-
摘要:
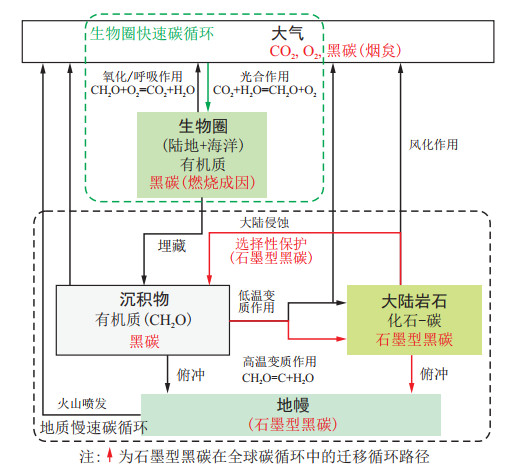
黑碳是由生物质和化石燃料不完全燃烧生成的碳质混合物。由于黑碳含碳量高,具有芳构化的分子结构,可在自然环境中长期存在,因此黑碳是全球碳循环的重要组分。虽然近年来有关黑碳的性质以及黑碳在地球各圈层中的循环通量及储量的研究取得了一定的进展,但仍需进一步厘清其源汇过程,探讨黑碳在全球碳循环中的作用。初步梳理了全球黑碳循环的路径、通量、时间尺度的相关数据,分析总结了海洋黑碳源汇过程中的迁移机制及相关制约因素。分析认为:海洋沉积物是黑碳的巨大储库,储量达569~1 380 Pg,黑碳可在海洋沉积物中持续存在数千年,符合当前“碳中和”背景下“有效碳汇”长周转时间这一重要条件;同时,黑碳在环境中的周转循环时间一般长于生物质碳,对全球变暖具有负反馈效应。因此,黑碳入海沉积是一种有效的海洋碳增汇和碳封存手段,可能是实施碳的捕集、利用和封存(CCUS)战略的有效途径。通过总结与评估海洋沉积物中的黑碳在“碳中和”领域的战略价值和气候意义,认为在生态环境友好的前提下,应积极调控生物质燃烧成因的黑碳的生产源头,优化黑碳入海沉积路径和埋藏海域,充分发挥黑碳在海洋负排放中的积极作用,为我国海洋“碳中和”目标的实现提供基础理论支撑。
Abstract:Objective Black carbon is a carbonaceous mixture formed by the incomplete combustion of biomass and fossil fuels. Since black carbon has a high carbon content and an aromatized molecular structure, it can persist in the natural environment, suggesting that black carbon is an important component of the global carbon cycle. Although pioneering studies have advanced the understanding of nature, circulation fluxes, and reserves of black carbon in the geosphere, it is still necessary to further clarify the source-sink processes of black carbon and explore the importance of black carbon in the global carbon cycle.
Methods Here, this study reviews the available data on pathways, fluxes, and time scales of the global black carbon cycle and analyses and summarizes the migration mechanisms and constraints in the source-sink process of marine black carbon.
Results This paper concludes that marine sediments serve as a large reservoir for black carbon, with a reserve of 569-1 380 Pg. Black carbon can persist over millennia in marine sediments, which is associated with a long turnover time as an "effective carbon sink" in the context of "carbon neutrality". Moreover, black carbon exerts a negative feedback effect on global warming due to its longer turnover cycle time than biomass carbon. The deposition of black carbon into the sea is an effective means to enhance carbon sequestration in the ocean and could be an effective way to implement the carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) strategy.
Conclusion In this paper, we propose that human-induced production of black carbon from biogenic combustion may be actively regulated and that the deposition pathways and burial areas of black carbon into the sea should also be optimized given the premise of ecological and environmental friendliness based on a summary and assessment of the strategic value and climate significance of black carbon in marine sediments in the context of "carbon neutrality". Therefore, the positive role of black carbon in "negative ocean carbon emissions" can provide a basic theoretical framework for achieving the goals of "carbon neutrality".
-
Key words:
- carbon neutrality /
- black carbon /
- source-sink processes /
- geological carbon sink /
- ocean
-
-
[1] FOSTER G L, ROYER D L, LUNT D J. Future climate forcing potentially without precedent in the last 420 million years[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 1-8. doi: 10.1038/s41467-016-0009-6 [2] 焦念志, 戴民汉, 翦知湣, 等. 海洋储碳机制及相关生物地球化学过程研究策略[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(15): 1600-1606. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB202215002.htmJIAO N Z, DAI M H, JIAN Z M, et al. Research strategies for ocean carbon storage mechanisms and effects[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(15): 1600-1606. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB202215002.htm [3] SANTÍN C, DOERR S H, KANE E S, et al. Towards a global assessment of pyrogenic carbon from vegetation fires[J]. Global Change Biology, 2016, 22(1): 76-91. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12985 [4] BIRD M I, WYNN J G, SAIZ G, et al. The pyrogenic carbon cycle[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2015, 43(1): 273-298. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060614-105038 [5] ASCOUGH P L, BIRD M I, FRANCIS S M, et al. Variability in oxidative degradation of charcoa: Influence of production conditions and environmental exposure[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2011, 75(9): 2361-2378. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2011.02.002 [6] PINGREE M R, DELUCA T H. Function of wildfire-deposited pyrogenic carbon in terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2017, 5: 1-7. [7] KUHLBUSCH T A J, ANDREAE M O, CACHIER H, et al. Black carbon formation by savanna fires: Measurements and implications for the global carbon cycle[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Atmospheres), 1996, 101(D19): 23651-23665. doi: 10.1029/95JD02199 [8] COPPOLA A I, WIEDEMEIER D B, GALY V, et al. Global-scale evidence for the refractory nature of riverine black carbon[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2018, 11(8): 584-588. doi: 10.1038/s41561-018-0159-8 [9] SCHMIDT M W I, NOACK A G. Black carbon in soils and sediments: Analysis, distribution, implications, and current challenges[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2000, 14(3): 777-793. doi: 10.1029/1999GB001208 [10] FLORES-CERVANTES D X, PLATA D L, MACFARLANE J K, et al. Black carbon in marine particulate organic carbon: Inputs and cycling of highly recalcitrant organic carbon in the Gulf of Maine[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2009, 113(3/4): 172-181. [11] 黄国培, 陈颖军, 田崇国, 等. 海洋溶解态黑碳的研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(12): 1326-1336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201212005.htmHUANG G P, CHEN Y J, TIAN C G, et al. Research progress of dissolved black carbon in seawater[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2012, 27(12): 1326-1336. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201212005.htm [12] REGNIER P, FRIEDLINGSTEIN P, CIAIS P, et al. Anthropogenic perturbation of the carbon fluxes from land to ocean[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6(8): 597-607. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1830 [13] VÖRÖSMARTY C J, MCINTYRE P B, GESSNER M O, et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity[J]. Nature, 2010, 467: 555-561. doi: 10.1038/nature09440 [14] MASIELLO C A. New directions in black carbon organic geochemistry[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2004, 92(1/4): 201-213. [15] COPPOLA A I, ZIOLKOWSKI L A, MASIELLO C A, et al. Aged black carbon in marine sediments and sinking particles[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2014, 41(7): 2427-2433. doi: 10.1002/2013GL059068 [16] 焦念志, 刘纪化, 石拓, 等. 实施海洋负排放践行碳中和战略[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2021, 51(4): 632-643. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202104010.htmJIAO N Z, LIU J H, SHI T, et al. Deploying ocean negative carbon emissions to implement the carbon neutrality strategy[J]. Science China(Earth Sciences), 2021, 51(4): 632-643. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202104010.htm [17] DRUFFEL E R, WILLIAMS P M, BAUER J E, et al. Cycling of dissolved and particulate organic matter in the open ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Oceans), 1992, 97(C10): 15639-15659. doi: 10.1029/92JC01511 [18] 包锐. "碳中和"目标背景下我国海洋碳汇与碳年龄的思考[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 53(4): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY202304001.htmBAO R. Evaluating the carbon sink in Chinese marginal seas in the context of carbon neutrality goals: Insight from carbon ages[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2023, 53(4): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY202304001.htm [19] JONES M W, COPPOLA A I, SANTÍN C, et al. Fires prime terrestrial organic carbon for riverine export to the global oceans[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2791-2798. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16576-z [20] BOND T C, DOHERTY S J, FAHEY D W, et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Atmospheres), 2013, 118(11): 5380-5552. [21] COPPOLA A I, WAGNER S, LENNARTZ S T, et al. The black carbon cycle and its role in the earth system[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2022, 3(8): 1-17. [22] SCHMIDT M W, TORN M S, ABIVEN S, et al. Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property[J]. Nature, 2011, 478: 49-56. doi: 10.1038/nature10386 [23] GALY V, BEYSSAC O, FRANCE-LANORD C, et al. Recycling of graphite during Himalayan erosion: A geological stabilization of carbon in the crust[J]. Science, 2008, 322: 943-945. doi: 10.1126/science.1161408 [24] FIERCE L, BOND T C, BAUER S E, et al. Black carbon absorption at the global scale is affected by particle-scale diversity in composition[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 1-8. [25] BOND T C. A technology-based global inventory of black and organic carbon emissions from combustion[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2004, 109(D14): D14203. [26] REISSER M, PURVES R S, SCHMIDT M W, et al. Pyrogenic carbon in soils: A literature-based inventory and a global estimation of its content in soil organic carbon and stocks[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2016, 4: 1-14. [27] JAFFÉ R, DING Y, NIGGEMANN J, et al. Global charcoal mobilization from soils via dissolution and riverine transport to the oceans[J]. Science, 2013, 340: 345-347. doi: 10.1126/science.1231476 [28] SEIDEL M, BECK M, GRESKOWIAK J, et al. Benthic-pelagic coupling of nutrients and dissolved organic matter composition in an intertidal sandy beach[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2015, 176: 150-163. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2015.08.011 [29] FIERCE L, RIEMER N, BOND T C. Explaining variance in black carbon's aging timescale[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2015, 15(6): 3173-3191. doi: 10.5194/acp-15-3173-2015 [30] JURADO E, DACHS J, DUARTE C M, et al. Atmospheric deposition of organic and black carbon to the global oceans[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42(34): 7931-7939. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.07.029 [31] NAKANE M, AJIOKA T, YAMASHITA Y. Distribution and sources of dissolved black carbon in surface waters of the Chukchi Sea, Bering Sea, and the North Pacific Ocean[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science(Lausanne), 2017, 5: 1-12. [32] FANG Z, YANG W, CHEN M, et al. Source and fate of dissolved black carbon in the western South China Sea during the southwest monsoon prevailing season[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Biogeosciences), 2017, 122(11): 2817-2830. [33] WAGNER S, HARVEY E, BAETGE N, et al. Investigating atmospheric inputs of dissolved black carbon to the Santa Barbara Channel during the Thomas Fire(California, USA)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Biogeosciences), 2021, 126(8): e2021J-e6442J. [34] JONES M W, QUINE T A, DE REZENDE C E, et al. Do regional aerosols contribute to the riverine export of dissolved black carbon?[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Biogeosciences), 2017, 122(11): 2925-2938. [35] WANG X, XU C, DRUFFEL E M, et al. Two black carbon pools transported by the Changjiang and Huanghe Rivers in China[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2016, 30(12): 1778-1790. doi: 10.1002/2016GB005509 [36] FANG Y, CHEN Y, HUANG G, et al. Particulate and dissolved black carbon in coastal China seas: Spatiotemporal variations, dynamics, and potential implications[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 55(1): 788-796. [37] MASIELLO C A, DRUFFEL E. Organic and black carbon13C and 14C through the Santa Monica Basin sediment oxic-anoxic transition[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2003, 30(4): 1-4. [38] STUBBINS A, NIGGEMANN J, DITTMAR T. Photo-lability of deep ocean dissolved black carbon[J]. Biogeosciences, 2012, 9(5): 1661-1670. doi: 10.5194/bg-9-1661-2012 [39] SINGH N, ABIVEN S, TORN M S, et al. Fire-derived organic carbon in soil turns over on a centennial scale[J]. Biogeosciences, 2012, 9(8): 2847-2857. doi: 10.5194/bg-9-2847-2012 [40] SANTÍN C, DOERR S H, PRESTON C M, et al. Pyrogenic organic matter production from wildfires: A missing sink in the global carbon cycle[J]. Global Change Biology, 2015, 21(4): 1621-1633. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12800 [41] LEHMANN J, SKJEMSTAD J, SOHI S, et al. Australian climate-carbon cycle feedback reduced by soil black carbon[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1(12): 832-835. doi: 10.1038/ngeo358 [42] KUZYAKOV Y, BOGOMOLOVA I, GLASER B. Biochar stability in soil: Decomposition during eight years and transformation as assessed by compound-specific 14C analysis[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2014, 70: 229-236. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.12.021 [43] CROFT B, LOHMANN U, VON SALZEN K. Black carbon ageing in the Canadian Centre for climate modelling and analysis atmospheric general circulation model[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2005, 5(7): 1931-1949. doi: 10.5194/acp-5-1931-2005 [44] GELENCSÉR A. Carbonaceous aerosol[M]. [S. l. ]: Springer Science & Business Media, 2007. [45] 曹军骥, 占长林. 黑碳在全球气候和环境系统中的作用及其在相关研究中的意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2011, 33(2): 177-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201102015.htmCAO J J, ZHAN C L. Research significance and role of black carbon in the global climate and environmental systems[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2011, 33(2): 177-184. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201102015.htm [46] 唐杨, 韩贵琳, 徐志方. 黑碳研究进展[J]. 地球与环境, 2010, 38(1): 98-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201001020.htmTANG Y, HAN G L, XU Z F. Black carbon: A review of recent research[J]. Earth and Environment, 2010, 38(1): 98-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201001020.htm [47] COPPOLA A I, DRUFFEL E R. Cycling of black carbon in the ocean[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(9): 4477-4482. doi: 10.1002/2016GL068574 [48] FU W, QI Y, LIU Y, et al. Production of ancient dissolved organic carbon in Arctic Ocean sediment: A pathway of carbon cycling in the extreme environment[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(5): e2020G-e87119G. [49] REN P, LIU Y, SHI X, et al. Sources and sink of black carbon in Arctic Ocean sediments[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 689: 912-920. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.437 [50] REN P, LUO C, ZHANG H, et al. Isotopic records of ancient wildfires in C4 grasses preservedin the sediment of the Ross Sea, Antarctica[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2022, 49(13): e2022G-e98979G. [51] MITRA S, ZIMMERMAN A R, HUNSINGER G, et al. Black carbon in coastal and large river systems[J]. Biogeochemical Dynamics at Major River-Coastal Interfaces Linkages with Climate Change, 2014, 2(9): 200-234. [52] ZHANG X, XU Y, XIAO W, et al. The hadal zone is an important and heterogeneous sink of black carbon in the ocean[J]. Communications Earth & Environment, 2022, 3(1): 1-9. [53] CHEW S T, GALLAGHERJ B. Accounting for black carbon lowers estimates of blue carbon storage services[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 2553-2558. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20644-2 [54] BRUNJES J, SEIDEL M, DITTMAR T, et al. Natural asphalt seeps are potential sources for recalcitrant oceanic dissolved organic sulfur and dissolved black carbon[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(12), 9092-9102. [55] DITTMAR T, PAENG J. A heat-induced molecular signature in marine dissolved organic matter[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2009, 2(3): 175-179. doi: 10.1038/ngeo440 [56] WAGNER S, BRANDES J, SPENCER R G, et al. Isotopic composition of oceanic dissolved black carbon reveals non-riverine source[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1-8. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07882-8 [57] 张旭东, 梁超, 诸葛玉平, 等. 黑碳在土壤有机碳生物地球化学循环中的作用[J]. 土壤通报, 2003, 34(4): 349-355. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB200304028.htmZHANG X D, LIANG C, ZHUGE Y P, et al. Roles of black carbon in the biogeochemical cycles of soil organic carbon[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2003, 34(4): 349-355. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB200304028.htm [58] JONES M W, SANTÍN C, VAN DER WERF G R, et al. Global fire emissions buffered by the production of pyrogenic carbon[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2019, 12(9): 742-747. doi: 10.1038/s41561-019-0403-x [59] KUHLBUSCH T A J U, CRUTZEN P J. Toward a global estimate of black carbon in residues of vegetation fires representing a sink of atmospheric CO2 and a source of O2[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 1995, 9(4): 491-501. doi: 10.1029/95GB02742 [60] SHRESTHA G, TRAINA S J, SWANSTON C W. Black carbon's properties and role in the environment: A comprehensive review[J]. Sustainability, 2010, 2(1): 294-320. doi: 10.3390/su2010294 [61] BAO H, NIGGEMANN J, LUO L, et al. Aerosols as a source of dissolved black carbon to the ocean[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 510-517. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00437-3 [62] LOHMANN R, BOLLINGER K, CANTWELL M, et al. Fluxes of soot black carbon to South Atlantic sediments[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2009, 23(1): 1-13. [63] MIDDELBURG J J, NIEUWENHUIZE J, VAN BREUGEL P. Black carbon in marine sediments[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1999, 65(3/4): 245-252. [64] DICKENS A F, GÉLINAS Y, HEDGES J I. Physical separation of combustion and rock sources of graphitic black carbon in sediments[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2004, 92(1/4): 215-223. [65] MASIELLO C A, DRUFFEL E. Black carbon in deep-sea sediments[J]. Science, 1998, 280: 1911-1913. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5371.1911 [66] MANNINO A, RODGER HARVEY H. Black carbon in estuarine and coastal ocean dissolvedorganic matter[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2004, 49(3): 735-740. doi: 10.4319/lo.2004.49.3.0735 [67] GUSTAFSSON O, GSCHWEND P M. The flux of black carbon to surface sediments on the New England continental shelf[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(3): 465-472. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00370-0 [68] 方引. 渤黄海黑碳的区域地球化学行为[D]. 山东烟台: 中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所, 2016.FANG Y. Regional geochemical behavior of black carbon in Bohai and Yellow Seas, China[D]. Yantai Shandong: Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) [69] 方仔铭. 南海及极地海域黑碳的源、汇及其对海洋碳循环的影响[D]. 福建厦门: 厦门大学, 2018.FANG Z M. Source and fate of black carbon in the South China Sea and polar oceans and its influences on ocean carbon cycling[D]. Xiamen Fujian: Xiamen University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) [70] JOLLY W M, COCHRANE M A, FREEBORN P H, et al. Climate-induced variations in global wildfire danger from 1979 to 2013[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 1-11. [71] ABATZOGLOU J T, WILLIAMS A P, BARBERO R. Global emergence of anthropogenic climate change in fire weather indices[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2019, 46(1): 326-336. doi: 10.1029/2018GL080959 [72] SANTÍN C, DOERR S H, MERINO A, et al. Carbon sequestration potential and physicochemical properties differ between wildfire charcoals and slow-pyrolysis biochars[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0028-x [73] OKIMORI Y, OGAWA M, TAKAHASHI F. Potential of CO2 emission reductions by carbonizing biomass waste from industrial tree plantation in South Sumatra, Indonesia[J]. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 2003, 8(3): 261-280. doi: 10.1023/B:MITI.0000005643.79908.5a [74] SUN T, GUZMAN J J, SEWARD J D, et al. Suppressing peatland methane production by electron snorkeling through pyrogenic carbon in controlled laboratory incubations[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1-9. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20314-w [75] BOWRING S P, JONES M W, CIAIS P, et al. Pyrogenic carbon decomposition critical to resolving fire's role in the earth system[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2022, 15(2): 135-142. doi: 10.1038/s41561-021-00892-0 [76] 邹才能, 薛华庆, 熊波, 等. "碳中和"的内涵, 创新与愿景[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(8): 46-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202108007.htmZOU C N, XUE H Q, XIONG B, et al. Connotation, innovation and vision of "carbon neutral"[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(8): 46-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202108007.htm [77] 王季康, 李华, 彭宇飞, 等. 碳中和目标下可再生能源的3种应用模式[J]. 现代化工, 2022, 42(5): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDHG202205001.htmWANG J K, LI H, PENG Y F, et al. Three application modes of renewable under carbon neutralization target[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2022, 42(5): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDHG202205001.htm [78] WOOLF D, AMONETTE J E, STREET-PERROTT F A, et al. Sustainable biochar to mitigate global climate change[J]. Nature Communications, 2010, 1(1): 1-9. [79] HEPBURN C, ADLEN E, BEDDINGTON J, et al. The technological and economic prospects for CO2 utilization and removal[J]. Nature, 2019, 575: 87-97. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1681-6 [80] HASAN M M F, FIRST E L, BOUKOUVALA F, et al. A multi-scale framework for CO2 capture, utilization, and sequestration: CCUS and CCU[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2015, 81: 2-21. [81] FRIEDLINGSTEIN P, O'SULLIVAN M, JONES M W, et al. Global carbon budget 2020[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2020, 12(4): 3269-3340. doi: 10.5194/essd-12-3269-2020 [82] 焦念志. 研发海洋"负排放"技术支撑国家"碳中和"需求[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2021, 36(2): 179-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX202102009.htmJIAN N Z. Developing ocean negative carbon emission technology to support national carbon neutralization[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021, 36(2): 179-187. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX202102009.htm [83] 王文涛, 刘纪化, 揭晓蒙, 等. 海洋支撑碳中和技术体系框架构建的思考与建议[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 52(3): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY202203001.htmWANG W T, LIU J H, JIE X M, et al. Perspective of technology system in the ocean for carbon neutrality[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2022, 52(3): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QDHY202203001.htm [84] GOLDBERG E D. Black carbon in the environment: Properties and distribution[M]. [S. l. ]: John Wiley, 1985. [85] SCHMIDT M W. Carbon budget in the black[J]. Nature, 2004, 427: 305-307. doi: 10.1038/427305a [86] JIAO N, HERNDL G J, HANSELL D A, et al. Microbial production of recalcitrant dissolved organic matter: Long-term carbon storage in the global ocean[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2010, 8(8): 593-599. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2386 [87] 张美琪, 陈波, 赵敏. 贵州省湿地碳储量与碳中和潜力分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 315-326. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220358ZHANG M Q, CHEN B, ZHAO M. Analysis of the carbon stock and carbon neutral potential of wetlands in Guizhou Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 315-326. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220358 [88] 章程, 肖琼, 孙平安, 等. 岩溶碳循环及碳汇效应研究与展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 190-198. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0193ZHANG C, XIAO Q, SUN P A, et al. Progress on karst carbon cycle and carbon sink effect study and perspective[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 190-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0193 [89] 韩文科, 杨玉峰, 苗韧, 等. 当前全球碳捕集与封存(CCS)技术进展及面临的主要问题[J]. 中国能源, 2009, 31(10): 5-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGLN200910007.htmHAN W K, YANG Y F, MAO R, et al. The progress and main problems of the present global Carbon Capture and Storage(CCS) technology[J]. Energy of China, 2009, 31(10): 5-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGLN200910007.htm [90] 魏宁, 王倩, 李小春, 等. CO2海洋管道运输的技术经济分析[J]. 油气储运, 2015, 34(11): 1141-1146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCY201511002.htmWEI N, WANG Q, LI X C, et al. Technical and economic assessments on CO2 transmission through subsea pipelines[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2015, 34(11): 1141-1146. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCY201511002.htm [91] LIU J, WANG N, XIA C, et al. Differential mobilization and sequestration of sedimentary black carbon in the East China Sea[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2022, 594: 117739. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2022.117739 -





 下载:
下载: