S and Pb isotopic compositions of the Qianchuiliu Gold Deposit on the northeastern margin of the Jiaolai Basin: Implication on the source of ore-forming material
-
摘要:
前垂柳金矿为胶东胶莱盆地东北缘新发现的蚀变岩型金矿床,金矿体主要赋存于牧牛山岩体(二长花岗岩)、荆山群地层和鹊山岩体(糜棱岩化二长花岗岩)之间厚大的构造蚀变带内,截止目前推测资源量达到中型规模,但矿床的成矿物质来源尚不明确。基于前人研究及野外调查,选择典型矿体中含金黄铁矿作为研究对象,开展了S、Pb同位素分析,探讨了矿床的成矿物质来源。测试结果显示:矿石硫化物
δ 34S值总体为10.13‰~12.39‰,极差为2.26‰,平均值10.98‰,均一程度高,具高δ 34S值特征,反映了深部成矿流体上侵过程中混染了更多的地层中的硫,显示了荆山群地层对成矿有一定贡献;矿石铅同位素206Pb/204Pb比值为17.149~18.886,207Pb/204Pb比值为15.482~15.677,208Pb/204Pb比值为37.860~40.073,显示前垂柳金矿铅为壳幔混合来源,且具有下地壳铅的特征。该矿床S、Pb同位素特征显示成矿物质来源为壳幔混源,与周边辽上、蓬家夼等典型矿床成矿物质来源一致,反映了该区燕山期大规模成矿事件,预示了胶莱盆地东北缘具有较大的找矿潜力。Abstract:The Qianchuiliu Gold Deposit on the northeastern margin of the Jiaolai Basin is a newly discoverd altered rock type gold deposit, and is a medium-sized gold deposit hosted in the structural alteration zone between Muniushan, Jingshan Group and Queshan monzonitic granites. However, the source of ore-forming materials and the ore genesis are not clear. Based on previous field and analytical studies, the authors conducted sulfur and lead isotopic analyses on gold-bearing pyrite from typical ores as the research target. The
δ 34S values are high and homogeneous ranging from 10.13‰-12.39‰, with an average of 10.98‰ and polar odds of 2.26‰. These sulfur isotopic results reveal a mixing process of sulfur in the Jingshan Group during the upwelling of deep ore-forming fluid. The ratios of 206Pb/204Pb, 207Pb/204Pb, and 208Pb/204Pb vary from 17.149-18.886, 15.482-15.677, and 37.860-40.073, respectively, suggesting a crust-mantle mixed source. In conclusion, sulfur and lead isotope analysis results of the Qianchuiliu Gold Deposit show a crust-mantle mixed source and are similar to those of typical gold deposits in this region. The gold deposits on the northeastern margin of the Jiaolai Basin formed at the large-scale Yanshanian metallogenic event, indicating great prospecting potential in this area. -
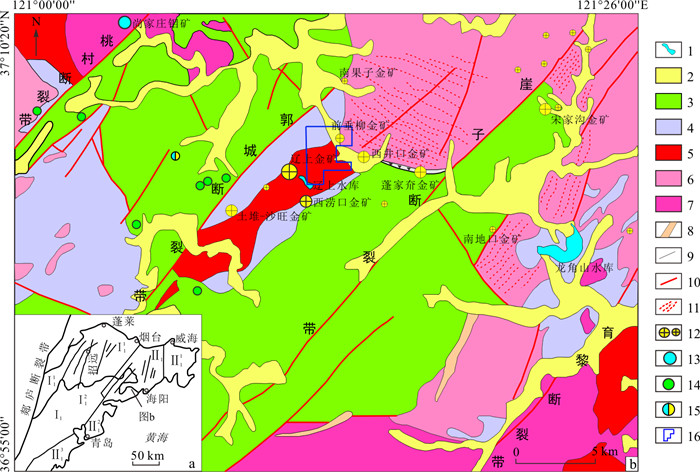
图 1 前垂柳金矿区及周边金矿区地质简图[1]
1.水库;2.第四系;3.下白垩统陆相沉积岩、火山岩;4.古元古界变质岩;5.前寒武纪侵入岩;6.晚侏罗世二长花岗岩;7.早白垩世花岗闪长岩;8.燕山晚期岩脉;9.地质界线;10.断裂;11.韧性剪切带;12.金矿床(点);13.钼矿床;14.铜矿点;15.铅锌矿点;16.胶莱盆地东北缘前垂柳矿区位置;Ⅰ.华北板块;Ⅰ1.胶莱-胶北断隆;Ⅰ11.胶北断隆;Ⅰ12.胶莱断陷;Ⅱ.秦岭-大别-苏鲁碰撞造山带;Ⅱ1.胶南-威海断隆;Ⅱ11.文登-威海断拱;Ⅱ12.胶莱断陷;Ⅱ13.胶南-临沭断拱
Figure 1. Geological map of the Qianchuiliu Gold Mining area and nearby gold mineral deposits
图 7 前垂柳金矿床矿石铅同位素Δγ-Δβ成因判别图解(底图据文献[42]; 投影点数据综合本文及文献[33-39])
1.地幔源铅; 2.上地壳源铅; 3.上地壳与地幔混合的俯冲铅: 3a.岩浆作用铅; 3b.沉积作用铅; 4.化学沉积型铅; 5.海底热水作用铅; 6.中深变质作用Pb; 7.深变质下地壳铅; 8.造山带铅; 9.古老页岩上地壳铅; 10.退变质铅
Figure 7. Δγ-Δβ genetic classification diagram showing ore mineral lead isotopic distribution in the Qianchuiliu Gold Deposit
表 1 前垂柳金矿床矿石硫同位素组成
Table 1. Sulfur isotope composition of the Qianchuiliu Gold Deposit
样品编号 采样位置 矿石中黄铁矿赋存特征 测试矿物 δ34S/% ZK3201-64 32线ZK3201孔117.2 m 细脉状黄铁矿 黄铁矿 11.20 ZK3201-97 32线ZK3201孔204.2 m 条带状黄铁矿 黄铁矿 11.23 ZK3201-128 32线ZK3201孔258.2 m 细脉状石英自形黄铁矿 黄铁矿 10.28 ZK3201-131 32线ZK3201孔262.1 m 细脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 12.39 ZK3201-338 32线ZK3201孔577 m 细脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 11.46 ZK3201-340 32线ZK3201孔579 m 细脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 10.13 ZK3201-343 32线ZK3201孔583 m 细脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 10.94 ZK1603-391 16线ZK1603孔543.16 m 细脉状黄铁矿 黄铁矿 10.80 ZK1603-393 16线ZK1603孔546.16 m 网脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 10.80 ZK1603-395 16线ZK1603孔548.46 m 网脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 10.60 ZK1603-401 16线ZK1603孔555.06 m 网脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 10.30 ZK1603-403 16线ZK1603孔557.46 m 网脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 11.10 ZK1603-405 16线ZK1603孔560.26 m 网脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 10.90 ZK1603-407 16线ZK1603孔562.96 m 网脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 11.10 ZK1603-409 16线ZK1603孔565.86 m 网脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 11.20 ZK1603-411 16线ZK1603孔568.76 m 网脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 11.40 ZK1603-413 16线ZK1603孔571.76 m 网脉状石英黄铁矿 黄铁矿 10.90 表 2 前垂柳金矿床矿石铅同位素组成
Table 2. Lead isotope composition of the Qianchuiliu Gold Deposit
样品编号 测试矿物 206Pb/204Pb 207Pb/204Pb 208Pb/204Pb μ ω κ Δα Δβ Δγ ZK1603-391 黄铁矿 17.149 15.482 37.860 9.41 40.58 4.17 62.22 15.29 52.05 ZK1603-392 黄铁矿 17.178 15.498 37.917 9.44 40.82 4.18 63.74 16.31 53.49 ZK1603-393 黄铁矿 17.941 15.540 38.432 9.40 38.61 3.98 67.17 15.45 44.73 ZK1603-394 黄铁矿 17.544 15.515 38.000 9.41 38.91 4.00 64.79 15.46 44.54 ZK1603-395 黄铁矿 17.390 15.497 37.995 9.40 39.71 4.09 63.23 14.96 48.55 ZK1603-399 黄铁矿 18.625 15.618 38.626 9.48 36.30 3.71 75.66 18.67 32.25 ZK1603-401 黄铁矿 17.753 15.535 38.227 9.42 38.81 3.99 66.68 15.91 45.01 ZK1603-402 黄铁矿 17.953 15.555 38.488 9.43 38.92 3.99 68.62 16.48 46.66 ZK1603-403 黄铁矿 18.886 15.677 39.676 9.57 39.56 4.00 88.21 22.39 58.86 ZK1603-404 黄铁矿 18.797 15.645 39.185 9.52 37.83 3.85 83.09 20.30 45.75 ZK1603-407 黄铁矿 18.019 15.566 38.600 9.44 39.11 4.01 69.75 17.01 48.16 ZK1603-408 黄铁矿 18.059 15.566 39.527 9.44 42.82 4.39 69.76 16.85 71.99 ZK1603-411 黄铁矿 18.474 15.644 40.073 9.54 43.26 4.39 77.88 20.95 77.37 ZK1603-412 黄铁矿 17.790 15.562 38.756 9.47 41.20 4.21 69.25 17.70 59.66 ZK1603-413 黄铁矿 18.552 15.613 39.395 9.48 39.72 4.05 75.00 18.52 54.87 注:Pb同位素特征参数μ为238U/204Pb、ω为232Th/204Pb、κ为Th/U、Δα为[α/αm(t)-1]×1 000、Δβ为[β/βm(t)-1]×1 000、Δγ为[γ/γm(t)-1]×1 000,其中α、β、γ为测定值、αm(t)、βm(t)、γm(t)为t时的地幔值,各参数使用GeoKit软件计算得到[26-27] -
[1] 郭云成, 段留安, 韩小梦, 等. 胶东前垂柳金矿区花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(3): 876-897. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202203009.htmGuo Y C, Duan L A, Han X M, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating and geochemical characteristics of the granites from the the Qianchuiliu Gold Mining area in the Jiaodong Peninsula and its geological significance[J]. Geosciencs, 2022, 36(3): 876-897(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202203009.htm [2] 陈原林, 李欢, 郑朝阳, 等. 胶莱盆地龙口-土堆金矿床成因: 微量元素特征与C-H-O-S同位素约束[J]. 矿床地质, 2021, 40(5): 977-996. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202105006.htmChen Y L, Li H, Zheng C Y, et al. Genesis of Longkou-Tudui Gold Deposit, Jiaolai Basin: Constraints of trace element characteristics and C-H-O-S isotopes[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2021, 40(5): 977-996(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202105006.htm [3] 李大兜. 胶莱盆地东北缘龙口-土堆金矿区矿床成因及成矿模式研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2020, 36(9): 6-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKB202009004.htmLi D D. Study on genesis and metallogenic model of Longkou-Tudui Gold Deposit in northeastern margin of Jiaolai Basin[J]. Modern Mining, 2020, 36(9): 6-11(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKB202009004.htm [4] 赵宝聚, 高明波, 李亚东, 等. 胶莱盆地东北缘龙口-土堆矿区金矿床成矿规律研究[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(增刊1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE2019S1001.htmZhao B J, Gao M B, Li Y D, et al. Study on metallogenic regularity of gold deposits in Longkou-Tudui mining area on the northeastern margin of Jiaolai Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(S1): 1-11(in Chinese wit-h English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE2019S1001.htm [5] 宋明春, 杨立强, 范宏瑞, 等. 找矿突破战略行动十年胶东金矿成矿理论与深部勘查进展[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(6): 903-935. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202206001.htmSong M C, Yang L Q, Fan H R, et al. Current progress of metallogenic research and deep prospecting of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peniusula during 10 years for exploration breakthrough strategic action[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(6): 903-935(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202206001.htm [6] 丁正江, 孙丰月, 赵财胜, 等. 山东胶莱盆地东北缘地区金矿成矿系列[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(增刊1): 919-920. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2010S1460.htmDing Z J, Sun F Y, Zhao C S, et al. Gold mineralization series in northeast margin of Jiaolai Basin, Shandong[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2010, 29(S1): 919-920(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2010S1460.htm [7] Li J J, Zhang P P, Li G H, et al. Formation of the Liaoshang Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China: Evidence from geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 5903-5913. doi: 10.1002/gj.3718 [8] 李国华, 丁正江, 纪攀, 等. 胶莱盆地东北缘地区金矿特征及找矿方向[J]. 地质与勘探, 2016, 52(6): 1029-1036. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201606003.htmLi G H, Ding Z J, Ji P, et al. Features and prospecting direction of the gold deposits in the northeastern margin of the Jiaolai Basin[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2016, 52(6): 1029-1036(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201606003.htm [9] Tan J, Wei J H, He H Y, et al. Noble gases in pyrites from the Guocheng-Liaoshang gold belt in the Shandong Province: Evidencefor a mantle source of gold[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 480: 105-115. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.09.027 [10] Zhang Y W, Hu F F, Fan H R, et al. Fluid evolution and gold precipitation in the Muping Gold Deposit(Jiaodong, China): Insights from in-situ trace elements and sulfur isotope of sulfides[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 218: 106617. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106617 [11] 耿科, 李大鹏. 胶东西涝口金矿深部110 Ma角闪辉长岩脉及其对成矿时代的约束[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(6): 974-994. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202006002.htmGeng K, Li D P. 110 Ma hornblende gabbro dyke in deep part of Xilaokou Gold Deposit, Jiaodong and its constraints on metallogenic time[J]. Mineral Deposit, 2020, 39(6): 974-994(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202006002.htm [12] 税棚. 胶莱盆地东北缘郭城-辽上金矿地质特征及成因机制[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.Shui P. Geological characteristics and genetic mechanism of Guocheng-Liaoshang Gold Mine on the northeast margin of Jiaolai Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [13] Cheng N N, Hou Q L, Shi M Y, et al. New insight into the genetic mechanism of shear zone type gold deposits from Muping-Rushan metallogenic belt(Jiaodong Peninsula of Eastern China)[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(12): 775. doi: 10.3390/min9120775 [14] 李国华, 丁正江, 宋明春, 等. 胶东新类型金矿: 辽上黄铁矿碳酸盐脉型金矿[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(3): 423-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201703012.htmLi G H, Ding Z J, Song M C, et al. The Liaoshang pyrite-carbonate veined deposit: A new type of gold deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(3): 423-429(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201703012.htm [15] 王德恩, 门业凯, 贾三石, 等. 胶东郭城金矿稀土元素地球化学特征及其对成矿的指示意义[J]. 稀土, 2014, 35(3): 6-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201403003.htmWang D E, Men Y K, Jia S S, et al. REE geochemical characters of the Guocheng Gold Deposit, eastern Shandong Province and its significance to mineralizations[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2014, 35(3): 6-12(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ201403003.htm [16] Tan J, Wei J H, Audétat A, et al. Source of metals in the Guocheng Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China Craton: Link to Early Cretaceous mafic magmatism originating from Paleoproterozoic metasomatized lithospheric mantle[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 48: 70-87. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.02.008 [17] Liu X Y, Tan J, He H Y, et al. Origin of the Tudui-Shawang Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China Craton: Constraints from fluid inclusion and H-O-He-Ar-S-Pb isotopic compositions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 35: 104-125. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136821001505 [18] 薄军委, 丁正江, 宋明春, 等. 胶东辽上金矿床C, O, S, Pb同位素组成及矿床成因[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2021, 40(2): 321-336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW202102010.htmBo J W, Ding Z J, Song M C, et al. C, O, S and Pb isotopic compositions and genesis of the Liaoshang Gold Deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2021, 40(2): 321-336(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW202102010.htm [19] 段留安, 魏有峰, 陈雄军, 等. 山东胶莱盆地东北缘前垂柳矿区金矿资源潜力分析[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2020, 28(5): 701-711. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ202005013.htmDuan L A, Wei Y F, Chen X J, et al. Potential analysis of gold resources in Qianchuiliu mining area, northeast margin of Jiaolai Basin, Shandong Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2020, 28(5): 701-711(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ202005013.htm [20] Duan L A, Guo Y C, Han X M, et al. Discovery of a medium-scale tectonic altered rock type gold deposit (13.5 t) on the northeastern margin of Jiaolai Basin, Shandong Province, China and its new application of exploration direction[J]. China Geology, 2022, 5(3): 543-545. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=7107948910 [21] 吕军阳, 胡秉谦, 王福江, 等. 山东省乳山市西涝口矿区金矿勘探报告[R]. 山东烟台: 山东省第六地质矿产勘查院, 2018.Lü J Y, Hu B Q, Wang F J, et al. Gold exploration report in Xilaokou Mine, Rushan City, Shandong Province[R]. Yantai, Shandong: The Sixth Geological and Mineral Exploration Institute of Shandong Province, 2018(in Chinese). [22] 李国华, 王志新. 山东省烟台市牟平区辽上矿区深部及外围金矿勘探报告[R]. 山东烟台: 山东省第三地质矿产勘查院, 2016.Li G H, Wang Z X. Exploration report on deep and peripheral gold mine in Liaoshang Mining area, Muping district, Yantai City, Shandong Province[R]. Yantai, Shandong: Shandong Province Third Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, 2016(in Chinese). [23] Guo J H, Chen F K, Zhang X M, et al. Evolution of syn- to post-collisional magmatism from north Sulu UHP belt, eastern China: Zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2005, 21(4): 1281-1301. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/94579x/20054/20945053.html [24] Deng J, Yang L, Li R, et al. Regional structural control on the distribution of world-class gold deposits: An overview from the Giant Jiaodong Gold Province, China[J]. Geological Journal, 2019, 54(1): 378-391. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040283706310_c347.html [25] 刘汉彬, 金贵善, 李军杰, 等. 铀矿地质样品的稳定同位素组成测试方法[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2013, 30(3): 174-179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD201303011.htmLiu H B, Jin G S, Li J J, et al. Determination of stable isotope composition in uranium geological samples[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2013, 30(3): 174-179(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD201303011.htm [26] 路远发. GeoKit: 一个用VBA构建的地球化学工具软件包[J]. 地球化学, 2004, 33(5): 459-464. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200405003.htmLu Y F. GeoKi: A geochemical toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Geochimica, 2004, 33(5): 459-464(inChinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200405003.htm [27] 吴开兴, 胡瑞忠, 毕献武, 等. 矿石铅同位素示踪成矿物质来源综述[J]. 地质地球化学, 2002, 30(3): 73-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200203012.htmWu K X, Hu R Z, Bi X W, et al. Ore lead isotopes as a tracer for ore-forming material sources: a review[J]. Geology Geochemistry, 2002, 30(3): 73-81(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200203012.htm [28] 于学峰, 张天祯, 王虹, 等. 山东省矿床成矿系列研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2016, 35(1): 169-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201601011.htmYu X F, Zhang T Z, Wang H, et al. A study of minerogenetic series of mineral deposits in Shandong Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2016, 35(1): 169-184(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201601011.htm [29] 吴开兴, 胡瑞忠, 毕献武, 等. 矿石铅同位素示踪成矿物质来源综述[J]. 地质地球化学, 2002(3): 73-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200203012.htmWu K X, Hu R Z, Bi X W, et al. Ore lead isotopes as a tracer for ore-forming material sources: A review[J]. Geology Geochemistry, 2002(3): 73-81in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200203012.htm [30] Mao J W, Wang Y T, Li H M, et al. The relationship of mantle-derived fluids to gold metallogenesis in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Evidence from D-O-C-S isotope systematics[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2008, 33(3/4): 361-381. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136807000364 [31] 聂飞, 刘书生, 董国臣, 等. 辽西二道沟金矿成矿物质来源: 来自S-Pb同位素证据[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(6): 1283-1291. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201806016.htmNie F, Liu S S, Dong G C, et al. The ore-forming material of the Erdaogou Gold Deposit in west Liaoning Province: Evidence from S-Pb isotopes[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(6): 1283-1291(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201806016.htm [32] 柳志进, 张新勇, 戚静洁, 等. 胶东山后金矿流体包裹体及H-O-S同位素特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(6): 190-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201706021.htmLiu Z J, Zhang X Y, Qi J J, et al. Fluid inclusion and H-O-S isotope characters of Shanhou Gold Ore in Jiaodong[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(6): 190-196(in Chinese with English ab-stract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201706021.htm [33] 孙兴丽. 山东胶莱盆地西涝口金矿床的特征和成因[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.Sun X L. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Xilaokou Gold Deposit in the margin of the Jiaolai Basin, Shandong[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [34] 梁辉, 韩作振, 王立功, 等. 胶东辽上金矿床的流体包裹体、氢-氧-碳-硫-铅同位素特征及矿床成因[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(6): 1053-1067. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202206012.htmLiang H, Han Z Z, Wang L G, et al. The fluid inclusions, H-O-C-S-Pb isotopic characteristics and genesis of the Liaoshang Gold Deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(6): 1053-1067(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202206012.htm [35] 张连昌, 沈远超, 曾庆栋, 等. 山东中生代胶莱盆地北缘金矿床硫铅同位素地球化学[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2001, 20(4): 380-384. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200104048.htmZhang L C, Shen Y C, Zeng Q D, et al. Sulfur and lead isotopic geochemistry of gold deposits at the northern margin of Jiaolai Basin, east Shandong[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2001, 20(4): 380-384(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200104048.htm [36] 李杰, 安梦莹, 宋明春, 等. 胶东金矿硫同位素组成特征及其来源[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(6): 994-1008. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202206008.htmLi J, An M Y, Song M C, et al. Sulfur isotopic composition and its source of Jiaodong Gold Deposit[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(6): 994-1008(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202206008.htm [37] 黄德业. 胶东金矿成矿系列硫同位素研究[J]. 矿床地质, 1994, 13(1): 75-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ401.007.htmHuang D Y. Study on the series of sulfur isotopes of Jiaodong Gold Mine[J]. Mineral Deposit, 1994, 13(1): 75-87(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ401.007.htm [38] 张铭, 谭俊. 王怀洪, 等. 山东范家庄金矿床S-Pb同位素组成及对成矿物质来源的示踪[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4): 124-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904013.htmZhang M, Tan J, Wang H H, et al. Sulfur and lead isotopic compositions of the Fanjiazhuang Gold Deposit and their implications for sources of ore-forming materials, Shandong Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(4): 124-133(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904013.htm [39] 李红梅, 魏俊浩, 王启, 等. 山东土堆-沙旺金矿床同位素组成特征及矿床成因讨论[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(6): 791-802. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201006004.htmLi H M, Wei J H, Wang Q, et al. Isotopic composition features and ore-forming mechanism of the Tudui-Shawang Gold Deposit in Shandong Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(6): 791-802(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201006004.htm [40] Raveggi M, Giles D, Foden J, et al. Lead and Nd isotopic evidence for a crustal Pb source of the giant Broken Hill Pb-Zn-Ag Deposit, New South Wales, Australia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65(2): 228-244. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S016913681400225X&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1469064534&md5=8845211368c6e932b70a2e5c165f9350 [41] Stasey J S, Kramers J D. Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a two stage model[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1975, 26(2): 207-221. http://ieg.or.kr/include/file_down.php?save_path=/data1/ref&filename=00030026002000207.pdf&filename2=00030026002000207.pdf [42] Zartman R E, Doe B R. Plumbotectonics: The model[J]. Tectonophysics, 1981, 75(1/2): 135-162. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0040195181902134 [43] 朱炳泉, 李献华, 戴谟, 等. 地球科学中同位素体系理论与应用: 兼论中国大陆壳幔演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998: 216-230.Zhu B Q, Li X H, Dai M, et al. Theory and application of isotope system in earth science: On Chinese mainland shell and mantle evolution[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998: 216-230(in Chinese). [44] 杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 等. 胶东中生代金成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9): 2447-2467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409001.htmYang L Q, Deng J, Wang Z L, et al. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong Gold Province, eastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(9): 2447-2467(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409001.htm [45] 梁亚运, 刘学飞, 李龚健, 等. 胶东地区脉岩成因与金成矿关系的研究: 年代学及Sr-Nd-Pb同位素的约束[J]. 地质科技情报, 2014, 33(3): 10-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201403003.htmLiang Y Y, Liu X F, Li G J, et al. Petrogenesis and connection with gold deposits of dikes in Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern of North China Craton: Constraint on geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb isotope[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2014, 33(3): 10-24(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201403003.htm [46] Goss S C, Wilde S A, Wu F Y, et al. The age, isotopic signature and significanee of the youngest Mesozoic granitoids in the Jiaodong terrane, Shandong Province, North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 120(3/4): 309-326. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S0024493710002215&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1491946587&md5=f6e5721a5daa60eba1868ec8b3fec8ae -





 下载:
下载: