Characteristics of gravity flow sedimentation of Chang 63 in the Huaqing area, Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
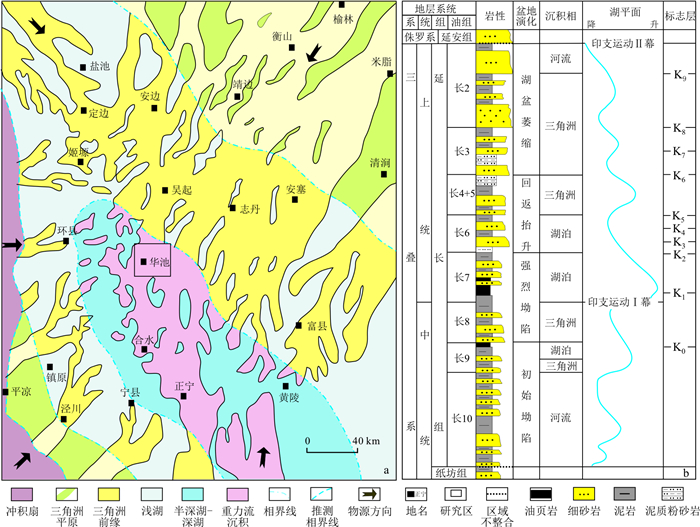
湖盆重力流沉积砂体是致密油勘探的有利目标区。综合利用岩心观察、分析化验及测录井资料, 对鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区长63砂层组重力流沉积类型、特征、主控因素及沉积模式展开了研究。研究表明: 华庆地区长63砂层组沉积粒度细, 粒度概率为上凸两段式, 跳跃和悬浮总体发育, 具有典型深水重力流沉积的层理构造; 华庆地区重力流沉积划分为滑塌沉积、碎屑流沉积和浊流沉积3种类型, 组成水道、朵叶及朵叶侧缘3种沉积微相。华庆地区长63深水重力流沉积发育主要受东北充足物源供给、足够湖盆水深、湖盆发育的深水坡折地形及延长期火山、地震等沉积事件影响, 不同相带重力流沉积类型、砂体厚度与内部结构表现出明显差异性。在靠近三角洲源区以水道为主, 由砂质碎屑流沉积和滑塌沉积组成, 砂体薄而分布局限; 中部沉积以朵叶为主, 主要是砂质碎屑流沉积夹浊流沉积, 沉积砂体垂向叠加, 厚层展布; 深湖区主要为朵叶侧缘, 以浊流沉积为主, 砂体呈薄互层分布。本研究不仅对湖盆重力流沉积认识有一定的补充作用, 同时为后期重力流砂体中油气勘探与开发提供了重要地质依据。
Abstract:Objective The gravity flow sedimentary sand body found in a lake basin is considered a promising target area for tight oil exploration.
Methods In this study, we investigated the characteristics, main controlling factors, and sedimentary model of the Chang 63 sand group in the Huaqing area of the Ordos Basin, through core observation, analysis, and logging data.
Results Our findings indicate that the sediments of the Chang 63 sand group in the Huaqing area have a fine grain size, with a probability of grain size distribution showing an upper convex two-stage type. The overall sedimentary structure is characterized by the development of jumping and suspension, typical of deep-water gravity flow deposits. We identified three types of gravity flow deposits in the Huaqing area: slump deposits, clastic flow deposits, and turbidity deposits. These deposits form three subfacies: channel, lobe, and lobe lateral. The development of deep-water gravity flow deposits in the Chang 63 area of the Huaqing area is primarily influenced by several factors. These include an abundant source supply in the Northeast, sufficient water depth in the lake basin, deep-water slope break topography in the lake basin, and volcanic and seismic sedimentary events of the Yanchang Formation. Notably, there are distinct differences in gravity flow deposition type, sand body thickness, and internal structure across different facies belts. In the vicinity of the delta source, the channel is mainly composed of slump deposits and some sandy debris flow deposits, with thin sand bodies and limited distribution. In the middle part of the sediment, the lobes consist mainly of sandy debris flow deposits, including some turbidity current deposits with vertically overlapping sedimentary sand bodies distributed as thick layers. In the deep lake area, the lateral margin of lobes is primarily composed of turbidity current deposits, with sand bodies distributed as thin interbeds.
Conclusion This study not only enhances our understanding of gravity flow sedimentation in lake basins but also provides a crucial geological foundation for future exploration and development of oil and gas resources in gravity flow sand bodies.
-
Key words:
- Huaqing area /
- gravity flow /
- sandy debris flow /
- turbidity current /
- Chang 63 of Yanchang Formation
-
图 3 华庆地区长63砂层组深水重力流沉积构造
a. S136井, 2 111.8 m, 沟模; b. B136井, 2 131.2 m, 重荷模; c. B152井, 2 156.3 m, 砂岩与深水泥岩突变接触; d. B516井, 2 067.7 m, 火焰构造; e. X176井, 1 727.4 m, 重力负荷压实作用下的火焰构造; f. B283井, 1 930.65 m, 滑塌变形; g. B464井, 2 093.6 m, 滑塌岩; h. L72井, 1 796.2 m, 滑动切截; i. B152井, 2 156.3 m, 正粒序砂岩与泥岩突变接触; j. L45井, 2 286.77 m, 具反粒序特征; k. B465井, 2 071.4 m, 发育较完整的鲍马序列浊积岩; l. B213井, 2 151.3 m, 泥岩包裹厚层块状砂岩,砂质碎屑流沉积
Figure 3. Sedimentary structures in deep-water gravity flow deposits from the Chang 63 sandstone in the Huaqing area
图 4 华庆地区长63砂层组微观储层特征
a. B152井, 长63, 2 132.4 m, 粒间孔, 钙质胶结; b. B411井, 长63, 2 123.45 m, 绿泥石胶结、石英微晶、铁白云石胶结; c. L46井, 2 266.9 m, 高岭石充填孔隙; d. B230井, 2 131.31 m, 长63, 致密, 钙化碎屑; e. B491井, 2 151.67 m, 高岭石、伊利石胶结; f. B491井, 长63, 2 151.67 m, 云母弯曲变形
Figure 4. Microscopic pore characteristics of the Chang 63 sandstone in the Huaqing area
图 7 华庆地区延长组长63沉积相连井剖面图(剖面位置见图 8)
a. 垂直物源方向;b. 顺物源方向
Figure 7. Sedimentary facies of Chang 63 among wells for Yangchang Formation in the Huaqing area
-
[1] Reading H G. Sedimentary environments: Processes, facies, and stratigraphy[J]. Encyclopedia of Geology, 1996, 688: 580-587. [2] Parsons D R, Peakall J, Aksu A E, et al. Gravity-driven flow in a submarine channel bend: Direct field evidence of helical flow reversal[J]. Geology, 2010, 38(12): 1063-1066. doi: 10.1130/G31121.1 [3] 王华, 周立宏, 韩国猛, 等. 陆相湖盆大型重力流发育的成因机制及其优质储层特征研究: 以歧口凹陷沙河街组一段为例[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(10): 3423-3444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201810009.htmWang H, Zhou L H, Han G M, et al. Large gravity flow deposits in the Member 1 of Paleogene Shahejie Formation, Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(10): 3423-3444(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201810009.htm [4] 朱筱敏, 董艳蕾, 刘成林, 等. 中国含油气盆地沉积研究主要科学问题与发展分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(1): 1-11.Zhu X M, Dong Y L, Liu C L, et al. Major challenges and development in Chinese sedimentological research on petroliferous basins[J]. Earth Science Fronties, 2021, 28(1): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). [5] 符勇, 李忠诚, 万谱, 等. 三角洲前缘滑塌型重力流沉积特征及控制因素: 以松辽盆地大安地区青一段为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(1): 198-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202101018.htmFu Y, Li Z C, Wan P, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and controlling factors of slump gravity flow in delta front: A case study of Qing 1 Member in Da'an area, Songliao Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(1): 198-208(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202101018.htm [6] 萧高健, 骆杨, 刘洪平. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部彬长区块延长组长6-长7段深水重力流沉积特征分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 69-82. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0135Xiao G J, Luo Y, Liu H P. Characteristic analysis of deep water gravity flow sediments in Ch6-Ch7 Section of Yanchang Formation in the Binchang Black, southern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 69-82(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0135 [7] 刘桠颖, 徐怀民, 李林, 等. 准噶尔盆地阜东斜坡带深水浊积扇沉积及油气勘探意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2009, 29(4): 29-34.Liu Y Y, Xu H M, Li L, et al. Deep-water turbidite fan deposits and their significance for the oil-gas exploration in the eastern Fukang slope zone, Junggar Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2009, 29(4): 29-34(in Chinese with English abstract). [8] 王华, 陈思, 巩天浩, 等. 牵引流化重力流沉积过程与堆积机制: 以渤海湾盆地歧口凹陷为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 95-104. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0111Wang H, Chen S, Gong T H, et al. Sedimentary process and accumulation mechanism of traction fluidization gravity flow: An example from Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 95-104(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0111 [9] 李专, 何幼斌, 肖彬, 等. 广西百色利周地区板纳组中段砂质碎屑流沉积[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(3): 93-100.Li Z, He Y B, Xiao B, et al. Sandy debris flow of middle Banna Formation in Lizhou area of Baise, Guangxi Province[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2014, 26(3): 93-100(in Chinese with English abstract). [10] 李相博, 刘化清, 完颜容, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组砂质碎屑流储集体的首次发现[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2009, 21(4): 19-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX200904004.htmLi X B, Liu H Q, Wan Y R, et al. First discovery of the sandy debris flow from the Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2009, 21(4): 19-21(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX200904004.htm [11] 谈明轩, 朱筱敏, 耿名扬, 等. 沉积物重力流流体转化沉积: 混合事件层[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(6): 1108-1119.Tan M X, Zhu X M, Geng M Y, et al. The flow transforming deposits of sedimentary gravityflow: Hybrid event bed[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(6): 1108-1119(in Chinese with English abstract). [12] 巩天浩, 吴琳娜, 陈思, 等. 歧口凹陷中部沙一下亚段异重流沉积识别特征与控制因素分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 69-83. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0061Gong T H, Wu L N, Chen S, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and controlling factors of hyperpycnal flow in the Lower Shahejie Formation of Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 69-83(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0061 [13] 操应长, 杨田, 王艳忠, 等. 超临界沉积物重力流形成演化及特征[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(6): 607-621.Cao Y C, Yang T, Wang Y Z, et al. Formation, evolution and sedimentary characteristics of super-critical sediment gravity-flow[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(6): 607-621(in Chinese with English abstract). [14] 操应长, 杨田, 王艳忠, 等. 深水碎屑流与浊流混合事件层类型及成因机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(3): 234-248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201703027.htmCao Y C, Yang T, Wang Y Z, et al. Types and genesis of deep-water hybrid event beds comprising debris flow and turbidity current[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(3): 234-248(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201703027.htm [15] Kuenen P H, Migliorini C I. Turbidity currents as a cause of graded bedding[J]. Journal of Geology, 1950, 58(2): 91-127. [16] Bouma A H. Sedimentology of some flysch deposits: A graphic approach to facies interpretation[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1962. [17] Walker R G. Deep-water sandstone facies and ancient submarine fan for model for exploration for stratigraphic traps[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1978, 62(6): 239-263. [18] Shanmugam G. New perspectives on deep-water sandstones: Implications[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(3): 316-324. [19] Felix M, Peakall J. Transformation of debris flows into turbidity currents: Mechanisms inferred from laboratory experiments[J]. Sedimentology, 2006, 53(1): 107-123. [20] 谈明轩, 吴峰, 马皓然, 等. 海底扇沉积相模式、沉积过程及其沉积记录的指示意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2022, 40(2): 435-449. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202202011.htmTan M X, Wu F, Ma H R, et al. Faciesmodel, sedimentary process and depositional record of submarine fans, and their implications[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022, 40(2): 435-449(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202202011.htm [21] 杨田, 操应长, 田景春. 浅谈陆相湖盆深水重力流沉积研究中的几点认识[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(1): 88-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202101007.htmYang T, Cao Y C, Tian J C. Discussion onresearch of deep-water gravity flow deposition in lacustrine basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(1): 88-111(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202101007.htm [22] 刘池洋, 赵红格, 桂小军, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地演化-改造的时空坐标及其成藏(矿)响应[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(5): 617-638.Liu C Y, Zhao H G, Gui X J, et al. Space-time coordinate of the evolution and reformation and mineralization response in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(5): 617-638(in Chinese with English abstract). [23] 刘芬, 朱筱敏, 李洋, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部延长组重力流沉积特征及相模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(5): 577-588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201505004.htmLiu F, Zhu X M, Li Y, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and facies model of gravity flow deposits of Late Triassic Yanchang Formation in southwestern Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(5): 577-588(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201505004.htm [24] 李鹏飞, 徐论勋, 李建明. 鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区长6期物源分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2010, 30(2): 61-65.Li P F, Xu L X, Li J M. Provenances of the Chang-6 oil measures in the Huaqing region, Ordos Basin[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2010, 30(2): 61-65(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] 操应长, 王思佳, 王艳忠, 等. 滑塌型深水重力流沉积特征及沉积模式: 以渤海湾盆地临南洼陷古近系沙三中亚段为例[J]. 古地理学报, 2017, 19(3): 419-432. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201703003.htmCao Y C, Wang S J, Wang Y Z, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and depositional model of slumping deep-water gravity flow deposits: A case study from the middle Member 3 of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Linnan Subsag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2017, 19(3): 419-432(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201703003.htm [26] 裴羽, 何幼斌, 李华, 等. 高密度浊流和砂质碎屑流关系的探讨[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(6): 1281-1292.Pei Y, He Y B, Li H, et al. Discuss about relationship between high-density turbidity current and sandy debris flow[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(6): 1281-1292(in Chinese with English abstract). [27] 杨田, 操应长, 田景春, 等. 陆相湖盆深水重力流混合事件层沉积及沉积学意义[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(12): 3842-3857. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202112019.htmYang T, Cao Y C, Tian J C, et al. Deposition of deep-water gravity-flow hybrid event beds in lacustrine basins and their sedimentological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(12): 3842-3857(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202112019.htm [28] 付锁堂, 邓秀芹, 庞锦莲. 晚三叠世鄂尔多斯盆地湖盆沉积中心厚层砂体特征及形成机制分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(6): 1081-1089.Fu S T, Deng X Q, Pang J L. Characteristics and mechanism of thick sandbody of Yanchang Formation at the center of Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(6): 1081-1089(in Chinese with English abstract). [29] 庞军刚, 杨友运, 田建锋, 等. 致密砂岩储集层单因素定量成岩相分析: 以华庆地区三叠系延长组长63为例[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(2): 369-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201502025.htmPang J G, Yang Y Y, Tian J F, et al. Single diagenetic factor analysis of diagenesis facies in the tight sandstone reservoir: An example from the Chang 63 Sub-member of the Yanchang Formation in the Huaqing area[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(2): 369-378(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201502025.htm [30] 陈全红, 李文厚, 高永祥, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组深湖沉积与油气聚集意义[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 2007, 37(增刊1): 39-48.Chen Q H, Li W H, Gao Y X, et al. The deep-lake deposit in the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin, China and its significance for oil-gas accumulation[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2007, 37(S1): 39-48(in Chinese with English abstract). [31] 邓秀芹, 罗安湘, 张忠义, 等. 秦岭造山带与鄂尔多斯盆地印支期构造事件年代学对比[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(6): 939-953. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201306001.htmDeng X Q, Luo A X, Zhang Z Y, et al. Geochronological comparison on Indosinian tectonic events between Qinling Orogeny and Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(6): 939-953(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201306001.htm [32] 王宏波, 李相博, 廖建波. 鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区长6油层组超低渗砂体成因分析[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2012, 24(5): 61-64.Wang H B, Li X B, Liao J B. Origin of super-low permeability sand bodies of Chang 6 oil reservoir set in Huaqing area, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2012, 24(5): 61-64(in Chinese with English abstract). [33] 傅强, 李璟, 邓秀琴, 等. 沉积事件对深水沉积过程的影响: 以鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区长6油层组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(1): 20-29.Fu Q, Li J, Deng X Q, et al. Influence of sedimentary events on deep water sedimentation process: A case of Chang 6 reservoir in Huaqing area, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(1): 20-29(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: