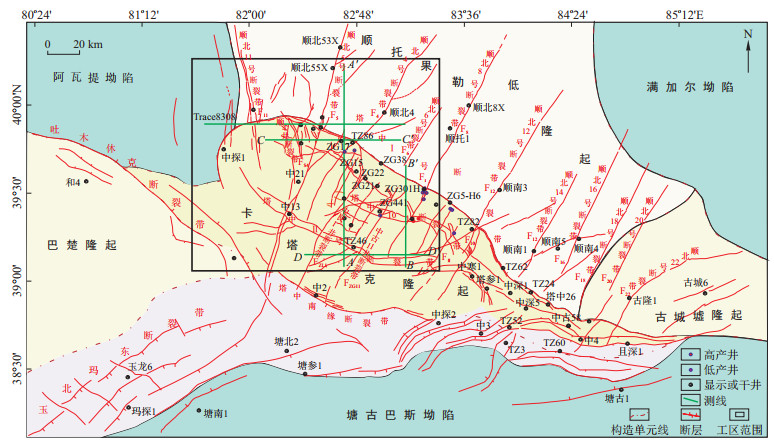
Structure and evolution of faults in central and northern parts of Tazhong Uplift, Tarim Basin
-
摘要:
为系统揭示塔里木盆地塔中隆起中北部地区断裂构造特征及其成因演化, 通过对该区大连片三维地震工区精细构造解析和相干体等分析, 并结合区域动力背景, 系统论述了该区的断裂构造类型、几何学特征、差异活动机制及其构造演化过程。研究结果表明, 塔中隆起中北部发育了4类7期断裂构造, 其中逆冲断裂和走滑断裂尤其发育。平面上北西向弧形逆冲断裂与北东向、北西向及南北向走滑断裂相互交切与耦合; 垂向上断裂分层差异活动特征明显, 下奥陶统及其以下地层, 断裂发育数量多且以线形为主, 中奥陶统-中下泥盆统多呈雁列式, 上泥盆统-二叠系仅在塔中Ⅱ号断裂带、顺北5号断裂带西南端等地区发育少量断裂。研究区断裂活动受多期、多方向不同性质应力场所控制, 经历了极其复杂的演化历史: 加里东早期以塔中Ⅱ号断裂带等少量北倾正断层活动为主; 加里东中期Ⅰ幕断裂活动强烈, 表现为逆冲断裂与走滑断裂协同演化和相互耦合特征, 走滑断裂对逆冲断裂的切割或限制作用明显; 加里东中期Ⅲ幕断裂活动基本继承了加里东中期Ⅰ幕的构造格局, 但在工区北部的顺北4号、5号等断裂带张扭性断裂活动特征显著; 加里东晚期-海西早期, 部分断裂发生继承性活动且张扭断裂发育范围进一步向南扩大; 印支-燕山期, 仅有少数断裂发生继承性活动; 喜山期该区构造比较稳定, 早期形成的复杂断裂构造进入深埋阶段。
Abstract:Objective To reveal the structures and evolutionary patterns of faults in the central and northern parts of Tazhong Uplift, Tarim Basin,
Methods this paper systematically discusses the types of fault structures, geometric characteristics, differential activity mechanisms, and tectonic evolution processes in this area by analysing detailed structural interpretations and coherent slices of combined large 3D seismic data along with the regional dynamic background.
Results The results show that there are 4 types and 7 evolution stages of faults in the central and northern parts of Tazhong Uplift, among which thrust faults and strike-slip faults are particularly common. On the plane, NW arc thrust faults intersect with NE-, NW- and NS-striking strike-slip faults; vertically, the fault stratification and differential activity characteristics are obvious. In the Lower Ordovician and the belowing layers, faults developed in large numbers and were mainly linear in their trending directions. As for the Middle Ordovician-Middle and Lower Devonian layers, faults are mostly in the echelon type. In the Upper Devonian-Permian layers, a few faults developed in the Tazhong Ⅱ fault zone and the southwestern end of the Shunbei 5 fault zone.
Conclusion The fault activity in the study area was controlled by stress sites exhibiting diverse properties across multiple phases and directions and experienced an extremely complex evolutionary history: In the Early Caledonian period, a small number of normal faults, such as the Tazhong Ⅱ fault zone, were mainly active; in the Middle Caledonian Ⅰ period, the fault activity was very strong and was characterized by coevolution and mutual coupling of thrust faults and strike-slip faults. The strike-slip faults obviously cut or restricted the thrust faults. The fault activity of the Middle Caledonian Ⅲ period basically inherited the tectonic framework of the Middle Caledonian Ⅰ period, but the characteristics of transtensional fault activity in the Shunbei 4 and 5 fault zones are significant. From the Late Caledonian to Early Hercynian, some of the faults inherited activities with obvious transtensional characteristics. Conversely, in the Indochina-Yanshan period, only a few faults inherited activity, and the development area of transtensinal fault is further expanded to the south. During the Himalayan period, the tectonic movement of this area was relatively stable, and the complex fault structures that formed in the early stage transitioned into the deep burial stage.
-
图 2 塔中隆起中北部典型断裂构造特征地震剖面图(剖面、断裂带位置及编号见图 1,下同)
T.三叠系;D3-P.上泥盆统-二叠系;S-D1-2.志留系-中、下泥盆统;O2.上奥陶统;O1-2.中、下奥陶统;∈3.上寒武统;∈2.中寒武统;∈1.下寒武统;∈1-2.中、下寒武统
Figure 2. Seismic section of typical fault structures in central and northern parts of Tazhong Uplift
表 1 塔里木盆地塔中隆起区地层格架(据文献[1]修改)
Table 1. Brief of the stratigraphic framework in Tazhong Uplift area, Tarim Basin

表 2 塔中隆起中北部地区断裂分期活动特征
Table 2. Characteristics of the fault stages and activities in central and northern parts of Tazhong Uplift

-
[1] 胡德胜. 塔里木盆地塔中隆起带主干断裂系统及其油气地质意义[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2010.HU D S. Research on the main fault systems and their implication to petroleum geology in Tazhong Uplift area, Tarim Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 任建业, 阳怀忠, 胡德胜, 等. 塔里木盆地中央隆起带断裂活动及其对海相克拉通解体的作用[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2012, 37(4): 645-653. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201204005.htmREN J Y, YANG H Z, HU D S, et al. Fault activity and its controlling to marine cratonic breakup in Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2012, 37(4): 645-653. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201204005.htm [3] 余卓颖. 塔里木盆地塔中隆起主要断裂运动学特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2017.YU Z Y. Kinematic characteristics of main faults in Tazhong Uplift of Tarim Basin[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 杨勇, 汤良杰, 郭颖, 等. 塔中隆起NNE向走滑断裂特征及形成机制[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(5): 1569-1578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201605007.htmYANG Y, TANG L J, GUO Y, et al. Deformation characteristics and formation mechanism of NNE-trending strike-slip faults in Tazhong Uplift[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(5): 1569-1578. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201605007.htm [5] DENG S, LI H L, ZHANG Z P, et al. Structural characterization of intracratonic strike-slip faults in the central Tarim Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2019, 103(1): 109-137. doi: 10.1306/06071817354 [6] HAN X Y, DENG S, TANG L J, et al. Geometry, kinematics and displacement characteristics of strike-slip faults in the northern slope of Tazhong Uplift in Tarim Basin: A study based on 3D seismic data[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 88: 410-427. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.08.033 [7] 梁鑫鑫. 塔里木盆地塔中隆起走滑断裂体系及形成机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2020.LIANG X X. Study on the strike-slip faults system and its formation mechanism in the Tazhong Uplift, Tarim Basin[D]. Bejing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 刘雨晴, 邓尚. 板内中小滑移距走滑断裂发育演化特征精细解析: 以塔里木盆地顺北4号走滑断裂为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2022, 51(1): 124-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202201012.htmLIU Y Q, DENG S. Structural analysis of intraplate strike-slip faults with small to medium displacement: A case study of the Shunbei 4 fault, Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2022, 51(1): 124-136. (in Chinese with Eng-lish abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202201012.htm [9] 张艳萍, 吕修祥, 于红枫, 等. 塔中隆起两组走滑断裂对岩溶储层发育的控制机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(5): 663-673. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201605007.htmZHANG Y P, LÜ X X, YU H F, et al. Controlling mechanism of two strike-slip fault groups on the development of the Ordovician karst reservoirs in the Tazhong Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(5): 663-673. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201605007.htm [10] 邓尚, 李慧莉, 张仲培, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北及邻区主干走滑断裂带差异活动特征及其与油气富集的关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 878-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805004.htmDENG S, LI H L, ZHANG Z P, et al. Characteristics of differential activities in major strike-slip fault zones and their control on hydrocarbon enrichment in Shunbei area and its surroundings, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 878-888. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805004.htm [11] 宁飞, 汤良杰, 张钰, 等. 塔中隆起早古生代反转构造及其石油地质意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2010, 31(1): 57-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201001015.htmNING F, TANG L J, ZHANG Y, et al. Eopaleozoic inversion structures in the Tazhong Uplift and their significance to petroleum geology[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2010, 31(1): 57-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201001015.htm [12] 云露. 顺北地区奥陶系超深断溶体油气成藏条件[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(2): 136-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202102002.htmYUN L. Hydrocarbon accumulation of ultra-deep Ordovician fault-karst reservoirs in Shunbei area[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(2): 136-142. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202102002.htm [13] 江同文, 韩剑发, 邬光辉, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中隆起断控复式油气聚集的差异性及主控因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(2): 213-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202002002.htmJIANG T W, HAN J F, WU G H, et al. Differences and controlling factors of composite hydrocarbon accumulations in the Tazhong Uplift, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(2): 213-224. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202002002.htm [14] 罗彩明, 梁鑫鑫, 黄少英, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中隆起走滑断裂的三层结构模型及其形成机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(1): 118-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202201009.htmLUO C M, LIANG X X, HUANG S Y, et al. Three-layer structure model of strike-slip faults in the Tazhong Uplift and its formation mechanism[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(1): 118-131. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202201009.htm [15] 何登发, 贾承造, 李德生, 等. 塔里木多旋回叠合盆地的形成与演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2005, 26(1): 64-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LMMT201312022.htmHE D F, JIA C Z, LI D S, et al. Formation and evolution of polycyclic superimposed Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2005, 26(1): 64-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LMMT201312022.htm [16] 邱登峰, 郑孟林, 张瑜, 等. 塔中地区构造应力场数值模拟研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2012, 36(2): 168-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201202005.htmQIU D F, ZHENG M L, ZHANG Y, et al. Numerical simulation of the tectonic stress field in the Tazhong area[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2012, 36(2): 168-175. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201202005.htm [17] 李梁, 孙庭斌, 陈迎楠, 等. 塔里木盆地肖塘南地区走滑断裂特征与断溶体勘探研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 239-245. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0148LI L, SUN T B, CHEN Y N, et al. Characteristics of strike-slip faults and exploration of fault-dissolution body in Xiaotangnan area of Tarim Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 239-245. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0148 [18] 严威, 邬光辉, 张艳秋, 等. 塔里木盆地震旦纪-寒武纪构造格局及其对寒武纪古地理的控制作用[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2018, 42(3): 455-466. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201803004.htmYAN W, WU G H, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Sinian-Cambrian tectonic framework in the Tarim Basin and its influences on the paleogeography of the Early Cambrian[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2018, 42(3): 455-466. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201803004.htm [19] 邬光辉, 杨海军, 屈泰来, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中隆起断裂系统特征及其对海相碳酸盐岩油气的控制作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(3): 793-805. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201203009.htmWU G H, YANG H J, QU T L, et al. The fault system characteristics and its controlling roles on marine carbonate hydrocarbon in the central uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(3): 793-805. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201203009.htm [20] 黄惠明, 李鹏飞, 胡万万, 等. 西天山伊犁地块早古生代拼贴: 来自碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学和Hf同位素的制约[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(4): 786-804. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202104010.htmHUANG H M, LI P F, HU W W, et al. Early Paleozoic amalgamation of the Yili Block (Chinese West Tianshan): Insight from detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(4): 786-804. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202104010.htm [21] 曹自成, 唐大卿, 骆满嵩, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北地区中新生界断裂构造特征及演化[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 226-238. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0176CAO Z C, TANG D Q, LUO M S, et al. Structural characteristics and tectonic evolution of Mesozoic-Cenozoic faults in the Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 226-238. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0176 [22] 云金表, 周波. 塔里木盆地塔中隆起及北围斜区断裂体系与油气成藏关系[J]. 世界地质, 2014, 33(1): 137-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ201401015.htmYUN J B, ZHOU B. Relationship between fault system and reservoir formating in Tazhong Uplift and North slope area in Tram Basin[J]. Global Geology, 2014, 33(1): 137-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ201401015.htm -





 下载:
下载: