Sectional 2D numerical modelling method for steady state well-flow in an unconfined aquifer
-
摘要:
经典Dupuit井流模型与考虑入渗的改进Dupuit井流模型, 都受到Dupuit假定的影响, 可能存在系统误差。建立反映三维流或轴对称二维流特性的潜水井流数值模型, 是检验Dupuit模型可靠性的重要手段。提出一种模拟潜水稳定井流的剖面二维数值模拟方法, 通过参数转换把柱坐标系的渗流方程变换为等效的直角坐标系方程, 利用MODFLOW方体网格有限差分模型实现剖面二维流场模拟。数值模型以抽水井的井中水位为已知条件, 渗出面的排水量按照Darcy定律差分公式计算, 潜水面则通过MODFLOW对干-湿单元的处理加以识别, 抽水流量经水均衡计算得到。通过采用精细化网格建立典型案例模型, 获得模拟精度很高的结果, 使反算抽水井流量的相对误差不超过0.2%。以此检验Dupuit井流模型, 发现解析公式得到的水位线总体与数值模拟结果一致, 仅在抽水井附近由于没有考虑水跃而偏低, 且误差受到含水层渗透系数各向异性的影响。在有入渗的情况下, 分水岭附近的渗流违反Dupuit假定。然而, 改进的Dupuit井流公式计算的分水岭水位相对误差低于1%。这一数值模拟方法简单实用, 但也受到MODFLOW本身局限性的约束。
Abstract:Objective Both the classical Dupuit model and the modified Dupuit model including infiltration are influenced by Dupuit's assumption and have potential systematic errors. Building a numerical model of well flow in an unconfined aquifer by characterizing the three-dimensional or axisymmetric two-dimensional (2D) flow is an essential approach to verify the performance of Dupuit-type models.
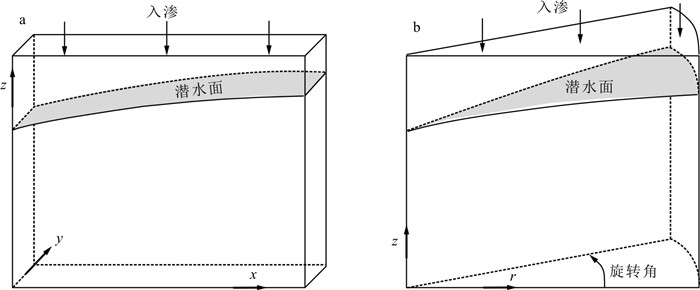
Methods In this study, a 2D numerical model is proposed for the steady state well-flow in an unconfined aquifer, in which the control equation of seepage in the cylindrical coordinates is transformed equivalently to the Cartesian coordinates through parameter transformation, and the sectional 2D modelling is implemented via the MODFLOW finite-difference grid of cubic blocks. In the numeric model, the water level in the pumping well is a given condition, the flux across the seepage face is estimated by difference equation according to Darcy's law, the phreatic surface is identified by the treatment of dry and wet cells in MODFLOW, and the pumping rate is determined from the water debug calculation.
Results Fine grids are constructed innumerical models of typical cases to obtain high-precision results, in which the relative error of the backwards estimated pumping rate is no more than 0.2%. This numerical model is used to check the Dupuit-type well-flow models. As indicated, the groundwater level estimated from the analytical formulas generally agrees well with the numerical modelling results, except that near the well, where the analytical solution underestimates the groundwater level due to ignoring the waterjump and the errors depend on the anisotropic permeability of the aquifer. When infiltration exists, the flow in the vicinity of watershed does not follow Dupuit's assumption. However, the estimated groundwater level on the watershed by modified Dupuit well-flow equation has a low level of relative error, which is less than 1%.
Conclusion This numerical method is simple and practical however it is also influenced by limitations in MODFLOW.
-
Key words:
- Dupuit's assumption /
- pumping well /
- infiltration recharge /
- seepage face /
- phreetic surface /
- anisotropic /
- finite difference method
-
表 1 模拟情景编号和参数
Table 1. Code and parameters of modelling scenarios
模拟情景 水平方向渗透系数Kh/(m·d-1) 各向异性比值Kv/Kh 入渗补给强度ε/(mm·d-1) 井中水位hw/m A 10 1 0.0 35 B 10 1 1.0 35 C 10 0.1, 10.0 1.0 35 D 1 0.1 1.0 20 -
[1] Dupuit A J E J. Etudes theoretiques et pratiques sur le mouvement des eaux[M]. Paris: Dunod, 1863. [2] Каменский Г И. Основы дина-мики подземных вод[M]. Москва: Госгеолиздат, 1943(in Russian). [3] Haitjema H M. Analytic element modeling of groundwater flow[M]. San Diego: Academic Press, Inc., 1995. [4] 陈崇希. Dupuit模型的改进: 具入渗补给[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(5): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202106001.htmChen C X. Improvement of Dupuit model: With infiltration recharge[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2020, 47(5): 1-4(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202106001.htm [5] Чарный И A. Строгое доказателъство формулм дюпюидля безнапорной филътрации с промеҗутком высачнвания[J]. Докл. АН СССР, 1951, 79(6): 937-948. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NWYJ202105015.htm [6] 陈崇希, 林敏. 地下水动力学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1999.Chen C X, Lin M. Groundwater hydraulics[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1999(in Chinese). [7] Boulton N S. The flow pattern near a gravity well in a uniform water-bearing medium[J]. Journal of the ICE, 1951, 36(10): 534-550. [8] 张有龄. 河床地下水运动的供水理论分析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1958.Zhang Y L. Theoretical analysis on water yield from groundwater flow beneath riverbed[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1958(in Chinese). [9] Taylor G S, Luthin J N. Computer methods for transient analysis of water-table aquifers[J]. Water Resources Research, 1969, 5(1): 144-152. doi: 10.1029/WR005i001p00144 [10] Neuman S P, Witherspoon P A. Finite element method of analyzing steady seepage with a free surface[J]. Water Resources Research, 1970, 6(3): 889-897. doi: 10.1029/WR006i003p00889 [11] McDonald M G, Harbaugh A W. A modular three-dimensional finite-difference ground-water flow model[R]. Denver: Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations of the U.S. Geological Survey, Chapter A1, Book 6, 1988. [12] 王旭升, 万力. 地下水运动方程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011.Wang X S, Wan L. Equations of groundwater movements[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011(in Chinese). [13] 陈崇希, 林敏, 成建梅. 地下水动力学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011.Chen C X, Lin M, Cheng J M. Groundwater hydraulics[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011(in Chinese). [14] Samani N, Kompani-Zarea M, Barry D. MODFLOW equipped with a new method for the accurate simulation of axisymmetric flow[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2004, 27(1): 31-45. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2003.09.005 [15] Langevin C D. Modeling axisymmetric flow and transport[J]. Groundwater, 2008, 46(4): 579-590. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2008.00445.x [16] Louwyck A, Vandenbohede A, Bakker M, et al. MODFLOW procedure to simulate axisymmetric flow in radially heterogeneous and layered aquifer systems[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2014, 22(5): 1217-1226. doi: 10.1007/s10040-014-1150-0 [17] 董佩, 王旭升. MODFLOW模拟自由面渗流的应用与讨论[J]. 工程勘察, 2009(7): 27-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC200907009.htmDong P, Wang X S. Application and discussion of MODFLOW's simulation to the seepage of free surface[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2009(7): 27-30(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCKC200907009.htm [18] Hill M C. Preconditioned conjugate-gradient 2 (PCG2), a computer program for solving, ground-water flow equations[R]. Water-Resources Investigations Report 90-4048, Denver: U.S. Geological Survey, 1990. [19] Pollock D W. User's Guide for MODPATH/MODPATH-PLOT, Version 3: A Particle tracking post-processing package for MODFLOW, the U.S. Geological survey finite difference groundwater flow model[R]. Open-file report 94-464, Denver: U.S. Geological Survey, 1994. [20] 陈崇希, 唐仲华, 胡立堂. 地下水流数值模拟理论方法及模型设计[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014.Chen C X, Tang Z H, Hu L T. Theory, method and model design for numerical simulation of groundwater flow[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2014 (in Chinese). [21] 成建梅, 罗一鸣. 岩溶多重介质地下水模拟技术及应用进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 220-229. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0220Chen J M, Luo Y M. Overview of groundwater modeling technology and its application in karst areas with multiple-void media[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 220-229(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0220 [22] 郑小康, 杨志兵. 岩溶含水层饱和-非饱和流动与污染物运移数值模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 357-366. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0211Zheng X K, Yang Z B. Numerical simulation of saturated-unsaturated groundwater flow and contaminant transport in a karst aquifer[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 357-366(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0211 [23] Wen Z, Liu Z T, Jin M G, et al. Numerical modeling of Forchheimer flow to a pumping well in a confined aquifer using the strong-form mesh-free method[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2014, 22(5): 1207-1215. doi: 10.1007/s10040-014-1136-y [24] Wang Q R, Zhan H B, Tang Z H, et al. Forchheimer flow to a well-considering time-dependent critical radius[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2014, 18(6): 2437-2448. doi: 10.5194/hess-18-2437-2014 [25] 陈崇希, 林敏, 叶善士, 等. 地下水混合井流的理论及应用[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1998.Chen C X, Lin M, Ye S S, et al. Theory of multi-layer mixed well flow and its application[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1998(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: