Current situation of karst groundwater environmental problems and spring source protection in the Gudui-Nanliang spring basin
-
摘要:
古堆-南梁泉域位于山西省南部, 是一个深循环与浅循环共存、冷水系统与热水系统循环转化、多级次排泄的复合型岩溶水系统, 因长期不合理的开发利用, 泉域内出现了一系列岩溶水环境地质问题。以水文地质调查工作为基础, 综合采用地下水流场对比分析、水文地球化学及同位素分析、岩溶水资源评价等方法, 详细论述了古堆-南梁泉域内岩溶水环境问题现状及其成因, 并提出了泉源区生态修复与规划方案。结果表明: 受气候变化与人类活动的叠加影响, 系统内古堆泉、南梁泉、海头泉分别于1999年、1992年、2002年断流, 2013-2021年区域地下水位平均下降速度达2.53 m/a; 水化学、同位素分析结果指示了排泄区九原山附近松散岩类孔隙水越流补给量、三泉水库渗漏补给量对岩溶地下水的影响已不可忽略; 泉域内岩溶水超Ⅲ类水水质标准样品占比由2014年的62.5%升高至2021年的81.25%;泉源区0.904 km2范围可细分为核心保护区、水库蓄水区、一般保护区, 应分区进行生态保护与修复规划。研究结果可为山西省超采区综合治理、古堆泉水生态修复与保护工作提供基础依据。
Abstract:Objective The Gudui-Nanliang spring basin located in southern Shanxi Province is a complex karst water system with the coexistence of deep and shallow circulation, the transformation of cold and hot water, and multistage discharge. Due to long-term unreasonable exploitation and utilization, a series of geological environment problems related to karst groundwater have emerged in the spring basin. The present study aims to propose an ecological restoration and planning scheme for the spring basin by discussing in detail the status of karst groundwater-related environmental problems and their causes.
Methods Based on a hydrogeological survey, this paper comprehensively employs a variety of methods, including comparative analysis of groundwater flow field, hydrogeochemical and isotopic analysis, and evaluation of karst water resources.
Results The results show that due to the superimposed effects of climate change and human activities, Gudui Spring, Nanliang spring, and Haitou spring cut off the flow in 1999, 1992, and 2002, respectively, and the average decline rate of the regional groundwater level from 2013 to 2021 reaches 2.53 m/a. The results of hydrochemical and isotopic analysis indicate that the recharge to the karst groundwater of porous groundwater from unconsolidated deposits through leakage and surface water from Sanquan Reservoir through seepage cannot be ignored. The proportion of karst water samples worse than the water quality standard of class Ⅲ in the spring basin increased from 62.5% in 2014 to 81.25% in 2021. The range of 0.904 km2 of the spring source area can be subdivided into core protection zone, general protection zone and reservoir storage zone. Ecological protection and restoration planning should be carried out considering the differences between the three zones.
Conclusion The results of the study can provide a basis for the comprehensive management of groundwater overexploitation areas in Shanxi Province and the ecological restoration and protection of Gudui spring basin.
-
多年来,岩溶水为我国华北地台区城镇生活、能源基地建设提供了不可替代的水源保障[1]。随着我国北方地区气候干旱化的发展[2]与人类活动对水资源需求的不断增加,加之对岩溶水系统复杂结构的认识薄弱,缺乏合理有效的管理,造成区内近1/3的岩溶大泉相继断流,80%以上泉水流量大幅度衰减,由此频繁引发环境地质问题[3]。山西省南部的古堆—南梁泉域是一个深循环与浅循环共存、冷水系统与热水系统循环转化、多级次排泄的复合型岩溶水系统[4-6]。因长期不合理的开发利用,古堆泉于1999年断流,此后泉口水位以年均3.5 m以上的速度持续下降,成为山西省乃至黄河流域区域岩溶地下水位下降幅度大、地下水超采严重、水环境问题较为突出的地区之一[7]。
山西省省委、省政府高度重视岩溶地下水保护和超采区治理工作,自2012年以来,先后在加强监督管理、强化岩溶大泉保护、完善监测体系、关井压采和水源置换等多个方面开展了工作[8],丰富和完善了地下水超采区综合治理体制。基于此,笔者以近年来在古堆-南梁泉域内开展的岩溶水文地质调查、地下水位统测、水化学同位素分析、岩溶水资源评价等工作为基础,详细论述古堆泉域内岩溶水环境问题的现状及其成因,针对古堆泉水复流与保护工作,提出泉源区生态修复与规划方案,以期为古堆泉水的生态修复与保护工作提供理论参考与基础依据。
1. 泉域概况
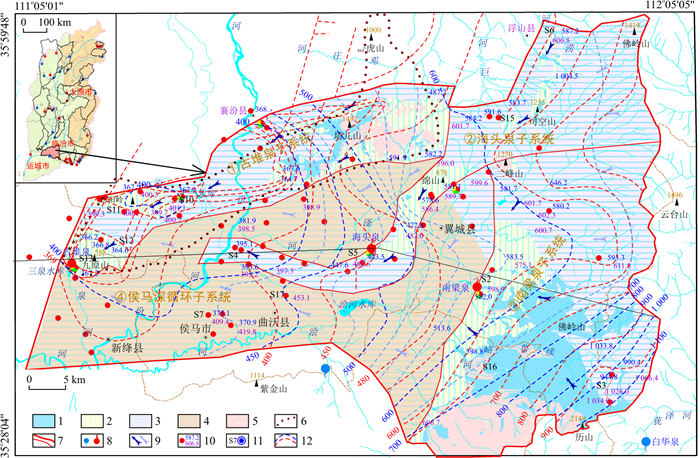
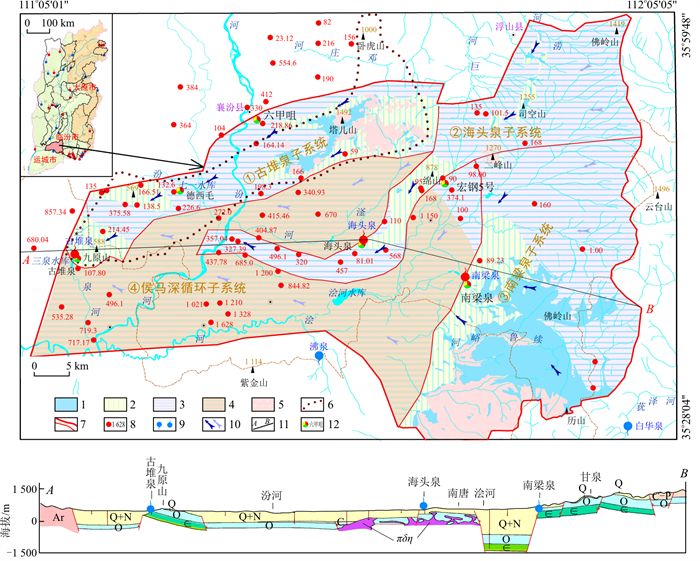
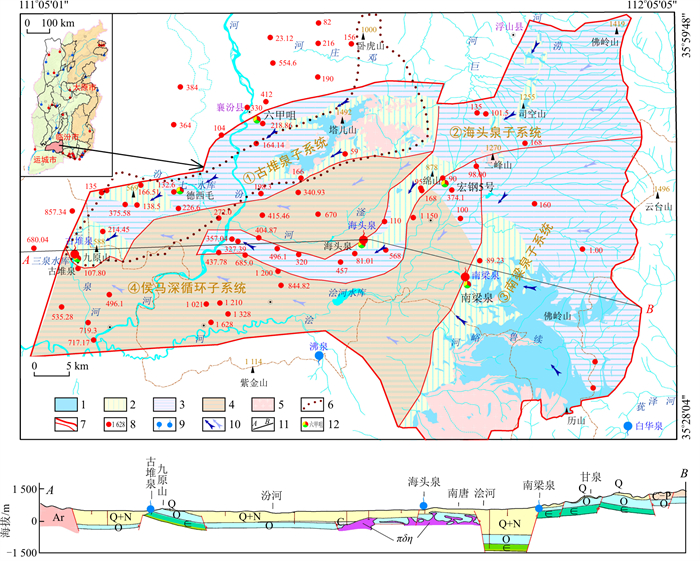
古堆泉又名“鼓水”,是山西省19处岩溶大泉之一,也是汾河流域唯一的中低温热泉,素有"石鼓神泓"的美誉,出流于山西省运城市新绛县三泉镇古堆村鼓山脚下,由22个泉点组成,出流标高441~445 m,多年平均水温23~25℃,天然平均流量1.3 m3/s[9-11]。区内属半干旱大陆性季风气候,降水稀少而蒸发强烈,地表水资源匮乏,岩溶地下水资源一度掌握着当地经济社会发展的命脉。受北部塔儿山、南部紫金山,东部中条山隆起与西部吕梁山山前凹陷的控制,泉域范围内地形整体南北高、中部低,东部高、西部低。区内河流属黄河流域汾河水系,汾河自北向南穿越泉域,另有汾河支流浍河、滏河、三泉河、汾城河和排碱沟等季节性河流(图 1)。
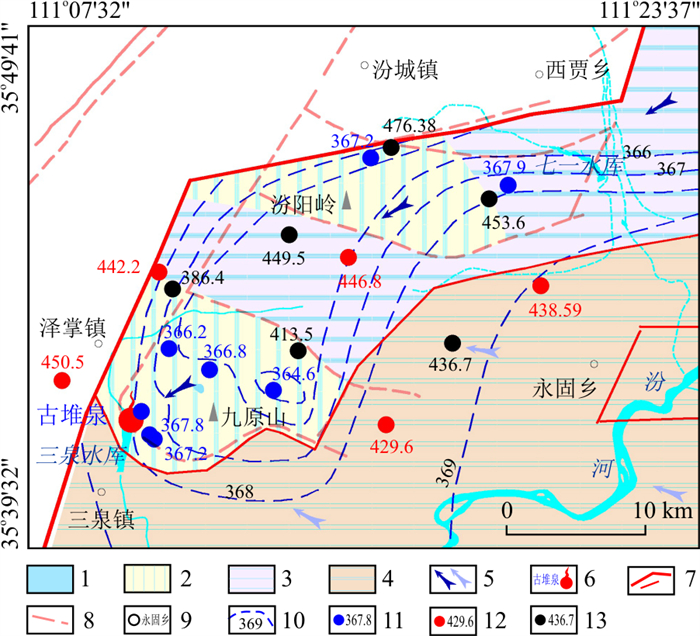
 图 1 古堆泉域水文地质略图1.碳酸盐岩裸露区;2.碳酸盐岩覆盖区;3.碳酸盐岩浅埋藏区;4.碳酸盐岩深埋藏区;5.非碳酸盐岩区;6.早期泉域边界;7.新泉域边界(下部细线为子系统边界);8.控制性钻孔碳酸盐岩埋藏深度(m);9.岩溶泉水(蓝色为出流下降泉,红色为断流上升泉);10.地下水流向(左侧为浅循环流向,右侧为深循环流向);11.剖面线及起止点标注;12.长观孔位置及名称。Ar.新太古界; ∈.寒武系; O.奥陶系;C.石炭系;C-P.石炭系-二叠系;Q+N.第四系+新近系;Q.第四系; πδη.火成岩侵入体Figure 1. Hydrogeological sketch of the Gudui spring basin
图 1 古堆泉域水文地质略图1.碳酸盐岩裸露区;2.碳酸盐岩覆盖区;3.碳酸盐岩浅埋藏区;4.碳酸盐岩深埋藏区;5.非碳酸盐岩区;6.早期泉域边界;7.新泉域边界(下部细线为子系统边界);8.控制性钻孔碳酸盐岩埋藏深度(m);9.岩溶泉水(蓝色为出流下降泉,红色为断流上升泉);10.地下水流向(左侧为浅循环流向,右侧为深循环流向);11.剖面线及起止点标注;12.长观孔位置及名称。Ar.新太古界; ∈.寒武系; O.奥陶系;C.石炭系;C-P.石炭系-二叠系;Q+N.第四系+新近系;Q.第四系; πδη.火成岩侵入体Figure 1. Hydrogeological sketch of the Gudui spring basin区内地层出露较为齐全,基底变质岩地层有新太古界界河口岩群及五台群;沉积盖层有古生界寒武系、奥陶系、石炭系、二叠系,中生界三叠系和新生界新近系、第四系等,另有中生代火成岩侵入体或盖层在塔儿山、二峰山地区出露,地层总体向西北方向倾斜。因地处汾渭地堑由南北向东西方向的转折端,同时受沁水向斜与吕梁山复背斜的共同影响,古堆泉域是一个地质结构在东西、南北方向上总体均呈“三隆、三陷”的结构框架,隆、陷间为组成地垒与地堑的大断距断裂构造。泉域岩溶含水层为下古生界中上寒武统及奥陶系碳酸盐岩,上覆石炭系-二叠系煤系地层为区域隔水顶板,下伏下寒武统碎屑岩及前寒武系变质岩为区域隔水底板。岩溶地下水主要接受北部、东部碳酸盐岩裸露区、覆盖区降水入渗补给及河流在碳酸盐岩裸露河段的渗漏补给,整体自东向西渗流。古堆—南梁泉域汇水面积2 942 km2,分为:①塔尔山-九原山古堆泉岩溶水子系统(以下简称古堆泉子系统);②佛岭山-高显-海头泉岩溶水子系统(以下简称海头泉子系统);③中条山-南梁泉岩溶水子系统(以下简称南梁泉子系统);④侯马盆地深循环岩溶水子系统(以下简称侯马深循环子系统),并以南梁泉(冷水泉,1992年断流)、海头泉(低温热泉,2002年断流)为中间排泄带,以古堆泉(低温热泉,1999年断流)为最终排泄点的冷水-热水复合型岩溶水系统[4]。
2. 泉域岩溶水环境问题及成因
近几十年来,受气候变化与人类活动影响,山西岩溶大泉流量出现不同程度的衰减甚至断流[12-13],由此引发了诸如泉水断流、区域地下水位下降、岩溶水流动特征改变、岩溶水水质退化等一系列水环境问题,古堆—南梁泉域也不例外。
2.1 泉水断流
20世纪80年代以来,随着经济社会建设对水资源需求的与日俱增,而我国北方整体呈干旱化趋势发展,加之对泉域水文地质条件认识不足,已有的水资源评价成果不能满足地下水资源管理的需求,使古堆—南梁泉域岩溶水“入不敷出”的局面日趋严重,古堆泉、南梁泉、海头泉分别于1999年、1992年、2002年断流。
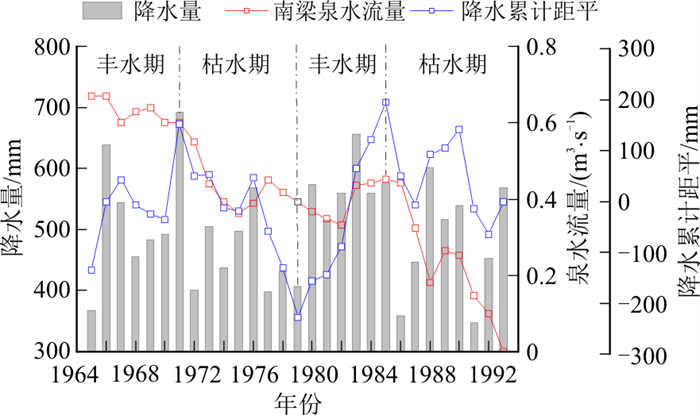
据三泉管理站监测资料(表 1),1970年以前古堆泉水流量一般稳定在1.2~1.3 m3/s,但之后的20多年,随着工、农业不断发展,汾阳岭、九原山地区灌溉井大量抽取地下水,袭夺了部分泉水流量,塔儿山、二峰山地区铁矿排水,减少了泉域部分天然补给量,使古堆泉水流量日益减小,最终于1999年彻底断流。
表 1 古堆泉水流量观测统计Table 1. Statistical table of Gudui spring flow observations观测时间(年) 1956以前 1964-1968 1974-1978 1979-1982 1983-1986 1987-1988 1989-1990 1991-1993 1999 泉流量/(m3·s-1) 1.3 1.2 0.9 0.715 0.618 0.495 0.715 0.532 断流 南梁泉流量具有连续性监测资料,因此绘制了泉水流量衰减过程曲线,并与同期降水量进行了对比分析,结果如图 2所示。根据泉域降水累计距平曲线斜率分布情况,可将1965-1992年降水量划分为丰水期与枯水期相间的4个阶段,期间特别是1970年以后,泉水流量过程曲线与降水累计距平曲线具有“峰谷同步”的特点,说明降水量是影响泉流量变化的重要因素之一。但同时可以1986年为界,将泉水流量衰减过程分为2个阶段:1965-1986年(20 a)泉水流量由0.67 m3/s衰减至0.442 m3/s,衰减速度为0.011 m3/(s·a);1987—1992年泉水断流,6 a内平均衰减速度达0.074 m3/(s·a),后期衰减速度为前期的6.5倍,而两阶段平均降水量衰减程度仅为9%(由512.23 mm衰减至465.88 mm),表明降水量减少不是引起南梁泉流量衰减的主要因素。资源评价结果表明,在不计河流渗漏量的条件下,南梁泉子系统的天然补给量占整个古堆—南梁泉域的61%(若计算河流渗漏量,该值将更大),而南梁泉天然排泄量只占3处泉水天然排泄量的30%,该子系统内现有开采量远小于其多年平均补给资源量,但系统内地下水位多年平均降幅也在1.5 m以上,分析认为引起南梁泉流量减小直至断流的主要原因应是周边3个岩溶水子系统水位下降使南梁泉子系统侧向径流排泄量增大。
海头泉出流于唐代, 开发利用始于宋代, 距今已有1 300 a的历史。1949年前泉水流量为0.163 m3/s, 水质良好, 水温高达36℃, 是一个古老的清水自流灌区。1960年加大了泉源开发, 由原来的三泉(七星海、八角海、南韩海)出水变为三泉六井出水, 泉水流量增加为0.168 m3/s。随着周边岩溶水开采量的逐渐增加, 20世纪70年代流量开始衰减, 至90年代末泉水流量仅为0.049 m3/s左右, 2002年1月泉源流量急剧下降至0.026 m3/s左右, 2002年3月20日泉源、自流井全部断流。海头泉水流量如表 2所示。
表 2 海头泉水流量观测统计Table 2. Statistical table of Haitou spring flow observations时间 泉流量/(m3·s-1) 时间 泉流量/(m3·s-1) 1949年以前 0.137 1975年 0.163 1949年 0.154 1976年 0.157 1950年 0.154 1978年 0.116 1951年 0.154 1986年 0.155 1960年 0.168 八十年代 0.120 1961年 0.170 1997-2001年 0.049 1968年 0.158 2002年1月 0.049 1974年 0.154 2002年3月20日泉、自流井
全部断流2.2 区域地下水位下降
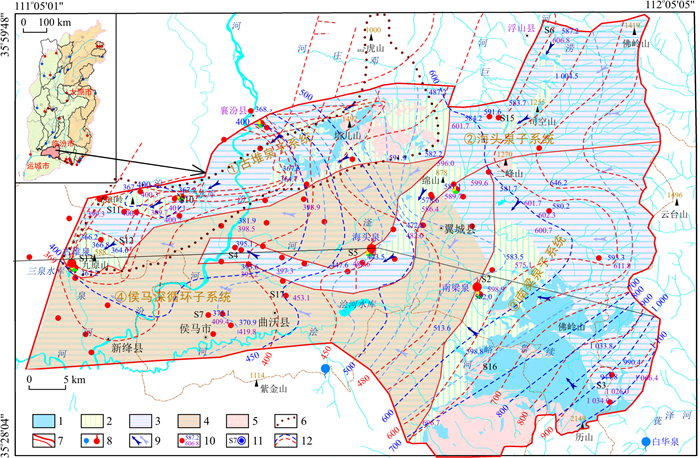
地下水动态规律的研究,是合理有效地对地下水资源进行管理和保护的前提与基础[14];地下水流场形态的研究,是从水动力学角度划分和研究地下水循环结构单元的有效途径[15],二者均可为实现水资源可持续开发利用及制定相应的用水管水方针政策提供重要理论依据。为掌握区域地下水流动特征及水位变化情况,2013年山西省水文水资源勘测局在古堆—南梁泉域内开展了45个点次的岩溶水位统测工作,2021年受山西省水利发展中心委托,中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所又在泉域内开展了40个点次的地下水位统测,并绘制了岩溶水流场,如图 3所示。本研究选取两期统测工作中位置相同的21个统测点及泉域内地理位置具代表性意义的6个长系列观测孔的水位资料来分析区域地下水位变化情况。
 图 3 古堆泉域地下水流场与取样点位置图1.碳酸盐岩裸露区;2.碳酸盐岩覆盖区;3.碳酸盐岩浅埋藏区;4.碳酸盐岩深埋藏区;5.非碳酸盐岩区;6.早期泉域边界;7.新泉域边界(下部细线为子系统边界);8.岩溶泉水(蓝色为出流下降泉,红色为断流上升泉);9.地下水流向(左侧为浅循环流向,右侧为深循环流向);10.地下水位统测点及水位(上部深蓝色为2021年水位标高,下部浅蓝色为2013年水位标高, 单位m);11.水质取样点及编号;12.岩溶水等水位线(红色表示2021年等水位线,蓝色表示2013年等水位线)Figure 3. Groundwater flow field and sampling point locations in the Gudui spring basin
图 3 古堆泉域地下水流场与取样点位置图1.碳酸盐岩裸露区;2.碳酸盐岩覆盖区;3.碳酸盐岩浅埋藏区;4.碳酸盐岩深埋藏区;5.非碳酸盐岩区;6.早期泉域边界;7.新泉域边界(下部细线为子系统边界);8.岩溶泉水(蓝色为出流下降泉,红色为断流上升泉);9.地下水流向(左侧为浅循环流向,右侧为深循环流向);10.地下水位统测点及水位(上部深蓝色为2021年水位标高,下部浅蓝色为2013年水位标高, 单位m);11.水质取样点及编号;12.岩溶水等水位线(红色表示2021年等水位线,蓝色表示2013年等水位线)Figure 3. Groundwater flow field and sampling point locations in the Gudui spring basin统计结果表明(表 3,4),21个相同统测点中,2013年水位标高最低值为393.17 m,最高值为1 026.04 m,平均520.87 m,对应的2021年水位标高最低值为364.6 m,最高值为944.8 m,平均500.66 m,8年内区域地下水位累计下降达20.21 m,年平均下降速度为2.53 m/a,区域地下水位下降已成为不争的事实。4个子系统中,除海头泉子系统(编号②)水位年均下降速度为1.81 m/a外,古堆泉子系统(编号①)、南梁泉子系统(编号③)及侯马深循环子系统(编号④)平均水位下降速度分别为3.93,3.26,3.55 m/a,出现此差异性下降的原因,应与各子系统内水资源要素构成、碳酸盐岩分布埋藏条件、人类开采活动及各子系统间的水力联系等多种因素有关。
表 3 两期水位统测统计对比分析Table 3. Statistical comparative analysis of water level measurements for the two periods地下水位/m 统计结果 2013年 2021年 水位变差 最小值 393.17 364.60 28.57 最大值 1 026.04 944.80 81.24 平均 520.87 500.66 20.21 表 4 各子系统内两期水位变差统计Table 4. Statistics on the variation of groundwater levels between the two periods with each subsystem子系统名称 统测点数 2013年平均水位/m 2021年平均水位/m 水位变差/m 下降速度/(m·a-1) 古堆泉 5 399.43 367.98 31.45 3.93 海头泉 7 534.63 520.14 14.49 1.81 南梁泉 5 682.83 656.76 26.07 3.26 侯马深循环 4 455.94 427.53 28.41 3.55 古堆泉子系统内西部汾阳岭-九原山一带为农业井灌区,东部塔儿山一带为铁矿区,农业灌溉与铁矿排水成为子系统内的用水大户,据初步统计2019年子系统内农业灌溉开采量为1 142.2万m3,铁矿排水量为280.2万m3,合计取水量为1 422.4万m3/a,已经接近该子系统天然补给量的2倍之多,开采量过大而补给量不足成为古堆泉子系统水位快速下降的直接原因。
海头泉子系统岩溶水在佛岭山山前和丹山-绵山隆起的碳酸盐岩裸露区及覆盖区接受降水入渗补给,并主要由佛岭山山前北东向断裂、高显-史村隆起、丹山-绵山隆起区导水,将东部地区岩溶地下水向西部地区输送,其地下水位主要受中部水源地开采、铁矿排水及西部侯马深循环水位变化3方面因素的影响。调查发现,近年来该子系统中部地区开采量及铁矿排水量明显减少,如酒钢水源地于2013年关停、海头泉泉口附近铁矿排水口已经关闭(2014年偶测排水量0.271 5 m3/s),这些成为海头泉子系统水位下降幅度相对较小的原因。由地下水流场变化情况可以看出,高显-史村一线(图 3中S4至S5一带)岩溶水流场由汇聚状转变为发散的分水岭状,这应是侯马深循环子系统与海头泉子系统差异性水位下降速度引起的区域地下水流场形态改变的原因。
南梁泉子系统岩溶地下水主要补给来源包括大气降水在碳酸盐岩裸露区的直接入渗补给、续鲁峪河在碳酸盐岩裸露河段的渗漏补给及碳酸盐岩浅埋藏区和覆盖区上层水的越流补给,其天然补给资源量更是占到整个泉域的61%以上,且南梁泉子系统岩溶地下水位在4个子系统中最高(表 4),因此在古堆—南梁泉域内起到了“天然水塔”的作用。天然条件下岩溶地下水向西径流过程中在南梁村附近受翼城凹陷内第四系松散沉积物的阻水作用,部分岩溶地下水出流形成南梁泉,未出流的岩溶地下水一部分补给松散岩类孔隙水,另一部分则进入侯马深循环子系统继续向西径流[4]。现状条件下,南梁泉水断流,子系统内本身的开采量很小,据国家地下水监测工程数据分析,近年来翼城凹陷内孔隙水水位下降幅度远小于岩溶水,因此侯马深循环子系统水位成为制约南梁泉子系统水位变化的关键因素。
侯马深循环子系统内无碳酸盐岩裸露,地下水主要接受海头泉子系统、南梁泉子系统的侧向径流补给,在九原山一带排泄至古堆泉子系统,碳酸盐岩埋藏深度大(图 1)、富水性差、多岩溶热水是其主要的特征,区内岩溶热水井的开采是其水位快速下降的主要原因。
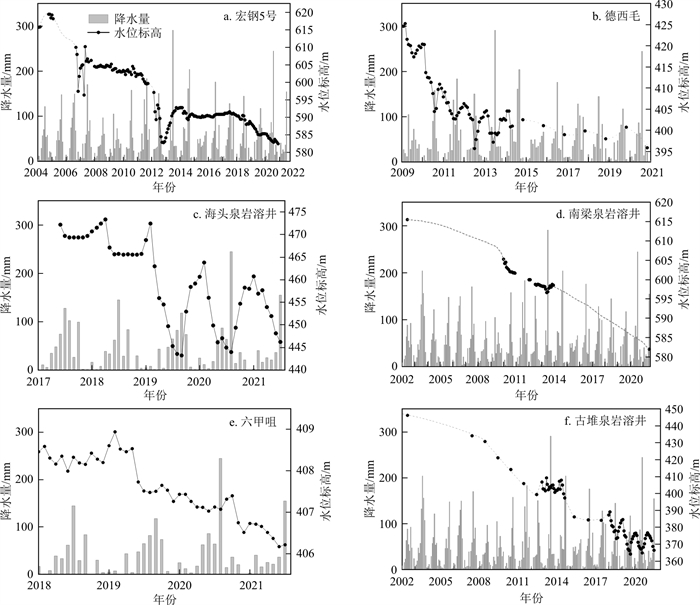
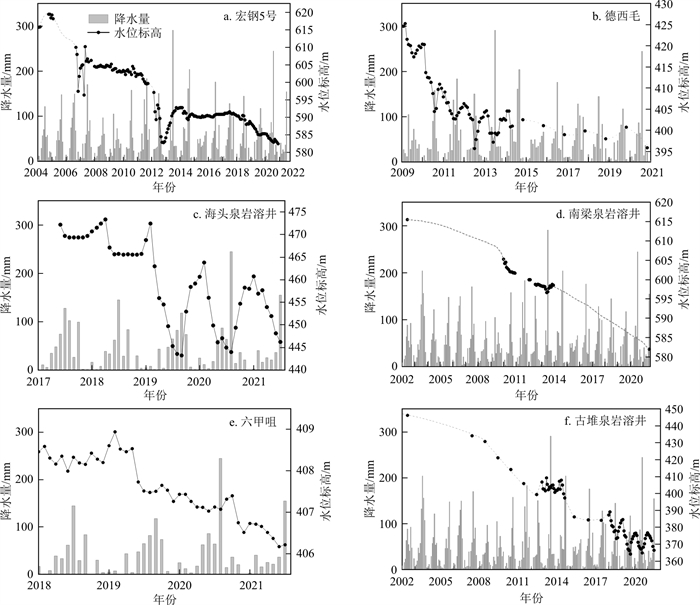
古堆泉水断流前,泉域内几乎无长系列岩溶水位动态监测资料,本研究收集到泉域内自2002年以来系列长度不等、观测精度不一的地下水位动态资料6个(位置见图 1),控制了3个浅循环子系统的排泄区及人工开采量较大的区域,各观测孔地下水位动态特征曲线如图 4所示。
由地下水位动态曲线(图 4)可知,自2002年以来,区内各观测孔水位变化趋势基本一致,均呈波动性下降态势,但从观测系列较长的宏钢5号(图 4-a)、德西毛(图 4-b)、古堆泉(图 4-f)3个观测孔水位变化过程可以看出,在采取关井压采、关停大水矿井、水源置换等一系列措施后,大致以2013、2014年为界,区域地下水位下降速度明显减缓。同时注意到南梁泉水位下降速度迟迟未迎来减缓的转折点(图 4-d),可能是因为南梁泉水位总体较高,西部地区各子系统水位下降速度虽有减缓,但总体水位仍处于较低状态,尚未对南梁泉子系统形成有效的壅水而促使其水位降幅减缓。
2.3 岩溶水流动特征改变
2013年进行地下水位统测时,泉水已断流多年,区内岩溶地下水经持续大规模开采,地下水流场已是不少地区水位出现趋势性下降后的状态,例如古堆泉口一带的水位下降幅度达45 m左右,显然与自然条件比较已发生了巨大的变化。但从流场的整体形态上看,还能体现岩溶水径流的基本概貌,地下水位下降主要发生在大规模开采的盆地内,虽局部地区的开采型漏斗已形成,但总体上水位的下降具有近于等幅和同步性(图 3)。反观2021年流场,其整体形态基本保持了原有的从东、南、北向泉域西部最终排泄区古堆泉方向径流的宏观趋势,但区域地下水位下降已经十分明显,这与前述两期统测点水位对比结果相吻合,同时根据流场局部形态还可看出以下几点较为明显的变化:
(1) 原本为天然排泄基准的古堆泉泉口因开采量大幅压缩以及三泉水库渗漏补给影响,泉口水位(2021年7月为367.8 m)高出周边1.0 m以上,沿柴庄隆起(曲沃蒙城-襄汾汾道沟一带)—汾阳岭—九原山(襄汾赵康一带)岩溶地下水强开采区形成区域性开采型降落漏斗,据2021年统测结果,该区内水位标高低于365 m的点有2处,分别是曲沃里村镇石滩汽车站附近岩溶井和襄汾县赵康镇窑儿上村井,表明排泄区岩溶地下水具有向隆起中部汇集的趋势。
(2) 塔儿山-二峰山由于火成岩大量侵入,岩溶含水层总体导水性较差,受南部翼城县、北部浮山县地下水开采影响,这一带形成了向南、北分流的地下水分水岭(由8个水位统测点控制)。
(3) 侯马深循环子系统是岩溶地下水弱富水区,补给条件差,高显-史村隆起南北两侧碳酸盐岩埋深均在1 000 m以上(图 1),含水层导水性差,导致开采条件下侯马深循环子系统无法从高显-史村隆起获得足够的补给,长期的岩溶热水开采已形成影响区域岩溶地下水流场形态的降落漏斗,特别是在侯马市区东部8年内水位下降幅度已达50 m以上,不同步的水位下降速度使高显-史村隆起的等水位线演变为向南、北侯马盆地深循环子系统分流的地下水分水岭。
(4) 2013年的岩溶地下水流场在翼城桥上村-中卫村一带沿瞿家桥河存在一个近东西向并向南梁泉方向渗流的低位槽谷,从水文地质条件上初步分析这一槽谷的形成,是由于自南部碳酸盐岩裸露区接受降水入渗补给的岩溶地下水顺地层倾向向北西渗流汇集,至瞿家桥河向北因岩溶含水层埋深加大,受上覆隔水顶板阻挡而折向西渗流,在地下水面与隔水顶板交界地带具有相对较大的水流通量,长期溶蚀作用可形成导水能力相对较强的径流带,在流场形态上表现出槽谷的特征。类似的状况在我国北方其他不少地区也有出现,如娘子关泉域内的昔阳-阳泉岩溶地下水强径流带[16]、太原西边山碳酸盐岩浅埋区的王封-赤桥岩溶地下水强径流带[17]等。2021年的地下水流场中这一槽谷更加显著,区域水位的大幅下降更加突出地显示了岩溶含水层的岩溶发育程度和导水性能的差异。
2.4 排泄区孔隙水、地表水倒灌补给岩溶水
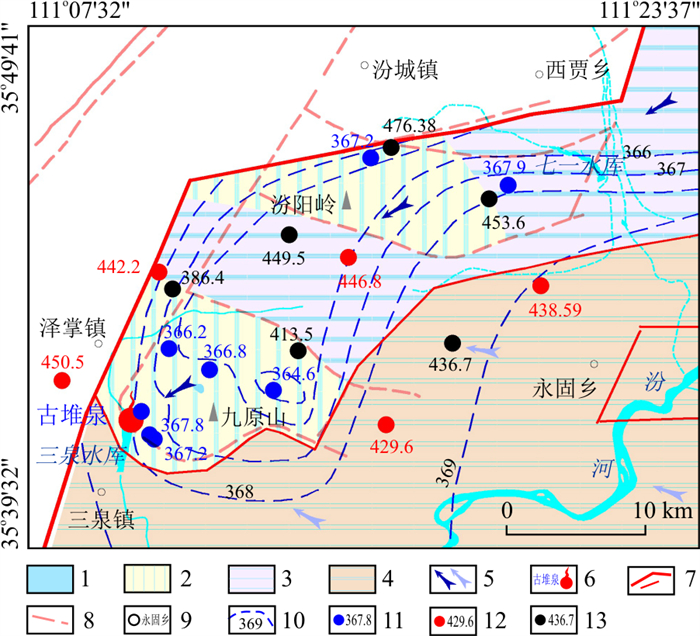
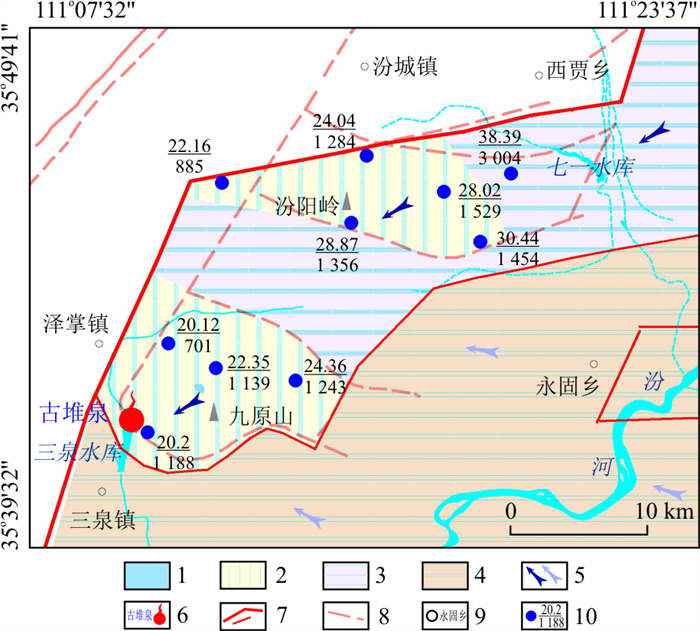
天然条件下,泉域内碳酸盐岩覆盖区周边地带的多数地段孔隙水位高于岩溶地下水,基于水文地质条件认为存在孔隙水对岩溶水的越流补给,但由于水位相差不大,如20世纪80年代排泄区九原山一带自东向西孔隙水位标高为440~460 m,周边岩溶水位标高也在440 m以上,因此这部分越流水量可被忽略。而近年来,城市的发展促进了人口的集中和工农业走向规模化,其正面效应是带来了财富的积累和社会的进步,但其负面效应也不可忽视[18],当地居民为追求经济发展,长期持续大规模开采岩溶地下水,造成古堆泉域内区域岩溶地下水位大幅下降,孔隙水位下降幅度却远小于岩溶水,两者的水位出现数十到百余米的水头差(图 5),因此越流量会大大增加。
 图 5 排泄区岩溶水位与孔隙水位对比图1.碳酸盐岩裸露区;2.碳酸盐岩覆盖区;3.碳酸盐岩浅埋藏区;4.碳酸盐岩深埋藏区;5.地下水流向(右侧为浅循环流向,左侧为深循环流向);6.断流泉水位置及名称;7.泉域边界(下部细线为子系统边界);8.断层;9.乡镇位置及名称;10.等水位线与水位标高(m);11.岩溶水孔位及水位标高(m);12.浅层孔隙水孔位及水位标高(m);13.中深层孔隙水孔位及水位标高(m)Figure 5. Comparison of the karst groundwater level and pore groundwater level in the discharge area
图 5 排泄区岩溶水位与孔隙水位对比图1.碳酸盐岩裸露区;2.碳酸盐岩覆盖区;3.碳酸盐岩浅埋藏区;4.碳酸盐岩深埋藏区;5.地下水流向(右侧为浅循环流向,左侧为深循环流向);6.断流泉水位置及名称;7.泉域边界(下部细线为子系统边界);8.断层;9.乡镇位置及名称;10.等水位线与水位标高(m);11.岩溶水孔位及水位标高(m);12.浅层孔隙水孔位及水位标高(m);13.中深层孔隙水孔位及水位标高(m)Figure 5. Comparison of the karst groundwater level and pore groundwater level in the discharge area汾阳岭-九原山一带的岩溶水水化学特征也指示了现状条件下孔隙水回灌补给岩溶水的现象。如图 6所示,天然条件下岩溶水由汾阳岭向九原山地区径流排泄,随着径流路径的延长,与围岩有更长的接触时间,地下水中溶滤的各项组分浓度将有所增加[19-20],同时此路径上还接受来自侯马深循环岩溶热水的混合作用,因此在九原山附近排泄区岩溶水的电导率与水温应较汾阳岭一带偏高,而现状条件却出现了与此相反的现象,说明汾阳岭-九原山一带孔隙水对岩溶水的越流补给量已不可忽略。
关于排泄区九原山附近岩溶水的电导率、温度较汾阳岭地区低(图 6)的原因,笔者认为除孔隙水越流补给外,三泉水库渗漏补给岩溶水也是重要的影响因素之一。三泉水库建于1956年,紧邻古堆泉排泄区,本为蓄积古堆泉水供给下游农业灌溉区使用,1999年泉水断流后三泉水库也随之干涸。2009年山西省兴建了禹门口提水东扩工程,三泉水库成为该工程的调蓄库。2012年9月,禹门口提水东扩工程试通水,三泉水库蓄水水位至443.5~444 m时,出现大量渗漏,山西省有关部门于2015年对库尾进行了防渗处理[21],但从水化学、同位素分析结果看其渗漏量仍是近年来泉口水位下降速度减缓的重要原因之一。
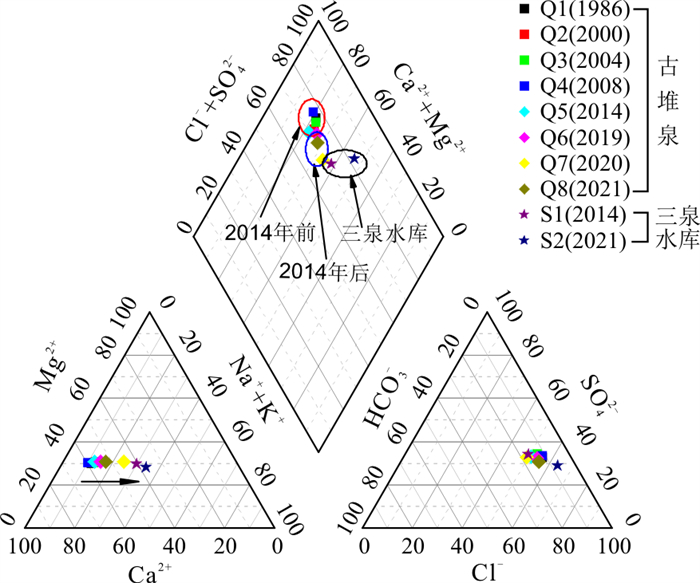
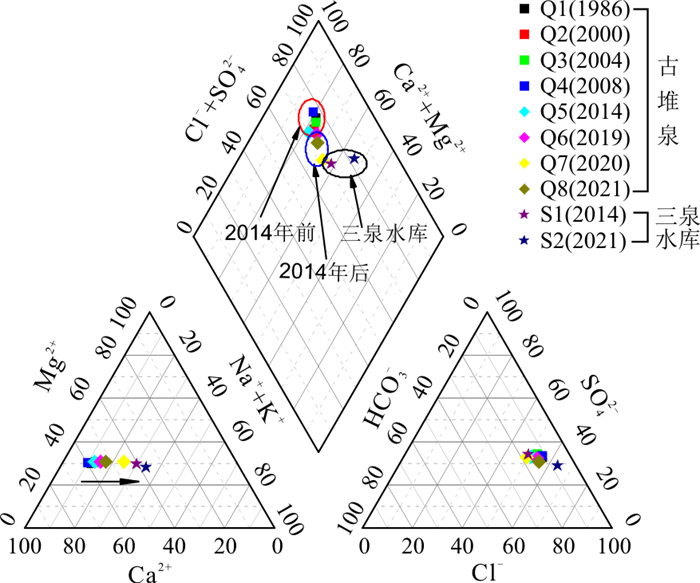
如表 5、图 7所示受三泉水库渗漏补给影响,古堆泉口岩溶水水化学组分浓度与同位素值均发生了较大变化,大致以2014年为界可将古堆泉口水质资料分为2个系列,可以看出在所列的11项水化学、同位素指标中除ρ(HCO3-)和ρ(F-)外(可能与上覆松散层孔隙水对岩溶地下水的反向补给有关),后一系列(2014年及以后)泉口岩溶地下水的其余9项指标均向三泉水库水样的浓度值靠拢,明显地受到了三泉水库渗漏补给的影响。
表 5 古堆泉、三泉水库多年水化学、同位素特征对比Table 5. Comparison of hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of Gudui spring and Sanquan Reservoir over the years取样位置 取样
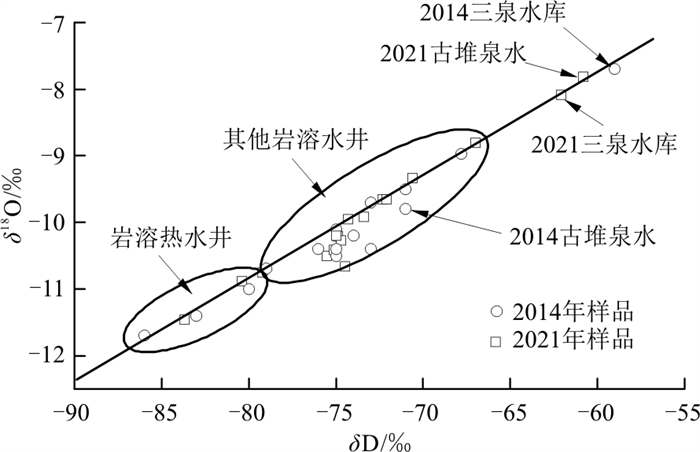
年份pH 温度/℃ Ca2+ SO42- HCO3- HB TDS NO3- F- δD/‰ δ18O/‰ ρB/(mg·L-1) 古堆泉 1986 7.44 22.50 109.82 270.53 256.28 437.55 790.27 4.00 2.00 -76.00 -10.30 古堆泉 2000 7.66 22.50 102.20 266.57 268.82 430.21 777.38 8.00 1.44 未采样 未采样 古堆泉 2004 8.03 22.50 105.20 290.60 238.00 430.08 787.00 2.50 1.30 未采样 未采样 古堆泉 2008 6.88 21.70 114.52 308.26 256.38 457.72 819.90 2.54 2.00 未采样 未采样 古堆泉 2014 7.96 23.80 101.00 239.00 282.00 417.50 747.00 8.92 0.93 -71.00 -9.80 古堆泉 2019 7.53 21.85 92.00 218.63 261.32 385.00 688.00 7.34 0.75 -63.80 -8.50 古堆泉 2020 8.06 21.64 63.26 154.52 208.53 275.32 528.00 6.18 0.60 -58.20 -7.64 古堆泉 2021 7.68 20.20 85.50 175.36 307.99 364.00 696.00 7.20 0.96 -60.80 -7.81 三泉水库 2014 7.49 30.10 51.90 149.00 168.00 230.00 500.00 0.79 0.35 -59.00 -7.70 三泉水库 2021 7.74 30.40 49.97 167.00 203.94 263.86 658.00 1.17 0.32 -62.10 -8.08 注:表中1986、2000、2004年数据详见参考文献[9],2008年数据详见参考文献[4],2014年及以后数据为笔者及团队实测。水化学组分由PHS-3CpH计、可见光光度计和离子色谱仪等测定。氢氧同位素利用稳定同位素质谱仪MAT253测定,氢同位素采用Pt水平衡法测定,氧同位素采用CO2-H2O水平衡法测定,以上均由国土资源部岩溶地质资源环境监督检测中心测试。HB.总硬度; TDS.溶解性总固体 氘氧同位素可以有效地指示水体的补给来源[22]。2014年古堆泉水的氘氧同位素值位于岩溶水井样品值的中部,表明泉域岩溶水向排泄区汇集混合,虽然也存在三泉水库的补给,但在泉域岩溶水流场中泉口水位仍然是泉域最低排泄点(图 3),接受泉域岩溶水的补给;至2021年,泉口多数开采井关闭,受其他地区岩溶水开采和三泉水库渗漏补给的影响,泉域内岩溶地下水位最低点出现在汾阳岭一带,泉口岩溶水形成了向泉域内倒流的态势(图 3),古堆泉口附近岩溶水所获补给量中,三泉水库渗漏量所占比例有所增加,使得在δD-δ18O关系图中泉口水样分布在与三泉水库水样非常接近的位置(图 8)。
2.5 岩溶水水质退化
笔者及团队分别于2014年8月、2021年7月在古堆—南梁泉域内开展了两期水化学样品采集工作,选择其中位置相同的16组岩溶地下水样品测试结果进行了对比分析,结果表明(表 6):与2014年相比,13项指标中除pH值有所减小外(与孔隙水、三泉水库水补给有关),其余各项指标质量浓度均有不同程度的增大。ρ(F-)增大19.06%,表明岩溶水明显受到孔隙水回灌补给影响;ρ(Sr2+)增大37.94%,表明岩溶地下水径流时间延长,地下水溶滤岩石的时间有所延长,这是区域地下水位下降引起水力坡度下降的水化学特征表现;ρ(NO3-)增加近一倍(90.86%),虽与2014年泉域ρ(NO3-)本身较低有一定关系,但泉域内续鲁峪、九原山、汾阳岭、南梁泉附近、海头泉附近等碳酸盐岩浅覆盖区均有农田分布,地下水中ρ(NO3-)主要与人类活动特别是农业氮肥的使用等有关,表明人类活动已经对泉域岩溶地下水水质产生了明显影响[23-24]。
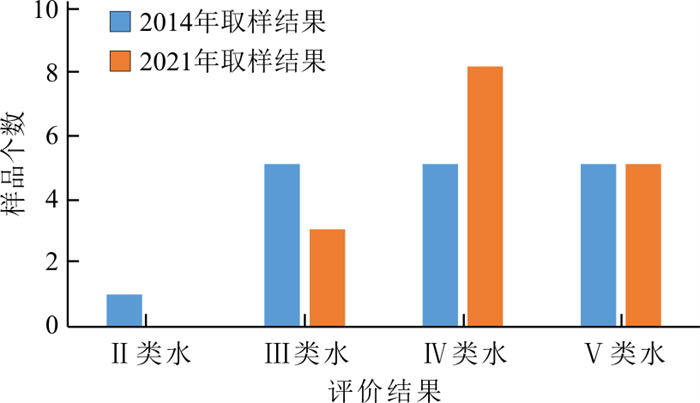
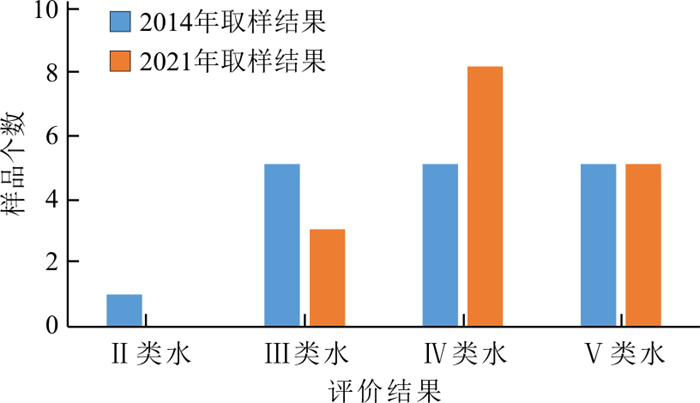
表 6 古堆泉域岩溶水两期水化学质量浓度对比统计Table 6. Comparative statistics of water chemistry of karst groundwater in the Gudui spring basin between the two periods取样时间 项目 pH K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ SO42- Cl- ρB/(mg·L-1) 2014年 最小值 7.49 0.80 8.15 37.70 15.30 21.10 7.66 最大值 8.23 13.00 479.00 152.00 58.60 868.00 488.00 平均 7.83 5.31 108.32 97.05 34.57 279.62 91.62 2021年 最小值 7.48 1.13 4.29 49.97 17.54 31.36 5.89 最大值 8.03 22.33 454.09 148.40 82.99 703.39 606.55 平均 7.68 5.80 125.52 97.27 38.34 300.60 92.29 单项指标变化率 -1.92% +9.19% +15.88% +0.23% +10.92% +7.51% +0.73% 取样时间 项目 HCO3- HB TDS NO3- F- Sr2+ ρB/(mg·L-1) 2014年 最小值 168.00 171.00 298.00 0.00 0.20 0.22 最大值 298.00 622.00 2265.00 8.92 2.58 3.14 平均 257.12 384.65 786.76 3.58 1.07 1.24 2021年 最小值 203.94 247.06 278.00 0.05 0.09 0.17 最大值 472.39 619.42 1854.00 25.53 2.62 4.30 平均 281.42 402.93 828.47 6.83 1.28 1.72 单项指标变化率 +9.45% +4.75% +5.30% +90.86% +19.06% +37.94% 注:水化学组分由PHS-3CpH计、可见光光度计和离子色谱仪等测定,由国土资源部岩溶地质资源环境监督检测中心测试 根据两期水化学分析项目情况(2014年样品分析项目较少),并结合研究区水环境问题的实际,选取pH值、总硬度(HB,以CaCO3计)、溶解性总固体(TDS)、SO42-、Cl-、TFe、Na+、NO3-(以N计)8项作为评价指标进行水质评价,结果表明(图 9):16个岩溶水样品中2014年Ⅱ类水有1个,Ⅲ类水、Ⅳ类水、Ⅴ类水各有5个,超Ⅲ类水标准的水样占62.5%;2021年评价结果中无Ⅱ类水,Ⅲ类水有3个,Ⅳ类水增加为8个,Ⅴ类水仍为5个,超Ⅲ类水标准的水样占比已达81.25%,说明泉域岩溶水水质退化的现象已经十分明显。
3. 泉源区保护措施
随着岩溶地下水保护和超采区治理工作的推进,学者们针对我国北方岩溶泉域水资源优化配置、泉水复流等方面已经开展了一定程度的研究[25-27],但针对泉源保护区的生态修复与规划研究相对较少。笔者从先分类分区、再分级保护的思路出发,提出了古堆泉源区生态保护与规划方案。
3.1 泉源保护区划分
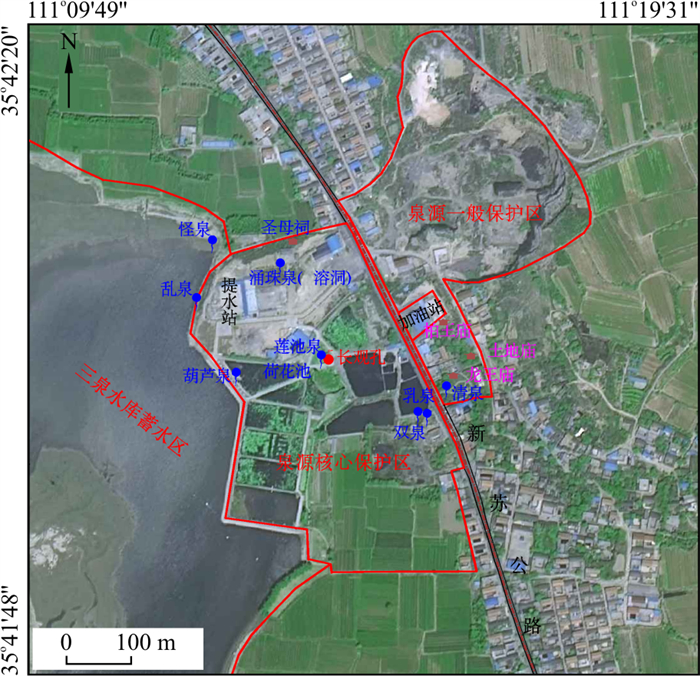
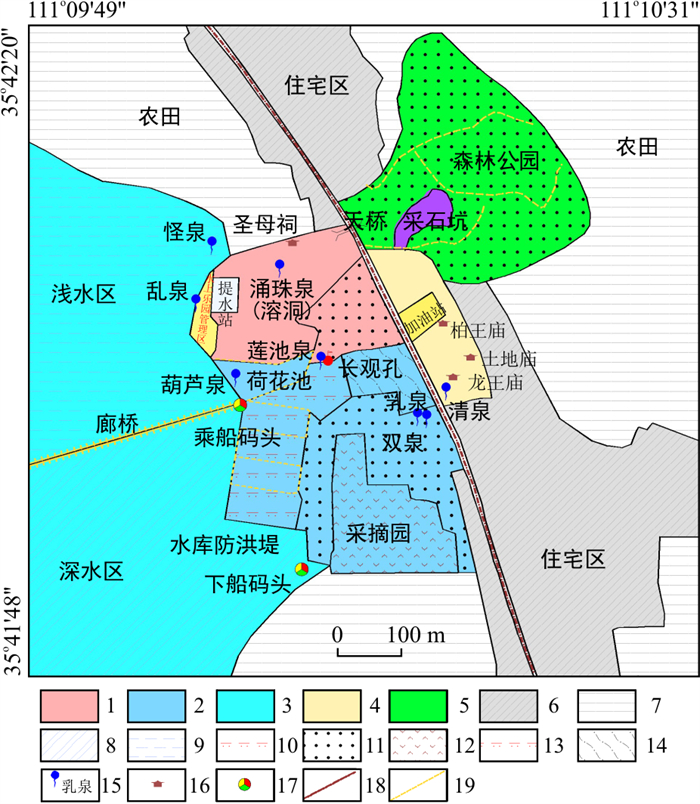
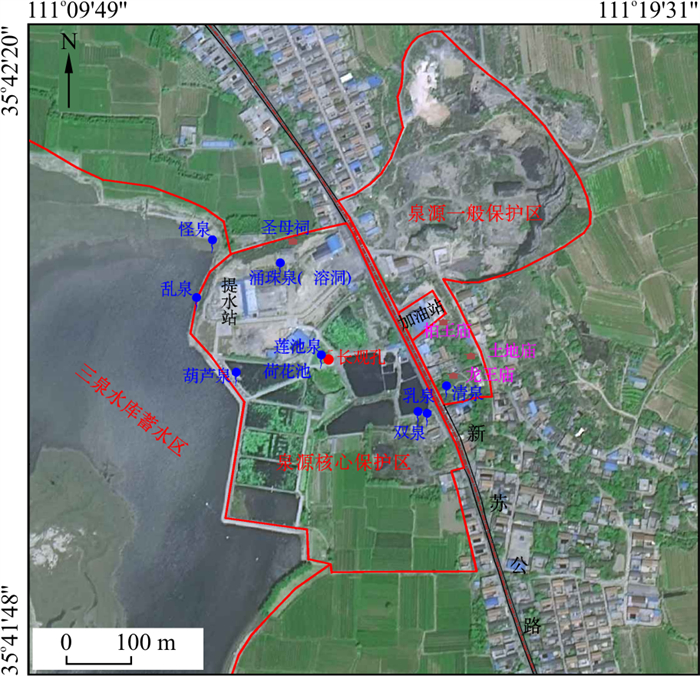
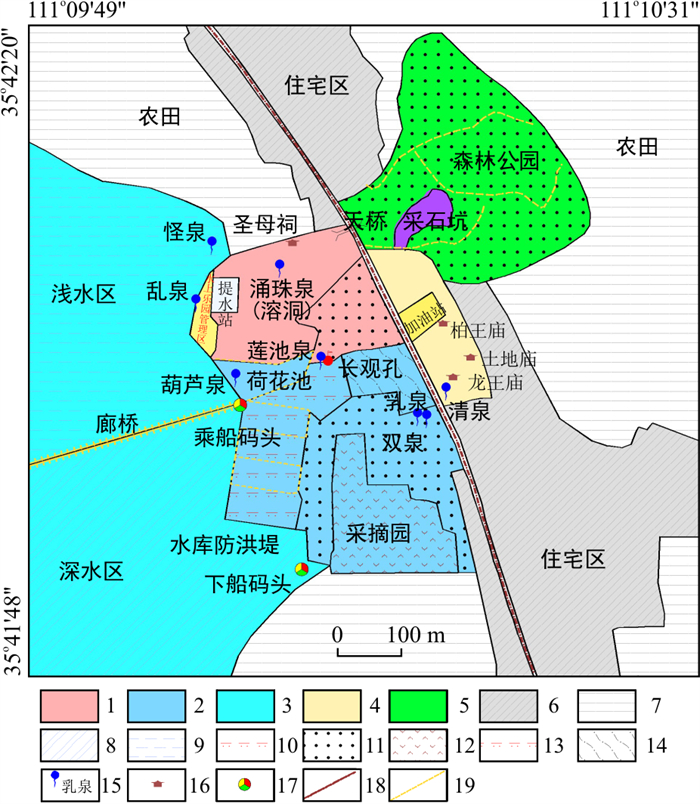
泉源保护区(泉水排泄区)的保护内容除泉水水量(保护水位)、水质外,自然景观与环境的保护也是其重要内容,根据相对位置及地物、地貌特征,将古堆泉源区划分为3类保护区,分别是:核心保护区、一般保护区、水库蓄水区(图 10),总面积0.904 km2。
核心保护区是古堆泉水集中排泄区,其北界从新苏公路沿圣母祠北侧小道向西至水库,西界从怪泉一带沿水库东岸向东偏南至防洪堤坝结束端,南界从防洪堤坝末端沿小路向东至古堆村居民民房北折转到乳泉一带,此后东界沿新苏公路西侧至圣母祠后小路,其中扣除了新绛提水管理站范围,所构成的面积为0.184 km2。新苏公路东侧包括九原山(西端)及南侧到龙王庙为一般保护区,西界为新苏公路,北及北东以九原山东端小路为界,东南界为龙王庙东侧小路至九原山山前,扣除其中加油站后,面积为0.131 km2。三泉水库库尾暂定为水库蓄水区,图面确定的面积为0.589 km2。
3.2 泉源区生态修复规划
泉源区(泉水排泄区)的生态修复应充分利用古堆泉排泄区的自然、人文条件,深挖旅游资源,实现以开发旅游资源为重点的泉源保护区生态修复。可将泉源保护区划分为旅游服务区、泉水排泄区、三泉水库区、文物修复与商业开发区和九原山森林公园区5个功能区(图 11)。其具体生态修复规划内容包括:
(1) 整治泉源区基础旅游环境,提升旅游服务水平与泉源区环境面貌。具体包括以下3方面的规划内容:①对古堆村等原有建筑进行环境综合治理,特别沿新苏公路商铺需进行合理规划布局,适度培育与公共旅游相关的餐饮、住宿产业;②在圣母祠南侧修建旅游服务区,包括停车场、娱乐设施售票点、医疗服务站等,开展修复服务和管理;③改造泉源区内居民和养殖业排水系统,制定生活垃圾、生产垃圾的堆放和清运制度。
(2) 修建三泉水库游览基础设施,适度开发库区旅游资源。将三泉水库以廊桥为界分为南北2部分,北部浅水区作为水上乐园开发,建设包括游泳、非机动游船设施;南部深水区进行游船游览开发,建设2座供游人上下船的小型码头,开辟库区游船服务,可开辟折返距离近3 km的航路,同时可在三泉水库东岸建设一些水畔人文景点,开发水上旅游文化。
(3) 泉水集中排泄区景观规划与建设。泉水集中排泄区主要在公路西侧,规划与建设内容可包括3方面:①美化葫芦泉、莲池泉出水口,在泉水断流的情况下,可引三泉水库水进行循环流动,恢复“鼓泉涌动”生态景观;②泉水出水口附近种植特色观赏花卉,建设花卉植被长廊,供游人观赏休憩;③进一步改造原有水产养殖、种植,建造林荫小径,开发有偿垂钓、有偿采摘园项目,供游人休闲娱乐等。
(4) 修复泉源区原有文物建筑,弘扬古堆泉水文化。对泉源区龙王庙、土地庙、柏王庙等文物建筑进行修复,梳理古堆泉水开发、利用、保护等方面的历史记录,修复并梳理原有碑文,宣传古堆泉水气势恢宏、源远流长的动人传说,适度建设一些特产商业设施,健全旅游环境。
(5) 扩大九原山区绿植面积,修建旅游健身设施,逐步将其发展为森林公园区。对九原山区绿植进行改造,引种一些特殊季节的树种,供游人观赏,同时修建一些山间便道、健身设施供游人健身、旅游。
4. 结论
(1) 古堆-南梁泉域是一个深循环与浅循环共存、冷水系统与热水系统循环转化、多级次排泄的复合型岩溶水系统。因早期对泉域岩溶水文地质条件认识不足,泉域内泉水长期不合理的开发利用已使古堆泉、南梁泉、海头泉分别于1999年、1992年、2002年断流,人文景观不复存在。
(2) 与2013年相比,2021年泉域内区域地下水位下降达20.21 m,年平均下降2.53 m。区域水位的大幅下降更加突显了岩溶含水层的岩溶发育程度和导水性能的差异,同时受资源要素组成结构、水文地质条件、人类活动等多因素影响,各子系统水位下降幅度差异明显,使古堆—南梁泉域流场形态在柴庄隆起-汾阳岭-九原山一带、塔儿山-二峰山一带、高显-史村隆起区、翼城桥上村-中卫村一带4处地区存在明显的变化。
(3) 水化学、同位素分析结果表明,排泄区九原山附近松散岩类孔隙水越流补给量、三泉水库渗漏补给量对岩溶地下水的影响已不可忽略;水质评价结果表明,16个岩溶水样品中,超Ⅲ类水水质标准的样品占比由2014年的62.5%升高至2021年的81.25%,说明泉域岩溶水水质退化的现象已十分明显。
(4) 泉源区(泉水排泄区)可细分为核心保护区、一般保护区及水库蓄水区,总面积0.904 km2,生态修复措施应充分利用古堆泉排泄区自然、人文条件,深挖旅游资源,划分旅游服务区、泉水排泄区、三泉水库区、文物修复与商业开发区和九原山森林公园区5个功能区,分别实施不同的生态环境修复措施,实现以开发旅游资源为重点的泉源保护区生态修复。
(所有作者声明不存在利益冲突) -
图 1 古堆泉域水文地质略图
1.碳酸盐岩裸露区;2.碳酸盐岩覆盖区;3.碳酸盐岩浅埋藏区;4.碳酸盐岩深埋藏区;5.非碳酸盐岩区;6.早期泉域边界;7.新泉域边界(下部细线为子系统边界);8.控制性钻孔碳酸盐岩埋藏深度(m);9.岩溶泉水(蓝色为出流下降泉,红色为断流上升泉);10.地下水流向(左侧为浅循环流向,右侧为深循环流向);11.剖面线及起止点标注;12.长观孔位置及名称。Ar.新太古界; ∈.寒武系; O.奥陶系;C.石炭系;C-P.石炭系-二叠系;Q+N.第四系+新近系;Q.第四系; πδη.火成岩侵入体
Figure 1. Hydrogeological sketch of the Gudui spring basin
图 3 古堆泉域地下水流场与取样点位置图
1.碳酸盐岩裸露区;2.碳酸盐岩覆盖区;3.碳酸盐岩浅埋藏区;4.碳酸盐岩深埋藏区;5.非碳酸盐岩区;6.早期泉域边界;7.新泉域边界(下部细线为子系统边界);8.岩溶泉水(蓝色为出流下降泉,红色为断流上升泉);9.地下水流向(左侧为浅循环流向,右侧为深循环流向);10.地下水位统测点及水位(上部深蓝色为2021年水位标高,下部浅蓝色为2013年水位标高, 单位m);11.水质取样点及编号;12.岩溶水等水位线(红色表示2021年等水位线,蓝色表示2013年等水位线)
Figure 3. Groundwater flow field and sampling point locations in the Gudui spring basin
图 5 排泄区岩溶水位与孔隙水位对比图
1.碳酸盐岩裸露区;2.碳酸盐岩覆盖区;3.碳酸盐岩浅埋藏区;4.碳酸盐岩深埋藏区;5.地下水流向(右侧为浅循环流向,左侧为深循环流向);6.断流泉水位置及名称;7.泉域边界(下部细线为子系统边界);8.断层;9.乡镇位置及名称;10.等水位线与水位标高(m);11.岩溶水孔位及水位标高(m);12.浅层孔隙水孔位及水位标高(m);13.中深层孔隙水孔位及水位标高(m)
Figure 5. Comparison of the karst groundwater level and pore groundwater level in the discharge area
表 1 古堆泉水流量观测统计
Table 1. Statistical table of Gudui spring flow observations
观测时间(年) 1956以前 1964-1968 1974-1978 1979-1982 1983-1986 1987-1988 1989-1990 1991-1993 1999 泉流量/(m3·s-1) 1.3 1.2 0.9 0.715 0.618 0.495 0.715 0.532 断流 表 2 海头泉水流量观测统计
Table 2. Statistical table of Haitou spring flow observations
时间 泉流量/(m3·s-1) 时间 泉流量/(m3·s-1) 1949年以前 0.137 1975年 0.163 1949年 0.154 1976年 0.157 1950年 0.154 1978年 0.116 1951年 0.154 1986年 0.155 1960年 0.168 八十年代 0.120 1961年 0.170 1997-2001年 0.049 1968年 0.158 2002年1月 0.049 1974年 0.154 2002年3月20日泉、自流井
全部断流表 3 两期水位统测统计对比分析
Table 3. Statistical comparative analysis of water level measurements for the two periods
地下水位/m 统计结果 2013年 2021年 水位变差 最小值 393.17 364.60 28.57 最大值 1 026.04 944.80 81.24 平均 520.87 500.66 20.21 表 4 各子系统内两期水位变差统计
Table 4. Statistics on the variation of groundwater levels between the two periods with each subsystem
子系统名称 统测点数 2013年平均水位/m 2021年平均水位/m 水位变差/m 下降速度/(m·a-1) 古堆泉 5 399.43 367.98 31.45 3.93 海头泉 7 534.63 520.14 14.49 1.81 南梁泉 5 682.83 656.76 26.07 3.26 侯马深循环 4 455.94 427.53 28.41 3.55 表 5 古堆泉、三泉水库多年水化学、同位素特征对比
Table 5. Comparison of hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of Gudui spring and Sanquan Reservoir over the years
取样位置 取样
年份pH 温度/℃ Ca2+ SO42- HCO3- HB TDS NO3- F- δD/‰ δ18O/‰ ρB/(mg·L-1) 古堆泉 1986 7.44 22.50 109.82 270.53 256.28 437.55 790.27 4.00 2.00 -76.00 -10.30 古堆泉 2000 7.66 22.50 102.20 266.57 268.82 430.21 777.38 8.00 1.44 未采样 未采样 古堆泉 2004 8.03 22.50 105.20 290.60 238.00 430.08 787.00 2.50 1.30 未采样 未采样 古堆泉 2008 6.88 21.70 114.52 308.26 256.38 457.72 819.90 2.54 2.00 未采样 未采样 古堆泉 2014 7.96 23.80 101.00 239.00 282.00 417.50 747.00 8.92 0.93 -71.00 -9.80 古堆泉 2019 7.53 21.85 92.00 218.63 261.32 385.00 688.00 7.34 0.75 -63.80 -8.50 古堆泉 2020 8.06 21.64 63.26 154.52 208.53 275.32 528.00 6.18 0.60 -58.20 -7.64 古堆泉 2021 7.68 20.20 85.50 175.36 307.99 364.00 696.00 7.20 0.96 -60.80 -7.81 三泉水库 2014 7.49 30.10 51.90 149.00 168.00 230.00 500.00 0.79 0.35 -59.00 -7.70 三泉水库 2021 7.74 30.40 49.97 167.00 203.94 263.86 658.00 1.17 0.32 -62.10 -8.08 注:表中1986、2000、2004年数据详见参考文献[9],2008年数据详见参考文献[4],2014年及以后数据为笔者及团队实测。水化学组分由PHS-3CpH计、可见光光度计和离子色谱仪等测定。氢氧同位素利用稳定同位素质谱仪MAT253测定,氢同位素采用Pt水平衡法测定,氧同位素采用CO2-H2O水平衡法测定,以上均由国土资源部岩溶地质资源环境监督检测中心测试。HB.总硬度; TDS.溶解性总固体 表 6 古堆泉域岩溶水两期水化学质量浓度对比统计
Table 6. Comparative statistics of water chemistry of karst groundwater in the Gudui spring basin between the two periods
取样时间 项目 pH K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ SO42- Cl- ρB/(mg·L-1) 2014年 最小值 7.49 0.80 8.15 37.70 15.30 21.10 7.66 最大值 8.23 13.00 479.00 152.00 58.60 868.00 488.00 平均 7.83 5.31 108.32 97.05 34.57 279.62 91.62 2021年 最小值 7.48 1.13 4.29 49.97 17.54 31.36 5.89 最大值 8.03 22.33 454.09 148.40 82.99 703.39 606.55 平均 7.68 5.80 125.52 97.27 38.34 300.60 92.29 单项指标变化率 -1.92% +9.19% +15.88% +0.23% +10.92% +7.51% +0.73% 取样时间 项目 HCO3- HB TDS NO3- F- Sr2+ ρB/(mg·L-1) 2014年 最小值 168.00 171.00 298.00 0.00 0.20 0.22 最大值 298.00 622.00 2265.00 8.92 2.58 3.14 平均 257.12 384.65 786.76 3.58 1.07 1.24 2021年 最小值 203.94 247.06 278.00 0.05 0.09 0.17 最大值 472.39 619.42 1854.00 25.53 2.62 4.30 平均 281.42 402.93 828.47 6.83 1.28 1.72 单项指标变化率 +9.45% +4.75% +5.30% +90.86% +19.06% +37.94% 注:水化学组分由PHS-3CpH计、可见光光度计和离子色谱仪等测定,由国土资源部岩溶地质资源环境监督检测中心测试 -
[1] Liang Y P, Gao X B, Zhao C H, et al. Review characterization, evolution, and environmental issues of karst water systems in northern China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26: 1371-1385. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1792-4 [2] 胡子瑛, 周俊菊, 张利利, 等. 中国北方气候干湿变化及干旱演变特征[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(6): 1908-1919. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201806003.htmHu Z Y, Zhou J J, Zhang L L, et al. Climate dry-wet change and drought evolution characteristics of different dry-wet areas in northern China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(6): 1908-1919(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201806003.htm [3] 梁永平, 王维泰, 赵春红, 等. 中国北方岩溶水变化特征及其环境问题[J]. 中国岩溶, 2013, 32(1): 34-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201301008.htmLiang Y P, Wang W T, Zhao C H, et al. Variations of karst water and environmental problems in northern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2013, 32(1): 34-42 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201301008.htm [4] 申豪勇, 梁永平, 赵春红, 等. 古堆泉岩溶地下水系统特征及系统圈划[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2020, 50(1): 217-225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202001018.htmShen H Y, Liang Y P, Zhao C H, et al. Hydro-geological characteristics and demarcation of Gudui spring karst groundwater system[J]. Journal of Jinlin University: Earth Science Edition, 2020, 50(1): 217-225(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202001018.htm [5] 梁永平, 王维泰. 中国北方岩溶水系统划分与系统特征[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(6): 860-868. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201006017.htmLiang Y P, Wang W T. The division and characteristics of karst water systems in northern China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(6): 860-868(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201006017.htm [6] Deng X, Xing L T, Yu M, et al. Characteristics of the water cycle of Jinan karst spring in northern China[J]. Water Practice and Technology, 2022, 17: 1470-1489. doi: 10.2166/wpt.2022.075 [7] 申豪勇, 李佳, 王志恒, 等. 黄河支流汾河流域水资源开发利用现状及生态环境问题[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(4): 1127-1138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202204007.htmShen H Y, Li J, Wang Z H, et al. Water resources utilization and eco-environment problem of Fenhe River, branch of Yellow River[J]. Geology of China, 2022, 49(4): 1127-1138(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202204007.htm [8] 王宏, 邓安利, 茹哲敏. 山西省地下水超采区范围的复核划分[J]. 山西农业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 32(4): 373-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXNY201204018.htmWang H, Deng A L, Ru Z M. Re-examination and partition of underground water over-exploitation area in Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University: Nature Science Edition, 2012, 32(4): 373-378 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXNY201204018.htm [9] 山西省水利厅, 中国地质科学院岩溶地质研究所, 山西省水资源管理委员会. 山西省岩溶泉域水资源保护[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2007: 64-75.Department of Water Resources of Shanxi Province, Institute of Karst Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Shanxi Provincial Water Resources Management Committee. Water resources protection of karst spring area in Shanxi Province[M]. Beijing: China Water Resources and Hydropower Press, 2007: 64-75(in Chinese). [10] 谢浩, 梁永平, 申豪勇, 等. 汾河流域岩溶大泉的亘古亘今[J]. 中国矿业, 2019, 28(增刊1): 358-360. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2019S1095.htmXie H, Liang Y P, Shen H Y, et al. The ancient and present of karst springs in Fenhe River Basin[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2019, 28(S1): 358-360(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2019S1095.htm [11] 徐永新, 张志祥, 张永波, 等. 山西岩溶泉研究进展与前瞻[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2017, 48(3): 413-426. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYGY201703020.htmXu Y X, Zhang Z X, Zhang Y B, et al. Research advance in karst springs of Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2017, 48(3): 413-426(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYGY201703020.htm [12] 郭清海, 王焰新, 马腾, 等. 山西岩溶大泉近50年的流量变化过程及其对全球气候变化的指示意义[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2005, 35(2): 167-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200502007.htmGuo Q H, Wang Y X, Ma T, et al. The discharge variation process of karst springs in Shanxi Province in recent 50 years and its significance for global climate change[J]. Science in China: Earth Sciences, 2005, 35(2): 167-175(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200502007.htm [13] 郭振中, 张宏达, 于开宁. 山西岩溶大泉衰减的多因复成性[J]. 工程勘察, 2004(2): 22-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC200402006.htmGuo Z Z, Zhang H D, Yu K N. Multifactorial complexity of the attenuation of karst spring in Shanxi Province[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2004(2): 22-25(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC200402006.htm [14] 王志恒, 梁永平, 申豪勇, 等. 自然与人类活动叠加影响下晋祠泉域岩溶地下水动态特征[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2021, 51(6): 1823-1837. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202106017.htmWang Z H, Liang Y P, Shen H Y, et al. Dynamic characteristics analysis of karst groundwater in Jinci spring under the superimposed influence of natural and human activities[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2021, 51(6): 1823-1837 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202106017.htm [15] 万力, 王旭升, 蒋小伟. 地下水循环结构的动力学研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 19-29. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0003Wan L, Wang X S, Jiang X W. Advances in dynamics of groundwater circulation patterns[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 19-29(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0003 [16] 霍建光, 赵春红, 梁永平, 等. 娘子关泉域径流-排泄区岩溶水污染特征及成因分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(5): 147-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201505023.htmHuo J G, Zhao C H, Liang Y P, et al. Characteristic and cause analysis in the runoff-drainage area of Niangziguan spring[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(5): 147-152(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201505023.htm [17] 王志恒, 梁永平, 唐春雷, 等. 北方断流岩溶大泉复流的生态修复模式与复流措施效果的定量评价: 以山西太原晋祠泉为例[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1726-1738. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006011.htmWang Z H, Liang Y P, Tang C L, et al. Ecological restoration pattern and quantitative evaluation of recirculation measures for northern discontinuous karst spring: A case study on Jinci spring in Taiyuan City[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1726-1738(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006011.htm [18] 王攀, 靳孟贵, 路东臣, 等. 永城市浅层地下水污染分布特征及来源识别[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 260-268. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0136Wang P, Jin M G, Lu D C, et al. Distribution characteristics and source identification of shallow groundwater pollution in Yongcheng City[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 260-268(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0136 [19] 林若静, 孙从建, 陈伟, 等. 汾河下游河谷地区地下水水质特征分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(11): 135-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202111019.htmLin R J, Sun C J, Chen W, et al. Groundwater quality characteristics in downstream valley of Fenhe River[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2021, 35(11): 135-142(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202111019.htm [20] 赵春红, 申豪勇, 王志恒, 等. 汾河流域地表水水化学同位素特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(10): 4440-4448. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202210015.htmZhao C H, Shen H Y, Wang Z H, et al. Hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics in the surface water of the Fenhe River Basin and influence factors[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(10): 4440-4448. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202210015.htm [21] 李扭串. 三泉水库库区渗漏模式及渗漏强度问题研究[J]. 水利建设与管理, 2017, 37(8): 59-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLJS201708017.htmLi N C. Study on seepage pattern and intensity in Sanquan Reservoir area[J]. Water Conservancy Construction and Management, 2017, 37(8): 59-63(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLJS201708017.htm [22] 许秀丽, 李云良, 高博, 等. 黄河中游汾河入黄口湿地水源组成与地表地下水转化关系[J]. 湖泊科学, 2022, 34(1): 247-261. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX202201020.htmXu X L, Li Y L, Gao B, et al. Composition of water sources and transformation relationship between surface water and groundwater in the Fenhe River estuarine wetland of the middle Yellow River[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2022, 34(1): 247-261(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX202201020.htm [23] 李晓欣, 王仕琴, 陈肖如, 等. 北方区域尺度地下水-包气带硝酸盐分布与变化特征[J]. 中国生态农业学报: 中英文, 2021, 29(1): 208-216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN202101021.htmLi X X, Wang S Q, Chen X R, et al. Spatial distribution and changes of nitrate in the vadose zone and underground water in northern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(1): 208-216(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTN202101021.htm [24] 高旭波, 王万洲, 侯保俊, 等. 中国北方岩溶地下水污染分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(3): 287-298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202003001.htmGao X B, Wang W Z, Hou B J, et al. Analysis of karst groundwater pollution in northern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3): 287-298(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202003001.htm [25] Zhang Z X, Xu Y X, Wang Z L, et al. Ecological restoration and protection of Jinci spring in Shanxi, China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2020, 13: 744. [26] 梁永平, 申豪勇, 赵春红, 等. 对中国北方岩溶水研究方向的思考与实践[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(3): 363-380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202103001.htmLiang Y P, Shen H Y, Zhao C H, et al. Thinking and practice on the research direction of karst water in northern China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(3): 363-380(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202103001.htm [27] 王焰新. 我国北方岩溶泉域生态修复策略研究: 以晋祠泉为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2022, 41(3): 331-344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202203001.htmWang Y X. Study on ecological restoration strategy of karst spring region in North China: Taking Jinci spring as an example[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2022, 41(3): 331-344(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202203001.htm -





 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载: