Resolution capability of ground-based transient electromagnetic method for low-resistivity thin layer
-
摘要:
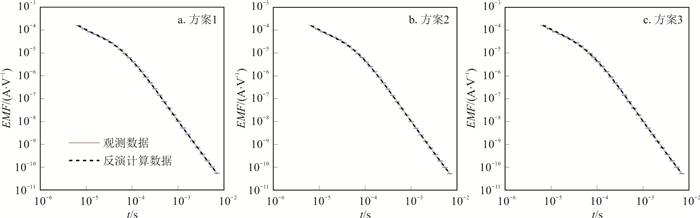
瞬变电磁法现阶段的资料处理解释仍以一维反演为主,因此分析瞬变电磁法对薄层的分辨能力对于更好地发挥瞬变电磁法优势仍具有重要意义。采用基于Occam算法的一维反演,以100 m深度内10 m层厚的低阻薄层为例,开展了地面回线源瞬变电磁法对低阻薄层分辨能力的定性和定量研究。数值结果表明:低阻薄层电阻率与背景电阻率差异越大,薄层反演电阻率和层厚越接近于真实值;反演电阻率极小值位置始终对应于薄层位置。低阻薄层电阻率与背景电阻率比值为1:5,1:10,1:20,背景电阻率小于100 Ω·m时,瞬变电磁法能够良好探测10 m薄层的最大埋深依次为40,50,80 m;背景电阻率为200 Ω·m时,上述3个最大埋深依次为30,30,60 m。上述研究成果有助于优化瞬变电磁法野外工作参数设计和提高资料处理解释精度。
Abstract:At present 1D inversion is commonly used for data processing and interpretation of transient electromagnetic (TEM) method. It is important to study the resolution-capability for the thin layer to take better advantage of ground-based loop-source TEM method. In this study, we employ 1D Occam's inversion method to qualitatively and quantitatively study the resolution capability for a thin layer. The thin layer has low resistivity, and its thickness is 10 m. The buried depth ranges from 10 to 100 m with 10 m intervals. The numerical modeling results show that the inverted resistivity and thickness will more coincide with the true values of the thin layer if the differences of resistivity between the thin layer and background medium increase. The depth of the inverted minimum resistivity agrees with the position of the low-resistivity thin layer. For background resistivity less than 100 Ω·m, the maximum depths are 40, 50 and 80 m for ratios of 1:5, 1:10 and 1:20 between the resistivities of the thin layer and the background medium, respectively. The maximum depth indicates the one within which the thin layer can be well detected by TEM methods. For the background resistivity of 200 Ω·m, the corresponding maximum depths are 30, 30 and 60 m. This study will help to optimize the field-work parameter designing and to improve the accuracy of data processing and interpretation.
-
-
[1] AUKEN E, CHRISTIANSEN A V, KIRKEGAARD C, et al. An overview of a highly versatile forward and stable inverse algorithm for airborne, ground-based and borehole electromagnetic and electric data[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 2015, 46(3): 223-235. doi: 10.1071/EG13097 [2] 殷长春, 刘云鹤, 熊彬. 地球物理三维电磁反演方法研究动态[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2020, 50(3): 432-435.YIN C C, LIU Y H, XIONG B. Status and prospect of 3D inversions in EM geophysics[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2020, 50(3): 432-435. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 薛国强, 邓湘. 瞬变电磁法对薄层的探测能力[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2007, 42(6): 709-713.XUE G Q, DENG X. Capacity of transient electromagnetic(TEM) method for detecting thin layer[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2007, 42(6): 709-713. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 王战军, 朱自强, 李建慧, 等. 瞬变电磁法对低阻薄层的分辨能力研究[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2012, 34(6): 646-651.WANG Z J, ZHU Z Q, LI J H, et al. Study on TEM's resolution capability for the thin layer of low resistivity[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 34(6): 646-651. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] 武军杰, 杨毅, 张杰, 等. TEM对于深部低阻层的分辨能力模拟分析[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2014, 36(5): 547-554.WU J J, YANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Resolution capability preliminary analysis of deep conductive layer with TEM method[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 36(5): 547-554. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 周楠楠, 薛国强, 李海. 回线源瞬变电磁水平分量对薄层的分辨能力[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2014, 29(5): 2347-2355.ZHOU N N, XUE G Q, LI H. Distinguishing ability to thin layer of loop-source TEM horizontal components[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2014, 29(5): 2347-2355. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] 陈卫营, 薛国强. 电性源瞬变电磁对薄层的探测能力[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(4): 775-779.CHEN W Y, XUE G Q. Detection capability of grounded electric source TEM for thin layer[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(4): 775-779. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 龙霞, 席振铢, 周胜, 等. 等值反磁通原理瞬变电磁法探测薄层能力[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(2): 753-759.LONG X, XI Z Z, ZHOU S, et al. Detection capability of opposing coils transient electromagnetic method for thin layers[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020, 35(2): 753-759. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 雷康信, 薛国强, 陈卫营, 等. 瞬变电磁法探测薄层的分辨能力与偏移距的关系[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2020, 42(6): 731-736.LEI K X, XUE G Q, CHEN W Y, et al. Relationship between the detection capability and offset of transient electromagnetic method for thin layers[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2020, 42(6): 731-736. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 王卫平, 吴成平, 于长春, 等. 频率域航空电磁法水资源探测深度及应用研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 191-197. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0221WANG W P, WU C P, YU C C, et al. Detecting depth of frequency domain airborne electromagnetic method for water resource investigation and its applications[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 191-197. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0221 [11] AUKEN E, CHRISTIANSEN A V, JACOBSEN L H, et al. A resolution study of buried valleys using laterally constrained inversion of TEM data[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2008, 65(1): 10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2008.03.003 [12] 殷长春, 邱长凯, 刘云鹤, 等. 时间域航空电磁数据加权横向约束反演[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2016, 46(1): 254-261.YIN C C, QIU C K, LIU Y H, et al. Weighted laterally-constrained inversion of time-domain airborne electromagnetic data[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2016, 46(1): 254-261. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 齐彦福, 殷长春, 王若, 等. 多通道瞬变电磁m序列全时正演模拟与反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(7): 2566-2577.QI Y F, YIN C C, WANG R, et al. Multi-transient EM full-time forward modeling and inversion of m-sequences[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(7): 2566-2577. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] LI Z, HUANG Q, XIE X, et al. A generic 1D forward modeling and inversion algorithm for TEM sounding with an arbitrary horizontal loop[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2016, 173(8): 2869-2883. doi: 10.1007/s00024-016-1336-6 [15] 孙怀凤, 张诺亚, 柳尚斌, 等. 基于L1范数的瞬变电磁非线性反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(12): 4860-4873.SUN H F, ZHANG N Y, LIU S B, et al. L1-norm based nonlinear inversion of transient electromagnetic data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(12): 4860-4873. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] LI J, LIU Y, YIN C, et al. Fast imaging of time-domain airborne EM data using deep learning technology[J]. Geophysics, 2020, 85(5): E163-E170. doi: 10.1190/geo2019-0015.1 [17] 邢涛, 袁伟, 李建慧. 回线源瞬变电磁法的一维Occam反演[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5): 1320-1328.XING T, YUAN W, LI J H. One-dimensional Occam's inversion for transient electromagnetic data excited by a loop source[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1320-1328. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] CONSTABLE S C, PARKER R L, CONSTABLE C G. Occam's inversion: A practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data[J]. Geophysics, 1987, 52(3): 289-300. doi: 10.1190/1.1442303 [19] 李建慧, 朱自强, 刘树才, 等. 基于Gaver-Stehfest算法的矩形发射回线激发的瞬变电磁场[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2011, 46(3): 489-492.LI J H, ZHU Z Q, LIU S C, et al. Rectangular loop transient electromagnetic field expressed by Gaver-Stehfest algorithm[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2011, 46(3): 489-492. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] LI J, FARQUHARSON C G, HU X. Three effective inverse Laplace transform algorithms for computing time-domain electromagnetic responses[J]. Geophysics, 2016, 81(2): E113-E128. doi: 10.1190/geo2015-0174.1 [21] ANDERSON W L. Fourier cosine and sine transforms using lagged convolutions in double-precision(subprograms DLAGF0/DLAGF1) Technical Report 83-320[R]. Denver: U.S. Geological Survey, 1983. [22] ASTEN M W. Full transmitter waveform transient electromagnetic modeling and inversion for soundings over coal measures[J]. Geophysics, 1987, 52(3), 279-288. doi: 10.1190/1.1442302 [23] ASTER R C, BORCHERS B, THURBER C H. Parameter estimation and inverse problems[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press, 2005. [24] 韩波, 胡祥云, 何展翔, 等. 大地电磁反演方法的数学分类[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2012, 47(1): 177-187.HAN B, HU X Y, HE Z X, et al. Mathematical classification of magnetotelluric inversion methods[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2012, 47(1): 177-187. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: