Geological characteristics of the Lower Carboniferous Heshirafu Formation reef in the Artashi section in the Southwest Tarim Basin
-
摘要:
生物礁研究对沉积环境与油气勘探具有重要意义, 但目前对于塔西南石炭系生物礁研究相对较少。深入解析了塔西南阿尔塔什剖面早石炭世维宪期中-晚期和什拉甫组生物礁地质特征, 并在此基础上深入探讨了塔西南早石炭世沉积环境以及该生物礁在全球早石炭世生物礁演化中的意义。结果表明: 该套生物礁的造礁生物主要为各种群体珊瑚以及少量单体珊瑚, 附礁生物主要为棘皮动物等, 造礁和附礁生物类型相对单一。礁体的生长受陆源物质的影响而中断, 这和塔西南山前早石炭世频繁的海平面变化有关。该生物礁是继晚泥盆世生物大灭绝后, 伴随着维宪期中-晚期气候变暖、全球海平面上升, 全球范围内后生动物骨架礁开始复苏的产物之一, 该生物礁的地质特征在全球早石炭世维宪期生物礁中具有普遍性。此外, 根据对阿尔塔什剖面和什拉甫组以及相邻的库山河剖面罕铁热克组的整体沉积相分析, 推测早石炭世维宪期, 受当时全球海平面上升的影响以及塔西南地区在早石炭世开始形成被动大陆边缘并开始下沉, 使得塔西南地区从早石炭世开始发生自南西向北东方向的海侵, 在塔西南山前也逐渐形成了狭长的台地边缘相带, 这有利于生物礁的发育, 并在和什拉甫组时期自陆向海形成了"滨岸相-泻湖相-台地边缘相-斜坡相-陆棚相"的沉积体系。沉积体系的划分不仅可以为塔西南地区石炭纪古气候、古环境研究而且可以为其油气勘探提供参考。
Abstract:Objective Research on reefs is highly important for determining sedimentary environments and for oil and gas exploration, but relatively few studies have been conducted on Carboniferous reefs in the Southwest Tarim Basin.
Methods Early Carboniferous reefs of the Heshirafu Formation in the Artashi section in the Southwest Tarim Basin formed in the Middle-Late Visean section of the Early Carboniferous. Reef-building organisms and accessory organisms were not quite diversified; the former mainly consisted of colonial corals of different kinds and solitary corals of a small number, and the latter were mostly echinoderms.
Results Their growth was suspended due to less supply of terrigenous materials largely related to the frequent sea level changes in the Early Carboniferous in the piedmont structures of the Southwest Tarim Basin. These reefs are among the products of the recovery of metazoan skeleton reefs across the globe after the Late Devonian mass extinction; their occurrence was accompanied by mid- to late-stage Visean climate warming and global sea level rise. These reefs are common in the Early Carboniferous Visean reefs worldwide. In addition, according to the overall sedimentary facies of the Heshirafu Formation in the Artashi section and the adjacent Hantiereke Formation in the Kushanhe section, it is speculated that a transgression occurred from southwest to northeast in the Visean period of the Early Carboniferous in the Southwest Tarim Basin when the global sea level was rising and a passive continental margin was simultaneously forming and beginning to sink. As a result, a narrow platform margin facies belt gradually took shape in the piedmont structure of the Southwest Tarim Basin. This belt was conducive to the development of biological reefs. Then, when the Heshirafu Formation formed, a depositional system of "shore facies-lagoon facies-platform margin facies-slope facies-continental shelf facies" developed in a seaward direction.
Conclusion The classification of sedimentary systems can provide a reference for Carboniferous sedimentary environments and oil and gas exploration in the Southwest Tarim Basin.
-
Key words:
- Artashi /
- reef /
- Early Carboniferous /
- coral /
- sea level /
- Heshirafu Formation
-
图 2 塔西南艾特沟-达木斯沟下石炭统和什拉甫组综合柱状图(据文献[17]修改)
Figure 2. Synthetic histogram of the Lower Carboniferous Heshirafu Formation in Aitegou-Damusigou, southwest Tarim Basin
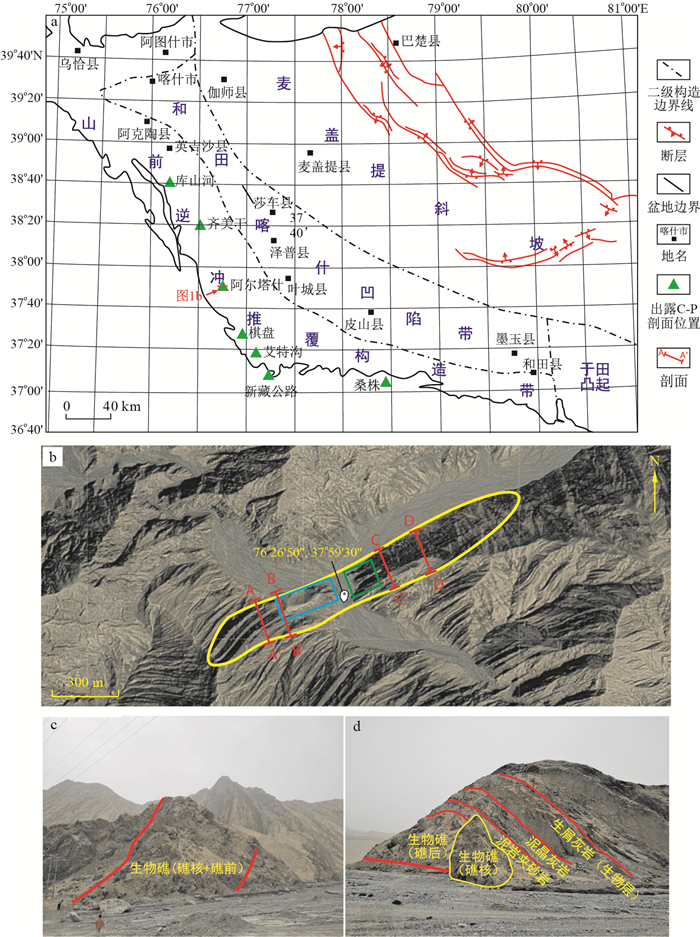
图 5 生物礁微相结构剖面图(剖面位置见图 1b)
Figure 5. Profiles of microfacies structures of the reef
图 6 阿尔塔什剖面和什拉甫组生物礁颗粒灰岩
a.砂屑灰岩野外照片,礁前高能带;b.含生屑砂屑灰岩,可见少量腕足类,礁前高能带;c.砂屑灰岩,局部核形石富集(红色圈部分),礁前高能带;d.生屑灰岩,可见腕足壳体(黄色圈部分),礁基;e.生屑灰岩,可见棘皮生屑和少量有孔虫以及大量无定形生屑,礁前高能带,单偏光;f.核形石灰岩镜下照片,单偏光;g.生屑灰岩,可见溶缝,单偏光;h.生屑灰岩,可见大量棘皮生屑和少量类,单偏光
Figure 6. Granular limestone of the Lower Carboniferous Heshirafu Formation reef in the Artashi section
图 7 阿尔塔什剖面和什拉甫组生物礁群体珊瑚
a.柱丛珊瑚(Cionodendron)野外照片;b.轴管珊瑚(Aulina)野外照片;c.原达勒姆珊瑚(Protodurhamina)野外照片;d.刺毛珊瑚(Chaetetes),周围可见砂屑颗粒,单偏光;e.原达勒姆珊瑚(Protodurhamina),个体间为粉屑和细砂屑充填,单偏光;f.原达勒姆珊瑚(Protodurhamina),个体间为灰泥充填,部分灰泥有重结晶现象,单偏光
Figure 7. Colonial corals of the Lower Carboniferous Heshirafu Formation reef in the Artashi section
表 1 阿尔塔什剖面下石炭统不同岩石类型碳氧同位素测试结果
Table 1. Carbon and oxygen isotope results of different lithologies in the Lower Carboniferous of the Artashi section
组 岩性 δ13CPDB/‰ δ18OPDB/‰ Z 和什拉甫组 泥晶灰岩 -2.566 -8.828 117.65 泥晶灰岩 1.439 -10.051 125.24 泥晶灰岩 1.346 -9.213 125.47 泥晶灰岩 -1.539 -5.427 121.45 泥晶灰岩 2.084 -8.118 127.53 泥晶灰岩 3.361 -8.456 129.97 泥晶灰岩 2.349 -6.222 129.01 克里塔克组 砂屑云岩 0.024 -10.857 121.94 泥晶灰岩 -1.113 -10.999 119.54 砂屑生屑云岩 0.009 -11.262 121.71 灰质云岩 0.099 -10.691 122.18 泥晶灰岩 -2.919 -11.846 115.42 -
[1] 王玉珏, 梁昆, 陈波, 等. 晚泥盆世F-F大灭绝事件研究进展[J]. 地层学杂志, 2020, 44(3): 277-298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ202003006.htmWANG Y J, LIANG K, CHEN B, et al. Research progress in the Late Devonian F-F massextinction[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2020, 44(3): 277-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ202003006.htm [2] YAN Z, LIU J B, JIN X C, et al. Construction model and paleogeographic distribution of Late Pennsylvanian phylloid algal microbial reefs: A case study in eastern Inner Mongolia, North China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2019, 383: 181-194. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2019.02.007 [3] ANDERSON K D, GEORGE A D. Evolution of Pennsylvanian inner-platform phylloid algal reef mounds, Pha Nok Khao Platform, northeastern Thailand[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 537: 109380. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.109380 [4] 李金梅, 巩恩普, 孙宝亮, 等. 贵州紫云晚石炭世叶状藻礁灰岩微相特征与沉积环境的研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(1): 26-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201001005.htmLI J M, GONG E P, SUN B L, et al. Microfacies and sedimentary environment of Late Carboniferous phylloid algal reef limestone in Ziyun, Guizhou[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(1): 26-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201001005.htm [5] 孙宝亮, 巩恩普, 李金梅, 等. 贵州紫云上石炭统叶状藻礁灰岩的成岩作用[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(1): 43-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201201005.htmSUN B L, GONG E P, LI J M, et al. Diagenesis of the Upper Carboniferous phylloid algal reef limestone in Ziyun County, Guizhou[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(1): 43-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201201005.htm [6] ZHANG Y L, GONG E P, WILSON M A, et al. A large coral reef in the Pennsylvanian of Ziyun County, Guizhou(South China): The substrate and initial colonization environment of reef-building corals[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 37(4): 335-349. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.09.002 [7] YAO L, WANG X D. Distribution and evolution of Carboniferous reefs in South China[J]. Palaeoworld, 2016, 25(3): 362-376. doi: 10.1016/j.palwor.2015.12.001 [8] GONG E P, ZHANG Y L, GUAN C Q, et al. The Carboniferous reefs in China[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2012, 1(1): 27-42. [9] 汪峰, 陈世悦, 马帅, 等. 柴达木盆地东北缘早石炭世生物礁发育特征及成礁模式[J]. 特种油气藏, 2017, 24(3): 37-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2017.03.007WANG F, CHEN S Y, MA S, et al. Developing feature and forming mode of Early Carboniferous reefs in NE margin of the Qaidam Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2017, 24(3): 37-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2017.03.007 [10] 王志金, 陈世悦, 马帅, 等. 柴达木盆地东北缘石炭系生物礁发育特征及其地质意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(6): 1177-1185. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201706009.htmWANG Z J, CHEN S Y, MA S, et al. Carboniferous organic reef development characteristics and geological significance in northeast margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(6): 1177-1185. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201706009.htm [11] 张新勇, 张雄华, 赵志刚, 等. 新疆阿合奇地区石炭系巴什索贡组珊瑚化石及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(1): 14-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201701002.htmZHANG X Y, ZHANG X H, ZHAO Z G, et al. Carboniferous Bashsogong Formation Coral fossils and their geological significance in Aheqi area, Xinjiang[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(1): 14-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201701002.htm [12] 王庆同, 陈伟, 马锦龙, 等. 新疆阿合奇县石炭系别根他乌组孢粉化石的发现及地质意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(3): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201703002.htmWANG Q T, CHEN W, MA J L, et al. Discovery of sporopollen fossils of Carboniferous Biegengtawu Formation in Aheqi, Xinjiang, and its geological significance[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(3): 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201703002.htm [13] 要乐, 黄兴, 王秋来, 等. 新疆东部托克逊马鞍桥剖面桑树园组刺毛-珊瑚礁的时代[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2019, 36(4): 362-369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGT201904006.htmYAO L, HUANG X, WANG Q L, et al. Age of the Chaetetid-Coral reef from the Sangshuyuan Formation at the Maanqiao section in Toksun County, eastern Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2019, 36(4): 362-369. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGT201904006.htm [14] 巩高阳, 张尚锋, 罗顺社, 等. 塔里木盆地西南缘生物礁特征: 以阿尔塔什剖面石炭系和什拉甫组为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2023, 39(4): 66-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT202304007.htmGONG G Y, ZHANG S F, LUO S S, et al. Characteristics of Carboniferous reef in Heshirafu Formation at Altash section in the southwestern margin of Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2023, 39(4): 66-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT202304007.htm [15] 李世臻, 康志宏, 邱海峻, 等. 塔里木盆地西南坳陷油气成藏模式[J]中国地质, 2014, 41(2): 387-398. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.02.007LI S Z, KANG Z H, QIU H J, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation modes of the Southwest Depression in Tarim Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(2): 387-398. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.02.007 [16] 陈中强. 塔里木盆地西南缘和什拉甫组的微地层分析: 点断加积旋回理论的应用[J]. 沉积学报, 1995, 13(增刊1): 38-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB5S1.004.htmCHEN Z Q. The application of punctuated aggradational cycle sequences to the analysis of the microstrata of the Visean Heshirafu Formation, SW Tarim, NW China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1995, 13(S1): 38-46. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB5S1.004.htm [17] 黄智斌, 钟瑞, 杜治利, 等. 叶城凹陷周缘地表地质综合研究[R]. 新疆库尔勒: 中国石油天然气股份有限公司塔里木油田分公司, 2012.HUANG Z B, ZHONG R, DU Z L, et al. Comprehensive study of surface geology around the Yecheng Depression[R]. Korla, Xinjiang: Tarim Oilfield Branch of CNPC, 2012. (in Chinese) [18] TANG Y, YE X Y, WANG X T, et al, A synthesis of Carboniferous stratigraphy in Xinjiang, Northwest China with emphasis on regional and global correlations[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2023, 241: 105476. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2022.105476 [19] CUMINGS E R. Reefs or bioherms?[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 1932, 43: 331-352. doi: 10.1130/GSAB-43-331 [20] 何登发. 中国多旋回叠合沉积盆地的形成演化、地质结构与油气分布规律[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(6): 24-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202206003.htmHE D F. Multi-cycle superimposed sedimentary basins in China: Formation, evolution, geological framework and hydrocarbon occurrence[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(6): 24-59. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202206003.htm [21] 马青, 马涛, 杨海军, 等. 塔里木盆地上泥盆统-下石炭统滨岸-混积陆棚三级层序发育特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(4): 666-674. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201904005.htmMA Q, MA T, YANG H J, et al. Development characteristics of the third-order sequence of Upper Devonian-Lower Carboniferous shore-mixed shelf in Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(4): 666-674. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201904005.htm [22] 邓发亮, 刘希军, 余红霞, 等. 晚泥盆世大陆风化作用增强及其海洋环境效应: 来自华南碳酸盐岩锶同位素的制约[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 207-214. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0071DENG F L, LIU X J, YU H X, et al. Enhanced continental weathering and its marine environmental effects in the Late Devonian: Constraints from strontium isotopes in carbonate rocks in South China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 207-214. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0071 [23] 白莹, 李建忠, 刘伟, 等. 塔里木盆地西北部下寒武统白云岩特征及多重白云石化模式[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(9): 1174-1191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202109005.htmBAI Y, LI J Z, LIU W, et al. Characteristics and multiple dolomitization mode of the Lower Cambrian dolomite reserveoir, northwestern Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(9): 1174-1191. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202109005.htm [24] 巩恩普, 黄文韬, 关长庆, 等. 石炭纪生物礁与晚古生代冰期的耦合关系[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(6): 1671-1692. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202106002.htmGONG E P, HUANG W T, GUAN C Q, et al. The coupled relationship between Carboniferous reefs and the Late Paleozoic iceage[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(6): 1671-1692. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202106002.htm [25] 林宝玉. 皱纹珊瑚与异形珊瑚[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1995: 512-521.LIN B Y. Monography of Palaeozoic corals Rugosa and Heterocorallia[M]. Beijing: The Geological Publishing House, 1995: 512-521. (in Chinese) [26] 陈晓红, 巩恩普, 王铁晖, 等. 广西田林县下垌村石炭纪早期珊瑚礁基本特征及其沉积环境分析[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(5): 597-608. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201305001.htmCHEN X H, GONG E P, WANG T H, et al. The basic characteristics of Early Carboniferous Coral reef at Xiadong Village in Tianlin, Guangxi, and its sedimentary environment[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(5): 597-608. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201305001.htm [27] 杨大勇, 巩恩普, 陈晓红, 等. 贵州、广西石炭纪晚期生物礁群落生态系统对比[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 35(1): 107-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDX201401025.htmYANG D Y, GONG E P, CHEN X H, et al. Comparison of the Late Carboniferous reef community ecosystem in Guizhou and Guangxi[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2014, 35(1): 107-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBDX201401025.htm [28] YAO L Y, ARETZ M. Upper Visean(Mississippian) metazoanmicrobial reefs from Guangxi, South China: Insights regarding reef recovery after the End-Devonian extinction[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 560: 109994. [29] 巩恩普, 杨大勇, 陈晓红, 等. 广西田林浪平地区晚石炭世生物礁古生态特征[J]. 地质论评, 2014, 60(3): 515-528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201403004.htmGONG E P, YANG D Y, CHEN X H, et al. The Late Carboniferous reefs palaeoecology characteristics of Langping, Tianlin County, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region[J]. Geological Review, 2014, 60(3): 515-528. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201403004.htm [30] MAILLET M, HUANG W T, MIAO Z W, et al, Coral reefs and growth dynamics of a low-angle Carboniferous platform: Records from Tianlin, southern China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2020, 396: 105550. [31] KERSHAW S, MUNNECKE A, JAROCHOWSKA E. Understanding Palaeozoic stromatoporoid growth[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 187: 53-76. [32] JEON J, VINN O, LIANG K, et al. Stromatoporoid-coral/tub-eworm intergrowths in the lowermost Silurian Varbola Formation of Estonia: First evidence of competitive interaction[J]. Lethaia, 2022, 55(2): 1-13. [33] WOLNIEWICZ P. From lagoons to mud mounds: Palaeoecology of the Givetian to Frasnian stromatoporoids from the Holy Cross Mountains, Poland[J]. Lethaia, 2020, 54(3): 378-398. [34] VINN O. Symbiosis in Late Devonian-Mississippian corals: A review[J]. Palaeobio Palaeoenv, 2017, 97: 723-729. [35] YAO L, ARETZ M, WIGNALL P B, et al. The longest delay: Reemergence of coral reef ecosystems after the Late Devonian extinctions[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 203: 103060. -





 下载:
下载: