Ore genesis and vertical variations of ore-forming fluids in the Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Constraints from fluid inclusions, ore forming elements, and H-O-S-Pb isotopes
-
摘要:
大尹格庄金矿位于招平成矿带中段, 是胶东地区典型的构造蚀变岩型金矿床, 储量达到超大型规模, 但关于该矿床的成因类型尚存在较大争议。在详细野外地质调查的基础上开展了该矿床成因和成矿流体纵向变化特征研究。流体包裹体研究表明, 成矿流体为中温、低盐度、中低密度的H2O-CO2-NaCl±CH4体系。从成矿早期到晚期各阶段(Ⅰ~Ⅳ阶段)均一温度和盐度逐渐降低, 密度逐渐增加。氢氧同位素组成显示成矿流体早期以岩浆水为主, 后期有大气降水的混入, 主成矿阶段可能存在流体沸腾作用; 黄铁矿硫铅同位素组成表明成矿物质来源于深源壳幔混合岩浆。成矿过程和背景总体与胶东其他金矿床类似, 形成于克拉通破坏环境。浅部与深部流体和物质组成的对比研究表明, 在垂向纵深范围内成矿流体性质、金银成矿强度和金成色稳定一致, 金沉淀具有宽泛而稳定的环境, 指示大尹格庄金矿床深部仍然具有很大的成矿潜力和找矿空间。
Abstract:Objective The Dayingezhuang gold deposit in the middle of the Zhaoping metallogenic belt represents a typical altered-rock type deposit with a giant Au reserve of 283 tons on the Jiaodong Peninsula. The genetic type of the deposit is still controversial.
Methods Based on detailed field observations, ore genesis and variations in ore-forming fluids from different depths were investigated in this study.
Results Fluid inclusion studies show that the ore-forming fluids formed an H2O-CO2-NaCl±CH4 system with moderate temperature, low salinity, and moderate-low density. Furthermore, the temperatures and salinities decrease gradually from the early to late mineralization stages(Ⅰ-Ⅳ), but the opposite occurs at densities. Hydrogen and O isotopic compositions show that the ore fluids were dominated by magmatic water in the early stage, with subordinate meteoric water input during the late stages. Fluid boiling occurred possibly during the main mineralization stages. Sulfur and Pb isotopes of pyrite indicate that the ore-forming materials were derived from deep crust-mantle mixed magma. Overall, the mineralization process and tectonic setting are similar to those of the other Jiaodong gold deposits in a craton-destruction environment.
Conclusion Comprehensive comparisons of ore fluids, Au and Ag contents, and gold fineness between shallow and deep ores show that ore fluids and mineralization intensity are consistent throughout the deposit. Gold precipitation has a broad and stable environment, indicating the great potential for mineral exploration in deep spaces.
-
Key words:
- fluid inclusion /
- H-O-S-Pb isotopes /
- gold fineness /
- ore genesis /
- deep exploration /
- ore-forming fluid /
- Dayingezhuang
-
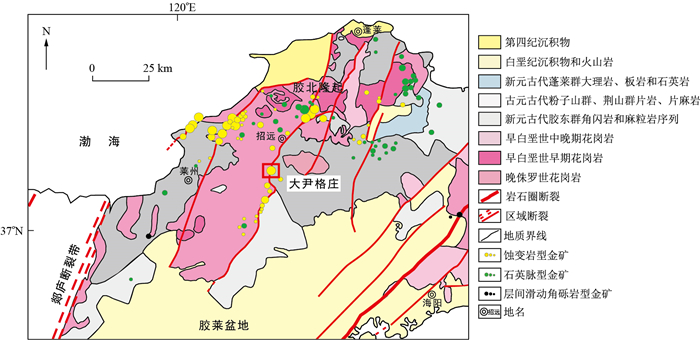
图 1 胶东区域地质图(据文献[36]修改)
Figure 1. Regional geological map of the Jiaodong Peninsula
图 2 大尹格庄金矿床地质简图(据文献[16]修改)
Figure 2. Geological map of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit
图 3 大尹格庄金矿床矿体地质图(据文献[15]修改)
Figure 3. Geological map of orebodies in the Dayingezhuang gold deposit
图 11 大尹格庄与胶东地区不同地质体铅同位素组成对比图(据文献[65]修改)
A.地幔;B.造山带;C.上地壳;D.下地壳
Figure 11. Lead isotopic compositions of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit compared to other geologic bodies in the Jiaodong province
表 1 大尹格庄矿床流体包裹体测温结果
Table 1. Characteristics and parameters of fluid inclusions in the Dayingezhuang gold deposit
成矿阶段 样品编号 深度/m 测定矿物 类型 Tm, CO2/℃ Tm, cl/℃ Th, CO2/℃ Tm, ice/℃ Th, TOT/℃ 盐度w(NaCleqv)/% 密度/(g·cm-3) 范围 均值 范围 均值 范围 均值 Ⅰ DYGZ-16-3 -94.6 石英 -10.1~ -2.1 -7.1 228.9~391.7 310.7 3.55~14.04 0.73~0.82 DYGZ-3 -213 -4.6~ -4.5 -4.2 310.7~365.9 330.7 5.71~7.31 0.67~0.74 DYGZ-21 -310 LH2O-VH2O -9.6~ -5.2 -7.3 316.2~445.6 361.2 8.14~13.51 0.53~0.82 DYGZ-7 -810 -10.6~ -3.6 -7.2 289.8~383.2 330.4 5.86~14.57 0.73~0.85 DYGZ-10 -456 -8.0~ -5.6 -6.9 280.0~389.0 333.0 8.68~11.70 0.70~0.84 DYGZ-10 -456 LH2O-LCO2-VCO2 -57.7~-56.6 6.7~7.9 23.3~31.1 27.2 270.1~352.8 346.0 4.08~6.29 Ⅱ DYGZ-4-2 -310 -9.0~ -3.5 -5.7 304.4~362.0 326.3 5.71~12.85 0.73~0.81 DYGZ-4-1 -310 -16.7~ -2.7 -7.1 288.0~385.0 332.2 4.49~19.99 0.71~0.91 DYGZ-5 -405 LH2O-VH2O -10.5~ -3.6 -6.0 288.0~348.5 319.5 5.86~14.46 0.68~0.85 DYGZ-11 -468 -14.3~ -4.6 -9.2 252.8~363.1 312.1 7.31~18.04 0.68~0.84 DYGZ-13 -538 -16.8~ -8.6 -12.3 210.6~386.6 309.8 12.96~20.07 DYGZ-18 -213 -10.2~ -2.1 -5.1 284.3~370.9 310.6 3.55~14.15 0.71~0.83 DYGZ-13 -538 LH2O-LCO2-VCO2 -59.0~-57.6 5.7~7.4 29.0~30.7 30.0 316.8~366.0 331.5 5.70~6.80 DYGZ-18 -213 -57.5~-57.1 6.2~6.6 29.8~31.1 30.6 280.0~298.1 284.6 6.20~6.60 Ⅲ DYGZ-16-2 -94.6 -8.5~ -3.1 -5.8 264.2~332.0 296.0 5.11~12.28 0.77~0.85 DYGZ-14 -100 LH2O-VH2O -8.6~ -2.4 -4.8 230.0~316.7 281.6 4.03~12.39 0.75~0.88 DYGZ-6 -405 -4.9~-8.0 -6.5 201.5~338.8 280.9 7.73~11.70 0.83~0.86 DYGZ-12 -540 -15.6~ -1.1 -9.2 209.0~360.0 297.7 1.91~19.13 DYGZ-12 -540 LH2O-LCO2-VCO2 -56.0~-55.6 7~8.5 19~24.1 21.7 262.0~289.0 276.4 7.00~8.50 Ⅳ DYGZ-1T -100 LH2O-VH2O -6.4~ -2.9 -4.2 159.8~261.8 200.5 4.80~9.73 0.85~0.94 DYGZ-16-1 -94.6 -6.7~ -4.6 -5.6 183.4~243.5 218.4 7.31~10.11 0.88~0.90 DYGZ-15-1 -100 -11.2~ -4.9 -9.4 179.9~267.4 237.8 7.73~15.17 0.89~0.91 注:Tm, CO2为固相CO2的溶化温度;Tm, cl为笼合物的溶化温度;Th, CO2为CO2的部分均一温度;Tm, ice为冰点温度;Th, TOT为完全均一温度;盐度、密度计算公式据文献[47] 表 2 大尹格庄金矿床氢氧同位素组成
Table 2. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions in the Dayingezhuang gold deposit
样品编号 成矿阶段 温度T/℃ δDV-SMOW/‰ δOV-SMOW/‰ δ18OH2O/‰ DYGZ-16-3 Ⅰ 324.5 -88.3 9.80 4.80 DYGZ-3 328.7 -92.5 12.8 7.92 DYGZ-21 353.8 -97.3 12.1 7.87 DYGZ-7 333.1 -90.3 11.2 6.44 DYGZ-10 336.8 -98.6 10.8 6.14 DYGZ-4-2 Ⅱ 308.1 -95.2 11.7 6.22 DYGZ-5 315.3 -93.4 12.1 6.84 DYGZ-11 334.2 -103.0 11.4 6.67 DYGZ-13 323.8 -102.0 12.2 7.18 DYGZ-18 320.5 -87.9 9.7 4.59 DYGZ-4-1 308.0 -94.9 8.7 3.22 DYGZ-1(D) Ⅲ 300.0 -81.8 8.8 2.75 DYGZ-16-2 304.3 -77.3 10.2 4.60 DYGZ-14 300.0 -84.4 10.5 4.77 DYGZ-6 299.0 -89.7 10.2 4.44 DYGZ-12 306.0 -81.5 10.0 4.46 DYGZ-15-1 Ⅳ 173.8 -87.3 10.8 -0.82 DYGZ-16-1 231.6 -87.8 12.7 4.32 DYGZ-1(T) 259.8 -87.4 8.6 1.44 注:T为流体包裹体均一温度;δ18OH2O采用1 000lnα石英-水=3.38×106T-2-3.40[38]换算 表 3 大尹格庄金矿床黄铁矿硫和铅同位素组成
Table 3. Sulfur and lead isotopic compositions of pyrite in the Dayingezhuang gold deposit
样品编号 成矿阶段 δ34SV-CDT/‰ 208Pb/204Pb 207Pb/204Pb 206Pb/204Pb μ ω DYGZ-16-3 Ⅰ 6.7 38.013 15.512 17.336 9.44 40.32 DYGZ-3 6.9 38.067 15.528 17.347 9.47 40.67 DYGZ-21 7.0 38.009 15.509 17.303 9.44 40.50 DYGZ-7 5.8 38.373 15.605 17.871 9.54 39.43 DYGZ-10 7.5 37.925 15.483 17.382 9.37 39.29 DYGZ-4-2 Ⅱ 5.9 38.020 15.511 17.306 9.44 40.55 DYGZ-5 5.3 38.115 15.540 17.371 9.49 40.86 DYGZ-11 7.6 38.105 15.527 17.431 9.45 40.26 DYGZ-18 4.7 38.040 15.525 17.306 9.47 40.79 DYGZ-4-1 6.3 37.996 15.508 17.306 9.44 40.40 DYGZ-1(D) Ⅲ 5.8 38.010 15.511 17.332 9.44 40.32 DYGZ-16-2 5.7 37.975 15.505 17.281 9.44 40.44 DYGZ-14 5.1 38.005 15.512 17.336 9.44 40.28 DYGZ-6 3.1 37.983 15.505 17.317 9.43 40.23 DYGZ-12 5.8 37.976 15.508 17.284 9.44 40.46 DYGZ-15-1 Ⅳ 4.4 38.044 15.525 17.327 9.47 40.67 DYGZ-16-1 3.4 38.027 15.523 17.299 9.47 40.76 DYGZ-1(T) 4.0 38.060 15.529 17.340 9.47 40.69 注: μ=238U/204Pb; ω=232Th/204Pb 表 4 大尹格庄金矿床不同阶段黄铁矿原位硫同位素组成
Table 4. Insitu S isotopic compositions of pyrite in the Dayingezhuang gold deposit
黄铁矿亚类 δ34SV-CDT/‰ 黄铁矿亚类 δ34SV-CDT/‰ 黄铁矿亚类 δ34SV-CDT/‰ Py1 6.00 Py2 6.20 Py2 7.42 Py1 7.05 Py2 5.90 Py2 6.74 Py1 7.43 Py2 5.99 Py3 6.41 Py1 7.26 Py2 7.07 Py3 6.47 Py1 5.81 Py2 6.47 Py3 6.52 Py1 7.13 Py2 6.76 Py3 6.41 Py2 7.14 Py2 6.77 Py3 6.49 Py2 7.17 Py2 6.40 Py3 6.26 Py2 6.95 Py2 6.64 Py3 6.29 Py2 6.98 Py2 7.01 Py3 6.40 Py2 6.95 Py2 7.04 Py3 6.03 Py2 7.10 Py2 6.56 Py3 6.18 表 5 大尹格庄矿石金及其他元素质量分数组成
Table 5. Compositions of Au and other elements in the Dayingezhuang gold deposit
分析元素含量单位 成矿阶段 Au* Au** Au Ag Cu Pb Zn wB/10-6 DYGZ-16-3 Ⅰ 0.056 — 0.056 3.36 60.8 2 160 4 610 DYGZ-3 4.48 — 4.48 14.65 942 132.5 35.0 DYGZ-21 — 12.20 12.20 20.20 700 1 090 34.0 DYGZ-7 0.029 — 0.029 1.81 10.1 64.1 16.0 DYGZ-10 1.155 — 1.16 2.81 5.50 70.7 19.0 DYGZ-4-2 Ⅱ 8.75 — 8.75 240 36 200 2 150 612 DYGZ-5 — 14.65 14.7 15.75 37.4 711 12.0 DYGZ-11 9.28 — 9.28 21.1 55.8 460 33.0 DYGZ-13 3.03 — 3.03 12.45 594 113.5 16.0 DYGZ-18 — 91.40 91.4 18.05 1 120 506 16.0 DYGZ-4-1 — 24.70 24.7 7.86 1 090 199 77.0 DYGZ-1(D) Ⅲ 3.57 — 3.57 6.87 78.1 714 43.0 DYGZ-16-2 — 182.5 182.5 610 1 210 50 800 585 DYGZ-14 9.99 — 9.99 92.6 6 990 200 000 384 DYGZ-6 — 28.60 28.6 85.5 7 800 1 315 20 DYGZ-12 — 112.5 112.5 830 6 980 41 500 291 DYGZ-15-1 Ⅳ — 43.7 43.7 111 2 470 2 870 28 DYGZ-16-1 — 23.2 23.2 109 6 110 1 700 3 670 DYGZ-1(T) — 22.7 22.7 238 4 100 7 770 87.0 注:“—”代表低于检出限; *电感耦合等离子体发射光谱分析法结果; **火试金-重量法结果;其他为等离子体发射光谱与等离子体质谱分析法结果 表 6 大尹格庄金矿床金矿物电子探针成分分析
Table 6. Composition of gold mineral in the Dayingezhuang gold deposit according to EPMA
样品编号 成矿阶段 Ag Te Fe S Au 总量 金成色 wB/% DYGZ-4 Ⅱ 21.82 0.00 0.31 0.04 76.51 98.77 778 DYGZ-4 24.06 0.00 1.37 0.10 74.42 99.99 756 DYGZ-4 23.55 0.08 0.94 0.09 74.27 99.02 759 DYGZ-4 25.14 0.05 1.82 0.09 73.30 100.44 745 DYGZ-4 15.21 0.01 2.05 0.23 80.74 98.39 842 DYGZ-4 15.14 0.00 1.18 0.04 82.45 98.92 845 DYGZ-4 12.74 0.05 0.71 0.07 84.91 98.60 870 DYGZ-4 10.80 0.25 0.90 0.06 87.99 100.19 891 DYGZ-13 19.14 0.21 0.22 0.09 79.10 98.76 805 DYGZ-13 21.89 0.01 0.60 0.12 75.44 98.11 775 DYGZ-13 21.67 0.08 0.32 0.05 76.94 99.10 780 DYGZ-13 21.81 0.15 0.63 0.06 75.83 98.64 777 DYGZ-13 19.82 0.00 1.79 0.13 80.05 101.93 802 DYGZ-13 17.18 0.20 0.85 0.07 79.93 98.44 823 DYGZ-12 Ⅲ 35.52 0.32 0.20 0.02 62.67 98.99 638 DYGZ-12 36.25 0.16 0.04 0.02 63.22 99.82 636 DYGZ-12 40.48 0.26 0.27 0.01 58.33 99.82 590 DYGZ-12 39.51 0.29 0.54 0.05 58.91 100.22 599 DYGZ-12 37.20 0.07 0.10 0.03 60.90 98.63 621 DYGZ-12 36.56 0.26 0.11 0.00 63.06 100.30 633 DYGZ-12 32.87 0.35 0.24 0.01 66.27 100.33 668 DYGZ-12 35.37 0.13 0.39 0.19 62.78 98.94 640 DYGZ-12 38.15 0.16 0.28 0.03 59.87 98.66 611 DYGZ-12 36.45 0.09 0.18 0.03 63.07 99.89 634 DYGZ-12 30.20 0.14 0.13 0.00 68.78 99.56 695 DYGZ-12 39.19 0.16 0.09 0.01 58.93 98.49 601 DYGZ-12 38.97 0.03 0.06 0.05 61.35 100.50 612 DYGZ-12 43.42 0.22 0.06 0.00 56.56 100.50 566 DYGZ-12 36.50 0.13 0.09 0.03 62.16 99.05 630 DYGZ-12 42.99 0.12 0.19 0.05 57.18 100.86 571 DYGZ-12 29.41 0.12 0.15 0.05 68.56 98.46 700 DYGZ-12 39.75 0.22 0.47 0.09 60.62 101.39 604 DYGZ-12 35.89 0.24 0.29 0.00 62.83 99.57 636 注:金成色计算方法: Au/(Au+Ag)×1 000,其中Au、Ag代表质量分数 -
[1] 宋明春, 林少一, 杨立强, 等. 胶东金矿成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(2): 215-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202002002.htmSONG M C, LIN S Y, YANG L Q, et al. Metallogenic model of Jiaodong Peninsula gold deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2020, 39(2): 215-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202002002.htm [2] DENG J, WANG Q, SANTOSH M, et al. Remobilization of metasomatized mantle lithosphere: A new model for the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2020, 55(2): 257-274. doi: 10.1007/s00126-019-00925-0 [3] 范宏瑞, 蓝廷广, 李兴辉, 等. 胶东金成矿系统的末端效应[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2021, 51(9): 1504-1523. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202109007.htmFAN H R, LAN T G, LI X H, et al. Conditions and processes leading to large-scale gold deposition in the Jiaodong province, eastern China[J]. Sciences China(Earth Sciences), 2021, 51(9): 1504-1523. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202109007.htm [4] MAO J W, WANG Y T, LI H M, et al. The relationship of mantle-derived fluids to gold metallogenesis in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Evidence from D-O-C-S isotope systematics[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2008, 33(3/4): 361-381. [5] GUO P, SANTOSH M, LI S. Geodynamics of gold metallogeny in the Shandong Province, NE China: An integrated geological, geophysical and geochemical perspective[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 24(3/4): 1172-1202. [6] 杨敏之, 吕古贤. 胶东绿岩带金矿地质地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996: 120-196.YANG M Z, Lü G X. The geochemical of gold desposits in Jiaodong greenstone belt[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1996: 120-196. (in Chinese) [7] 刘殿浩, 吕古贤, 张丕建, 等. 胶东三山岛断裂构造蚀变岩三维控矿规律研究与海域超大型金矿的发现[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(4): 162-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201504021.htmLIU D H, Lü G X, ZHANG P J, et al. A study of 3D ore-controlling of the tectonic altered rocks of the Sanshandao fault in Jiaodong Peninsula and the discovery of an offshore super-large gold deposit in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(4): 162-172. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201504021.htm [8] 王铁军, 刘晓阳, 林锐华, 等. 津巴布韦舒鲁圭透镜状铬铁矿成因[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2012, 27(4): 485-490. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201204014.htmWANG T J, LIU X Y, LIN R H, et al. Genesis of lenticular Cr deposits in Selugwe, Zimbabwe[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2012, 27(4): 485-490. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201204014.htm [9] 陈衍景. 造山型矿床、成矿模式及找矿潜力[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(6): 1181-1192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200606002.htmCHEN Y J. Orogenic-type deposits and their metallogenic model and exploration potential[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(6): 1181-1192. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200606002.htm [10] 蒋少涌, 戴宝章, 姜耀辉, 等. 胶东和小秦岭: 两类不同构造环境中的造山型金矿省[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(11): 2727-2738. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911004.htmJIANG S Y, DAI B Z, JIANG Y H, et al. Jiaodong and Xiaoqinling: Two orogenic gold provinces formed in different tectonic settings[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(11): 2727-2738. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911004.htm [11] GROVES D I, SANTOSH M. The giant Jiaodong gold province: The key to a unified model for orogenic gold deposits?[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2016, 7(3): 409-417. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2015.08.002 [12] 孙丰月, 石准立. 煌斑岩与某些热液矿床关系新探: 兼论幔源C-H-O流体的分异演化[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 1995, 10(2): 72-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK502.006.htmSUN F Y, SHI Z L. The relationship between lamprophyres and some hydrothermal deposits: Implications foe a differentiation model of mantle-derived C-H-O fluids[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 1995, 10(2): 72-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK502.006.htm [13] 翟明国, 范宏瑞, 杨进辉, 等. 非造山带型金矿: 胶东型金矿的陆内成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(1): 85-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200401006.htmZHAI M G, FAN H R, YANG J H, et al. Large-scale cluster of gold deposits in East Shandong: Anorogenic metallogenesis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(1): 85-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200401006.htm [14] 朱日祥, 范宏瑞, 李建威, 等. 克拉通破坏型金矿床[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 45(8): 1153-1168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201508006.htmZHU R X, FAN H R, LI J W, et al. Decratonic gold deposits[J]. Sciences China(Earth Sciences), 2015, 45(8): 1153-1168. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201508006.htm [15] 张瑞忠, 王中亮, 王偲瑞, 等. 胶西北大尹格金矿床成矿机理: 载金黄铁矿标型及硫同位素地球化学约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(8): 2451-2464. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201608015.htmZHANG R Z, WANG Z L, WANG S R, et al. Metallognic mechanism of Dayingezhuang gold deposit, northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula: Geochemistry constrains from the gold bearing pyrite typomorph and sulfur isotope[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(8): 2451-2464. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201608015.htm [16] YANG L Q, DENG J, GOLDFARB R J, et al. 40Ar/39Ar geochronological constraints on the formation of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit: New implications for timing and duration of hydrothermal activity in the Jiaodong gold province, China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(4): 1469-1483. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.07.001 [17] 魏瑜吉, 邱昆峰, 郭林楠, 等. 胶东大尹格庄金矿床成矿流体特征与演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(6): 1821-1832.WEI Y J, QIU K F, GUO L N, et al. Characteristics and evolution of ore-fluids of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(6): 1821-1832. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] YUAN Z Z, LI Z K, ZHAO X F, et al. New constraints on the genesis of the giant Dayingezhuang gold(silver) deposit in the Jiaodong district, North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 112: 103038. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103038 [19] 张良, 刘跃, 李瑞红, 等. 胶东大尹格庄金矿床铅同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9): 2468-2480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409002.htmZHANG L, LIU Y, LI R H, et al. Lead isotope geochemistry of Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(9): 2468-2480. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409002.htm [20] 戴雪灵. 山东招远大尹格庄金矿成岩: 成矿机理研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.DAI X L. Study on petrogenesic-metallogenic mechanism in Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Zhaoyuan Country, Shandong Province[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] 王枫. 胶东大尹格庄金矿黄铁矿成因矿物学与深部远景研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012.WANG F. Pyrite genetic mineralogy and deep prospects of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit in Jiaodong region[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] 刘育, 杨立强, 郭林楠, 等. 胶东大尹格庄金矿床成矿流体组成[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9): 2507-2517.LIU Y, YANG L Q, GUO L N, et al. Composition of ore-forming fluids in the Dayingezhuang gold deposit of the Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(9): 2507-2517. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 卢晶. 胶东大尹格庄金矿成矿流体特征及成矿年代学研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012.LU J. The ore-forming fluids characteristics and mineralogentic epoch of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit in Jiaodong region[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 姜晓辉, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 等. 胶东三山岛金矿中深部成矿流体对比及矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(5): 1327-1340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105009.htmJIANG X H, FAN H R, HU F F, et al. Comparative stuidies of fluid inclusion in different depths and ore genesis of the Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(5): 1327-1340. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105009.htm [25] CRAW D, UPTON P, HORTON T, et al. Migration of hydrothermal systems in an evolving collisional orogen, New Zealand[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2013, 48(2): 233-248. doi: 10.1007/s00126-012-0421-8 [26] WEN B, FAN H, HU F, et al. Fluid evolution and ore genesis of the giant Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China: Constrains from geology, fluid inclusions and H-O-S-He-Ar isotopic compositions[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 171: 96-112. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.01.007 [27] DENG J, ZHAI Y S, WANG J P, et al. Shear alteration, mass transfer and gold mineralization: An example from Jiaodong ore deposit concentrating area, Shandong, China[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2000, 11(3): 281-287. [28] DENG J, YANG L, LI R, et al. Regional structural control on the distribution of world-class gold deposits: An overview from the giant Jiaodong gold province, China[J]. Geological Journal, 2019, 54(1): 378-391. doi: 10.1002/gj.3186 [29] QIU K, YU H, WU M, et al. Discrete Zr and REE mineralization of the Baerzhe rare-metal deposit, China[J]. American Mineralogist, 2019, 104(10): 1487-1502. doi: 10.2138/am-2019-6890 [30] GOLDFARB R J, GROVES D I, GARDOLL S. Orogenic gold and geologic time: A global synthesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2001, 18(1/2): 1-75. [31] 郭敬辉, 陈福坤, 张晓曼, 等. 苏鲁超高压带北部中生代岩浆侵入活动与同碰撞-碰撞后构造过程: 锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(4): 1281-1301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200504025.htmGUO J H, CHEN F K, ZHANG X M, et al. Evolution of syn-to post-collisional magmatism from north Sulu UHP belt, eastern China: Zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2005, 21(4): 1281-1301. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200504025.htm [32] YANG J H, CHUNG S L, WILDE S A, et al. Petrogenesis of post-orogenic syenites in the Sulu Orogenic Belt, East China: Geochronological, geochemical and Nd-Sr isotopic evidence[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 214(1/2): 99-125. [33] 苗来成, 罗镇宽, 黄佳展, 等. 山东招掖金矿带内花岗岩类侵入体锆石SHRIMP研究及其意义[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 1997, 40(3): 207-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199703002.htmMIAO L C, LUO Z K, HUANG J Z, et al. Zircon sensitive high resolution ion microprobe(SHRIMP) study of granitoid intrusions in Zhaoye gold belt of Shandong Province and its implications[J]. Science China(Earth Sciences) 1997, 40(3): 207-213. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199703002.htm [34] WANG L G, QIU Y M, MCNAUGHTON N J, et al. Constraints on crustal evolution and gold metallogeny in the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, China, from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon studies of granitoids[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 1998, 13(1): 275-291. [35] 张田, 张岳桥. 胶东半岛中生代侵入岩浆活动序列及其构造制约[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007, 13(2): 323-336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200702014.htmZHANG T, ZHANG Y Q. Geochronological sequence of Mesozoic intrusive magmatism in Jiaodong Peninsula and its tectonic constraints[J]. Geology Journal of China University, 2007, 13(2): 323-336. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200702014.htm [36] YANG L Q, DENG J, WANG Z, et al. Relationships between gold and pyrite at the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Implications for gold source and deposition in a brittle epizonal environment[J]. Economic Geology and the Bulletin of the Society of Economic Geologists, 2016, 111(1): 105-126. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.111.1.105 [37] 李金祥. 胶东西北部招平断裂带构造特征与成矿[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2005.LI J X. Study on the structural nature and minerlization of Zhaoping fault belt in northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] 张志航. 胶东招-平断裂带中段金矿床地质特征及找矿预测[D]. 南昌: 东华理工大学, 2015.ZHANG Z H. Geological characteristic of gold deposit and prospecting prediction in the middle of Zhaoping fault zone, Jiaodong[D]. Nanchang: East China Institution of Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) [39] 于昆. 招平断裂带金矿床岩石地球化学特征及其地质意义[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2014.YU K. Geochemical characteristics of the gold deposits on Zhaoping fault zone and its implications[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract) [40] 张瑞忠. 招平金矿带构造控矿机理及深部成矿预测[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.ZHANG R Z. Structural control on gold minerlization and deep metallogenic forecast in Zhaoping gold belt, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) [41] 林祖苇. 胶东玲珑金矿田石英脉型与蚀变岩型矿体黄铁矿矿物学和地球化学的对比及对成因的指示[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2019.LIN Z W. A comparative stude on pyrite mineralogy and geochemistry of vein type and dissemination type of gold mineralization in the Linglong gold ore field, Jiaodong: Implications for ore genesis[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) [42] YANG K F, FAN H, SANTOSH M, et al. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust: Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of Late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2012, 146/147: 112-127. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.035 [43] HOU M, JIANG Y, JIANG S, et al. Contrasting origins of Late Mesozoic adakitic granitoids from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, east China: Implications for crustal thickening to delamination[J]. Geological Magazine, 2007, 144(4): 619-631. doi: 10.1017/S0016756807003494 [44] 梁平, 祝培刚, 祝德成, 等. 胶西北大尹格庄斑状花岗岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 37(4): 22-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDKY201804003.htmLIANG P, ZHU P G, ZHU D C, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significal of porphyritic granite in Dayingezhuang, northwestern Jiaodong[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science), 2018, 37(4): 22-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDKY201804003.htm [45] 梁亚运, 刘学飞, 李龚健, 等. 胶东地区脉岩成因与金成矿关系的研究: 年代学及Sr-Nd-Pb同位素的约束[J]. 地质科技情报, 2014, 33(3): 10-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201403003.htmLIANG Y Y, LIU X F, LI G J, et al. Petrogenesis and connection with gold deposits of dikes in Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern of North China Craton: Constraint on geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb isotope[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2014, 33(3): 10-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201403003.htm [46] YANG L Q, GUO L N, WANG Z L, et al. Timing and mechanism of gold mineralization at the Wang'ershan gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 88: 491-510. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.06.027 [47] BODNAR R J. Revised equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H2O-NaCl solutions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(3): 683-684. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90378-A [48] ROEDDER E. Fluid inclusions[M]. Chantilly: Mineralogical Society of America, 1984. [49] XIE W, ZENG Q, ZHOU L, et al. Ore genesis of the Narenwula quartz-vein type W polymetallic deposit in the southern Great Xing'an Range W belt, NE China: Constraints from wolframite geochronology and individual fluid inclusion analysis[J]. Ore Geologr Reviews, 2022, 149: 105100. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.105100 [50] Van den KERKHOF A M, HEIN U F. Fluid inclusion petrography[J]. Lithos, 2001, 55(1/4): 27-47. [51] CLAYTON R N, O'NEIL J R, MAYEDA T K. Oxygen isotope exchange between quartz and water[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1972, 77(17): 3057-3067. doi: 10.1029/JB077i017p03057 [52] 杨忠芳, 徐景奎, 赵伦山, 等. 胶东区域地壳演化与金成矿作用地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998.YANG Z F, XU J K, ZHAO L S, et al. Jiaodong regional crustal evolution and gold mineralization geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1998. (in Chinese) [53] 李兆龙, 杨敏之. 胶东金矿床地质地球化学[M]. 天津: 天津科学技术出版社, 1993.LI Z L, YANG M Z. The geology and geochemistry of gold deposits in Jiaodong region[M]. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Press, 1993. (in Chinese) [54] 林文蔚, 殷秀兰. 胶东金矿成矿流体同位素的地质特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 1998, 17(3): 58-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW803.006.htmLIN W W, YIN X L. Isotope geological characteristics of mineralzing fluids of gold deposits in Jiaodong area[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 1998, 17(3): 58-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW803.006.htm [55] 张旭, 李胜荣, 卢晶, 等. 山东招远金翅岭金矿床H-O-He-Ar同位素组成及其对成矿流体示踪的研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2012, 32(1): 40-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201201006.htmZHANG X, LI S R, LU J, et al. H-O-He-Ar isotopic compositions of fluid inclusions for tracing the source of ore-forming fluids of Jinchiling gold deposit, northwest Jiaodong area[J]. Miner. Petrol., 2012, 32(1): 40-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201201006.htm [56] TAYLOR H P. The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal, alteration and ore deposition[J]. Econ. Geol., 1974, 69(6): 843-883. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.843 [57] YANG L Q, DENG J, GUO C, et al. Ore-forming fluid characteristics of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China[J]. Resource Geology, 2009, 59(2): 181-193. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-3928.2009.00089.x [58] 盛夏, 张达, 阙朝阳, 等. 滇东南洒西钨铍矿床成矿流体来源和演化: 来自流体包裹体和H-O同位素证据[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 158-169. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0103SHENG X, ZHANG D, QUE C Y, et al. Sources and evolution of ore-forming fluids from the Saxi tungsten-beryllium deposit in southeastern Yunnan: Evidence from fluid inclusions and H-O isotopes[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 158-169. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0103 [59] 张七道, 肖长源, 李致伟, 等. 黔西北普宜地区富关键金属元素硫铁矿地质、地球化学和S同位素特征及其对成因的约束[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 149-164. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0086ZHANG Q D, XIAO C Y, LI Z W, et al. Geological, geochemical and sulfur isotopic characteristics of critical metal-enriched pyritic ore in the Puyi area, northwest Guizhou Province: Constrains on the genesis of the deposit[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 149-164. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0086 [60] 黄德业. 胶东金矿成矿系列硫同位素研究[J]. 矿床地质, 1994, 13(1): 75-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ401.007.htmHUANG D Y. Sulfur isotope studies of the metallogenic series of gold deposits in Jiaodong(East Shandong) area[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1994, 13(1): 75-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ401.007.htm [61] 张竹如, 陈世桢. 胶东金成矿域胶莱盆地中超大型金矿床找矿远景[J]. 地球化学, 1999, 28(3): 203-212. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX199903000.htmZHANG Z R, CHEN S Z. Superlarge gold deposit exploration perspective in Jiaolai Basin of Jiaodong gold metallogenetic domain[J]. Geochimica, 1999, 28(3): 203-212. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX199903000.htm [62] 王义文, 朱奉三, 宫润谭. 构造同位素地球化学: 胶东金矿集中区硫同位素再研究[J]. 黄金, 2002, 23(4): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ200204000.htmWANG Y W, ZHU F S, GONG R T. Tectonic isotope geochemistry: Further study on sulphur isotope of Jiaodong gold concentration area[J]. Gold, 2002, 23(4): 1-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ200204000.htm [63] 邢树文, 孙景贵, 李东旭, 等. 胶东晚中生代金矿成矿的硫同位素组成及热动力源[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2003, 23(2): 141-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200302006.htmXING S W, SUN J G, LI D X, et al. The sulfur isotopic composition and dynamothermal source of Mesozoic gold mineralization, Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Journal of Jilin University, 2003, 23(2): 141-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200302006.htm [64] WAN Y, SONG B, LIU D, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of Palaeoproterozoic metasedimentary rocks in the North China Craton: Evidence for a major Late Palaeoproterozoic tectonothermal event[J]. Precambrian Research, 2006, 149(3/4): 249-271. [65] ZARTMAN R E, DOE B R. Plumbotectoincs-themodel[J]. Tectonophysics, 1981, 75(5): 135-162. [66] DOE B R, ZARTMAN R E. Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1979: 22-70. [67] 梁俊红, 刘海波, 王建国, 等. 自然金的标型及成色特征在金矿床研究中的意义[J]. 黄金, 2000, 21(12): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ200012000.htmLIANG J H, LIU H B, WANG J G, et al. The meaning of the typomorphic charateristics of native gold and its fineness feature in researches of gold deposit[J]. Gold, 2000, 21(12): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ200012000.htm [68] MORRISON G W, ROSE W J, JAIRETH S. Geological and geochemical controls on the silver content(fineness) of gold in gold-silver deposits[J]. Ore Geologogy Reviews, 1991, 6(4): 333-364. doi: 10.1016/0169-1368(91)90009-V [69] SEWARD T M. The hydrothermal geochemistry of gold: Gold metallogeny and exploration[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 1993: 37-62. [70] SEWARD T M. The transport and deposition of gold in hydrothermal systems[C]//Anon. Gold'82: The geology, geochemistry and genesis of gold deposits(Symposium). [S. l.]: [s. n.], 1984: 165-181. -





 下载:
下载: