Effect of Cr(Ⅲ) on the activity and function of Mn(Ⅱ)-oxidizing bacteria Pseudomonas putida MnB1
-
摘要:
三价铬(Cr(Ⅲ))与锰氧化菌在环境中通常伴同存在,锰氧化菌介导生成的锰氧化物是Cr(Ⅲ)的主要天然氧化剂,探究Cr(Ⅲ)对锰氧化菌活性和功能的影响对于阐明环境中的锰循环和铬的迁移转化行为具有重要意义。以锰氧化模式菌
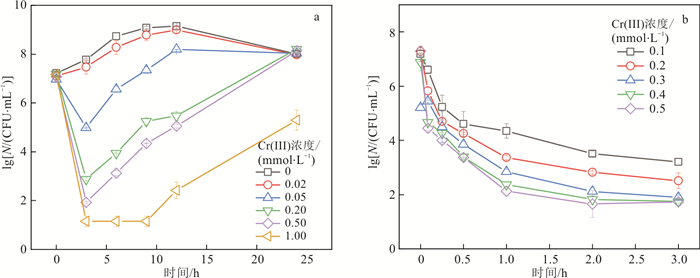
Pseudomonas putida MnB1为研究对象,通过批实验探究了Cr(Ⅲ)对MnB1活性与功能的影响及其机制。结果表明,Cr(Ⅲ)浓度高于0.05 mmol/L时会造成MnB1的显著死亡,且Cr(Ⅲ)浓度越高杀菌作用越显著,当Cr(Ⅲ)高于0.02 mmol/L时会推迟锰的生物氧化,当Cr(Ⅲ)浓度高于0.2 mmol/L时完全抑制锰的生物氧化。机制研究表明,Cr(Ⅲ)诱导产生的胞内活性氧和Cr(Ⅲ)颗粒引起的细胞膜通透性改变共同影响了MnB1的生长代谢和功能。研究结果为认识锰的生物地球化学循环和铬的迁移转化行为提供了新的理论依据。Abstract:Objective Cr(Ⅲ) often occurs together with Mn-oxidizing bacteria in natural environments. Manganese oxides, which are commonly generated from the biotic oxidation of Mn2+ by Mn(Ⅱ)-oxidizing bacteria, and are considered the main oxidants of Cr(Ⅲ) in nature.
Methods Investigating the impact of Cr(Ⅲ) on the activity and function of Mn(Ⅱ)-oxidizing bacteria is important for understanding Mn cycling and the transformation of Cr in natural environments. In this study,
Pseudomonas putida MnB1 was chosen as a representative Mn(Ⅱ)-oxidizing bacterium, and the effect and mechanisms of Cr(Ⅲ) on the activity and function of MnB1 were investigated by batch experiments.Results The results showed that Cr(Ⅲ) at a concentration higher than 0.05 mmol/L Cr(Ⅲ) caused significant death of MnB1, and the bactericidal effect became stronger with increasing Cr(Ⅲ) concentration. The concentration of Cr(Ⅲ) higher than 0.02 mmol/L Cr(Ⅲ) delayed the biotic oxidation of Mn(Ⅱ), and 0.2 mmol/L Cr(Ⅲ) completely inhibited the oxidation of Mn(Ⅱ). A mechanistic study revealed that the intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced by Cr(Ⅲ) and cell membrane permeability changes caused by Cr(Ⅲ) particles collaboratively inhibited the metabolism and function of MnB1.
Conclusion This study provides a new theoretical basis for further understanding the biogeochemical cycle of manganese and the migration and transformation behavior of chromium in the natural environment.
-
Key words:
- Cr(Ⅲ) /
- Mn(Ⅱ)-oxidizing bacteria /
- reactive oxygen species /
- Mn cycling /
- chromium pollution
-
-
[1] NAZAROVA T, ALESSI D S, JANSSEN D J, et al. In situ biostimulation of Cr(Ⅵ) reduction in a fast-flowing oxic aquifer[J]. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2020, 4(11): 2018-2030. doi: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.0c00200 [2] THOMPSON S L, MANNING F, MCCOLL S M. Comparison of the toxicity of chromium Ⅲ and chromium Ⅵ to cyanobacteria[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology, 2002, 69(2): 286-293. [3] FRAGA C G. Relevance, essentiality and toxicity of trace elements in human health[J]. Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 2005, 26(4/5): 235-244. [4] DAVIDSON A B, HOLMDEN C, NOMOSATRYO S, et al. Cr isotopes and the engineered attenuation of Cr(Ⅵ)-rich runoff[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(21): 14938-14945. [5] 廉晶晶, 罗泽娇, 靳孟贵. 某厂电镀车间场地土壤与地下水污染特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(2): 150-155.LIAN J J, LUO Z J, JIN M G. Characteristics of soil and groundwater pollution in electroplating workshop of a factory[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(2): 150-155. (in Chinese and English abstract [6] 刘婷, 郑有业, 郭统军. 大中型豆荚状铬铁矿床地球化学特征研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 217-225.LIU T, ZHENG Y Y, GUO T J. Optimal geochemical features of medium and large sized podiform chromite ores[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2): 217-225. (in Chinese and English abstract [7] RAJAPAKSHA A U, VITHANAGE M, OK Y S, et al. Cr(Ⅵ) formation related to Cr(Ⅲ)-muscovite and birnessite interactions in ultramafic environments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(17): 9722-9729. [8] TEBO B M, BARGAR J R, CLEMENT B G, et al. Biogenic manganese oxides: Properties and mechanisms of formation[J]. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet, 2004, 32(1): 287-328. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.32.101802.120213 [9] TEBO B M, JOHNSON H A, MCCARTHY J K, et al. Geomicrobiology of manganese(Ⅱ) oxidation[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2005, 13(9): 421-428. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2005.07.009 [10] BUTTERFIELD C N, SOLDATOVA A V, LEE S W, et al. Mn(Ⅱ, Ⅲ) oxidation and MnO2 mineralization by an expressed bacterial multicopper oxidase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(29): 11731-11735. [11] BROUWERS G J, VIJGENBOOM E, CORSTJENS P L A M, et al. Bacterial Mn2+ oxidizing systems and multicopper oxidases: An overview of mechanisms and functions[J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2000, 17(1): 1-24. doi: 10.1080/014904500270459 [12] 孟佑婷. 生物氧化锰的形成及其对重金属离子的吸附、氧化作用机理[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2009.MENG Y T. Formation of biogenic Mn oxides and reactive mechanisms with heavy metals in environment[D]. Beijing: Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2009. (in Chinese and Engish abstract) [13] FATHIMA A, RAO J R. Is Cr(Ⅲ) toxic to bacteria: To xicity studies using Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli as model organism[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2013, 200(3): 453-462. [14] VILLAGRASA E, BONET G N, SOLÉ A. Ultrastructural evidences for chromium(Ⅲ) immobilization by Escherichia coli K-12 depending on metal concentration and exposure time[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 285: 131500-131500. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131500 [15] NIU A, BIAN W P, FENG S L, et al. Role of manganese superoxide dismutase(Mn-SOD) against Cr(Ⅲ)-induced toxicity in bacteria[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 403: 123604-123604. [16] BENCHEIKHLATMANI R, OBRAZTSOVA A, MACKEY M, et al. Toxicity of Cr(Ⅲ) to Shewanella sp. strain MR-4 during Cr(Ⅵ) reduction[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(1): 214-220. [17] MURRAY K J, MOZAFARZADEH M L, TEBO B M. Cr(Ⅲ) oxidation and Cr toxicity in cultures of the manganese(Ⅱ)-oxidizing Pseudomonas putida strain GB-1[J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2005, 22(3/4): 151-159. [18] POETSCH A R. The genomics of oxidative DNA damage, repair, and resulting mutagenesis[J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18: 207-209. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.12.013 [19] JOMOVA K, VALKO M. Advances inmetal-induced oxidative stress and human disease[J]. Toxicology: An International Journal Concerned with the Effects of Chemicals on Living Systems, 2011(2/3): 283. [20] WANG J, FANG Z, GAO J, et al. Comparative study of cytotoxicity, DNA damage and oxidative stress induced by heavy metals Cd(Ⅱ), Hg(Ⅱ) and Cr(Ⅲ) in yeast[J]. Current Microbiology, 2021, 78(5): 1856-1863. doi: 10.1007/s00284-021-02454-4 [21] KHASSANOVA L A, IVANOV A Y, KHASSANOVA Z M, et al. Electrophysical analysis of Cr(Ⅲ) and Cr(Ⅵ) influence on sulfate reductive bacterium Desulfobacterium sp. 63[C]//Anon. 9th International Symposium on Metal Ions in Biology and Medicine. Lisbon: [s. n. ], 2006: 226. [22] ASADISHAD B, GHOSHAL S, TUFENKJI N. Short-term inactivation rates of selected gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria attached to metal oxide mineral surfaces: Role of solution and surface chemistry[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2013, 47: 5729-5737. doi: 10.1021/es4003923 [23] LIU Z R, MUKHERJEE M, WU Y C, et al. Increased particle size of goethite enhances the antibacterial effect on human pathogen Escherichia coli O157∶H7∶A raman spectroscopic study[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 405: 124174. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124174 [24] WU Y X, DENG B L, XU H F, et al. Chromium(Ⅲ) oxidation coupled with microbially mediated Mn(Ⅱ) oxidation[J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2005, 22(3/4): 161-170. [25] 孙群群, 屈婧祎, 童曼, 等. 地下水水化学组成对Fe(Ⅱ)氧化过程中锰氧化菌失活的影响[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2021, 28(3): 101-107.SUN Q Q, QU J Y, TONG M, et al. Effect of groundwater hydrochemical components on the inactivation of Mn-oxidizing bacteria upon Fe(Ⅱ) oxygenation[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2021, 28(3): 101-107. (in Chinese and Engish abstract) [26] KRUMBEIN W E. New method for thedetection and enumeration of manganese oxidizing and reducing microorganisms in soil and recent marine sediments[J]. Soil Biol. Int. News Bull., 1972, 25(2/3): 347-356. [27] GHERIANY I E, BOCIOAGA D, HAY A G, et al. Iron requirement for Mn(Ⅱ) oxidation by Leptothrix discophora SS-1[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2009, 75(5): 1229-1235. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02291-08 [28] LIAO W J, YE Z L, YUAN S H, et al. Effect of coexisting Fe(Ⅲ)(oxyhydr)oxides on Cr(Ⅵ) reduction by Fe(Ⅱ)-bearing clay minerals[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(23): 13767-13775. [29] 屈婧祎, 童曼, 袁松虎. 二价铁氧化对铁锰循环功能微生物活性的影响及机制[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(2): 632-641QU J Y, TONG M, YUAN S H. Effect andmechanism of Fe(Ⅱ) oxygenation on activities of iron and manganese cycling functional micobes[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(2): 632-641. (in Chinese and Engish abstract) [30] FRANCIS C A, TEBO B M. cumA multicopper oxidase genes from diverse Mn(Ⅱ)-oxidizing and non-Mn(Ⅱ)-oxidizing Pseudomonas strains[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2001, 67(9): 4272. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.9.4272-4278.2001 [31] WANG Y F, SU H, GU Y, et al. Carcinogenicity of chromium and chemoprevention: A brief update[J]. Onco Targets and Therapy, 2017(10): 4065-4079. [32] TONG M, ZHAO Y X, SUN Q Q, et al. Fe(Ⅱ) oxygenation inhibits bacterial Mn(Ⅱ) oxidation by P. putida MnB1 in groundwater under O2-perturbed conditions[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 435: 128972. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128972 [33] ZHENG Y J, LI Y M, LONG H Y, et al. BifA regulates biofilm development of Pseudomonas putida MnB1 as a primary response to H2O2 and Mn2+[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 1490. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01490 [34] BROUWERS G J, DE VRIND J P M, CORSTJENS P L A M, et al. Involvement of genes of the two-step protein secretion pathway in the transport of the manganese-oxidizing factor cross the outer membrane of Pseudomonas putida strain GB-1[J]. American Mineralogist, 1998, 83(11/12): 1573-1582. -





 下载:
下载: