物源体系规模大、成藏条件好,是下一步勘探最具潜力的目标。
Abstract:Objective The exploration direction of the Weixinan Sag in the Beibuwan Basin has shifted from structural traps to lithological traps, and the key problem in searching for lithological traps is to clarify the distribution of sandstones.
Methods In this study, the high-frequency sequence division and depositional system of the First Member of the Liushagang Formation in the Weixinan Sag were analyzed using zircon dating, logging, core and seismic data.
Results Then, the types and distributions of depositional facies in the First Member of the Liushagang Formation in the Weixinan Sag were clarified. The results show that the First Member of the Liushagang Formation was deposited as a third-order sequence, which can be divided into three system tracts and eight parasequence sets. Based on the analysis of the source to sink systems and sedimentary facies, the sediments in the Weixinan Sag mainly sourced from the Wanshan provenance in the northwest, the Qixi provenance in the east, the Wexinan provenance in the southeast, and the Xinan provenance in the southwest. The First Member of the Liushagang Formation in the Weixinan Sag mainly contains three sedimentary facies types: delta, lacustrine and sublacustrine fan. The lowstand system tract is dominated by mid-deep lake and sublacustrine fan deposits, including turbidity channels, natural levee, and sheet lobes. The expanding system tract mainly contains the sedimentary microfacies of deep lacustrine mud. The highstand system tract consists of front-delta deposition, among which the subaqueous distributary channel and subaqueous distributary interchannel are widely developed, and sedimentary microfacies such as mouth bar and sheet sand are less developed.
Conclusion Three types of sublacustrine fan are mainly developed in the B subsag, including the western delta progradation slump type, southern near source fault slope belt type, and eastern far source gentle slope type.Among them, the southern provenance system with large-scale and good reservoir-forming conditions is the most promising target for further exploration.
-
图 3 涠西南凹陷流一段碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄谱峰及重矿物分布图[34]
Figure 3. Detrital zircon U-Pb age spectrum peak and heavy mineral distribution map of the First Member of the Weixinan Sag
-
[1] 邓孝亮, 杨希冰, 尤丽, 等. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷始新统流沙港组一段低渗储层特征及控制因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(4): 628-637.DENG X L, YANG X B, YOU L, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of low permeability reservoir in the First Member of Liushagang Formation of Eocene in Weixinan Sag, Beibuwan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(4): 628-637. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 陈奎, 李茂, 邹明生, 等. 涠西南凹陷涠洲组构造圈闭有效性定量评价技术及应用[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(12): 1370-1378.CHEN K, LI M, ZOU M S, et al. Quantitative evaluation technology and application of structural trap effectiveness of Weizhou Formation in Weixinan Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(12): 1370-1378. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 李茂, 朱绍鹏, 邹明生, 等. 涠西南凹陷复杂断块和隐蔽油气藏滚动勘探开发实践[J]. 中国海上油气, 2015, 27(4): 73-79.LI M, ZHU S P, ZOU M S, et al. Rolling exploration and development practice of complex fault blocks and subtle reservoirs in Weixinan Sag[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2015, 27(4): 73-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 胡德胜, 范彩伟, 朱红涛, 等. 涠西南凹陷流一段高位体系域湖底扇沉积特征及勘探意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(5): 23-31.HU D S, FAN C W, ZHU H T, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and exploration significance of sublacustrine fan in Liu-1 highstand system tract of Weixinan Sag[J]. Petroleum Exploration of China, 2020, 25(5): 23-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] 徐新德, 王碧维, 李旭红, 等. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷流沙港组隐蔽油气藏油源及成藏特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2012, 23(1): 92-98.XU X D, WANG B W, LI X H, et al. Oil source and accumulation characteristics of Liushagang Formation subtle reservoirs in Weixinan Sag, Beibuwan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2012, 23(1): 92-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 严恒, 王丽君, 高凌, 等. 涠西南凹陷流一段沉积相研究及岩性地层圈闭识别[J]. 中国矿业, 2017, 26(增刊2): 207-212.YAN H, WANG L J, GAO L, et al. Research on sedimentary facies on the First Member of Liushagang Formation in Weixinan Depression and lithologic stratigraphic traps identification[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2017, 26(S2): 207-212. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] 刘杰, 李茂, 杨朝强, 等. 涠西南凹陷流一段构造坡折带及其对层序、沉积相带的控制[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 29(3): 49-57.LIU J, LI M, YANG C Q, et al. Structural slope break zone of Liu 1 member in Weixinan Sag and its control on sequence and sedimentary facies belt[J]. Journal of Xi'an Petroleum University(Natural Science Edition), 2014, 29(3): 49-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 陶倩倩, 周家雄, 孙文钊, 等. 滑塌浊积扇内幕结构及成因: 以涠西南凹陷流一段上亚段为例[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2019, 54(2): 423-432.TAO Q Q, ZHOU J X, SUN W Z, et al. Inside structure and genesis of slump turbidite fan: A case study of the upper submember of First Member of Liushagang Formation in Weixinan Sag[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2019, 54(2): 423-432. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 张智武, 刘志峰, 张功成, 等. 北部湾盆地裂陷期构造及演化特征[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2013, 35(1): 6-10.ZHANG Z W, LIU Z F, ZHANG G C, et al. Structure and evolution characteristics of Beibu Gulf Basin during rifting period[J]. Journal of Petroleum and Natural Gas, 2013, 35(1): 6-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 刘震, 谭卓, 蔡东升, 等. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷流沙港组岩性圈闭形成条件[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(2): 239-246.LIU Z, TAN Z, CAI D S, et al. Formation conditions of lithologic traps in Liushagang Formation, Weixinan Sag, Beibuwan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(2): 239-246. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 姜平, 张建光, 姚光庆, 等. 涠西南凹陷11-7区块流沙港组沉积体系构成及演化特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(2): 97-104.JIANG P, ZHANG J G, YAI G Q, et al. Sedimentary system composition and evolution characteristics of Liushagang Formation in Block 11-7 of Weixinan Sag[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(2): 97-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 张辉, 曾小明, 黄冬梅, 等. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷富砾型和富砂型湖底扇沉积特征差异分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(5): 633-639.ZHANG H, ZENG X M, HUANG D M, et al. Difference analysis of sedimentary characteristics of gravel-rich and sand-rich sublacustrine fan in Weixinan Sag of Beibuwan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(5): 633-639. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 金杰华, 操应长, 王健, 等. 涠西南凹陷陡坡带流一段上亚段异重流沉积新发现[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(4): 250-258.JIN J H, CAO Y C, WANG J, et al. New discovery of heavy current deposits in the upper submember of the First Member of the steep slope belt flow in Weixinan Sag[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(4): 250-258. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 严恒, 王丽君, 方小宇, 等. 涠西南凹陷南部斜坡带中段流一段湖底扇沉积特征研究及油气勘探[J]. 复杂油气藏, 2015, 8(4): 7-12.YAN H, WANG L J, FANG X Y, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and oil and gas exploration of sublacustrine fan in the middle section of the southern slope belt of Weixinan Sag[J]. Complex Reservoirs, 2015, 8(4): 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 李凡异, 张厚和, 李春荣, 等. 北部湾盆地海域油气勘探历程与启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(3): 337-345.LI F Y, ZHANG H H, LI C R, et al. Oil and gas exploration in Beibu Gulf Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(3): 337-345. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 姜平, 秦春雨, 杨希冰, 等. 涠西南凹陷一号断裂陡坡带扇体沉积展布特征及主控因素[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(2): 534-546.JIANG P, QIN C Y, YANG X B, et al. Sedimentary distribution characteristics and main controlling factors of fan body in steep slope zone of No.1 fault in Weixinan Sag[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(2): 534-546. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 刘一鸣, 胡林, 张强, 等. 涠西南凹陷流沙港组二段至一段构造特征及其对沉积的控制作用[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2018, 42(6): 52-61.LIU Y M, HU L, ZHANG Q, et al. Structural characteristics of the 2nd to 1st members of Liushagang Formation in Weixinan Sag and its control on sedimentation[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2018, 42(6): 52-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 陈奎, 周家雄, 张辉, 等. 涠西南凹陷二号断裂带断裂控藏研究及应用[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(7): 92-102.CHEN K, ZHOU J X, ZHANG H, et al. Research and application of fault control reservoir in No.2 fault zone of Weixinan Sag[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 41(7): 92-102. [19] ZHAO Y P, WANG H, YAN D T, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and model of gravity flows in the eocene Liushagang Formation in Weixi'nan Depression, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 190(10): 70-82 [20] CAO L, ZHANG Z H, LI H Y, et al. Mechanism for the enrichment of organic matter in the Liushagang Formation of the Weixinan Sag, Beibuwan Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 122(10): 46-49. [21] 叶加仁, 赵牛斌, 杨宝林, 等. 涠西南凹陷流沙港组烃源岩生产力及发育模式[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 105-113. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0112YE J R, ZHAO N B, YANG B L, et al. Productivity and development model of source rock of Liushagang Formation in Weixinan Sag[J]. Bulletion of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 105-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0112 [22] 高阳东, 张向涛, 李智高, 等. 珠江口盆地恩平凹陷北带下-中中新统层序构型及其差异性分析: 对岩性圈闭发育的启示[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(5): 1758-1770.GAO Y D, ZHANG X T, LI Z G, et al. Sequence configuration and difference analysis of Lower-Middle Miocene in the northern belt of Enping Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin: Implications for the development of lithologic traps[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(5): 1758-1770. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 王乔, 宋立新, 韩亚杰, 等. 辽河西部凹陷雷家地区古近系沙三段沉积体系及层序地层[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(6): 102-113.WANG Q, SONG L X, HAN Y J, et al. Sedimentary system and sequence stratigraphy of Paleogene Es3 in Leijia area, Western Sag of Liaohe Basin[J]. Lithological Reservoirs, 2021, 33(6): 102-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 汪彦, 彭军, 游李伟, 等. 中国高分辨率层序地层学的研究现状[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(3): 352-358.WANG Y, PENG J, YOU L W, et al. Research status of high-resolution sequence stratigraphy in China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(3): 352-358. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] 刘波. 基准面旋回与沉积旋回的对比方法探讨[J]. 沉积学报, 2002, 20(1): 112-117.LIU B. Discussion on the comparison method of base level cycle and sedimentary cycle[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(1): 112-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] WANG J, CAO Y C, LI J L. Sequence structure and non-structural traps of the Paleogene in the Weixi'nan Sag, Beibuwan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development Online, 2012, 39(3): 325-334. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(12)60048-2 [27] LIU E T, WANG H, FENG Y X, et al. Sedimentary architecture and provenance analysis of a sublacustrine fan system in a half-graben rift depression of the South China Sea[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2020, 409(10): 57-81. [28] 许鉴源, 龚齐宝, 刘芮. 基于测井曲线小波变换的煤系地层对比方法研究[J]. 现代盐化工, 2021, 48(5): 69-73.XU J Y, GONG Q B, LIU R. Study on coal measure strata correlation method based on wavelet transform of logging curve[J]. Modern Salt Chemical Industry, 2021, 48(5): 69-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] 曹庆超, 白壮壮, 李浩武, 等. 测井数据小波变换在川中寒武系洗象池群层序地层划分中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 242-251. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0418CAO Q C, BAI Z Z, LI H W, et al. Application of well logging data wavelet transform in sequence stratigraphic division of Cambrian Xixiangchi Group in central Sichuan[J]. Bulletion of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 242-251. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0418 [30] 刘金水, 陆永潮, 秦兰芝. 源-汇系统分析方法在大型储集体研究中的应用: 以西湖凹陷中央反转带花港组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(3): 303-310.LIU J S, LU Y C, QIN L Z. Application of source-sink system analysis method in large reservoir research: A case study of Huagang Formation, central inversion belt, Xihu Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(3): 303-310. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] 谈明轩, 朱筱敏, 张自力, 等. 古"源-汇"系统沉积学问题及基本研究方法简述[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(5): 1107-1118.TAN M X, ZHU X M, ZHANG Z L, et al. Brief introduction of sedimentology problems and basic research methods of paleo "source-sink" system[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2020, 41(5): 1107-1118. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] 王宏宇, 王义龙, 刘平华, 等. 华北克拉通胶北地体蓬莱群辅子夼组碎屑锆石U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(9): 3074-3090.WANG H Y, WANG Y L, LIU P H, et al. Detrital zircon U-Pb dating of Fuzikuang Formation in Penglai Group, Jiaobei Terrane, North China Craton and its geological significance[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(9): 3074-3090. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] 刘强虎, 朱红涛, 舒誉, 等. 珠江口盆地恩平凹陷古近系恩平组物源体系及其对滩坝的控制[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(3): 286-299.LIU Q H, ZHU H T, SHU Y, et al. Provenance system of Paleogene Enping Formation in Enping Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin and its control over beach and dam[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(3): 286-299. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] 秦春雨. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷古近系双层构造演化及沉积响应[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2020.QIN C Y. Tectonic evolution and sedimentary response of the Paleocene bilayer in the Weixinan Depression, Beibuwan Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] 李海东, 王红, 陈少勇, 等. 扇三角洲沉积体系小层划分与对比: 以南堡凹陷高123X2井区Es3~(2+3)亚段为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2016, 23(1): 21-24.LI H D, WANG H, CHEN S Y, et al. Sublayer division and correlation of fan delta sedimentary system: Taking Es3(2+3) submember of Gao 123X2 well area in Nanpu Sag as an example[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Amp, 2016, 23(1): 21-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] ZHOU X X, GAO G, Lü X X, et al. Petroleum source and accumulation of WZ12 oils in the Weixi'nan Sag, south China Sea, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 177(2): 681-698. [37] 张辉, 吴子瑾, 周伟, 等. 北部湾盆地WZA区流一上亚段源-汇分析及沉积相展布[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(5): 55-66.ZHANG H, WU Z J, ZHOU W, et al. Source-sink analysis and sedimentary facies distribution of upper submember Liuyi in WZA area of Beibuwan Basin[J]. Lithological Reservoirs, 2017, 29(5): 55-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] 李勇, 张辉, 曾小明. 涠洲A油田流沙港组一段Ⅱ油组沉积微相及优质储层预测[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(22): 182-190.LI Y, ZHANG H, ZENG X M. Sedimentary microfacies and high quality reservoir prediction of Ⅱ oil formation of Liushagang Formation in Weizhou A Oilfield[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(22): 182-190. (in Chinese with English abstract) [39] 袁丙龙, 张辉, 张连枝, 等. 涠西南凹陷浅水三角洲前缘砂体类型及分布模式[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(2): 78-87.YUAN B L, ZHANG H, ZHANG L Z, et al. Sand body types and distribution patterns of shallow water delta front in Weixinan Sag[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(2): 78-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) [40] 李思田, 林畅松, 解习农, 等. 大型陆相盆地层序地层学研究: 以鄂尔多斯中生代盆地为例[J]. 地学前缘, 1995, 2(4): 133-136.LI S T, LIN C S, XIE X N, et al. Sequence stratigraphy of large continental basins: A case of Ordos Mesozoic Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1995, 2(4): 133-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) [41] 谭程鹏, 李茂, 于兴河, 等. 涠西南凹陷涠洲11区南部流沙港组流一段沉积微相特征[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2012, 32(1): 62-71.TAN C P, LI M, YU X H, et al. Sedimentary microfacies characteristics of Liushagang Formation in southern Weizhou 11 area, Weixinan Sag[J]. Sedimentary and Tethys Geology, 2012, 32(1): 62-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) [42] 年涛, 姜在兴, 刘惠民, 等. 东营凹陷孔一段"红-灰"岩层旋回沉积记录: 以王家岗地区王46井为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 32-43. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0072NIAN T, JIANG Z X, LIU H M, et al. Sedimentary records of 'red-gray' rock cycle in the First Member of Kongdian Formation in Dongying Depression: Taking Wang 46 well in Wangjiagang area as an example[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 32-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0072 [43] LI Y, LIN S, WANG H, et al. Depositional setting analysis using seismic sedimentology: Example from the Paleogene Lishagang sequence in the Fushan Depression, South China Sea[J]. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2017, 8(5): 347-355. doi: 10.1016/j.geog.2017.05.001 [44] CAO Y C, JIN J H, LIU H N, et al. Deep-water gravity flow deposits in a lacustrine rift basin and their oil and gas geological significance in eastern China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(2): 286-298. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(21)60023-X [45] DONG G Y, HE Y B, LENG C P, et al. Mechanism of sand body prediction in a continental rift basin by coupling paleogeomorphic elements under the control of base level[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development Online, 2016, 43(4): 579-590. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(16)30068-4 [46] HUANG B J, TIAN H, WILKINS R W T, et al. Geochemical characteristics, palaeoenvironment and formation model of Eocene organic-rich shales in the Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 48(7): 77-89. [47] LIU E T, WANG H, LI Y, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and tectonic setting of sublacustrine fans in a half-graben rift depression, Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 52(1): 9-21. [48] ZHAO K, DU X B, LU Y C, et al. Are light-dark coupled laminae in lacustrine shale seasonally controlled?: A case study using astronomical tuning from 42.2 to 45.4 Ma in the Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2019, 528(4): 35-49. [49] 欧阳柳芸, 贺琦, 刘昆, 等. 马岭地区嘉陵江组沉积环境演化分析: 来自沉积学和主微量元素的证据[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 44-53. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0095OUYANG L Y, HE Q, LIU K, et al. Evolutionary analysis of the sedimentary environment of the Jialingjiang Formation in the Maling area: Evidence from sedimentology and main trace elements[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 44-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0095 [50] 付鑫, 杜晓峰, 官大勇, 等. 地震沉积学在河流-浅水三角洲沉积相研究中的应用: 以渤海海域蓬莱A构造区馆陶组为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 96-108. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0304FU X, DU X F, GUAN D Y, et al. Application of seismic sedimentology in the study of sedimentary phases in riverine-shallow-water deltas: An example from the Tian tao Formation, Penglai A tectonic zone, Bohai Sea[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 96-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0304 -





 下载:
下载: