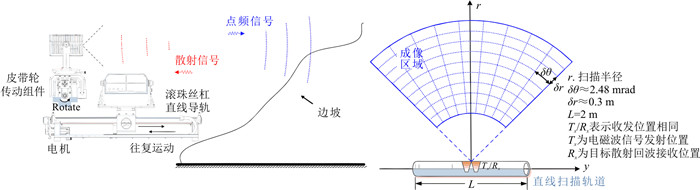
Principle and application of S-SARⅡ technology for collapse emergency monitoring
-
摘要:
崩塌灾害具有高隐蔽性、强突发性、重危害性等特点, 其预警监测是各类重大基础工程准备阶段以及施工期间的重要研究工作, 同时也是崩塌临灾监测救援现场指挥工作的重要科学依据。结合地基合成孔径干涉雷达技术(GB-InSAR)和最新的MIMO技术, 将应急边坡救援雷达S-SARⅡ的系统量程扩大了60倍, 并通过监测内蒙古某矿场主矿坑西南帮崩塌隐患点生成雷达形变图, 结合三维高程模型DEM以及多种预测模型预测崩塌发生时间。结果表明, S-SARⅡ精准地确定了形变区域及形变量, 并预测崩塌发生时间为8月29日9∶32-10∶27之间, 最终崩塌发生时间为8月29日10点26分。因此, S-SARⅡ准确预测了崩塌灾害的发生时间, 最大程度地保障了矿区的生产安全, 并通过实际应用分析证明, 优化后的S-SARⅡ的系统量程得到了数量级提升, 满足崩塌监测的需要, 且以S-SARⅡ为代表的遥测预警技术在地质灾害险情处置和应急救援中具有明显的技术优势。
Abstract:The collapse disaster has the characteristics of high concealment, strong paroxysm and serious harmfulness. Its early warning monitoring is an important research work in the preparation phase and construction period of various major foundation projects, and it is also an important scientific basis for the on-site command of collapse disaster monitoring and rescue. In this paper, combined with GB-InSAR and the latest multiple input multiple output(MIMO) technologies, the measurement range of emergency slope rescue radar S-SAR II has expanded by 60 times.The radar deformation map is generated by monitoring the potential collapse points on the southwest side of a open pit in Inner Mongolia, and the occurrence time of collapse is predicted by using DEM and various prediction models. The results show that S-SAR Ⅱ accurately determines the deformation area and corresponding magnitude and predicts that the time of collapse is between 9:32 a.m. and 10:27 a.m. on August 29, and the actual time of collapse is 10:26 on August 29. Therefore, S-SAR Ⅱcan predict the occurrence time of collapse disaster and guarantee the production safety of the mining regions. Through practical application analysis, it is proved that the range of S-SAR Ⅱ system has been significantly improved after optimization to meet the needs of collapse monitoring, and the telemetry and early warning technology represented by S-SAR Ⅱ has obvious technical advantages in geological disaster risk disposal and emergency rescue.
-
Key words:
- S-SAR Ⅱ /
- collapse /
- MIMO /
- disaster emergency monitoring /
- GB-InSAR
-
表 1 S-SARⅡ与其他监测技术的优势对比
Table 1. Comparison of the performance between S-SARⅡand other monitoring technologies
对比对象 对比对象的技术特性 S-SARⅡ的技术优势 GPS、全站仪等传统的监测手段 离散点形变量监测 大范围空间连续覆盖 埋置式监测,需要人员进入 远程监测 受天气、视通条件等限制 全天时全天候实时监测 激光扫描仪等遥测手段 测量距离为2 km 测量距离为5 km 测量精度为毫米量级 测量精度为亚毫米量级 需要人工多次跑点测量 全自动测量,无需人工参与 星载、机载雷达 重复观测周期最短需要11 d,难以实现定点连续观测 重复观测周期最短可达几分钟甚至几十毫秒,可以实现对形变区域的定点连续监测 时间和空间分辨率低,不适合获取小区域形变信息 可以获得很高的空间分辨率和测量精度 运行轨道固定、观测周期固定,易受地形、观测视角等影响 可根据监测目标特性选择观测时间基线 实孔径雷达 受极端天气影响较大 更强的环境适应性,搭配应急救援拖车平台,受环境影响小 每个分辨单元在每次扫描过程中只能被进行一次采样 每个分辨单元在每次扫描过程中可以被上百次采样,数据采集更全面 表 2 S-SAR Ⅱ监测参数
Table 2. S-SARⅡ monitoring parameters
精度 ±0.1 mm视线方向 发射功率 30 dBm 空间分辨率 距离向:0.25 m
方位向:4/8 mrad发射带宽/MH 600 波束宽度/(°) 水平向:60
俯仰向:30监测距离/m 30~5 000 极化方式 水平极化 监测周期/min < 10 工作温度/℃ -40~+55 防护等级 IP65 工作频段/GHz 17.2~17.8 功耗/W < 120 -
[1] 王彤. 应急管理部发布2021年全国自然灾害基本情况[J]. 中国减灾, 2022(3): 7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJI202203023.htmWang T. Ministry of Emergency Management released the basic information of national natural disasters in 2021[J]. Disaster Reduction in China, 2022(3): 7(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJI202203023.htm [2] 杜岩, 谢谟文, 蒋宇静, 等. 岩体崩塌灾害成因机制与早期预警研究综述[J]. 金属矿山, 2021(1): 106-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS202101009.htmDu Y, Xie M W, Jiang Y J, et al. Review on the formation mechanism and early warning of rock collapse[J]. Metal Mine, 2021(1): 106-119(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS202101009.htm [3] 吴星辉, 马海涛, 张杰. 地基合成孔径雷达的发展现状及应用[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2019, 44(7): 1073-1081. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201907013.htmWu X H, Ma H T, Zhang J. Development status and application of ground based synthetic aperture radar[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 1073-1081(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH201907013.htm [4] 黄健, 巨能攀, 何朝阳, 等. 基于新一代信息技术的地质灾害监测预警系统建设[J]. 工程地质学报, 2015, 23(1): 140-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201501026.htmHuang J, Ju N P, He C Y, et al. Establishment of early geohazard warning system using modern information technology[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 23(1): 140-147(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201501026.htm [5] 黄跃文, 牛广利, 李端有, 等. 大坝安全监测智能感知与智慧管理技术研究及应用[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2021, 38(10): 180-185, 198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB202110033.htmHuang Y W, Niu G L, Li D Y, et al. Research and application of intelligent perception and intelligent management technology for dam safety monitoring[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2021, 38(10): 180-185, 198(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB202110033.htm [6] 何满潮, 韩雪, 张斌, 等. 滑坡地质灾害远程实时监测预报技术与工程应用[J]. 黑龙江科技学院学报, 2012, 22(4): 337-342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJI201204005.htmHe M C, Han X, Zhang B, et al. Realtime remote monitoring and forecasting technology for landslide disasters based on sliding force variation and its engineering application[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Institute of Science and Technology, 2012, 22(4): 337-342(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJI201204005.htm [7] 靳玉鹏, 胡庆忠, 覃事河. 微芯桩监测在猴子岩水电站开顶滑坡体中的应用[J]. 四川水力发电, 2020, 39(2): 119-121, 127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCSL202002034.htmJin Y P, Hu Q Z, Qin S H. The application of micro core pile monitory in the opentop landslide body of Houziyan Hydropower Station[J]. Sichuan Water Power, 2020, 39(2): 119-121, 127(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCSL202002034.htm [8] Janeras M, Jara J A, Roya' N M J, et al. Multitechnique approach to rockfall monitoring in the Montserrat massif (Catalonia, NE Spain)[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 219: 420. [9] Zhang J Y, Li H B, Yang X G, et al. Quantitative assessment of rockfall hazard in postlandslide high rock slope through terrestrial laser scanning[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology & the Environment, 2021, 80(10): 1-17. [10] Marija L, Martin Z, Jordan A, et al. Rockfall susceptibility and runout in the Valley of the Kings[J]. Natural Hazards, 2021, 110: 451-485. [11] Du Y, Wu Z X, Xie M W, et al. Early warning method of rock collapse and its experimental verification[J]. Journal of the China Coal Society, 2019, 44(10): 3069-3075. [12] Miles C, Gomez F, Rosenblad B L, et al. Quantifying measurement capabilities of ground based interferometric radar for rockfall hazard applications[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2020, 43(4): 985-1002. [13] Ali M F, Biswajeet P. A novel rockfall hazard assessment using laser scanning data and 3D modelling in GIS[J]. Catena, 2019, 172: 435-450. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2018.09.012 [14] Herlan D, Pamungkas Y, Afif R, et al. Dynamic velocity and seismic characteristics of gravitational rockfalls at the Merapi lava dome[J]. Journal of Volcanology & Geothermal Research, 2020, 404: 107010. [15] Albert P V, Jordi C, Nieves L, et al. Capturing rockfall kinematic and fragmentation parameters using highspeed camera system[J]. Engineering Geology, 2022, 302: 106629. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106629 [16] Gili J A, Ruiz C R, Matas G, et al. Rockfalls: Analysis of the block fragmentation through field experiments[J]. Landslides, 2022, 19(5): 1009-1029. doi: 10.1007/s10346-021-01837-9 [17] Hu J, Li S, Shi S, et al. Development and application of a model test system for rockfall disaster study on tunnel heading slope[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2019, 78(14): 391. [18] Wu H, Pai L, Wang F, et al. Research on the dynamic response of rockfall with different structure to impact on slope[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2020, 37(7): 13-17, 28. [19] Xu Q, Dong X, Li W. Integrated space air ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 957-966. [20] Crosta G B, Agliardi F, Rivolta C, et al. Longterm evolution and early warning strategies for complex rockslides by realtime monitoring[J]. Landslides, 2017, 14(5): 1615-1632. [21] Osasan K S, Stacey T R. Automatic prediction of time to failure of open pit mine slopes based on radar monitoring and inverse velocity method[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2014, 24(2): 275-280. [22] Lauren N, Federico D, Estelle C, et al. Monitoring volcano slope instability with Synthetic Aperture Radar: A review and new data from Pacaya (Guatemala) and Stromboli (Italy) volcanoes[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2019, 92: 236-257. [23] 林德才, 马海涛, 宋宝宏. 边坡雷达在滑坡应急救援行动中的应用[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2016, 12(增刊1): 284-289. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK2016S1051.htmLin D C, Ma H T, Song B H. Application of slope radar in emergency rescue of landslide[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2016, 12(S1): 284-289(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK2016S1051.htm [24] 吕权儒, 曾斌, 孟小军, 等. 基于无人机倾斜摄影技术的崩塌隐患早期识别及影响区划分方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 313-325, 334. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0631Lü Q R, Zeng B, Meng X J, et al. Early identification and influence range division method of collapse hazards based on UAV oblique photography technology[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 313-325, 334(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0631 [25] 岳发政, 郭金城, 汪娟, 等. GBInSAR技术在山体崩塌残余危岩体监测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2018, 29(5): 78-80, 88.Yue F Z, Guo J C, Wang J, et al. The application of GBInSAR technique in monitoring of residual body of rock avalanch[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(5): 78-80, 88(in Chinese with English abstract). [26] 赵东寅, 申其鸿, 马海涛, 等. 国产地基合成孔径雷达监测预警系统在紫金山金铜矿露天采场边坡位移监测的应用[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2015, 11(4): 54-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK201504010.htmZhao D Y, Shen Q H, Ma H T, et al. Application of domestic ground based synthetic aperture radar monitoring and warning system in slope displacement monitoring on open pit of Zijinshan gold/copper mine[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2015, 11(4): 54-58(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDBK201504010.htm [27] 郭延辉, 杨溢, 杨志全, 等. 国产GBInSAR在特大型水库滑坡变形监测中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2021, 32(2): 66-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202102009.htmGuo Y H, Yang Y, Yang Z Q, et al. Application of GBInSAR in deformation monitoring of huge landslide in reservoir area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(2): 66-72(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202102009.htm [28] 马海涛, 张亦海, 于正兴. 滑坡速度倒数法预测模型加速开始点识别及临滑时间预测研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(2): 355-364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202102011.htmMa H T, Zhang Y H, Yu Z X. Research on the identification of acceleration starting point in inverse velocity method and the prediction of sliding time[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(2): 355-364(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202102011.htm [29] 王治华, 贾伟洁. 基于数字滑坡技术的三峡新滩滑坡研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2017, 25(3): 762-771. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201703024.htmWang Z H, Jia W J. Study on xintan landslide in three gorgebased on digital landslide technique[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(3): 762-771(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201703024.htm [30] 李聪, 朱杰兵, 汪斌, 等. 滑坡不同变形阶段演化规律与变形速率预警判据研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(7): 1407-1414. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201607011.htmLi C, Zhu J B, Wang B, et al. Critical deformation velocity of landslides in different deformation phases[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(7): 1407-1414(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201607011.htm [31] Du Y, Xie M W, Jiang Y J, et al. Research progress on dynamic monitoring index for early warning of rock collapse: Review[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2019, 41(4): 427-435. [32] Li Y. MIMO radar waveform design: An overview[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2021, 30(1): 44-59. [33] Assaf H. Discussion "An empirical model of fatalities and injuries due to floods in Japan" by Guofang Zhai, Teruki Fukuzono, and Saburo Ikeda[J]. JAWRA Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 2007, 43(5): 1344-1346. [34] Qin H N, Ma H T, Yu Z X. Analysis method of landslide early warning and prediction supported by ground based SAR technology[J]. Geomatics & Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(11): 1697-1706. [35] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. 崩塌、滑坡、泥石流监测规范: DZ/T 02212006[S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国国土资源部, 2006.Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. Code for professional monitoring of rockfall, landslideand debris flow: DZ/T 02212006[S]. Beijing: Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China, 2006(in Chinese). [36] 朱冬雪, 许强, 李松林. 三峡库区大型特大型层状岩质滑坡成因模式及地质特征分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 158-167. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0217Zhu D X, Xu Q, Li S L. Genetic types and geological features of large scale and extralarge scale layered landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2020, 39(2): 158-167(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0217 [37] 文广超, 苏林雪, 谢洪波, 等. "5·12"汶川地震前后四川省主要地质灾害时空发育规律[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 143-152. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0430Wen G C, Su L X, Xie H B, et al. Spatio-temporal development characteristics of major geohazards in Sichuan Province around "5· 12" Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021.40(4): 143-152(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0430 [38] 温鑫, 范宣梅, 陈兰, 等. 基于信息量模型的地质灾害易发性评价: 以川东南古蔺县为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 290-299. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0054Wen X, Fan X M, Chen L, et al. Susceptibility assessment of geological disasters based on an information value model: A case of Gulin County in Southeast Sichuan[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 290-299(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0054 [39] 刘宇, 刘明鑫, 徐湘涛. 基于非连续变形分析的贵州典型崩塌研究[J]. 山地学报, 2015, 33(1): 94-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201501013.htmLiu Y, Liu M X, Xu X T. Research on the typical collapse of Guizhou based on the discontinues deformation analysis[J]. Mountain Research, 2015, 33(1): 94-99(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201501013.htm [40] 冯振, 李滨, 贺凯. 近水平厚层高陡斜坡崩塌机制研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2014, 20(2): 123-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201402003.htmFeng Z, Li B, He K. Rock collapse mechanism on highsteep slope failure in subhorizontal thick bedded mountains[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2014, 20(2): 123-131(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201402003.htm -





 下载:
下载: