Hydrocarbon generation potential and oil source comparison of source rocks in the central and western regions of Xihu Depression
-
摘要:
西湖凹陷作为中国东部油气勘探主战场,一直以来都受到油气地质学家们的广泛关注。前人对西湖凹陷油气资源的研究主要集中在深部地层(平湖组及其下伏层),而对中浅层系(花港组及其上覆层)烃源岩的关注度相对较少。近年来已有勘探发现西湖凹陷中浅层系具有规模成藏的潜力,针对西湖凹陷烃源岩开展研究,利用多项地球化学测试手段分别分析了西湖凹陷中西部地区的烃源岩生烃潜力和生物标志化合物特征。结果显示:西湖凹陷煤和炭质泥岩的生烃潜力好,而泥质烃源岩生烃潜力变化较大,深部地层的泥质烃源岩评价为好或极好烃源岩,中浅层系为差烃源岩。烃源岩有机质类型主要为Ⅱ2~Ⅲ型,热演化阶段可划分为开始生烃阶段(
R o>0.6%)和大量排烃阶段(R o>0.8%)。基于原油和各类烃源岩的生物标志化合物特征对比显示研究区泥质烃源岩为主要原油来源。本研究对西湖凹陷未来油气勘探与开发具有参考意义。Abstract:Objective The Xihu Depression, located in eastern China, is a significant area for oil and gas exploration. While previous studies have focused on deep strata, such as the Pinghu Formation, little research has been conducted on the middle and shallow strata, including the Huagang Formation. Recent findings suggest that these shallow and middle strata have hydrocarbon accumulation potential, but their hydrocarbon-generating capacity and the source of crude oil in the Xihu Depression remain uncertain.
Methods To address these gaps, we collected 203 source rock samples from 13 drilling boreholes in the western slope zone and central inversion tectonic zone of the Xihu Depression. These samples spanned from the Eocene Baoshi Formation to the Miocene Longjing Formation. Geochemical tests and analysis were conducted to assess the hydrocarbon potential and biomarker characteristics of the source rocks.
Results The results indicate that coal and carbonaceous mudstone in the Xihu Depression have excellent hydrocarbon generation potential, while the hydrocarbon generation potential of mudstone varies. Deep layer source rocks are evaluated as good or excellent sources of hydrocarbons, while the middle and shallow layers are considered poor sources. The organic matter in the source rocks mainly consists of types Ⅱ2-Ⅲ, and the thermal evolution stage can be divided into a hydrocarbon generation stage (
R o>0.6%) and a large hydrocarbon expulsion stage (R o>0.8%).Comparing the biomarkers of crude oil and different types of source rocks, we found that the argillaceous source rock in the study area is the primary source of crude oil.Conclusion This research provides valuable guidance for future oil and gas exploration in the Xihu Depression.
-
Key words:
- source rock /
- hydrocarbon generation potential /
- geochemical feature /
- biomarker /
- Xihu Depression
-
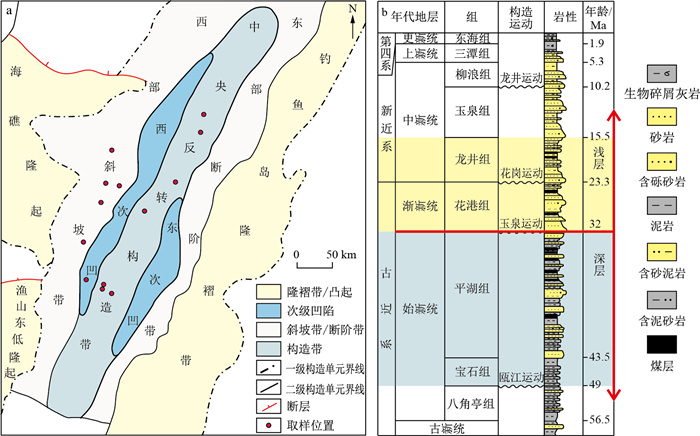
图 1 西湖凹陷构造单元划分(a)与地层综合柱状图(b) (据文献[6]修改)
图b中蓝底表示深部地层,黄底表示中浅层系
Figure 1. Structural units (a) and stratigraphic chart (b) of the Xihu Depression
图 9 西湖凹陷不同类型烃源岩饱和烃质量(质荷比m/z=191,217)色谱图
Ol为奥利烷;Dia为C27重柏甾烷;其余同图 7
Figure 9. Chromatograms of saturated hydrocarbon mass (m/z=191 and 217) in different source rocks in the Xihu Depression
表 1 未成熟烃源岩有机质丰度评价表(据文献[14]修改)
Table 1. Evaluation of organic matter abundance
有机质丰度 w(TOC)/% (S1+S2)/(mg·g-1) EOM/(μg·g-1) HC/(μg·g-1) 差烃源岩 [0, 0.5) [0, 3) [0, 500) [0, 300) 中等烃源岩 [0.5, 1.0) [3, 6) [500, 1 000) [300, 600) 好烃源岩 [1.0, 2.0] [6, 12] [1 000, 2 000] [600, 1 200] 极好烃源岩 >2.0 >12 >2 000 >1 200 表 2 西湖凹陷烃源岩有机质丰度统计
Table 2. Statistical analysis of the abundance of organic matter in the Xihu Depression
烃源岩 w(TOC)/% (S1+S2)/(mg·g-1) EOM/(μg·g-1) HC/(μg·g-1) 煤 $\frac{48.56 \sim 65.79}{55.16(4)}$ $\frac{166.30 \sim 253.33}{211.89(4)}$ $\frac{11\;439 \sim 30\;561}{18\;674(4)}$ $\frac{3\;768 \sim 8\;710}{5\;795(4)}$ 炭质泥岩 $\frac{6.55 \sim 31.69}{13.00(14)}$ $\frac{18.01 \sim 99.36}{43.31(14)}$ $\frac{181 \sim 1\;9330}{5\;301(4)}$ $\frac{81 \sim 8\;203}{2\;348(14)}$ 泥岩 $\frac{0.12 \sim 5.59}{1.27(185)}$ $\frac{0.10 \sim 21.11}{1.65(179)} $ $\frac{46 \sim 6\;240}{801(80)}$ $\frac{14 \sim 2\;884}{374(80)}$ 泥质烃源岩 龙井组 $\frac{0.35 \sim 2.35}{0.74(14)}$ $\frac{0.23 \sim 3.14}{1.07(14)}$ $\frac{118 \sim 704}{346(13)}$ $\frac{41 \sim 372}{170(13)}$ 花港组 $\frac{0.13 \sim 2.79}{0.59(57)}$ $\frac{0.10 \sim 4.85}{0.98(53)}$ $\frac{60 \sim 3\;131}{492(33)}$ $\frac{44 \sim 919}{234(33)}$ 平湖组 $\frac{0.12 \sim 5.59}{1.52(91)}$ $\frac{0.20 \sim 21.11}{3.25(89)} $ $\frac{46 \sim 19\;930}{2\;662(38)}$ $\frac{14 \sim 8\;203}{1\;294(38)}$ 宝石组 $\frac{0.32 \sim 5.43}{2.28(23)}$ $\frac{0.58 \sim 16.57}{4.78(23)}$ $\frac{324 \sim 2\;638}{1\;294(6)}$ $\frac{62 \sim 890}{286(6)}$ 注:横线上方表示最小值与最大值; 下方为平均值,括号内为样品数 表 3 西湖凹陷3类烃源岩典型生物标志化合物特征
Table 3. Biomarker characteristics of three main types of source rocks in the Xihu Depression
陆源输入 低等藻类 细菌改造 盐度分层 氧化还原 煤 高C19/C23 低C27/C29 低S/H高补身烷/升补身烷 低Gam/C30H 高Pr/Ph 高CPI 高TAR 高Pr/nC17 高二萜化合物 低C17/C31 低Ts/Tm 炭质泥岩 中C19/C23 中C27/C29 中S/H中补身烷/升补身烷 低Gam/C30H 中Pr/Ph 中CPI 低TAR 中Pr/nC17 中二萜化合物 中C17/C31 中Ts/Tm 泥岩 低C19/C23 高C27/C29 高S/H低补身烷/升补身烷 高Gam/C30H 低Pr/Ph 低CPI 中TAR 低Pr/nC17 低二萜化合物 高C17/C31 高Ts/Tm -
[1] 田海芹. 西湖凹陷含油气系统研究[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2000, 24(1): 38-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200001009.htmTIAN H Q. Research on the oil-bearing series of Xihu Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2000, 24(1): 38-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200001009.htm [2] 吴江, 侯读杰, 许汇源, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷原油轻烃地球化学特征及油源区分[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2015, 39(5): 23-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY201505004.htmWU J, HOU D J, XU H Y, et al. Oil's light hydrcarbon, geochemical characteristics and sources in Xihu Sag, the East China Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2015, 39(5): 23-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY201505004.htm [3] 李纯洁, 李上卿, 许红. 西湖凹陷中-下始新统宝石组油气地质与勘探潜力[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(4): 81-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200404016.htmLI C J, LI S Q, XU H. Petroleum geologic characteristics and exploration potential of Middle-Lower Eocene Baoshi Formation in the Xihu Sag[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(4): 81-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200404016.htm [4] 朱扬明, 周洁, 顾圣啸, 等. 西湖凹陷始新统平湖组煤系烃源岩分子地球化学特征[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(1): 32-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201201003.htmZU Y M, ZHOU J, GU S X, et al. Molecular geochemistry of Eocene Pinghu Formation coal-bearing source rocks in the Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(1): 32-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201201003.htm [5] 张先平, 张树林, 陈海红, 等. 东海西湖凹陷平湖构造带异常压力与油气成藏[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(3): 93-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200703017.htmZHANG X P, ZHANG S L, CHEN H H, et al. Abnormal pressure and related reservoir formation in the Pinghu structural belts of Xihu Depression, East China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(3): 93-97. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200703017.htm [6] 陈琳琳, 孙伯强, 王乐闻, 等. 西湖凹陷中央背斜带北部花港组天然气特征及气源分析[J]. 海洋石油, 2017, 37(1): 21-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201701005.htmCHEN L L, SUN B Q, WANG L W, et al. Characteristics and source of natural gas from Huagang Formation in north segment of central anticline belt of Xihu Sag[J]. Offshore Oil, 2017, 37(1): 21-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201701005.htm [7] 周心怀. 西湖凹陷地质认识创新与油气勘探领域突破[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202001001.htmZHOU X H. Geological understanding and innovation in Xihu Sag and breakthroughs in oil and gas exploration[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(1): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202001001.htm [8] 赵珂, 杜学斌, 贾冀新, 等. 西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带的物源分析: 来自碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学及重矿物的证据[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 68-76. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0308ZHAO K, DU X B, JIA J X, et al. Provenance analysis of the Pinghu slope belt in Xihu Depression: Evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb chronology and heavy minerals[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 68-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0308 [9] ZHU X, CHEN J, LI W, et al. Hydrocarbon generation potential of Paleogene coals and organic rich mudstones in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin, offshore eastern China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 184: 106450. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106450 [10] 傅宁, 李友川, 陈桂华, 等. 东海西湖凹陷油气"蒸发分馏"成藏机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(2): 39-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200302012.htmFU N, LI Y C, CHEN G H, et al. Pooling mechanisms of "evaporating fractionation" of oil and gas in the Xihu Depression, East China Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(2): 39-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200302012.htm [11] XU H, HOU D, CAO B, et al. Geochemical characteristics of high-maturity crude oils in the Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2016, 50(2): 163-178. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.0402 [12] 曹倩, 宋在超, 周小进, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷原油地化特征及来源分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(2), 251-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201902014.htmCAO Q, SONG Z C, ZHOU X J, et al. Geochemical characteristics and source of crude oil in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(2): 251-259. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201902014.htm [13] 李文俊, 岳大力, 何贤科, 等. 地质模式约束的SVR属性融合在浅水三角洲储层描述中的应用: 以西湖凹陷X气田为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 106-113. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0611LI W J, YUE D L, HE X K, et al. Application of SVR attribute fusion constrained by geological model in reservoir description of shallow water delta: A case study of X gas field in Xihu Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 106-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0611 [14] PETERS K E, CASSA M R. Applied source-rock geochemistry[M]//MAGOON L B, DOW W G. The petroleum system: From source to Trap. Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 1994: 93-120. [15] 梁霄, 马韶光, 李郭琴, 等. 上斜坡区筇竹寺组沉积环境及其页岩气勘探潜力: 以四川盆地威远地区威207井为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 68-82. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0159LIANG X, MA S G, LI G Q, et al. Sedimentary environment and shale gas exploration potential of Qiongzhusi Formation in the upslope area: A case study on Well W-207, Weiyuan area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 68-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0159 [16] 黄谦, 陈容涛, 彭晓波, 等. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷古近系烃源岩生物标志物特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 180-192. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0085HUANG Q, CHEN R T, PENG X B, et al. Characteristics and geological significance of biomaarkers from the Paleogene source rocks in Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 180-192. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0085 [17] 杨鹏程, 刘峰, 沈珊, 等. 西湖凹陷平北地区平湖组煤系烃源岩生烃潜力研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(4): 139-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202004012.htmYANG P C, LIU F, SHEN S, et al. A study on the hydrocarbon generation potential of the coal-bearing sourse rocks in the Pinghu Formation of Pingbei area, Xihu Depression[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(4): 139-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202004012.htm [18] 赵兰全. 西湖凹陷平湖地区油气源分析及其对成藏的影响[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2011, 18(1): 26-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201101007.htmZHAO L Q. Analysis on hydrocarbon source and influence on reservoir formation, Pinghu area, Xihu Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2011, 18(1): 26-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201101007.htm [19] LIVSEY A, DOUGLAS A G, CONNAN J. Diterpenoid hydrocarbons in sediments from an offshore(Labrador)well[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1984, 8(6): 73-81. [20] ZHU Y, LI Y, ZHOU J, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Tertiary coal-bearing source rocks in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 35(1): 154-165. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.01.005 [21] CRANWELL P A, EGLINTON G, ROBINSON N. Lipids of aquatic organisms as potential contributors to lacustrine sediments-Ⅱ[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1987, 11(6): 513-527. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(87)90007-6 [22] SCHWARK L, EMPT P. Sterane biomarkers as indicators of Palaeozoic algal evolution and extinction events[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 240(1/2): 225-236. [23] QUAN Y, HAO F, LIU J, et al. Source rock deposition controlled by tectonic subsidence and climate in the western Pearl River Mouth Basin, China: Evidence from organic and inorganic geochemistry[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 79: 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.10.028 [24] OURISSON G, ALBRECHT P, ROHMER M. Predictive microbial biochemistry-from molecular fossils to procaryotic membranes[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 1982, 7(7): 236-239. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(82)90028-7 [25] ROSENBERG R. Benthic macrofaunal dynamics, production, and dispersion in an oxygen-deficient estuary of west Sweden[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology & Ecology, 1977, 26(2): 107-133. [26] WAPLES D W. Reappraisal of anoxia and organic richness with emphasis on Cretaceous of North Atlantic[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1983, 67(6): 963-978. [27] DIDYK B M, SIMONEIT B R T, BRASSELL S C, et al. Organic geochemical indicators of palaeoenvironmental conditions of sedimentation[J]. Nature, 1978, 272: 216-222. doi: 10.1038/272216a0 [28] HANSON A D, ZHANG S C, MOLDOWAN J M, et al. Molecular organic geochemistry of the Tarim Basin, Northwest China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2000, 84(8): 1109-1128. [29] MOLDOWAN J M, SEIFERT W K, GALLEGOS E J. Relationship between petroleum composition and depositional environment of petroleum source rocks[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1985, 69(8): 1255-1268. [30] QUAN Y, LIU J, HAO F, et al. Paleosalinity assessment and its influence on source rock deposition in the western Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2020, 132(7/8): 1741-1755. [31] ZHAO K, DU X B, JIA J X, et al. Orbitally controls of climate recorded in a series of thin-multiple-layers coal seams in marine-continent transition environment during Late Eocene[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2022, 606: 111233. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2022.111233 [32] KATZ B J, ROYLE R A, MERTANI B. Southeast Asian and southwest Pacific coals contribution to the petroleum resource base[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the Indonesian Petroleum Association 19th Annual Convention. [S. l. ]: [s. n. ], 1990: 299-329. -





 下载:
下载: