Pore throat structure characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs and their influence on movable fluid occurrence: Taking the Chang-7 Member of Qingcheng area of Ordos Basin as an example
-
摘要:
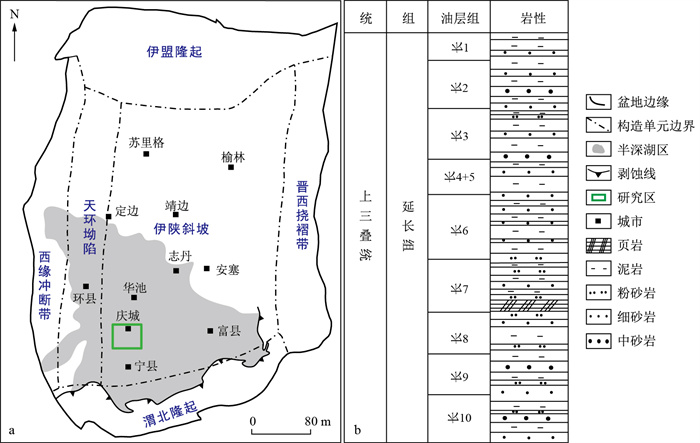
分析孔隙结构和可动流体分布特征是储层研究的关键要素,也是当前研究的重点与热点,对致密砂岩油气勘探及提高油气采收率具有重要意义。以鄂尔多斯盆地庆城地区长7段致密砂岩储层为例,通过物性测试、铸体薄片、扫描电镜、高压压汞和核磁共振实验,结合分形理论,分析了致密砂岩储层孔隙结构、非均质性和可动流体分布特征,讨论了孔喉结构和非均质性对可动流体赋存的影响。结果表明:研究区长7段储层储集空间主要由微纳米级孔隙贡献,孔隙连通性较差,孔喉半径主要分布在0.050~0.500 μm;孔喉结构非均质性较强,分形维数分布在2.65~2.90;流体可动性较差,可动流体饱和度分布在16.68%~51.74%,可动流体多分布在中孔和小孔内。研究区长7段储层可分为3类:从Ⅰ类到Ⅲ类储层,剩余粒间孔和粒间溶蚀孔发育变少,孔隙连通性变差,孔喉尺寸变小,较大孔喉变少,非均质性变强,流体可动性变差,中孔和大孔内可动流体含量趋于降低, 可动流体倾向于在小孔内赋存。研究成果为致密砂岩油气勘探及油气采收率提高提供了理论依据。
Abstract:Objective The analysis of pore structure and movable fluid distribution characteristics is the key element of reservoir research and is also the focus and hotspot of current research. It is of great significance for exploring tight sandstone oil and gas and improving oil and gas recovery.
Methods The Chang-7 Member tight sandstone reservoir in the Qingcheng area of Ordos Basin was selected as the research object in this paper. Combined with fractal theory, through physical property tests, casting thin section, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), high-pressure mercury injection, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments, the pore throat structure, heterogeneity, and movable fluid distribution characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs were analysed, and the influence of the pore throat structure and heterogeneity on movable fluid occurrence was discussed.
Results The results show that the reservoir space of the Chang-7 Member reservoir in the study area is mainly contributed by micro-nanopores, which have poor pore connectivity. The pore throat radius is mainly 0.050-0.500 μm. The heterogeneity of the pore throat structure is strong, and the fractal dimension distribution is between 2.65 and 2.90. The fluid mobility is poor, and the movable fluid saturation is distributed between 16.68 % and 51.74 %, the movable fluid is mostly distributed in medium and small pores. The Chang-7 Member reservoirs in the study area can be divided into three types. From the type Ⅰ reservoir to the type Ⅲ reservoir, the development of residual intergranular pores and intergranular dissolution pores decreases, and the pore connectivity becomes poorer, and the pore throat size decreases, and the content of larger pore throats decreases, and the heterogeneity becomes stronger, and the fluid mobility is worse, and the movable fluid content in the medium and large pores tends to decrease, and movable fluid tends to occur in the small pores.
Conclusion This study provides a theoretical basis for tight sandstone oil and gas exploration and improving oil and gas recovery.
-
图 2 研究区长7段砂岩储层孔隙类型及微观特征
a.Z283井, 1 820.42 m, 粒内溶蚀孔、粒间溶蚀孔和片状喉道,铸体薄片,单偏光; b.N86井, 1 723.74 m, 粒间溶蚀孔、粒内溶蚀孔、剩余粒间孔和弯片状喉道,铸体薄片,单偏光; c: Z193井, 1 755.73 m, 粒间溶蚀孔和粒内溶蚀孔,铸体薄片,单偏光; d.Z283井, 1 823.73 m, 微裂缝,铸体薄片,单偏光; e.Z193井, 1 763.28 m, 晶间微孔和剩余粒间孔,扫描电镜照片; f.T40井, 1 689.13 m, 晶间孔和管束状喉道,扫描电镜照片
Figure 2. Pore types and microscopic characteristics of sandstone reservoir of the Chang-7 Memeber in the study area
表 1 研究区各实验样品基本信息
Table 1. Basic information on testing samples in the study area
编号 井名 埋深/m 空气渗透率/10-3 μm2 孔隙度/% 岩性 #1 Z193 1 755.73 0.069 8 8.02 灰色粉砂岩 #2 Z193 1 763.28 0.120 1 9.38 浅灰色细砂岩 #3 Z193 1 778.45 0.017 3 7.04 浅灰色粉砂岩 #4 Z193 1 770.59 0.007 9 4.31 灰色粉砂岩 #5 Z283 1 820.42 0.130 0 10.59 浅灰色细砂岩 #6 Z283 1 822.57 0.100 5 10.12 浅灰色细砂岩 #7 Z283 1 823.73 0.123 0 11.91 浅灰色细砂岩 #8 N86 1 715.69 0.055 4 7.58 浅灰色粉砂岩 #9 N86 1 719.38 0.027 9 7.05 灰色粉砂岩 #10 N86 1 723.74 0.113 6 11.79 浅灰色细砂岩 #11 N86 1 724.82 0.018 7 4.69 浅灰色粉砂岩 #12 T40 1 685.74 0.011 2 4.12 灰色粉砂岩 #13 T40 1 688.69 0.007 3 3.90 灰色粉砂岩 #14 T40 1 689.13 0.008 9 4.21 灰色粉砂岩 #15 T40 1 691.69 0.009 8 4.06 浅灰色粉砂岩 表 2 研究区各长7段测试分析样品孔喉结构参数及主要孔隙类型的面孔率
Table 2. Pore throat structure parameters and face rate of main pore types of the Chang-7 Member testing samples in the study area
编号 最大孔喉半径/μm 平均孔喉半径/μm 孔喉半径中值/μm 最大汞饱和度/% 排驱压力/MPa 分选系数 歪度 占比/%(半径≥0.1 μm) 占比/%(半径<0.1 μm) 主要孔隙类型的面孔率/% 储层类型 剩余粒间孔 粒间溶蚀孔 粒内溶蚀孔 #1 0.263 0.079 0.039 61.35 2.79 1.40 0.39 11.62 88.38 1.0 0.5 0.5 Ⅱ #2 0.265 0.059 0.021 67.05 2.78 1.52 0.20 22.56 77.44 0.5 1.0 1.0 Ⅰ #3 0.267 0.077 0.033 61.76 2.76 1.59 0.23 42.92 57.08 0.0 0.0 0.0 Ⅱ #4 0.133 0.045 0.021 57.14 5.54 1.60 -0.05 7.08 92.92 0.0 0.0 0.5 Ⅱ #5 0.359 0.098 0.035 68.68 2.05 2.50 -0.01 47.55 52.45 1.5 2.0 1.0 Ⅰ #6 0.554 0.169 0.074 67.03 1.33 1.61 0.49 68.09 31.91 2.0 2.0 0.5 Ⅰ #7 1.112 0.197 0.096 69.02 0.66 1.68 0.46 66.77 33.23 2.5 1.5 0.25 Ⅰ #8 0.183 0.057 0.028 61.79 4.02 1.52 0.13 23.97 76.03 0.0 0.0 0.5 Ⅱ #9 0.251 0.073 0.025 60.75 2.93 2.43 -0.02 39.00 61.00 0.5 0.0 0.0 Ⅱ #10 0.186 0.058 0.040 72.41 3.95 1.49 0.06 22.86 77.14 1.5 1.0 0.5 Ⅰ #11 0.096 0.030 0.011 52.61 7.66 3.03 -0.59 0.00 100 0.0 0.0 0.0 Ⅱ #12 0.094 0.023 0.008 51.64 7.82 2.29 -0.41 0.00 100 0.0 0.0 0.5 Ⅱ #13 0.075 0.019 / 34.75 9.80 2.57 -0.54 0.00 100 0.0 0.0 0.0 Ⅲ #14 0.057 0.018 / 34.90 13.00 3.98 -0.73 0.00 100 0.0 0.0 0.5 Ⅲ #15 0.098 0.017 / 40.07 7.50 2.56 -0.42 0.00 100 0.0 0.0 0.0 Ⅲ 表 3 研究区各长7段测试样品分形维数及相关系数
Table 3. Fractal dimension and correlation coefficient of the Chang-7 Member testing samples in the study area
样品编号 #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 #6 #7 #8 分形维数 2.789 8 2.719 5 2.792 9 2.868 6 2.708 9 2.713 7 2.779 7 2.707 3 R2 0.871 4 0.994 5 0.922 6 0.960 1 0.988 1 0.916 6 0.936 2 0.962 2 储层类型 Ⅱ Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅰ Ⅱ 样品编号 #9 #10 #11 #12 #13 #14 #15 分形维数 2.743 9 2.686 9 2.728 1 2.780 5 2.930 4 2.817 9 2.834 9 R2 0.973 0 0.986 6 0.985 5 0.982 5 0.948 2 0.980 7 0.980 3 储层类型 Ⅱ Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅲ Ⅲ 表 4 研究区长7段实验样品可动流体分布参数
Table 4. Movable fluid distribution parameters of the Chang-7 Member testing samples in the study area
编号 储层类型 可动流体饱和度/% 可动流体分布体积分数/% 微孔(T2≤1 ms) 小孔(1 ms<T2≤10 ms) 中孔(10 ms<T2≤100 ms) 大孔(100 ms<T2≤1 000 ms) 微裂缝(T2>1 000 ms) #1 Ⅱ 43.46 1.86 46.85 47.65 3.64 0.00 #2 Ⅰ 45.86 0.00 35.43 60.23 4.34 0.00 #3 Ⅱ 39.26 0.45 47.94 50.37 1.24 0.00 #4 Ⅱ 32.76 0.79 64.89 34.32 0.00 0.00 #5 Ⅰ 49.08 0.00 6.15 63.17 30.68 0.00 #6 Ⅰ 51.74 0.00 7.76 60.97 31.27 0.00 #7 Ⅰ 49.39 0.00 3.51 56.69 39.81 0.00 #8 Ⅱ 38.95 2.44 22.41 44.69 30.46 0.00 #9 Ⅱ 39.79 0.00 34.12 59.46 6.26 0.15 #10 Ⅰ 40.06 1.39 0.96 83.23 14.42 0.00 #11 Ⅱ 41.57 13.43 61.97 21.79 2.82 0.00 #12 Ⅱ 30.73 7.17 53.72 36.03 2.85 0.06 #13 Ⅲ 16.68 0.00 90.09 3.16 6.75 0.00 #14 Ⅲ 32.78 3.29 49.55 34.39 12.77 0.00 #15 Ⅲ 28.51 43.21 16.42 29.28 10.30 0.03 -
[1] 姚泾利, 邓秀芹, 赵彦德, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组致密油特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(2): 150-158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201302002.htmYAO J L, DENG X Q, ZHAO Y D, et al. Characteristics of tight oil in Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(2): 150-158. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201302002.htm [2] 杨华, 李士祥, 刘显阳. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密油、页岩油特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201301000.htmYANG H, LI S X, LIU X Y. Characteristics and resource potential of tight oil and shale oil in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(1): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201301000.htm [3] 黄何鑫. 鄂尔多斯盆地长6致密砂岩储层特征差异及其对流体可动用能力的制约机理研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2019.HUANG H X. Study on the difference in characteristics of the tight sandstone reservoir and its restrictive mechanism to the fluid availability of Chang 6 Member in the Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] ZHANG F, JIANG Z, SUN W, et al. A multiscale comprehensive study on pore structure of tight sandstone reservoir realized by nuclear magnetic resonance, high pressure mercury injection and constant-rate mercury injection penetration test[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 109: 208-222. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.06.019 [5] HUANG H, LI R, XIONG F, et al. A method to probe the pore-throat structure of tight reservoirs based on low-field NMR: Insights from a cylindrical pore model[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 117: 104344. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104344 [6] 钟红利, 张凤奇, 赵振宇, 等. 致密砂岩储层微观孔喉分布特征及对可动流体的控制作用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(1): 77-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202101009.htmZHONG H L, ZHANG F Q, ZHAO Z Y, et al. Micro-scale pore-throat distributions in tight sandstone reservoirs and its constrain to movable fluid[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(1): 77-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202101009.htm [7] 陈富瑜, 周勇, 杨栋吉, 等. 基于分形理论的致密砂岩储层孔隙结构研究: 以鄂尔多斯盆地庆城地区延长组长7段为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2022(5): 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202205011.htmCHEN F Y, ZHOU Y, YANG D J, et al. Study on pore structure of tight sandstone reservoir based on fractal theory: A case study from Chang 7 tight sangstone of Yanchang Formation in Qingcheng area of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2022(5): 1-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202205011.htm [8] XU Y, LIU L, ZHU Y. Characteristics of movable fluids in tight sandstone reservoir and its influencing factors: A case study of Chang 7 reservoir in the southwestern of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 2021, 11(9): 3493-3507. doi: 10.1007/s13202-021-01250-x [9] WANG B, ZHAO X, ZHOU W, et al. Quantitative characterization of pore connectivity and movable fluid distribution of tight sandstones: A case study of the Upper Triassic Chang 7 Member, Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin, China[J]. Geofluids, 2020, 97: 1-13. [10] 王永诗, 高阳, 方正伟. 济阳坳陷古近系致密储集层孔喉结构特征与分类评价[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(2): 266-278. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202102005.htmWANG Y S, GAO Y, FANG Z W. Pore throat structure and classification of Paleogene tight reservoirs in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(2): 266-278. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202102005.htm [11] 闫健, 秦大鹏, 王平平, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密砂岩储层可动流体赋存特征及其影响因素[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(6): 47-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202006007.htmYAN J, QIN D P, WANG P P, et al. Occurrence characteristics and main controlling factors of movable fluid in tight sandstone reservoirs in Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(6): 47-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202006007.htm [12] 卢振东, 刘成林, 臧起彪, 等. 高压压汞与核磁共振技术在致密储层孔隙结构分析中的应用: 以鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 300-310 doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0256LU Z D, LIU C L, ZANG Q B, et al. Application of high pressure mercury injection and nuclear magnetic resonance technology in analysis of the pore structure of dense sandstone: A case study in Heshui area of Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Scientific and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 300-310. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0256 [13] LI P, JIA C, JIN Z, et al. The characteristics of movable fluid in the Triassic lacustrine tight oil reservoir: A case study of the Chang 7 Member of Xin'anbian Block, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 102: 126-137. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.11.019 [14] 熊林芳, 刘池阳, 邱欣卫, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地晚三叠世构造活动及对优质烃源岩发育的影响[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2): 109-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502016.htmXIONG L F, LIU C Y, QIU X W, et al. Tectonic activity of Later Triassic in Ordos Basin and its effect on the formation of high quality source rocks[J]. Geological Scientific and Technology Information, 2015, 34(2): 109-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502016.htm [15] 阮壮, 罗忠, 于炳松, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中-晚三叠世盆地原型及构造古地理响应[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(1): 12-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202101003.htmRUAN Z, LUO Z, YU B S, et al. Middle-Late Triassic Basin prototype and tectonic paleogeographic response in the Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(1): 12-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202101003.htm [16] YANG Y, LI W, MA L. Tectonic and stratigraphic controls of hydrocarbon systems in the Ordos Basin: A multicycle cratonic basin in central China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2005, 89(2): 255-269. doi: 10.1306/10070404027 [17] 李士祥, 牛小兵, 柳广弟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7段页岩油形成富集机理[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(4): 719-729. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004007.htmLI S X, NIU X B, LIU G D, et al. Formation and accumulation mechanism of shale oil in the 7th Member of Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(4): 719-729. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004007.htm [18] 付金华, 李士祥, 牛小兵, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系长7段页岩油地质特征与勘探实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(5): 870-883. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202005005.htmFU J H, LI S X, NIU X B, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration of shale oil in Chang 7 Member of Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(5): 870-883. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202005005.htm [19] 付金华, 牛小兵, 淡卫东, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中生界延长组长7段页岩油地质特征及勘探开发进展[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(5): 601-614. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.007FU J H, NIU X B, DAN W D, et al. The geological characteristics and the progress on exploration and development of shale oil in Chang 7 Member of Mesozoic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(5): 601-614. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.007 [20] 李涛涛. 鄂尔多斯盆地庆城地区延长组长7段致密油成藏特征及成藏条件分析[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2018.LI T T. Accumulation characteristics and analysis accumulation conditions of tight oil reservoir in Chang 7 Member of Yanchang Formation in Qingcheng area, Ordos Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum(Beijing), 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] 付锁堂, 付金华, 牛小兵, 等. 庆城油田成藏条件及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(7): 777-795. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202007003.htmFU S T, FU J H, NIU X B, et al. Accumulation conditions and key exploration and development technologies in Qingcheng Oilfield[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(7): 777-795. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202007003.htm [22] 张晓辉, 冯顺彦, 梁晓伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组长7段沉积微相及沉积演化特征[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(3): 957-967. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202003020.htmZHANG X H, FENG S Y, LIANG X W, et al. Sedimentary Microfacies identification and inferredevolution of Chang 7 Member of Yanchang Formation in the Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(3): 957-967. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202003020.htm [23] 王昊, 杨友运, 李元昊, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区长7段重力流沉积特征及分布规律[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 34(2): 39-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201902006.htmWANG H, YANG Y Y, LI Y H, et al. Characteristics and distribution of gravity flow deposition of Chang 7 Member in Heshui area, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Petroleum University(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 34(2): 39-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201902006.htm [24] 杨华, 窦伟坦, 刘显阳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7沉积相分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(2): 254-263. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201002007.htmYANG H, DOU W T, LIU X Y, et al. Analysis sedimentary facies of Chang 7 in Yanchang Formation of Triassic in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(2): 254-263. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201002007.htm [25] 李文厚, 刘溪, 张倩, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中晚三叠世延长期沉积演化[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 49(4): 605-621. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201904014.htmLI W H, LIU X, ZHANG Q, et al. Deposition evolution of Middle-Late Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 49(4): 605-621. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201904014.htm [26] 刘芬. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组重力流沉积特征及成因机制[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2016.LIU F. Sedimentary characteristics and genetic mechanism of gravity flow in Triassic Yanchang Formation of Longdong area, Ordos Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum(Beijing), 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 窦伟坦. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组沉积体系、储层特征及油藏成藏条件研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2005.DOU W T. Research for sediment system, reservoir character and oil-reservoir forming of Yanchang Formation, Triassic, Ordos Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] 付金华, 郭正权, 邓秀芹. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南地区上三叠统延长组沉积相及石油地质意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2005, 7(1): 34-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200501004.htmFU J H, GUO Z Q, DENG X Q. Sedimentary facies of the Yanchang Formation of Upper Triassic and petroleum geological implication in southwestern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2005, 7(1): 34-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200501004.htm [29] 王福伟, 陈冬霞, 解广杰, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地庆城地区延长组7段源-储结构控制下致密砂岩油的差异富集机制[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(7): 941-956. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202207005.htmWANG F W, CHEN D X, XIE G J, et al. Differential enrichment mechanism of tight sandstone oil under the control of the source-reservoir structure in the Member 7 of Yanchang Formation in Qingcheng area, Ordos Basin[J]Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(7): 941-956. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202207005.htm [30] 刘凯, 石万忠, 王任, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区盒1段致密砂岩孔隙结构分形特征及其与储层物性的关系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 57-68.Liu K, Shi W Z, Wang R, et al. Pore structure fractal characteristics and its relationship with reservoir properties the First Member of Lower Shihezi Formation tight sandstone in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 57-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] MANDELBROT B B, PASSOJA D E, PAULLAY D E. Fractal character of fracture surfaces in porous media[J]. Nature, 1984, 308: 721-722. doi: 10.1038/308721a0 [32] 王伟, 陈朝兵, 许爽, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组致密砂岩不同尺度孔喉分形特征及其控制因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(1): 33-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202201004.htmWANG W, CHEN C B, XU S, et al. Fractal characteristics and controlling factors of pore throat at different scales in tight sandstone of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(1): 33-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202201004.htm [33] 王伟, 宋渊娟, 黄静, 李亚辉, 陈朝兵, 朱玉双. 利用高压压汞实验研究致密砂岩孔喉结构分形特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 22-30.WANG W, SONG Y J, HUANG J, et al. Fractal characteristics of pore-throat structure in tight sandstone using high-pressure mercury injection intrusion porosimetry[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 22-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] SHAO X, PANG X, LI H, et al. Fractal analysis of pore network in tight gas sandstones using NMR Method: A case study from the Ordos Basin, China[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31: 10358-10368. [35] TIMUR A. Pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance studies of porosity, movable fluid, and permeability of sandstones[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1969, 6: 775-786. [36] 高树生, 胡志明, 刘华勋, 等. 不同岩性储层的微观孔隙特征[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(2): 248-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201602012.htmGao S S, Hu Z M, Liu H X, et al. Microscopic pore characteristics of different lithological reservoirs with[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(2): 248-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201602012.htm -





 下载:
下载: