Strength characteristics of the sliding zone soil of bedding deep cutting slopes and early warning analysis of the reserved thickness of the base
-
摘要:
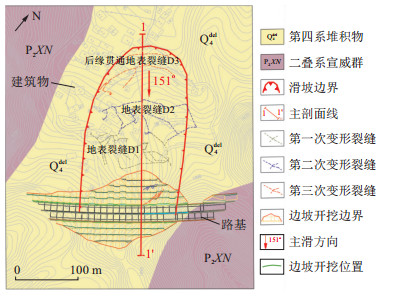
含软弱夹层的顺层深路堑边坡在边坡工程中普遍存在, 滑带土强度和基底预留厚度(开挖边坡基底到软弱夹层的距离)是影响其稳定性的2个关键性因素。以杨宣(杨柳-宣城)高速K42路堑边坡为例, 分析了边坡变形演化过程和基底隆起变形特征, 通过适合研究大剪切位移下土体抗剪强度的环剪试验揭示了边坡深部滑带土的特性, 应用滑带土的饱和残余强度参数进行了边坡开挖基底预留厚度分析。结果表明: K42滑带土有明显的应变软化特性, 且法向应力越小滑带土应变软化特性表现越明显; 由峰值抗剪强度到残余抗剪强度, 黏聚力和内摩擦角均表现出衰减效应, 且黏聚力衰减程度大于内摩擦角; 滑带土残余抗剪强度参数中的残余黏聚力随剪切速率的变化很小, 而残余内摩擦角和剪切速率呈对数函数
φ =0.130 3lnv +7.319 7关系变化, 当剪切速率 < 2 mm/min时, 滑带土残余抗剪强度参数对剪切速率较为敏感, 反之敏感性较差; 最后, 依据边坡不同临界状态的回归方程h 1、h 2、h 3将不同坡率下的基底预留厚度分成A(失稳)、B(欠稳定)、C(基本稳定)以及D(稳定)4个区, 并且在此基础上建立了基底预留厚度判据和边坡开挖基底预留厚度预警模型。Abstract:Objective Bedding deep cutting slopes containing weak interlayers are commonly found in slope engineering, whose stability is influenced by two key factors: The strength of the sliding zone soil and the reserved thickness of the base (the distance from the base of an excavated slope to the weak interlayer).
Methods In this research, taking the K42 cutting slope of the Yang-Xuan Expressway as an example, the evolution process of slope deformation was analyzed, especially the characteristics of basal heave deformation. The properties of the deep sliding zone soil in the slope were revealed by ring shear tests, which are suitable for studying the shear strength of soil that has experienced large shear displacements. Moreover, the residual strength parameters of the saturated sliding zone soil were applied to analyze the reserved thickness of the base.
Results The results show that sliding zone soils exhibit obvious strain softening characteristics, which become more evident as the normal stress decreases. As the soil shear strength transitions from peak strength to residual strength, both the cohesion force and internal friction angle decrease, with the cohesion force decreasing to a greater extent than the internal friction angle. The residual cohesion force of sliding zone soil varies slightly with the shear rate, while the relationship between the residual internal friction angle and shear rate varies as a logarithmic function. When the shear rate is less than 2 mm/min, the residual shear strength parameter of sliding zone soil is more sensitive to the shear rate and vice versa.
Conclusion Furthermore, according to the regression equations of the critical states of slope stability, the reserved thickness of the base under different slope rates was divided into four zones: A (extremely unstable zone), B (unstable zone), C (basically stable zone) and D (stable zone), and based on this, the criterion and early warning model of the reserved thickness of the base for slope excavation were established.
-
表 1 不同剪切速率下残余抗剪强度
Table 1. Residual shear strength at different shear rates
剪切速率v/(mm·min-1) 残余抗剪强度/kPa 残余抗剪强度参数 法向应力100 kPa 法向应力200 kPa 法向应力400 kPa c/ kPa φ/ (°) 0.2 16.56 27.53 53.75 5.81 7.12 2 17.30 29.15 55.80 5.86 7.35 20 19.01 31.51 59.80 5.87 7.74 注:c为残余黏聚力;φ为残余内摩擦角 表 2 基底预留厚度判据及预警模型
Table 2. Reserved thickness of the base criterion and early warning model
预警级别 警报 警戒 注意 安全 预警形式 红 橙 黄 蓝 预警分区 A B C D 预留厚度h h<h1 h1≤h<h2 h2≤h<h3 h≥h3 边坡状态 失稳 欠稳定 基本稳定 稳定 注意及措施 停止或禁止进行边坡开挖 防止慢速蠕变变形破坏和基底隆起剪出,采取反压等抗滑措施 注意局部变形滑移和基底隆起,及时判断边坡稳定性状态 边坡稳定,基底不会隆起变形,注意施工规范 注:h1、h2、h3对应为稳定性系数分别为1, 1.05, 1.15时的基底预留厚度 -
[1] 杨晓华, 张建伟, 张莎莎, 等. 黄土地区高速公路地基处理技术研究进展[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 42(1): 16-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL202201002.htmYANG X H, ZHANG J W, ZHANG S S, et al. Research progress on foundation treatment techniques of expressway in loess area[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 42(1): 16-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGL202201002.htm [2] 肖景红, 王敏, 王川, 等. 含优势渗流层边坡降雨入渗下的可靠度分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 193-204. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0619XIAO J H, WANG M, WANG C, et al. Reliability analysis of slope with dominant seepage interlayer under rainfall infiltration[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 193-204. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0619 [3] 冯霄, 王禹, 刘洋, 等. 考虑软弱夹层控滑机制及其空间不确定性的顺层岩质滑坡易发性评价: 万州区铁峰乡应用研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 254-266. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0049FENG X, WANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Susceptibility assessment of a translational rockslide considering the control mechanism and spatial uncertainty of a weak interlayer: Application study in Tiefeng Township, Wanzhou District[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 254-266. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0049 [4] 马金莲, 朱彦鹏, 杨晓宇, 等. 兰永一级公路顺层滑坡抗剪强度参数确定及应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2018, 40(增刊1): 118-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC2018S1020.htmMA J L, ZHU Y P, YANG X Y, et al. Determination and application of shear strength parameters of bedding landslide of Lanzou-Yongjing Highway[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(S1): 118-123. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC2018S1020.htm [5] 张迪, 李岚星, 胡新丽, 等. 长期静水浸泡对三峡库区滑带土物理-化学-力学性质的影响[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 281-289. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0041ZHANG D, LI L X, HU X L, et, al. Effect of long-term immersion in static water on the physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of sliding zone soil in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 281-289. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0041 [6] MESRI G, ABDEL-GHAFFAR M E M. Cohesion intercept in effective stress-stability analysis[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1993, 119(8): 1229-1249. [7] SKEMPTON A W. Residual strength of clays in landslides, folded strata and the laboratory[J]. Géotechnique, 1985, 35(1): 3-18. [8] 汤罗圣, 殷坤龙, 刘艺梁, 等. 滑坡残余强度预测[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(3): 1116-1121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201303040.htmTANG L S, YIN K L, LIU Y L, et al. Prediction of landslide residual strength[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2013, 44(3): 1116-1121. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201303040.htm [9] 陈传胜, 张建敏. 滑带土抗剪强度参数确定方法研究进展[J]. 中外公路, 2012, 32(6): 65-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWGL201206016.htmCHEN C S, ZHANG J M. Research progress on determination methods of shear strength parameters of sliding zone soil[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2012, 32(6): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWGL201206016.htm [10] 刘小丽, 邓建辉, 李广涛. 滑带土强度特性研究现状[J]. 岩土力学, 2004, 25(11): 1849-1854. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX200411040.htmLIU X L, DENG J H, LI G T. Shear strength properties of slip soils of landslides: An overview[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2004, 25(11): 1849-1854. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX200411040.htm [11] TIKA T E, VAUGHAN P R, LEMOS L J L J. Fast shearing of pre-existing shear zones in soil[J]. Géotechnique, 1996, 49(2): 197-233. [12] 魏占玺, 谢东武, 毋远召, 等. 基于动态残余强度的不同含水率条件下滑坡稳定性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2022, 49(2): 126-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202202015.htmWEI Z X, XIE D W, WU Y Z, et al. Research on landslide stability under different water content conditions based on the dynamic residual strength[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(2): 126-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202202015.htm [13] 王鲁男, 晏鄂川, 宋琨, 等. 滑带土残余强度的速率效应及其对滑坡变形行为的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 48(12): 3350-3358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201712028.htmWANG L N, YAN E C, SONG K, et al. Rate effect of residual strength of slip soils and its impact on deformation process of landslides[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2017, 48(12): 3350-3358. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201712028.htm [14] HABIBBEYGI F, NIKRAZ H. Effect of shear rate on the residual shear strength of pre-sheared clays[J]. Cogent Geoscience, 2018, 4(1): 1453989. [15] RAJ-BHAT D. Shear rate effect on residual strength of typical clay soils[J]. Innovative Infrastructure Solutions, 2021, 7(1): 36. [16] MIAO F S, ZHAO F C, WU Y P, et al. A novel seepage device and ring-shear test on slip zone soils of landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Engineering Geology, 2022, 307: 106779. [17] 罗战友, 郑耀, 陶燕丽, 等. 扭剪试验剪切速率对黏性土力学性能影响[J]. 科技通报, 2019, 35(10): 162-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJTB201910031.htmLUO Z Y, ZHENG Y, TAO Y L, et al. Effect of shear rate on mechanical behavior of cohesive soil in torsional shear test[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2019, 35(10): 162-165. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJTB201910031.htm [18] JUNG B C. Modeling of strain rate effects on clay in simple shear[D]. Texas: Texas AM University, 2006. [19] 徐靓, 朱鸿鹄, 程刚, 等. 十字板剪切速率对粉质黏土不排水抗剪强度的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(12): 4372-4380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD202112014.htmXU J, ZHU H H, CHENG G, et al. Effect of vane shear rate on undrained shear strength of silty clay[J]. Journal of Cental South University (Science and Technology), 2021, 52(12): 4372-4380. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD202112014.htm [20] SCHLUE F B, MOERZ T, KREITER S. Influence of shear rate on undrained vane shear strength of organic harbor mud[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2010, 136(10): 1437-1447. [21] 董文萍, 戴福初, 张洪影, 等. 向家坝水电站库区某滑坡滑带土的残余强度试验研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2018, 24(4): 619-626. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201804015.htmDONG W P, DAI F C, ZHANG H Y, et al. Laboratory study on soil residual strength of slip zone of a landslide in the Xiangjiaba Reservoir area[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2018, 24(4): 619-626. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201804015.htm [22] 赵帆程, 苗发盛, 吴益平, 等. 不同环剪条件下三峡库区童家坪滑坡滑带土强度特性[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 315-324. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0045ZHAO F C, MIAO F S, WU Y P, et al. Strength characteristics of slip zone soils of the Tongjiaping landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area under different ring shear conditions[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 315-324. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0045 [23] WANG G H, SUEMINE A, SCHULZ W H. Shear-rate-dependent strength control on the dynamics of rainfall-triggered landslides, Tokushima Prefecture, Japan[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2010, 35(4): 407-416. [24] LI Y R, WEN B P, AYDIN A, et al. Ring shear tests on slip zone soils of three giant landslides in the Three Gorges Project area[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 54(1): 106-115. [25] 陈晓利, 王明明, 张凌. 道路开挖位置对边坡稳定性影响的数值模拟[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(6): 1390-1401. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201806014.htmCHEN X L, WANG M M, ZHANG L. Simulation study of road-cut effects on slope stability[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2018, 40(6): 1390-1401. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201806014.htm [26] 冉孟辉. 红层泥质岩地区高铁深路堑持续上拱整治技术研究[J]. 工程建设与设计, 2022, 29(7): 72-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCJS202207023.htmRAN M H. Study on continuous upward arch treatment technology of high-speed railway deep cutting in red-bed mudstone area[J]. Construction & Design for Engineering, 2022, 29(7): 72-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCJS202207023.htm [27] 纪宇, 梁庆国, 郭俊彦, 等. 红层软岩地区高速铁路深路堑基底变形规律研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2021, 18(3): 572-580. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD202103003.htmJI Y, LIANG Q G, GUO J Y, et al. Study on deformation law of deep foundation of high speed railway in red layer soft rock area[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2021, 18(3): 572-580. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSTD202103003.htm [28] 杨吉新, 马旭超, 刘前瑞. 关于成渝高铁路基上拱问题的探讨[J]. 铁道建筑, 2016, 56(8): 112-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDJZ201608028.htmYANG J X, MA X C, LIU Q R. Exploring on subgrade swelling of Chengdu-Chongqing high-speed railway subgrade[J]. Railway Engineering, 2016, 56(8): 112-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDJZ201608028.htm [29] 钟志彬, 李安洪, 邓荣贵, 等. 高速铁路红层软岩路基时效上拱变形机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(2): 327-340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202002012.htmZHONG Z B, LI A H, DENG R G, et al. Study on time-dependent upheaval deformation mechanisms of red-bed soft rock subgrade of high-speed railways[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(2): 327-340. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202002012.htm [30] 吴沛沛. 基于流变的高速铁路深挖路堑长期上拱变形数值分析[J]. 路基工程, 2019(1): 135-139 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGC201901027.htmWU P P. Numerical analysis on the long-term upheaval deformation of high-speed railway deep excavation cutting based on rheology[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2019(1): 135-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGC201901027.htm -





 下载:
下载: